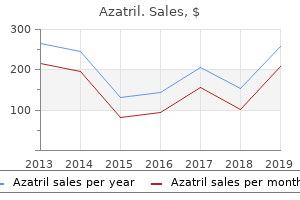
"Buy azatril 500mg on line, antimicrobial hand sanitizer."By: Lilja Bjork Solnes, M.B.A., M.D. - Program Director, Diagnostic Radiology Residency
- Assistant Professor of Radiology and Radiological Science
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/5251718/lilja-solnes
Discount 500 mg azatril fast deliveryThis may be particularly efficient when performing augmented procedures that increase the girth at the distal tendon or when the native pores and skin is contracted. Positioning the inclined place allows the best access when approaching the Achilles tendon. Approach the popular method is a posteromedial incision adjacent to the Achilles tendon. This permits the surgeon to keep away from injury to the brief saphenous vein and sural nerve. Simple extension of the incision is performed for the secondstage definitive restore. The posteromedial incision may be prolonged right into a lazy-S, L form, or a direct medial approach. The affected person is instructed on the rationale for the staged process and the significance of weekly follow-up visits between every stage. After sterile preparation, make a longitudinal incision along the medial facet of the ankle, adjacent to the course of the Achilles tendon. Perform superficial subcutaneous elevation till a pocket about 6 4 cm is created. Insert a McGhan tissue expander into this cavity and place the injection catheter away from the implant. Patients hardly ever tolerate greater than 30 to forty cc of total quantity inside the implant. The expansion price might have adjustment (from 10 mL/week) depending on individual skin pliability. After expander elimination and second-stage reconstruction the operative limb is positioned into a short-leg splint in 10 to 15 degrees of plantarflexion. Non�weight-bearing with immobilization in a short-leg solid is maintained for three weeks. Avoiding wound complications after uncared for Achilles tendon repair: tissue growth technique. Reconstruction of pores and skin and tendon defects from wound issues after Achilles tendon rupture. Local flap coverage for delicate tissue defects following open restore of Achilles tendon rupture. Free tissue coverage of wound problems following Achilles tendon rupture surgery. Neglected rupture of the Achilles tendon: treatment by modified Strayer gastrocnemius recession. As a end result, Haglund syndrome is commonly characterized by inflammation inside the retrocalcaneal or Achilles tendon bursa and sometimes secondarily presents as insertional Achilles tendinopathy. The posterior heel ache and swelling associated with Haglund syndrome is the end result of mechanical irritation by the calcaneal prominence on the surrounding gentle tissues and the Achilles tendon. After conservative measures have failed, Haglund deformity and retrocalcaneal bursitis may be treated surgically using both an open or an endoscopic technique. There is a brief restoration time and a quick while to achieve preprocedure exercise level. Appropriate visualization of the Achilles tendon and elimination of the calcaneal prominence and retrocalcaneal bursa can be successfully achieved utilizing an endoscopic approach. Pathology within the retrocalcaneal area is detected on medical examination with level tenderness along the anteromedial and anterolateral aspects of the Achilles tendon and an related prominence of the calcaneus. Palpation of the affected hindfoot often reveals tenderness on the distal portion of the Achilles tendon proximal to its insertion on the calcaneus. It may be troublesome to distinguish whether or not signs are attributable to retrocalcaneal bursitis or insertional Achilles tendinosis or tendinitis, and the two conditions usually coexist. Achilles tendinopathy is a degenerative process throughout the tendon substance inflicting microtears, edema, and reactive fibrosis with scar formation. These changes cause secondary mechanical irritation of the encompassing tissues and may even stimulate an inflammatory course of. Local injections may be given in the retrocalcaneal house, however the concomitant use of native anesthesia and corticosteroids might additional weaken the substance of the Achilles tendon and risk weakness and further micro- or macro-rupture of the tendon. Open procedures embrace resection of the calcaneal prominence proximal to the Achilles tendon insertion with retrocalcaneal bursa elimination. A dorsal closing wedge osteotomy can rotate the posterior calcaneus to less prominence. Achilles tenolysis and partial resection of the diseased portion of the tendon could also be necessary, often with augmentation by the flexor hallucis longus or flexor digitorum. Complications associated with these procedures include hematomas, tendon or skin breakdown, nonunion, Achilles tendon avulsion, tenderness around the operative scar, cosmetic issues, altered sensation across the heel, and stiffness. The endoscopic technique of decompressing the retrocalcaneal area was developed to scale back morbidity and reduce the functional time to recovery for patients with retrocalcaneal bursitis. Positioning the operation is carried out with the affected person within the supine place and underneath both common or regional anesthesia. This enables the surgeon to place the foot towards his or her body while using each hands to function the arthroscopic instruments. The leg rests on a firm padded 12-inch-long and 4-inchdiameter cylindrical bump that permits the surgeon ample room to work and to control ankle dorsiflexion and plantarflexion. The incision is barely anterior to the Achilles tendon and posterior to the sural nerve. It is necessary to bluntly dissect and spread the gentle tissues when making the lateral portal to reduce the risk of harm to the sural nerve. This expanded working area creates visualization and entry to the posterior calcaneus and the Achilles tendon attachment. Take special care to stop the rotating or oscillating shaver or burr usage when the instrumentation enters or exits the portal. Carry out the resection each medially and laterally into the sulcus of the calcaneal tendon (retrocalcaneal bursa) and distally to the attachment of the Achilles tendon. Damaged or diseased Achilles tendon can be selectively uncovered and with a nerve hook or probe identified. Insert an arthroscopic probe into the retrocalcaneal house to affirm continuing effective attachment of the Achilles tendon. Endoscopic bony and soft-tissue decompression of the retrocalcaneal area for the remedy of Haglund deformity and retrocalcaneal bursitis. Apply a compression dressing and splint the foot into slight equinus with the posterior splint and sugar-tong "trilaminar splint. Develop entire operative field from posteromedial to posterolateral corner so panoramic view of Achilles tuberosity attachment.
Purchase cheap azatril lineIf multiple cross-connectors are used, they want to be spread as far apart as attainable from one another for maximal construct rigidity. A claw figuration consists of two hooks directed towards each other, separated by one or two ranges. It is useful to resect sufficient of the facet so that the lateral edge of the spinal canal is identified so that it can be avoided throughout implant placement. They ought to be used with warning as a portion of the implant is positioned inside the spinal canal. Generally, placing two laminar hooks into the canal on the identical degree (eg, two downgoing hooks or two upgoing hooks on the same lamina) should be prevented to minimize implant quantity within the canal unless canal quantity is capacious. The ligamentum flavum is dissected off the lamina, and the laminar floor receiving the hook is prepared with a Kerrison rongeur so the hook will be flush in opposition to the bone. Although weaker than sublaminar or pedicle hooks, they avoid violation of the spinal canal. Fluoroscopy can be used to identify proper pedicle starting factors when affected person anatomy is distorted. Too medial a starting point for pedicle screw entry may injure the supra-adjacent facet joint. A 1% infection price has been noted for discectomies, a 6% infection fee for discectomies and fusion. Pseudarthrosis (nonunion rates, particularly crossing the lumbosacral junction) the incidence of nonunion after posterior lateral intertransverse fusion ranges from 3% to 25%. A big selection of fusion charges across the lumbosacral junction has been reported (22% to 89%). Functional and radiographic outcomes after surgery for adult scoliosis utilizing third-generation instrumentation methods. Pedicle diameter decided by computed tomography: its relevance to pedicle screw fixation within the lumbar backbone. Randomized medical trial of lumbar instrumented fusion and cognitive intervention and workout routines in sufferers with continual low back pain and disc degeneration. Chronic low back pain and fusion: a comparison of three surgical methods: a prospective multicenter randomized study from the Swedish lumbar spine research group. Prophylactic antibiotics and wound an infection following laminectomy lumbar disc herniation. Trunk muscle strength, crosssectional space, and density in sufferers with chronic low again ache randomized to lumbar fusion or cognitive intervention and exercises. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective long-term study comparing fusion and pseudarthrosis. Management of persistent disabling low again ache with 360 levels fusion: outcomes from ache provocation check and concurrent posterior lumbar interbody fusion, posterolateral fusion, and pedicle screw instrumentation in patients with chronic disabling low again ache. Mechanical stability of thoracolumbar pedicle screw fixation: the impact of crosslinks. Natural history of degenerative spondylolisthesis: pathogenesis and natural course of the slippage. Complications in the surgical remedy of pediatric high-grade isthmic dysplastic spondylolisthesis: a comparability of three surgical approaches. Degenerative disc disease handled with mixed anterior and posterior arthrodesis and posterior instrumentation. The consequence of posterolateral fusion in highly chosen patients with discogenic low back pain. The efficacy of pedicle screw/plate fixation on lumbar/lumbosacral autogenous bone graft fusion in adult patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. Health and performance of patients with untreated idiopathic scoliosis: a 50-year natural historical past research. They directly handle the disc as a potential pain generator in patients with discogenic pain syndromes. They have demonstrated a excessive price of fusion that approximates the arthrodesis rate achieved with a extra intensive mixed anterior and posterior fusion procedure. They permit some correction of spinal deformities, together with asymmetric disc house collapse, spondylolisthesis, and gentle kyphosis. They protect a virgin anterior method should revision surgical procedure turn out to be necessary or ought to an adjoining section arthroplasty turn into an option in the future. The triangular working window consists of the next: the traversing nerve root and thecal sac form the medial border of the triangle. The superior aspect of the pedicle of the distal vertebra forms the base of the triangle. A confluence of epidural veins traveling longitudinally and transversely drapes the ground of the spinal canal and neuroforamen. A noncollapsed disc house of an grownup lumbar spine averages between 12 and 14 mm in height, with an anteroposterior diameter of about 35 mm. Since interbody structural grafts are load-sharing, they significantly reduce the cantilever bending forces utilized to posterior spinal implants, thus protecting them from failure. The interbody space has been shown to provide an optimal milieu for selling arthrodesis for a quantity of reasons: A giant floor area of extremely vascular cancellous bone is on the market. Addition of the interbody fusion raises the arthrodesis rate over stand-alone posterior fusion. Medial retraction of the neurologic parts is critical to facilitate access to the disc area. The outer annulus serves as a barrier that reduces fibrous tissue ingrowth into the fusion mass throughout therapeutic of an interbody arthrodesis. They enable for restoration of interbody top and some correction of local kyphosis without placing undue stress on the posterior implants. They permit decompression of the exiting and traversing nerve roots not directly by restoring foraminal top and immediately via open laminectomy and foraminotomy. Note the dorsal displacement of the traversing left S1 nerve root (thin arrow) by the disc and the previous left-sided laminotomy defect (thick arrow). Several latest displays (not but published) have found that routine instances of degenerative spondylolisthesis might not benefit from the addition of an interbody arthrodesis and could also be best managed with commonplace posterior laminectomy and fusion procedures. Given their versatility, the well-trained spinal surgeon must concentrate on the indications for these procedures and have to be capable of executing them correctly. Preoperative Planning Preoperative imaging research ought to be reviewed to determine the appropriate size and trajectories essential for pedicle screw insertion in addition to the anteroposterior diameter of the disc house. Disc space top in addition to adjoining disc top and overall lumbar alignment must be measured to assist determine optimum interbody implant dimension. An assessment ought to be made as to whether or not direct or oblique neurologic decompression might be essential. Deformity at the degree of the deliberate fusion needs to be assessed in order that intraoperative measures could be taken to provide for correction.
Diseases - Preaxial deficiency postaxial polydactyly hypospadia
- Familial porencephaly
- Wooly hair syndrome
- Fetal thalidomide syndrome
- Delleman Oorthuys syndrome
- Cutaneous larva migrans
- Gingivitis
- Fetal warfarin syndrome
- Overhydrated hereditary stomatocytosis
- Ehrlichiosis
Buy azatril 500mg on lineThe surgeon ought to intraoperatively assess for equinus and the need for percutaneous tendo Achilles lengthening or gastrocnemius slide. Every effort is made to maximize the pores and skin bridge between the 2 incisions to prevent wound necrosis or slough. Aggressive pores and skin retraction should be minimized and accomplished through deeper layers and never superficially. Positioning Patients are positioned supine on a radiolucent table with a padded wedge or bump beneath the ipsilateral hip to right external rotation. If proximal tibial bone graft is considered, the tourniquet should be utilized on the thigh. Identify the deep peroneal nerve with the accompanying dorsalis pedis artery just deep to the medial side of the extensor hallucis brevis tendon, coursing toward the first net space. Avoid using an oscillating noticed, as it can predispose to the risk of metatarsal shortening. Again, break up the periosteum according to the joint to avoid extreme periosteal stripping. Place the first from the dorsal medial cuneiform to the plantar side of the primary metatarsal base. Place the second from the dorsal first metatarsal shaft to the plantar aspect of the medial cuneiform. Reduce the second metatarsal to the center cuneiform and the first metatarsal base. Make a stab incision over the medial aspect of the medial cuneiform by way of the pores and skin solely. Make a stab incision on the lateral forefoot to facilitate insertion of one other guide pin from the 3. Examine the foot place to confirm plantigrade place before last stabilization. Use similar steps to place an extra lag screw from the primary metatarsal to the cuneiform. Use an analogous approach to insert the screw from the third metatarsal to the center cuneiform. We often use cancellous allograft mixed with a platelet-rich spinoff to promote both osteoconduction and osteoinduction. Autograft may be harvested from the calcaneus, proximal or distal tibia, or iliac crest. Close the skin with horizontal or vertical mattress nylon sutures with minimal rigidity. Analgesic control is optimal with a neighborhood or regional anesthetic along with oral narcotics. Progressive weight bearing is permitted between 6 and 12 weeks in a removable boot. Dowel arthrodesis for degenerative arthrodesis of the tarsometatarsal (Lisfranc) joints. Mid-tarsal arthrodesis for major degenerative osteoarthrosis or osteoarthrosis after trauma. With appropriate surgical indications, surgical method, and affected person compliance, patient satisfaction rates exceed 90%. Anatomic alignment in the longitudinal airplane is somewhat easy to assess on weight-bearing radiographs of the foot. Physiologically, the medial and center columns (first by way of third rays) have congruent joints and tight ligaments, leaving little movement. With progressive midfoot deformity, the hindfoot may eventually lose its physiologic alignment, sometimes with greaterthan-physiologic valgus. This usually leads to shortening of the Achilles tendon and equinus contracture. In the sagittal (lateral) aircraft this leads to loss of the longitudinal arch at the midfoot, with a midfoot sag. A plantigrade foot balances comparatively evenly on the weightbearing surfaces of the first and fifth metatarsals and the heel. When the midfoot collapses, this steadiness is disrupted and weight bearing ultimately may be on the midfoot as properly. Also, a affected person with neuropathy could develop midfoot destabilization but with out recollection of trauma or with a historical past of what appeared to be only a minor trauma. Patients expertise pain with weight bearing, especially with push-off through the gait cycle. With advanced disease, loss of the longitudinal arch and forefoot abduction are current. Midfoot tenderness and ache with stress Tenderness is often focused on the midfoot. The "piano key check" isolates the primary target of the pathology to the particular tarsometatarsal joint. Preoperative Planning Preoperative weight-bearing radiographs of the foot are important to decide the preoperative plan. The diploma of destruction or distortion of the midfoot anatomy (particularly with erosive changes of an inflammatory arthropathy) is essential and components in how to finest reconstruct the midfoot. Equinus contracture the preoperative evaluation should embrace the condition of the Achilles tendon. Often Achilles lengthening, both with a triple cut or gastrocnemius-soleus recession, is critical to realign the foot and will serve to unload stresses on the midfoot. Equipment Various screw and plating techniques, some even devoted to the midfoot, can be found. Procedures might embody arthrodesis in situ or arthrodesis in combination with realignment midfoot osteotomy. Occasionally, adjunctive hindfoot procedures and Achilles tendon lengthening may be warranted. Rongeur in junction between base of second metatarsal and first cuneiform (it is important to ensure the second metatarsal absolutely reduces). Note that the windlass mechanism is still being maintained with dorsiflexion of the toes. Large bone reduction clamp to ensure that the second metatarsal base is reduced, much like open discount and internal fixation of an acute Lisfranc fracture-dislocation. Provisional fixation for second metatarsal is the information pin for the drill for the screw to be positioned from the primary cuneiform to the second metatarsal base, a standard "Lisfranc screw. Note that the information pin place was checked on fluoroscopy and measured to determine optimal screw size, after which the information pin was pushed totally by way of the second metatarsal to exit the lateral wound.
Discount azatril 100mg lineThe nerve and its "conduit to nowhere" is buried posteromedially, typically into the retrocalcaneal house. Accuracy of the pores and skin incision the pores and skin incision should be correct and the anatomy clearly seen. Bleeding Use of loupes and careful hemostasis will stop bleeding, which prevents accurate visualization of the buildings. Postoperative bleeding will irritate the nerve and create more scarring, and can compromise the outcome. Make positive the tourniquet is of correct dimension for the size of the thigh, and exsanguination must be proper as a lot as the tourniquet. Completeness of the release All constructions noted within the description should be absolutely released. Gentle range-of-motion train of the ankle is re-emphasized to promote gliding of the nerve, but non�weight-bearing continues for 2 extra weeks. At 4 weeks, the affected person is allowed to bear weight using the custom orthotic described earlier. If the patient fails to comply, ache might be skilled, normally on the dorsum and lateral border of the foot, presumably from "arch strain. Revision Surgery Less predictable results have been reported for revision surgery. Although 73% of sufferers indicated they have been better off than earlier than surgical procedure, total satisfaction was reported by solely 27%, and 36% have been dissatisfied with the procedure. In revision situations, sufferers with evidence of insufficient prior distal tarsal tunnel launch and those with persistent mechanical plantar fasciitis are more than likely to have good resolution of their symptoms. Data on the utilization of collagen conduits and wraps are being collected, with encouraging early outcomes. This is a significant enchancment over the lower than 50% total satisfaction reported in most recent studies of limited plantar fascia release with a limited nerve release, or nerve release without plantar fascia release. The improved rate of total satisfaction is reflective of the lower charges of residual ache and exercise limitations. Improved surgical results in primary surgery patients are thought to be as a result of the excellent surgical approach with the objective of addressing all potential sites of pathology-nerve and plantar fascia. Meticulous technique is needed to keep away from potential issues, which embody wound dehiscence, perineural scarring, and direct nerve injury. Plantar fascia release with proximal and distal tarsal tunnel release: surgical approach to persistent, disabling plantar fasciitis with related nerve ache. Chronic, disabling heel pain with associated nerve ache: major and revision surgical procedure results. Podium presentation and summary on the 17th Annual Summer Meeting of the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society, San Diego, July 2001. American Sports Medicine Institute evaluate of 104 feet (92 patients) following the entire plantar fascia and tarsal tunnel release between 1996�2000. Heel pain triad: the combination of plantar fasciitis, posterior tibial tendon dysfunction, and tarsal tunnel syndrome. Effects of tarsal tunnel release and stabilization procedures on tibial nerve rigidity in a surgical created pes planus foot. The predominant symptom is pain within the plantar region of the foot when initiating strolling. The trigger is a degenerative tear of part of the fascial origin from the calcaneus, adopted by a tendinopathy-type reaction. Rarely, pain may be positioned distally; this condition known as distal plantar fasciitis. Careful comparison to the contralateral heel is useful in confirming tenderness typical for plantar fasciitis. As the toes lengthen during the stance part of gait, the plantar fascia is tightened by a windlass mechanism, resulting in elevation of the longitudinal arch, inversion of the hindfoot, and external rotation of the leg. Endoscopically, the pertinent anatomy is the abductor hallucis muscle medially, then the plantar fascia. After fasciotomy, the flexor digitorum brevis comes into view because the medial intermuscular septum. Stress fractures, unicameral bone cysts, and big cell tumors are often recognized with plain radiography. Three-phase technetium bone scans are hardly ever essential but are positive in up to 95% of circumstances of plantar fasciitis. Ultrasound is cost-effective and simply measures the thickness of the plantar fascia, documenting plantar fasciitis when thickness exceeds three mm. These pathologic adjustments are more according to fasciosis (degenerative process) than fasciitis (inflammatory process), but fasciitis stays the accepted description in the literature. Tarsal tunnel syndrome: Compression of the tibial nerve could cause numbness and ache in the heel, sole, or toes. Positive percussion and compression checks are elicited, and electromyography and nerve conduction research are optimistic in 50% of circumstances. In our opinion, these two entities are separate, and with cautious examination plantar fasciitis may be isolated and effectively handled with endoscopic plantar fascia launch. Strain of the plantar fascia may result from prolonged standing, running, or leaping and actions that create repetitive stress on the plantar fascia. Pain is often achy, constant, nocturnal, and even present without weight bearing and at rest. Laboratory tests may show elevated erythrocyte sedimentation price, C-reactive protein, or white blood cells. Painful heel pad syndrome: Occurs most frequently in runners; thought to result from disruption of fibrous septa of the heel pad Heel pad atrophy: Occurs in the aged, often not characterized by morning pain, and a "central heel pain syndrome" with tenderness extra plantar than in plantar fasciitis, directly under the bony prominence in the calcaneus Inflammatory arthritis: Usually bilateral and diffuse in nature. The incision is made along a line that bisects the medial malleolus 1 to 2 cm superior to the junction of keratinized and nonkeratinized pores and skin. A level simply anterior and inferior to the calcaneal tubercle is marked and measurements are made to the inferior and posterior pores and skin traces. From left to right: obturator with cannula, plantar fascia elevator, probe, disposable triangle knife with nondisposable deal with, disposable hook knife with nondisposable deal with, and disposable triangle knife without handle. Several cotton-tipped applicators frivolously fluffed with a Bovie scratch pad are needed. Make an 8-mm vertical incision just anterior and plantar to the medial tubercle of the calcaneus. Place the plantar fascia elevator via the incision and sweep it from medial to lateral just plantar to the plantar fascia. Pass the obturator and cannula by way of this pathway and convey them out through a lateral incision overlying the tip of the obturator. The quantity of fascia divided is normally 14 mm, which may be measured off markings on the probe. The hook knife can be utilized to reduce the fascia, however the triangle knife could be more simply manipulated with much less likelihood of cutting into the muscle.
Purchase azatril 500mg onlinePostoperative weight-bearing radiographs of instance patient with traditional screw fixation and supplemental anterior plate. Preoperative radiographs of affected person present process double anterior plating arthrodesis approach. Lateral anterior plate applied and secured to talus and proximal compression system in place. Intraoperative fluoroscopic views of ankle of a special patient present process twin anterior plating, with provisional fixation and lateral plate in place. While the locking plate creates axial compression, a mild however desirable valgus moment may be introduced since the lateral plate is being used for compression. To get hold of optimum compression, provisional fixation is removed before compression is utilized but after the screws are locked into the talar neck and the compression gadget is secured proximally. Since compression has already been carried out, this medial plate, which can also be precontoured, serves to statically lock the arthrodesis. Standard wound closure I routinely close the capsule, extensor retinaculum, subcutaneous layer, and pores and skin (to a tensionless closure). The deep neurovascular bundle, extensor tendons, and superficial peroneal nerve need to be protected throughout closure. Intraoperative fluoroscopic views of two screws positioned via the plate into the posterior talus for extra stability. Intraoperative fluoroscopic views of various patient with supplemental screw to anterior plating. Lateral view (note damaged information pin; it is necessary to observe the precise trajectory of the guide pin with cannulated screw systems). In some instances, I even have carried out a staged arthrodesis, with initial d�bridement and antibiotic bead place- ment. The external fixator could also be placed at that preliminary procedure or on the definitive procedure when the antibiotic beads are removed and the joint is reduced and compressed with the exterior fixator. Preoperative radiographs of instance patient for ankle arthrodesis with exterior fixation; affected person has failed ankle arthrodesis with internal fixation. The external rotation malunion of the distal tibia creates extreme exterior rotation of the foot relative to the tibial axis. Forty-five-year-old patient with posttraumatic arthritis and deformity of the ankle, failing to reply to a previous try at ankle arthrodesis. A normal anterior method is simply too dangerous and, for my part, would leave an insufficient skin bridge to the prior incision. I additionally switched the lamina spreader to the medial wound in order that I could put together the rest of the joint via the lateral incision. However, that is more important with inside fixation; with external fixation such malrotation might still be corrected postoperatively with exterior fixator body adjustment. Medial incision is being used for joint preparation whereas joint is being distracted by lamina spreader positioned through lateral incision. Ankle could be manually decreased to a physiologic position with the second metatarsal aligned to the anterior tibial shaft axis. Joint discount Neutral dorsiflexion�plantarflexion Slight hindfoot valgus Correct malrotation Align second metatarsal with the anterior tibial crest. I routinely shut the wounds at this level because as soon as the exterior fixator is in place, suturing is particularly tedious. However, should you favor to delay the wound closure till the exterior fixator is in place, one or two struts can simply be mirrored to permit enough access to the wound or wounds. Foot plate I droop the foot plate ("horseshoe") from a transverse forefoot wire. Before tensioning the skinny wires, I close the horseshoe-shaped foot plate anteriorly. Having two foot plate components affords less interference between the struts (that will connect the proximal ring block to the foot plate) and the skinny wires to be handed via the foot from the foot plate. These two wires either have to be built up from a single foot plate or connected to the proximal element of a two-ring foot plate set-up. Foot plate suspended from forefoot wire and calcaneal wires being passed to stabilize the hindfoot. The ring has been closed on the foot body in order that tension in all wires can be effectively maintained. Closing the highest ring permits the foot frame to be closed even without putting a half-ring on the anterior portion of the "horseshoe. Without talar wires compression would be positioned not only on the tibiotalar joint but in addition on the subtalar joint. A perhaps more refined (but no more complicated) construction of the foot plate is to distract between the 2 elements of the foot plate, so that the subtalar joint is distracted whereas the tibiotalar joint is compressed. Adding struts to be used for compression between the proximal ring block and the foot body. Ankle with neutral dorsiflexion�plantarflexion and plantar foot is distal to most distal ring�plate. If adjustments have to be made, the computer program could additionally be used to run an effective correction at this time. However, on the operating table, the struts might merely be loosened, a gross manual adjustment may be made (with the provisional fixation removed), and the struts once more secured. Final examine to be sure that all bolts and connections are steady Sterile dressings on the wound Sterile dressings on the wires and half-pins Pin irritation typically occurs due to skin movement or rigidity concerning the half-pins or thin wires. I routinely place thick dressings around the thin wires and half-pins, creating reasonable pressure from the dressing on the skin immediately adjacent to the halfpin or wire and thereby stabilizing the pores and skin. Optimal place is neutral dorsiflexion�plantarflexion, slight hindfoot valgus, and the second metatarsal aligned with the anterior tibial crest. Internal fixation for ankle arthrodesis might be contraindicated; nevertheless, arthrodesis remains to be potential with external fixation. Internal and external fixation could stabilize the joint, but satisfactory joint preparation for arthrodesis is crucial for fusion to happen. This allows adjustments in dorsiflexion�plantarflexion place with out forfeiting bony apposition on the arthrodesis site before fixation. No want for pin care; perhaps much less intimidating to the patient Further compression and adjustments on the arthrodesis web site are possible postoperatively; maybe earlier weight bearing. However, we typically maintain these sufferers no much less than in a single day for ache management, nasal oxygen (which could have some constructive effect on anterior wound healing), and prophylactic intravenous antibiotics. Follow-up in 10 to 14 days Internal fixation Suture removal Short-leg, touch-down weight-bearing cast External fixation Suture removal Radiographs to assess bony apposition at the arthrodesis site and alignment. We routinely add more compression to the arthrodesis web site at this and subsequent visits.
Syndromes - Eyesine
- Fatigue
- Lightheadedness
- Infections
- Wheezing
- Osteomyelitis
- Hydrocortisone (Cortef)
- Growth failure
- Areas of dullness or redness
Purchase azatril overnight deliveryNeurologic retraction ought to be launched frequently to permit for reperfusion of these sensitive constructions. Free run electromyographic monitoring can provide stay feedback and assist reduce the chance of neurologic harm from overzealous neurologic retraction. Great care must be taken to account for the dura and neurologic parts each time that an instrument or graft is inserted into the disc area. Should important difficulties come up corresponding to obstructing anomalous neural anatomy, major epidural bleeding, or a complex dural tear, one must be prepared to abandon the interbody portion of the fusion quite than threat causing a catastrophic harm. Great care have to be taken to establish the neurologic buildings when using bipolar cautery. Should a dural tear happen, it should be repaired as soon as technically possible, as decreased intrathecal pressure will produce engorgement of the epidural veins with considerably more bleeding. Graft placement Bony resection must permit adequate entry to the interbody region to permit placement of an adequately sized graft. Graft sort ought to be chosen fastidiously in conditions where access to the disc is proscribed or a tall disc area exists. Due to their narrower widths, rectangular grafts or cages could be inserted extra simply right into a tall disc house than cylindrical grafts, which require a bigger transverse exposure. Fluoroscopy and offset impactors should be used throughout graft insertion to facilitate optimal last implant place. Properly sizing the interbody implants and totally packing the disc house with graft materials might help scale back the danger of this complication. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a protected approach with satisfactory three- to five-year outcomes. Radiographic evaluation of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of adult isthmic spondylolisthesis. Clinical and radiologic 2to 4-year outcomes of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis grades 1 and 2. Chronic disabling low again pain syndrome brought on by inside disc derangements: the outcomes of disc excision and posterior lumbar interbody fusion. The indications for interbody fusion cages within the treatment of spondylolisthesis: analysis of a hundred and twenty circumstances. Is local bone viable as a supply of bone graft in posterior lumbar interbody fusion Surgical problems of posterior lumbar interbody fusion with whole facetectomy in 251 patients. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: scientific and radiographic results and complications in 100 consecutive sufferers. Perioperative issues in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion versus anterior-posterior reconstruction for lumbar disc degeneration and instability. Many of those accidents characterize a neuropraxia because of extreme nerve root retraction and resolve spontaneously. The thoracic pedicles are oval and are larger superoinferiorly than mediolaterally. Trauma the articulation of the vertebral column, ribs, and sternum makes the thoracic spine relatively secure. Forces related to damage are axial compression, flexion, lateral compression, flexion�rotation, shear, flexion� distraction, and extension. Patients with decrease extremity symptoms and myelopathy are likely to require surgical intervention. Neurologic penalties happen from direct anterior compression of the spinal twine from a herniated disc. Infection Vertebral osteomyelitis is rare and accounts for 2% to 4% of all instances of osteomyelitis. Staphylococcus aureus is the commonest organism, accounting for nearly 50% of pyogenic infections. Before medical and surgical treatment, spinal osteomyelitis carried a mortality fee of larger than 70%. Proposed routes of infection include hematogenous spread from other infected foci, local extension from nearby infections, and direct inoculation. Advocates of venous hematogenous spread argue that organisms are carried to the spine through the plexus of Batson, much like the mechanism of tumor metastasis. Primary tumors from the breast, prostate, lung, kidney, and thyroid are more than likely to metastasize to the vertebral column. Benign major tumors which have a predilection for the anterior elements embody large cell tumors and hemangiomas. Malignant tumors that commonly have an effect on the anterior components embody osteosarcomas, chondrosarcomas, myelomas, and lymphomas. The thoracic backbone configuration of vertebrae, sternum, and ribcage confers an inherent stability. Patients can have related accidents such as pneumothoraces, pulmonary contusions, and vascular accidents. A conservative remedy plan ought to include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories, relaxation, exercise modification, and bodily remedy focusing on trunk stabilization. Infection Vertebral infections must be handled nonoperatively with culture-specific antibiotics and spinal immobilization. Treatment frequently entails 6 weeks of parenteral antibiotics followed by a course of oral antibiotics. External immobilization with an orthosis can help stabilize the spine, lower ache, and prevent deformity. Manual motor testing Pin-prick and light contact sensory examination may assist to localize the wire stage of damage based on dermatome. Reflex examination of the patellar and Achilles tendons: hyperactivity is an higher motor neuron sign. Tumor A multidisciplinary strategy including a neuroradiologist, pathologist, oncologist, and backbone surgeon is used to deal with spinal tumors. Trauma Most thoracic and thoracolumbar spine accidents could be effectively handled nonoperatively. Conservative treatment can embody recumbency, bracing, and ache management for sufferers with out neurologic deterioration and with a structurally stable harm. The superior fringe of the pedicle of the caudal vertebra is resected with a rongeur to expose the dural tube. To find the disc herniation, the surgeon follows the superior fringe of the pedicle to the vertebral body and disc space. The disc herniation is eliminated using small angled curettes and pituitary rongeurs. Discectomy may be facilitated by eradicating a small portion (1 to 2 cm) of the adjoining vertebral our bodies. Diaphragm Costovertebral articulations Segmental vessels Rib head removal Sympathetic trunk the portion of the disc that lies away from the ventral aspect of the spinal cord ought to be eliminated first. Once a cavity is created by removing this initial disc and bone, the the rest of the disc could be eliminated into this cavity, ensuring that all forceful maneuvers are directed anteriorly away from the thecal sac. For retropulsed fracture fragments, the fragments are first thinned utilizing a high-speed 4-mm ball-tipped burr.
Purchase on line azatrilThe surgeon ought to try to place a graft that fills the area as a lot as potential without overdistracting, which might trigger posterior neck pain, or getting into the spinal canal. One way to improve fusion charges is to place as much bone into the interspace as possible. Space lateral to the structural bone graft within the uncinate areas can be filled with bone or bone graft substitutes. If the area is extensive enough, two grafts may be placed side by aspect to fill the entire space. This plate size permits for screws that angle away from the disc area, which in turn allows for screws that are longer than ones directed parallel to the disc house, but are brief enough to avoid entry into the supra- and infra-adjacent disc areas. The plate ought to be contoured into lordosis to lie flush towards the vertebral our bodies. It must also be centered coronally throughout the margins of the uncinate processes. Screws must also be angled medially to decrease the chance of lateral harm to nerve roots or vertebral arteries. Variable screw techniques enable for toggling inside a set screw gap with settling of the assemble. Slotted plates have holes that permit screws to translate longitudinally as the construct shortens. Telescoping plates use mounted screws in nonslotted holes, but the ends of the plate telescope with respect to each other as settling occurs. The size of an optimally sized plate is such that the screw holes at the high and bottom of the assemble are instantly adjoining to their respective endplates. In this instance, despite the fact that this was carried out, the plate is still nearer to the cephalad adjoining disc space than ideal as a outcome of the vertebral bodies on this patient are comparatively brief. Screws should be angled away from the disc space to provide larger length and divergent fixation, which can higher resist pullout. However, this plate was positioned too near the adjacent disc, resulting in adjacent-level ossification disease (arrow). As demonstrated by these examples, correct plate sizing is very essential in sufferers with shorter vertebrae, the place the adjacent discs are nearer together. In distinction to the variable and slotted plates, with the telescoping plate design shown, the connection between the ends of the plate and the adjoining disc areas stays fastened as the plate dynamizes, as a end result of the plate shortens internally. If dynamic plates are used, the surgeon must carry out the plating process to accommodate the anticipated settling without overlapping uninvolved adjoining discs. Although plates may higher preserve lordosis and achieve larger fusion rates in multilevel instances, avoiding plates may lower operative time, decrease the quantity of retraction on the soft tissue structures of the neck throughout surgery, and keep away from plate-related complications similar to screw backout or esophageal erosion. However, if one chooses not to use a plate, autograft must be used quite than allograft, and rigid postoperative immobilization in a cervical orthosis is obligatory. Up to three adjacent interbody cervical fusions may be safely carried out without instrumentation. The interspaces ought to be fused sequentially, that means a decompression and fusion is accomplished at one interspace earlier than the subsequent is addressed. Without distraction, the peak is usually 6 mm; with distraction, it might be to up to 12 mm. The top of the graft must be greater than the resting top however less than the distracting peak in order that the inherent compression of the vertebral our bodies will hold the graft firmly in place. Postoperatively, if the graft is secure, a easy gentle collar must be used for four to 6 weeks. Without distraction, the graft is compressed by the natural elasticity of the cervical spine. There is about 2 to 6 mm of free space between the posterior floor of the graft and the spinal twine. This will generally require larger preparation of the inferior endplate of the cephalad vertebrae. When entering the foramen to remove bone spurs, the curette or Kerrison ought to hug the posterior aspect of the uncinate to avoid the nerve root, which exits ventrally at a 45-degree angle. The uncinate ought to be thinned first with a burr in order that a small instrument could be inserted into the foramen to full the foraminotomy without injuring the underlying root. The surgeon ought to select the shortest plate that will match, such that the screw holes are instantly adjoining to the endplates, to avoid adjacent-level plate or screw impingement. In instances of a quantity of fusions, each decompression and fusion should be accomplished before the next interspace is addressed. A deep drain is placed in the retropharyngeal area to stop hematoma formation. It is typically removed the morning after surgical procedure unless its output is larger than 30 cc within the last 8 hours. Cold drinks and ice cream may help with dysphagia and reduce swelling in the instant perioperative interval. Midline axial neck ache may enhance whether it is related to radicular pain, however sufferers should be recommended that the first aim of treatment is neural decompression and relief of radicular or myelopathic signs. Similarly, unilateral neck ache could be a manifestation of radiculopathy and also typically improves. Incidence of dysphagia after anterior cervical backbone surgical procedure: a prospective study. Anatomic basis of the anterior surgery on the cervical spine: relationships between uncus-artery-root advanced and vertebral artery harm. Robinson anterior cervical fusion: comparability of the standard and modified methods. Radiculopathy and myelopathy at segments adjoining to the location of a previous anterior cervical arthrodesis. Development of adjacent-level ossification in patients with an anterior cervical plate. Epidemiology of cervical radiculopathy: a population-based examine from Rochester, Minnesota, 1976 through 1990. Outcome in patients with cervical radiculopathy: prospective, multicenter research with independent medical evaluation. The therapy of sure cervical backbone problems by anterior removing of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion. The majority of patients with dysphagia have only mild signs, with clinical enchancment inside three weeks. The superior laryngeal nerve innervates the cricothyroid muscle, which adjusts the tension on the vocal folds and also offers supraglottic sensation. Superior laryngeal nerve palsies due to this fact could lead to issue with singing high notes in addition to aspiration.
Proven 100 mg azatrilAt the time of session, the affected person has usually already been admitted to the hospital with the initiation of intravenous antibiotics, bed relaxation with elevation of the extremity, and a non�weight-bearing status, thus blurring the flexibility to distinguish whether or not the affected person improved due to easy rest or medicines. A history of fevers and chills, incapability for diabetics to management their blood sugar levels, and a history of earlier or current ulceration enhance the chance of energetic infection at presentation. Any ulceration ought to be rigorously documented, as well as its depth and Wagner grade. Typical radiographic modifications include fracture and dislocation, bony destruction, periosteal reaction, and malalignment. These findings are difficult to distinguish from acute or continual osteomyelitis and alone are unreliable for figuring out the presence or absence of infection. Radiographs alone are adequate for diagnosing the illness process, but different imaging research are often necessary to decide the presence or absence of an infection. Referral to a vascular surgeon ought to be thought of for staged arterial reconstruction if vital insufficiency is current. Nonsurgical therapy sometimes entails a period of solid immobilization utilizing a total-contact solid, and possibly a interval of limited or non�weight-bearing. The aim of nonsurgical remedy with casting is to have the foot consolidate to a plantigrade structure without vital bony prominence. Surgery is often reserved for patients with acute fracture dislocations, these with progressive or unbraceable deformities, and those with recurrent ulceration despite multiple makes an attempt at accommodative bracing. Enhancement with intravenous gadolinium offers stronger support to the presence of infection. Nuclear Imaging Nuclear imaging is especially useful in helping differentiate an infected Charcot course of from a noninfected course of. A three-phase technetium bone scan alone shall be of little worth as increased uptake will normally be present in all three phases. However, when this study is immediately followed by a labeled white blood cell scan, the combined research may be useful to resolve whether the method is Charcot course of alone, soft tissue infection, or osteomyelitis. Other isotopes could additionally be helpful in differentiating an infection from a sterile Charcot course of and include 99mTc sulfur colloid and mixed bone and white cell "dual peak imaging. Active an infection or osteomyelitis is a contraindication for this method because the hardware is often permanent and difficult or inconceivable to take away with out significant bony destruction. The involvement of an astute internist is necessary in command of diabetes and medical comorbidities. Acute trauma with out bony dissolution or important swelling can be safely reduced and fused within every week or two of damage, providing the dislocation is acknowledged and the patient has not entered the inflammatory stage of the neuroarthropathy process. Once the patient enters the inflammatory section, we choose to forged the patient for six to eight weeks to enable the edema to resolve and perform the reconstruction in a staged manner. Electrodiagnostic Testing this is often pointless when peripheral neuropathy may be documented on bodily examination. It is beneficial for documentation of deficits and also may be useful in prognosis of the underlying reason for neuropathy. This approach is most helpful for deformity on the tarsometatarsal stage, and can be extended throughout the naviculocuneiform joints. Vascular Testing We recommend rigorous workup of any suspected vascular insufficiency. Clinical photographs present midfoot deformity after spontaneous midfoot fracture-dislocation. Positioning the patient is positioned supine with a bump beneath the hip so that the toes face perpendicular to the working table. A threestep tendo-Achilles lengthening, gastroc�soleus recession, or both is performed to achieve ankle dorsiflexion of 15 degrees earlier than inflating the tourniquet. Approach A two- or three-incision method is used to scale back deformity and to prepare the arthrodesis mattress. A subperiosteal dissection is carried out above and under the extent of the deformity. The center column of the foot is approached although a dorsal incision centered between the second and third metatarsal bases. A third incision is often essential for exposure and discount of the lateral column and is carried out dorsally on the degree of the fourth and fifth tarsometatarsal joints. Care have to be taken to provide an enough skin bridge between the dorsal incisions or wound necrosis or dorsal slough might occur. Adequate bone resection is critical to stop excessive pressure on the dorsal gentle tissue envelope and vascular structures. Bone resection is at the degree of the deformity and often includes resection of some bone from the proximal and distal fragments. Carry out bone resection medially for the medial column, and dorsally for the center and lateral columns. Adequate bone resection is indicated by the power to manually cut back the deformity. Resect bone slowly in order that a balanced reduction could be achieved between the metatarsal bases. Place guidewires within the metatarsal shafts without crossing the apex of the deformity. After bony resection, flex the foot via the center and enter the metatarsal base with a curved curette, then a guidewire, which is handed into the metatarsal shaft. It is greatest to start with a small guidewire and a small cannulated drill and then change to a larger guidewire and bigger cannulated drills. Once the guidewires are in place in the reamed metatarsal shafts, hold the deformity decreased and advance the guidewires into the midfoot. Measure screw length from the middle part of the primary metatarsal head within the medial column, and from the metaphyseal�diaphyseal junction of the lesser metatarsals. A counter-sink should be utilized by way of the metatarsal head or it might fracture as the screw head is applied. After making use of the screws, sequentially tighten them to present compression across the arthrodesis web site. Medial column is exposed: observe the tibialis anterior tendon insertion, which have to be reattached whether it is released for reduction. The noticed is used to resect bone plantarly and medially to restore axial alignment and to relieve soft tissue tension. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2010;92(Supplement 1 Part 1):1�19; reprinted with permission. Application of the screws axially throughout the arthrodesis site after advancing the guidewires to the desired stage. Surgery is indicated for grossly instability, recurrent ulceration, a nonplantigrade foot and unbraceable deformity. When surgery is done: span the world of dissolution; adequate bone resection, use larger, stronger implants; place implants the place they offer mechanical benefit. This is usually modified inside a few days of the surgical procedure and switched to a cast. The affected person is non�weight-bearing for 10 to 16 weeks, and should start weight bearing in a pneumatic walking boot once bony consolidation is obvious radiographically (average 12 weeks).

Cheap azatril 100 mg overnight deliveryLocking the foot in plantarflexion will tilt the talar reduce towards the subtalar joint. There is often sufficient bone to insert one or two screws for fixation, or a rigidity band wire method could presumably be used. A leg walker is applied, and the patient can begin with non�weight-bearing vary of movement for 5 minutes 3 times a day. At 6 weeks radiographs are obtained, and if there are adequate signs of syndesmosis healing the patient can progress to full weight bearing and begin bodily therapy to increase vary of movement, proprioception, and energy. Further perioperative issues embody tibial nerve harm, tendon accidents, and wound issues. The use of autologous concentrated development factors to promote syndesmosis fusion within the Agility total ankle alternative: a preliminary examine. Total ankle arthroplasty with the Agility prosthesis: clinical and radiographic analysis. At a imply 9-year follow-up the revision rate was 11% (either a revision or a fusion). Eighty-nine (76%) of the 117 ankles had some proof of peri-implant radiolucency. Syndesmosis nonunion had a negative influence on the medical and radiologic outcome. Overall, 37 of 38 patients had been glad with the outcome of their surgery and would have the identical procedure under related circumstances. It could also be necessary both comparatively early after the index procedure, or delayed because of late mechanical failure. By definition, revision may be required around a secure arthroplasty (ie, correcting imbalance creating deformity within the prosthesis or repairing fractures around the prosthesis) or by implant removal and subsequent alternative of the prosthesis (whole or in part). Micro- or macromotion may happen by way of the prosthesis�bone interface on the fibula from lack of a syndesmotic fusion, creating the potential for lateral malleolar fracture. Distal tibia and talus: Failure is sustained through axial load utilized to this portion of bone, compounded by the physiologic results of the prosthesis. Osteolysis could happen from shed polyethylene particles, making a macrophage reaction and autodestruction of bone. This weakened, cystic bone allows the prosthesis to subside by way of the resection margin, creating deformity and failure. Often deformity exacerbates this downside, as chronic pressure through weight bearing continues to attenuate the ligaments, creating further compromise. In extra superior circumstances, wound protection is required because of tendon publicity. Compromised blood provide to the anterior pores and skin, multiple prior incisions in posttraumatic or reconstructive conditions, and direct apposition of the tendon advanced in opposition to the pores and skin may all accelerate anterior incision failure. Early intervention in the form of parenteral antibiotics or operative d�bridement could permit salvage of the prosthesis. Bacteria might cling to the prosthesis, making a situation proof against antibiotic intervention. They may form a glycocalyx, insulating themselves from both antibiotics and operative irrigation. In both case, decision of the fracture is compromised by the restricted bone obtainable due to elimination for implantation of the prosthesis. The natural history could thus progress to either successful union after repair, or nonunion. Ligament compromise follows a similar predictable course, with the endpoint being instability and subsequent deformity concerning the prosthesis. Lack of medial or lateral restraint allows edge-loading of the polyethylene, leading to osteolysis and implant subsidence. Necrosis presents as peri-incisional devascularized skin, which may be restricted in extent or of greater breadth; either allows slough of the zone of damage. As such, scar tissue accumulates in regards to the anterior tendon complicated as motion have to be restricted to present one of the best healing setting. With uncovered tendon, granulation tissue is less likely and plastic surgery involvement becomes a risk. Infection may current along side wound compromise as cellulitis within the early postoperative interval. Without consideration, cellulitis could permit deep bacterial infestation, creating osteomyelitis or septic arthritis of the bogus joint. Malleolar fracture, ligament compromise, prosthesis subsidence, incision compromise, and an infection will be mentioned separately. Repetitive stress from the medial corner of the tibial implant creates the vertical fracture line that permits the prosthesis to shift into varus. The examiner ought to search for increased swelling about the ankle joint after postsurgical decision. The examiner should consider for deep vein thrombosis, but normally together with pain, one thinks of malleolar fracture. Unlike malleolar fractures with out ankle arthroplasty, immobilization is usually extended beyond the standard 6 weeks, as the decreased floor area for healing as a outcome of the space-occupying prosthesis increases the probability of nonunion. If immobilization is terminated earlier than complete union, refracture or separation of the fragments becomes probably, mandating surgical correction. Obvious fractures are visible on the stage of the prosthesis, generally on the apex or superior corners of the prosthesis. In iatrogenic instances, the fractures occur at the stage of the superior noticed cut line on the tibia, the place the sagittal saw violates the medial or lateral malleolus. Significant distraction by way of the uniplanar fixator upon osteoporotic bone may create avulsion fractures at the malleoli after saw cuts, where the thinned malleoli are subject to increased force per unit area. Subtle fractures are typically delayed in appearance and will involve periosteal reactions seen on the medial malleolus proximal to the prosthesis. Tc99 bone scans: this study is mostly not helpful, as elevated uptake is visible surrounding the prosthesis, making it troublesome to discern a fracture from regular pooling. Use of pulsed electromagnetic fields or ultrasound to stimulate union might improve union. As the rehabilitative goal of whole ankle arthroplasty is early vary of movement, prolonged immobilization to enable conservative union could result in undue ankle stiffness, compromising affected person satisfaction. Thus, upon visualization of a malleolar fracture (either acute or delayed), surgical repair is indicated. Preoperative Planning In acute or iatrogenic situations, no preoperative planning is possible. This position improves the accuracy of sagittal imaging and prevents the necessity to raise or manipulate the concerned extremity in the course of the more tenuous parts of the surgical process.

Buy cheap azatril 500 mg lineEndoscopic plantar fasciotomy two portal endoscopic surgical strategies: scientific results of sixty five procedures. Uniportal endoscopic plantar fasciotomy: a potential research on athletic patients. Sensory nerves are expendable in many instances and most sufferers adapt properly to elimination. The resected proximal finish of a nerve will often type a neuroma as new development seeks to reconnect with the distal nerve; thus, makes an attempt to bury the nerve into a protected haven are fascinating. The tibial nerve splits into medial and lateral plantar nerves (this is combined motor as well). The saphenous nerve is an extension of the femoral nerve, found alongside the lesser saphenous vein. The deep peroneal nerve lies along the anterior tibia with a neurovascular bundle, passes beneath the extensor retinaculum, and innervates the first web space. It has some muscle elements to the flexor hallucis brevis muscle and a few innervation to the sinus tarsi as well. The superficial peroneal nerve, with the peroneal muscles, emerges from the peroneal retinaculum to innervate the dorsum of the foot. The terminal medial branch, the dorsomedial cutaneous nerve, is in danger with bunionectomy alongside the dorsomedial hallux. The sural nerve runs superficial to the gastrocnemius muscle and then between the peroneals and the Achilles tendon to innervate the lateral foot and two toes. Bunion procedures threaten the dorsomedial cutaneous nerve, a distal department of the superficial peroneal nerve. Achilles tendon procedures and Haglund resections can harm the sural nerve and particularly a posterior department of that nerve. The stretch often involves a pathologic extreme of motion as could be seen with ankle fracture5 or with ligament sprain. Stretch injuries may cause dysfunction resulting in decreased sensation, in hypersensitivity, or even in extreme pain with independent nerve sign generators. Arthroscopic ankle lateral portal placement dangers damage to the superficial peroneal nerve. Leprosy Diabetic neuropathy Peripheral vascular disease Tarsal tunnel syndrome Joint arthrosis or synovitis Tenosynovitis Giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath Intrinsic nerve damage, crush damage Rheumatoid arthritis Ganglion cyst Lipoma Neurilemmoma Abscess or infection Fracture Malalignment (varus or valgus foot or ankle) Plantar fasciitis Nerves can undergo a stretch injury, particularly the superficial peroneal nerve with severe ankle inversion due to sprain or fracture. The saphenous nerve is especially in danger with contusion, as are all of the nerves, especially the deep peroneal nerve with a dorsal foot damage. Iatrogenic damage remains the most typical type of nerve damage within the foot and ankle. The nerve can often be suspected when the pores and skin or subcutaneous tissues are hypersensitive (or hyposensitive) rather than the deep tissues. One of the best physical diagnostic findings is a nerve block using lidocaine hydrochloride (1% or 2%), Marcaine hydrochloride (0. The bicarbonate acts to titrate the acidity of the native anesthetic and ease the burning ache of administration. The physician ought to return a couple of minutes after the injection to reexamine the affected person somewhat than having him or her report on the effect of the injection at the subsequent office visit. Electrodiagnostic research may help differentiate between local and extra proximal nerve pathology. Cervical spine or lumbosacral impingement in addition to extra generalized neuropathies can masquerade as native phenomena. Electrodiagnostic research must be performed in patients suspected of getting tarsal tunnel syndrome. Periods of immobilization in a short-leg solid or walking boot might allow neuritic signs to subside, particularly when traction causes ache. Braces and splints can present added stability and stop recurrent stretching accidents, particularly to the superficial and deep peroneal nerves. Tarsal tunnel signs attributable to mechanical imbalances-such as acquired pes planus secondary to posterior tendon dysfunction-may be alleviated with orthotic devices that restore foot balance. Multiple types of pharmacologic intervention exist: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories Narcotics (caution must be exercised because of addiction potential, particularly with chronic nerve pain) Neuromodulators might help quiet nerve response. Anticonvulsants corresponding to pregabalin, gabapentin, or tricyclics often quiet nerve hypersensitivity. A variety of newer medications could also be useful; thus, referral to a pain administration specialist typically aids in full patient care. Lidoderm patches: Applied instantly over the symptomatic area, lidocaine hydrochloride is released in a time-dependent manner via the pores and skin. Neuromodulators and local anesthetics and nonsteroidals in an absorbent gel for topical software; these lotions could be found in compounding pharmacies. Steroid injection, combined with native anesthetic, may serve a twin function as each therapeutic and diagnostic agent. Risks include pores and skin discoloration, tendon rupture, atrophy of subcutaneous fat, and collateral ligament attenuation. Ethanol injections: 4% ethanol in a Marcaine solution has been used for interdigital neuroma remedy. The benefit, in addition to avoiding at journey to the operating room, entails lack of nerve conduction with out formation of postresection neuroma. The resection of a nerve stays basically a "one-way street," and careful dialogue helps alleviate complicated outcomes. The motor lack of the deep peroneal nerve branches is relatively nicely tolerated, whereas the posterior tibial nerve governs much more muscle exercise in the foot. The posterior tibial nerve has been resected only in salvage procedures as a precursor to potential amputation if unsuccessful. Some surgeons proceed to manage these issues with implantable nerve stimulators. Under tourniquet, the vessel and the nerve can look very similar; thus, examination of the cross-section of the presumed nerve is essential on the time of surgical procedure. Even the most skilled surgeons have been fooled by a vein impersonating the nerve: better to know at surgical procedure than to be informed by the pathologist the following day. If a patient had reflex sympathetic dystrophy or a posh regional ache syndrome concerned with the leg, then consideration should be given to performing the surgical procedure beneath epidural anesthesia. In concept, the diminution of painful stimulation might diminish the prospect of triggering further hypersensitivity reactions. The saphenous nerve is best explored with the affected person supine and the leg externally rotated. The superficial and deep peroneal nerves are finest approached with the affected person positioned supine. Sural nerve exposure usually requires use of a rolled towel beneath the ipsilateral hip to present better entry to the nerve as it courses posteriorly. Currently, as a result of resection of the sural nerve very proximally in the leg, the affected person is positioned in a semilateral decubitus position with the usage of a beanbag. Preoperative Planning the preoperative planning consists of affected person education, careful patient evaluation, and decisions concerning the location of nerve burial.
References - Krambeck AE, LeRoy AJ, Patterson DE, et al: Longterm outcomes of percutaneous nephrolithotomy compared to shock wave lithotripsy and conservative management, J Urol 179:2233n2237, 2008. Krambeck AE, LeRoy AJ, Patterson DE, et al: Percutaneous nephrolithotomy success in the transplant kidney, J Urol 180:2545n2549, 2008. Krambeck AE, Lingeman JE: Percutaneous management of caliceal diverticuli, J Endourol 23(10):1723n1729, 2009.
- Campbell EW, Filderman PS, Jacobs SC: Ureteral injury due to blunt and penetrating trauma, Urology 40(3):216n220, 1992.
- Barski D, Gerullis H, Otto T: Review of surgical implant procedures for male incontinence after radical prostatectomy according to IDEAL framework, Updates Surg 69(3):327n338, 2017.
- Henke RP, Erbersdobler A: Numerical chromosomal aberrations in papillary renal cortical tumors: relationship with histopathologic features, Virchows Arch 440:604n609, 2002.
|
|