"Order cheap aricept online, treatment 8th february."By: Danielle Marie Brander, MD - Assistant Professor of Medicine
- Member of the Duke Cancer Institute
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/danielle-marie-brander-md
Order generic aricept pillsBile salts, synthesized from cholesterol, represent the two main bile acids, cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. Cholesterol is just barely soluble in aqueous media but is made soluble via formation of combined micelles with bile salts and phospholipids, mainly lecithin. The enterohepatic circulation of bile acids ensuing from bile reabsorption from the terminal ileum, together with hepatic synthesis, keeps the bile acid pool physiologically optimal to maintain the cholesterol in answer. At least 4 mechanisms are concerned in the formation of ldl cholesterol gallstones: (1) supersaturation of bile with cholesterol, (2) nucleation of cholesterol monohydrate with subsequent crystallization and stone progress, (3) delayed emptying or gallbladder stasis, and (4) decreased enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. When the rate of bile acid secretion or the return of bile acid via enterohepatic circulation is decreased, as in sufferers with terminal ileal disease. The highest prevalence is in Native Americans (Pima Indians) and in Latin American populations. In white women, the prevalence is 5% to 15% in those youthful than 50 years and about 25% in these older than 50, compared with 4% to 10% and 10% to 15%, respectively, in white men. Several genes are related to the principal metabolic pathways involved within the formation of gallstones. In common, all gallstones form as a result of a change in bile composition, either an increase within the composition of a normal biliary element that exceeds its solubility or a decrease in a solubilizing component, or both. Consequently, an insoluble substance referred to as a nidus turns into supersaturated, and insoluble particles become sequestered and mixture. Table 201-1 Risk Factors for Cholesterol Stones Risk Factor Age Gender Nationality Race/ethnicity Comments Uncommon before age 20 years (exception: Mexican American girls). Highest: Pima Indians of southern Arizona (70% of Pima girls older than 25 years), different Native American tribes, and Alaskans. Relative risk rises sharply as degree of obesity will increase; girls more usually affected. Usually, sludge and pigment stones brought on by bile stasis and gallbladder distention. When bile becomes saturated with cholesterol, vesicles fuse to type liposomes, or liquid crystals, from which crystals of cholesterol monohydrate nucleate. Lithogenic bile that stays throughout the gallbladder alters gallbladder motility and stimulates mucous secretion by the gallbladder epithelium. Gallbladder sludge, the reversible but early stage of gallstone formation, is the suspension of precipitated bile dispersed in a viscous, mucin-rich liquid phase. Its chemical composition is generally ldl cholesterol monohydrate crystals, calcium bilirubinate, calcium phosphate, and calcium carbonate. Brown pigment stones are morphologically, chemically, and clinically distinct from black pigment stones. The brown pigment stone is laminated with alternating areas of brown and tan material and tends to cake when powdered. Brown pigment stones contain only small amounts of calcium phosphates and calcium carbonates. They develop in the gallbladder and in the intrahepatic and extrahepatic ducts and are related to polymicrobial infection. Bacterial degradation by enzymes, primarily -glucuronidase, deconjugates bilirubin and lecithin to free fatty acids. The predominant symp- toms of brown pigment stone disease are jaundice, chills, fever, and stomach ache. Black pigment stones are composed largely of calcium salts of unconjugated bilirubin, carbonate, and phosphate. Almost 50% of sufferers with sickle cell anemia and 15% to 40% of those with sickle cell illness have pigment stones by age 20 years. More than 66% of black pigment stones however solely 10% of ldl cholesterol stones are radiopaque on abdominal plain films. The increased concentration of unconjugated bilirubin within the pathogenesis of black pigment stones is probably nonbacterial and nonenzymatic. Gallbladder stasis and defective acidification of gallbladder bile in an alkaline setting favor the formation of calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate. In hemolytic anemias, bilirubin ranges increase 10-fold, with elevated gallbladder volume and stasis. As the gallbladder space is palpated, the affected person is requested to take a deep breath that brings the gallbladder down to the palpating hand. At the peak of inspiration, as the gallbladder touches the palpating hand, the breath is arrested with a puff (Murphy sign). Complications of acute cholecystitis are empyema of the gallbladder, gangrene with perforation, intraabdominal abscess, and diffuse peritonitis. Laboratory findings include leukocytosis with a shift to the left and mildly elevated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase ranges. The differential prognosis includes acute pancreatitis, appendicitis, acute hepatitis, peptic ulcer illness, disease of the best kidney, right-sided pneumonia, Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome (gonococcal perihepatitis), liver abscess, perforated viscus, and cardiac ischemia. Approximately 10% to 20% of sufferers with symptomatic gallstones develop acute cholecystitis. Imaging studies additionally help diagnose extreme problems similar to emphysematous cholecystitis and perforation, which require emergency surgical procedure. Abdominal ultrasound findings embody gallstones, sludge, lumen distention, mural thickening with a hypoechoic or anechoic zone inside the thickened wall, increased flow on color Doppler sonography, and pericholecystic fluid; none of these, however, is pathognomonic of acute cholecystitis. Sonographic Murphy sign is defined because the presence of maximal tenderness elicited by direct stress of the transducer over the gallbladder. Gallstones, sludge, gallbladder distention, mural thickening, pericholecystic fluid, and subserosal edema are main findings. Common organisms include Escherichia coli, Enterococcus, Klebsiella, and Enterobacter. The want for antibiotics in uncomplicated cholecystitis is debatable, although in medical follow, most patients receive antibiotics. A combination of ampicillin (2 g intravenously each 4 hours) and gentamicin (dosed in accordance with weight and renal function) is among the many selections for empiric therapy. Early laparoscopic cholecystectomy, inside 7 days of onset of symptoms, has become the preferred strategy. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy eliminates the necessity to incise the rectus abdominis muscle, reduces postoperative pain, and shortens hospital stay and convalescence. Patients at high danger could additionally be handled with percutaneous cholecystostomy in association with antibiotic therapy as a temporary measure. Other complications of laparoscopic cholecystectomy embody bowel and liver lacerations, bile leak, gallstone spillage and abscess formation, and major bleeding. However, the danger for most of these problems is low with the rising expertise of the surgeon. A new era in gastrointestinal surgical procedure includes cholecystectomy with access to the peritoneal cavity through normal anatomy, known as "natural orifice" transluminal endoscopic surgical procedure. Pitchumoni 203 angrenous cholecystitis is a time period used to describe extreme gallbladder irritation with mural necrosis related to an elevated threat for perforation. Computed tomography of the stomach might present mural necrosis, gas within the wall or lumen, intramural hemorrhage, pericholecystic abscess, or absent gallbladder wall enhancement.
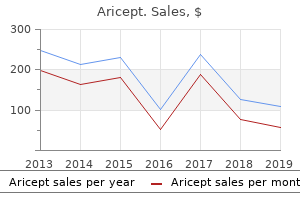
Purchase aricept 10mg without a prescriptionSymptoms o systemic toxicity happen when the whole serum iron exceeds the iron-binding capability o trans errin. A excessive serum iron concentration (usually greater than 500 �g/mL) may be associated with metabolic acidosis, cardiovascular collapse, coma, and liver ailure. Most iron is required or the synthesis o heme by reticulocytes and their precursors. The iron content material o the every day food regimen must be 10 to 20 times larger than the every day want. Iron is absorbed mostly within the duodenum and jejunum and stored briefly within the cytosol in a erritin advanced. From there, iron is launched into the bloodstream through the iron transporter erroportin, except the hormone hepcidin inhibits this transport by inducing the degradation o erroportin. The liver secretes hepcidin in response to in ammation and excessive liver iron shops. Hepcidin inhibits the release o iron not solely rom intestinal epithelial cells, but in addition rom Kupf er cells, macrophages in the spleen, and macrophages within the bone marrow. Peripheral cells endocytose the trans errin-iron complex through speci c sur ace trans errin receptors, retrieve the iron, and release trans errin back into the circulation. Iron de ciency is most o en caused by gastrointestinal or menstrual bleeding however may also be brought on by extreme blood donation. Patients with persistent in ammation secrete too much hepcidin and thus release too little iron rom the intestine, liver, and spleen; ultimately, this results in anemia. Hemochromatosis is a hereditary situation o extreme iron absorption that sometimes leads to iron accumulation in the liver, pituitary, pancreas, and the center. Hereditary hemochromatosis is often associated with abnormally low concentrations o circulating hepcidin. Abnormally low concentrations o Iron Metabolis m: Iron-De ciency Anemia and Iron Overload 163 circulating hepcidin may also be the end result o persistent ine ective erythropoiesis, anemia, or hypoxia. Iron overload could be secondary to requent erythrocyte trans usions which might be needed to deal with diverse types o chronic anemia. Large, excessive amounts o supplemental iron, especially in small children, damage the gastrointestinal mucosa and enhance serum iron to levels that exceed the iron-binding capability o trans errin. A 49-year-old girl presents with hypermenorrhea (menorrhagia; excessive menstrual ow). Iron poisoning: a literature-based, evaluation o epidemiology, prognosis, and management. Which o the ollowing is the more than likely clarification or the abnormal laboratory ndings Excessive dietary iron consumption Folate de ciency Hemochromatosis Iron de ciency Pernicious anemia Re vie w Que s tio ns 1. Her serum erritin is 510 �g/L (normal, 15-200 �g/L), her serum iron is a hundred and eighty �g/dL (normal, 50-170 �g/dL), and her whole iron-binding capability is 240 �g/dL (normal, 220-420 �g/dL). Radiographs o her arms are consistent with an abnormality o iron homeostasis because the trigger o arthritis. Serum rom sufferers with which one o the ollowing diseases reveals the highest focus o hepcidin Erythrocytes are made within the bone marrow under the regulation of the hormone erythropoietin, which is secreted from the kidneys, relying on the local focus of oxygen. The binding of oxygen to hemoglobin is regulated by pH, the concentration of carbon dioxide, and the concentration of two,3-bisphosphoglycerate inside red blood cells. Blood loss and diseases that have an effect on the lungs, kidneys, bone marrow, coronary heart, or erythrocytes, may have an effect on oxygen delivery to tissues and the manufacturing of pink blood cells. In regular adults, erythropoiesis (the production o erythrocytes) is restricted to the axial skeleton and the proximal ends o the humeri and emora. Adult sufferers with a markedly increased fee o erythropoiesis have an increased amount o bone marrow and likewise produce purple blood cells in additional bones. Children with an elevated price o erythropoiesis may develop bone de ormities, similar to tower skull and rontal bossing. List therapy choices to enhance the speed of erythropoiesis in an anemic patient. Explain how oxygen is delivered from the mom to the fetus, taking into account the structural variations between adult and fetal hemoglobin and O2 binding af nity. Compare and distinction the structure and the O2 binding properties of hemoglobin and methemoglobin. Explain the role of amyl nitrite and sodium nitrite within the treatment of cyanide poisoning. Hematopoietic stem cells within the bone marrow (through uneven division) give rise to progenitor cells, which might flow into in the blood and populate new sites in the bone marrow. The unique progenitor cells can provide rise to progenitor cells that have a extra restricted cell ate. Erythroid progenitor cells finally give rise to proerythroblasts, which in flip give rise to erythroblasts. T en, macrophages in the spleen or liver degrade it (or the degradation o heme, see Chapter 14; or the reuse o iron, see Chapter 15). Cytokines are an illde ned, massive amily o proteins that control cell development and dif erentiation. Erythropoietin is the cytokine that often exerts the best control over the speed o pink blood cell production. Erythropoietin is secreted rom endothelial cells in capillaries around tubules and/or. In sufferers with a pronounced de ciency o both olates or iron, purple blood cell precursors die at an abnormally high rate. The rate o erythropoietin secretion is decided by the concentration o oxygen in these peritubular cells (see below). In sufferers with extreme hypoxia (a condition o insu cient oxygen in tissues), the liver also synthesizes and releases some erythropoietin. These sufferers are o en handled with injections o recombinant erythropoietin, which is isolated rom cultured mammalian cells that specific the human erythropoietin gene. Erythropoietin may additionally be used to reduce the necessity or blood trans usion in other clinical settings, corresponding to radiation therapy or chemotherapy or most cancers. The most commonly encountered normal hemoglobins are hemoglobin A (composition: 2 2) and hemoglobin F (composition: 22). Each globin molecule has a hydrophobic pocket that binds one heme molecule (see Chapter 14) noncovalently. Globins constrain the reactivity o heme in order that the heme-Fe2+ atom can reversibly bind O2. Globins and heme are synthesized through the roughly week-long dif erentiation o erythroblasts into erythrocytes. High-res olution x-ray s tudy of deoxyhemoglobin Roths youngster 37 beta Trp-Arg: a mutation that creates an inters ubunit chloride-binding s ite.
Order cheap aricept onlineThe pores and skin, brain, retina, and sperm synthesize small amounts o atty acids with up to 40 carbons; the unction o these lipids is essentially a thriller. Most double bonds are launched into C-9 o palmitate (16: 0) or stearate (18: 0), thus giving rise to palmitoleate (16: 1, 9) and oleate (18: 1, 9), respectively. In the complete body, about 25% o the atty acids are palmitate (16: 0) and about 50% are oleate (18: 1). Like atty acid elongases, atty acid desaturases are certain to the cytosolic ace o the endoplasmic reticulum. Linoleic acid (18: 2, 9,12) and -linolenic acid (18: three, 9,12,15) are each essential atty acids. In different phrases, solely the double bond closest to the -end is considered when classi ying important atty acids into -3 and -6. While this gure s hows the fatty acids in prolonged conformations, polyuns aturated fatty acids which might be a half of phos pholipids in membranes als o as s ume looped conformations. Fatty Acids, Ketone Bodies, and Ketoacidos is 293 Bacteria, algae, and crops make some -3 atty acids and lots o -6 atty acids, and we acquire these important atty acids either directly rom ood or indirectly via the ood chain. Essential atty acids may be desaturated and elongated like nonessential atty acids. In this ashion, linoleic acid offers rise to arachidonic acid (20: 4, nonetheless an -6 atty acid; see construction in in a position 27. Since elongation happens at the carboxyl-end, an -3 atty acid always remains an -3 atty acid, and an -6 atty acid all the time remains an -6 atty acid. Metabolites o -3 and -6 atty acids act as lipid messengers or as short-lived local hormones (see Chapter 32). Some use the time period important atty acid only or linoleic and linolenic acid; others use it more broadly or all -3 and -6 atty acids in the physique. Fatty acid transporters improve the transport o atty acids throughout plasma membranes, and some o the transporters probably play a job in orming atty acyl-CoA. As with glucose transporters (see Chapter 18), some atty acid transporters are always inserted into the plasma membrane, and others are inserted only on demand. Fatty acids that contain eight or ewer carbons can e ciently cross membranes without the necessity or a transporter. Inside cells, the focus o malonyl-CoA controls the uptake o atty acids into mitochondria. Fatty acids are transported by way of the cytosol bound to atty acid� binding proteins. At the cytosolic ace o the mitochondrial outer membrane, an acyl-CoA synthetase prompts atty acids to atty acyl-CoAs. A er transport into the mitochondrial matrix, atty acyl carnitines are transformed back into atty acyl-CoAs. The blood incorporates triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particles that may additionally give rise to atty acids or use as uel. These triglycerides can be hydrolyzed by lipoprotein lipase, which is tethered to the wall o capillaries within the adipose tissue and muscle and by hepatic lipase within the capillaries o the liver. The price o hydrolysis o triglycerides in lipoprotein particles changes markedly with eeding and asting, as does the use o the ensuing atty acids. Fatty acid oxidation occurs primarily in muscle and liver cells, which extract the atty acids rom the blood. Hence, insulin inhibits the uptake o atty acids into mitochondria and thus prevents the oxidation o atty acids. In the ed state, newly synthesized atty acids can there ore not enter mitochondria. Under regular circumstances, humans can synthesize sufficient carnitine and in addition get well sufficient o it rom the glomerular ltrate in the kidneys; carnitine is there ore not a vitamin. In medicine, carnitine supplementation is sometimes used within the therapy o diseases by which extra acyl-CoA depletes ree CoA in a harm ul means (see Section 7. Carnitine then results in the ormation o acyl-carnitines with a concomitant increase in available ree CoA. Fibrates are a class o medication that improve the rate o atty acid -oxidation and are used to decrease the concentration o triglycerides within the blood. When a cell is hypoxic, it has a decreased capacity to oxidize atty acids and glucose and must resort to anaerobic glycolysis (see Chapter 19). The -oxidation o atty acids with an odd quantity o carbons also proceeds just like that o saturated atty acids, but it yields a nal propionyl-CoA (three carbons), which is then converted to succinyl-CoA. Odd-chain atty acid metabolism produces only a minor amount o propionyl-CoA; a a lot larger amount is produced rom the metabolism o isoleucine, valine, and methionine. Very-long-chain atty acids o 22 or extra carbons are oxidized to medium-chain atty acids in peroxisomes and then trans erred to mitochondria. During hunger, liver mitochondria convert some o the acetoacetyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA rom the -oxidation o atty acids to ketone our bodies. The concentration o acetyl-CoA in liver mitochondria is the main controller o ketone physique synthesis. The graph s hows means � s tandard error of means for ve obes e volunteers who had been s tudied after longer than a 12-hour fas t. Protein, fats, and carbohydrate necessities throughout s tarvation: anapleros is and catapleros is. Ac e tyl-Co A focus o acetyl-CoA within the liver is significantly greater within the asting state than in the ed state. In individuals who devour a typical Western food regimen (roughly 30% o energy rom at, 15% rom protein, and 55% rom carbohydrates), the focus o ketone our bodies within the plasma considerably will increase only with a ast o greater than 1 day. Labo rato ry The s ts fo r Ke to ne Bo die s ests or ketone our bodies measure the focus o either acetoacetate or -hydroxybutyrate. Most exams based mostly on nitroprusside (sodium nitro erricyanide) are predominantly sensitive to acetoacetate. There are also take a look at strips or -hydroxybutyrate that use a small amount o capillary blood and are analyzed in a handheld meter. Hence, a test that measures solely the acetoacetate has to be interpreted with caution. The rate o ketone body oxidation is roughly proportional to the ketone physique concentration in the blood. Ke to s is, Ke to ne mia, and Ke to nuria Ketosis is a state o elevated manufacturing o ketone our bodies; this can be regular or irregular. In persons who eat a typical, weight-maintaining Western food regimen (more than about 50% o energy rom carbohydrates), ketosis occurs physiologically solely with extended asting. I ketosis is secure or a chronic interval, the control o lipolysis by insulin is often intact.
Order cheapest ariceptA meta-analysis showed that sclerotherapy was more effective than balloon tamponade, no therapy, or vasopressin, with a 90% rate of bleeding management. Sodium tetradecyl sulfate (15%), morrhuate sodium (5%), and ethanolamine (5%) are the most widely used sclerosants. No consensus exists as to the preferred sclerosant; variable charges of ulceration are reported with these agents. Variceal band ligation is now the endoscopic therapy of selection because of the lower complication fee associated with this procedure. In one examine, band ligation was shown to be equally or more practical in controlling acute bleeding than sclerotherapy and was related to higher survival. Although dearer, multiband ligators ought to be used due to the chance for esophageal perforation related to the overtubing essential with the single-band ligator. Patients must be treated with -blockers or continued variceal band ligation, or a combination, for secondary prophylaxis towards rebleeding. Endotracheal intubation must be strongly thought of for these patients, though complications are widespread (10%-30%) and extreme, ranging from esophageal perforation to aspiration pneumonia. Ectopic varices are more common in patients with extrahepatic portal hypertension than in those with cirrhosis. In a instructed administration algorithm for sufferers with ectopic varices, angiographic embolization has been used with good preliminary management of bleeding. Because bleeding from stomal varices can typically be managed by direct strain, mortality has been estimated at lower than 5%, and conservative measures have been advocated quite than surgery. Injection sclerotherapy of stomal Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Kris V. This procedure was introduced in 1982, but long-term success was demonstrated only after improvement of expandable steel stents. A needle is then used to create a tract to the portal vein, normally the proper portal vein, underneath fluoroscopic management. The tract is dilated and an expandable metal stent placed, bridging the hepatic vein to the portal vein. Immediate complications include bleeding (hemoperitoneum, capsular hematoma, and hemobilia) and, in uncommon cases, cardiorespiratory failure, which can be associated to hemodynamic alterations ensuing from the procedure. Other immediate problems embody fever (possibly associated with bacteremia), renal insufficiency, and shunt thrombosis. Renal insufficiency may be multifactorial and primarily attributable to radiographic contrast administration. Careful evaluation of the intravascular fluid status and administration of mannitol could additionally be applicable for patients with gentle renal insufficiency. Reichelderfer M: Bleeding stomal varices: case collection and systematic review of the literature, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 6(3):346-352, 2008. Zheng M, Chen Y, Bai J, et al: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt versus endoscopic remedy within the secondary prophylaxis of variceal rebleeding in cirrhotic sufferers: meta-analysis replace, J Clin Gastroenterol 42(5):507-516, 2008. Previous research have shown that a portosystemic gradient (difference between portal and hepatic venous pressures) higher than 12 mm Hg is associated with an elevated danger for bleeding varices. Variable-sized stents of 10 and 12 mm are available to enhance the size of the shunt. Balloon deflated and removed; stent remains to keep patency of portosystemic shunt Liver Biopsy Kris V. Kowdley 229 would occur throughout the vascular compartment and could be related to a decrease danger for intraabdominal bleeding. Percutaneous liver biopsy is usually performed using native anesthesia alone, although many hepatologists have begun using a mild sedative to scale back nervousness. After local anesthesia with lidocaine, a trocar is used to create a tract to facilitate passage of a 16-gauge needle. Different forms of needles can be found for liver biopsy; the Klatskin needle is often used. Hematoxylin and eosin stain is used to evaluate for irritation and necrosis; trichrome stain is used to assess the presence and diploma of fibrosis; and stains such as reticulin can be used to consider the structure. In addition, particular stains are helpful to display for specific liver ailments, similar to periodic acid�Schiff with diastase for 1-antitrypsin deficiency, Perls Prussian blue stain for iron, and a particular stain for hepatitis B core antigen. Biochemical measurement of iron or copper can be carried out from contemporary or paraffin-embedded tissue to establish a selected diagnosis of hemochromatosis or Wilson illness, respectively. However, liver biopsy remains a vital process for determining the diagnosis and prognosis of liver illness. More importantly, liver biopsy stays one of the best methodology for establishing the presence or absence of cirrhosis. In many liver ailments, including alcoholic liver illness, hemochromatosis, and hepatitis C, the chance for hepatocellular carcinoma is associated primarily with the presence of cirrhosis. Therefore, identification of cirrhosis can facilitate decisions about screening for liver most cancers. Furthermore, findings on liver biopsy are essential for making treatment decisions in plenty of continual liver ailments, together with hepatitis B and hepatitis C. Liver biopsy stays the criterion for the diagnosis of chronic hepatic illnesses corresponding to Wilson illness, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, and autoimmune hepatitis. Liver biopsy occasionally identifies surprising findings that may change administration. Evaluating the minute construction of the liver is critical for assessing patients with drug-induced hepatitis or fulminant liver failure. Managing sufferers after liver transplantation additionally largely is dependent upon liver biopsy, significantly in situations related to a high fee of recurrence, corresponding to hepatitis C and hepatitis B. Pain may be localized over the biopsy website, diffusely unfold over the stomach, or more usually, referred to the best shoulder from irritation of the diaphragm. Bleeding is extra severe and will result in hepatic capsular hematoma or even intraabdominal bleeding, although that is rare. Other complications include an infection, pneumothorax or hemothorax, and perforation of the gallbladder or the bile ducts. Risk factors for complications of liver biopsy embody coagulopathy and increased variety of passes. Most facilities require that the patient lie on the proper facet for several hours after the biopsy to permit internal compression of the liver in opposition to the rib cage. Contraindications to liver biopsy embrace lack of affected person cooperation, bacterial cholangitis, extrahepatic bile duct obstruction, and vital coagulopathy or thrombocytopenia. Some advocate avoiding liver biopsy in patients with cystic liver lesions due to infection danger and in these with amyloidosis due to hemorrhage threat. This location is marked, and the biopsy is subsequently carried out on the bedside, normally in a day-surgery or ambulatory setting. This technique is usually chosen when biopsy is performed to study focal lesions, corresponding to suspected hepatocellular carcinoma or adenoma. Liver biopsy may also be carried out using laparoscopy, although usually solely when the affected person is already present process laparoscopic surgery. In addition to the percutaneous method, liver biopsy could be carried out utilizing transjugular methods, usually by interventional radiologists and for sufferers with a higher risk for bleeding, corresponding to those with thrombocytopenia or coagulation abnormalities.
Order genuine ariceptMorphine and all related opiates, used for hundreds of years as antidiarrheal agents, usually decrease the propulsive motility and improve tonus, particularly of the big intestine, typically to the point of spasms, which may clarify the stomach discomfort associated with opiates. The endless variety of medicine and preparations that promote defecation are referred to as cathartics and are regularly listed as "laxatives" or "purgatives. Acquired types are additionally related to quite a lot of neurologic ailments, intestinal clean muscle illness, and metabolic issues (see Chapter 106). The congenital type is Hirschsprung disease and contains classic, short-segment, and ultrashort-segment sorts, as well as complete colonic aganglionosis. The pathophysiology is attributed to a lack of ganglionic cells within the section of bowel. Functional constipation brings extra kids to medical consideration than does aganglionic megacolon, but the differential diagnosis contains these two circumstances. Great variations in scientific signs and symptoms are anticipated, however typical conditions are readily characterized. The child with continual functional constipation is a healthy-looking youngster of regular body appearance, whereas a baby with aganglionic megacolon appears to be chronically ill, has a protuberant abdomen, and bears the stigma of malnutrition in growth and development. However, well-documented circumstances of regular development and improvement present the illness progressing into adolescence, with rare reports in adults, up to age forty. Typically, the child or adolescent has never had a standard bowel movement and requires laxatives and enemas to evacuate. Occasionally, the presentation is diarrhea characterized by liquid stool moving round an impaction. On rectal examination, the sphincter may be regular or relaxed, and stool or a dilated rectum is palpated; fecal impaction is usually extreme, and the rectal sphincter may be extraordinarily tight. Often, suction or punch biopsy is tried first, but deeper biopsy is required to verify the analysis. However, the remark of ganglion cells on colon biopsy tends to rule out the prognosis of Hirschsprung disease. Acquired megacolon is often confused with congenital megacolon (Hirschsprung disease). Certainly, when the rectum is significantly dilated and short-segment Hirschsprung disease is suspected, the diagnosis depends on biopsy and histologic interpretation. When the 2 circumstances are difficult to distinguish, full-thickness biopsy is essential. The grownup affected person could have undergone repeated laxative and possibly enema remedy. Because of the nice variation in displays and laxative applications used, course and prognosis differ. In the classic case of Hirschsprung illness, the prognosis is good after profitable surgical procedure. Long-term follow-up research reveal roughly a 90% remedy rate, with residual fecal soiling in some circumstances. Even although course and prognosis can differ greatly, especially in older age teams, the prognosis is nice if the aganglionic section may be removed. Kahn E, Daum F: Anatomy, histology, embryology, and developmental anomalies of the small and large gut. In early childhood or adolescence or in maturity, nevertheless, making the diagnosis turns into harder. Barium enema shows the basic presentation of a narrowed phase with dilated bowel above. It is now recognized that in the atypical presentations, the aganglionic or narrowed phase may be extremely brief and may contain only the inner anal sphincter. At times, if the dilatation is longstanding, it may be tough to look at the complete bowel endoscopically. If the fecal impaction is persistent, traumatic ulceration of the mucosa may be famous. Barium contrast enema could reveal the narrow section and confirm the suspected diagnosis, however additional analysis is required before surgery can be carried out. In the basic presentation, physiologic testing reveals that the anal sphincter fails to chill out after distention of the rectum. The analysis of Hirschsprung illness is definitively made by inspecting biopsy specimens that reveal aganglionosis, or a Sigmoid Volvulus Martin H. If bowel is ischemic, instant surgical procedure should be seriously considered to relieve any compromise in the vasculature. In uncommon cases, the signs could be delicate and recurrent, and a thorough analysis is necessary. Primary volvulus of the colon usually occurs in the sigmoid colon and within the cecum; the opposite elements of the big bowel are properly fixed within the posterior abdominal wall. This chapter discusses volvulus of the sigmoid, and Chapter 140 discusses volvulus of the cecum. Sigmoid volvulus is a comparatively uncommon type of intestinal obstruction in the Western world, occurring more frequently in middle-aged and aged patients. It is more common in Eastern Europe and Asia, presumably reflecting completely different dietary habits. Cultures with a diet high in bulky vegetables have a higher incidence of sigmoid volvulus. The high-fiber bulk causes larger fecal residue and ends in a more distended and elongated bowel prone to rotation. It is essential to think about whether the patient is ambulatory or institutionalized. If the patient experiences vascular compromise and gangrene has set in, mortality may be very excessive (>50%). Surgical evaluation and timing of surgery are extremely important in predicting the course and progress for every patient. Ballantyne G, Brandner M, Beart R, Ilstrup D: Volvulus of the colon, Ann Surg 202:83-92, 1985. Burrell H, Baker V, Wardrop B, Evans A: Significant plain movie findings in sigmoid volvulus, Clin Radiol 49:317-319, 1994. Sigmoid volvulus develops extra regularly in sufferers with neurologic or psychiatric problems corresponding to Alzheimer or Parkinson illness. Onset of symptoms is normally sudden, nevertheless, with lower stomach pain, obstipation, and belly distention. When vascular compromise happens, ischemia and peritoneal indicators might evolve quickly. Possible ischemia and perforation, as nicely as acute volvulus, mandate fast evaluation.
Purchase aricept ukGlycogen synthase is activated by insulin however could be inhibited completely by epinephrine and glucagon. With increasing duration o mild train, skeletal muscles derive more o their vitality rom glucose and ree atty acids (both taken up rom the blood). The skeletal muscular tissues synthesize glycogen mainly a er a meal rom glucose that they take up rom the blood. Prior train and depletion o glycogen shops render skeletal muscle cells especially sensitive to insulin. In skeletal muscle, glycogenolysis is stimulated by an elevated focus o which one o the ollowing A 5-month-old boy is ound to have hepatomegaly, asting hypoglycemia, and high levels o ree atty acids in his blood. His liver glycogen content material was ound to be excessive, however the glycogen had a standard structure. A er an overnight ast, there was no detectable increase in the serum glucose focus a er an oral administration o galactose (which offers rise to glucose 6-phosphate). A muscle biopsy exhibits that the glycogen is o normal construction, and the size o the glycogen particles is within the normal range. This patient could have a de ciency o which one o the ollowing enzymes in his muscles As part o gluconeogenesis, pyruvate is carboxylated inside mitochondria to oxaloacetate, which in flip is transformed to phosphoenolpyruvate within the cytoplasm. From phosphoenolpyruvate, glucose is synthesized by way of the reversible reactions o glycolysis and the irreversible reactions which would possibly be unique to gluconeogenesis. The liver and the kidneys are the 2 main organs which are recognized to perform gluconeogenesis. In the transition rom the ed to the asting state, the body reduces its glucose consumption. Muscle and liver retailer some glucose as glycogen, and the liver converts a small amount o glucose into atty acids. Some cells, corresponding to neurons within the mind, pink blood cells, cells within the medulla o the kidney, and cells in the dermis o the pores and skin, need glucose even in the asting state. During an extended ast, gluconeogenesis accounts or nearly all o the endogenous glucose manufacturing. In the night o day 1, volunteers consumed a standardized meal ollowed by an in a single day ast. In the morning o day 2, measurements had been started and continued till virtually midday on day 3. By that time, glycogenolysis produced nearly no glucose, and gluconeogenesis accounted or nearly all of the endogenous glucose production. A er a ast, the intake o ood leads to a decrease in glucose manufacturing rom glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis. A er asting, the volunteers got 75 g o glucose in water by mouth (similar to a standard oral glucose tolerance take a look at; see Chapter 39). A er three hours, about hal o the glucose had been transported rom the gut into the blood. Over the identical period, glucose manufacturing rom glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis is a course of by which lactate, many amino acids (chie y alanine and glutamine), and glycerol give rise to glucose. Gluconeogenesis bene ts glucose-dependent tissues, such as the mind, pink blood cells, and exercising muscle. Gluconeogenesis proceeds by way of the reversible reactions of glycolysis and by way of unique, irreversible reactions that bypass the irreversible reactions of glycolysis. Gluconeogenesis is dependent upon the breakdown of body protein (mostly muscle protein) or, in individuals who eat a high-protein, low-carbohydrate food regimen, on the breakdown of dietary protein. Gluconeogenesis is excessive in patients who secrete too little insulin or who secrete an excessive quantity of cortisol, thyroid hormone, epinephrine, norepinephrine, or glucagon. Describe the roles of protein degradation and fatty acid oxidation vis-�-vis gluconeogenesis. Compare and contrast glycolysis and gluconeogenesis with regard to reactants, merchandise, pathways, and regulation. The effects of carbohydrate variation in is ocaloric diets on glycogenolys is and gluconeogenes is in wholesome males. Meas urement of fractional whole-body gluconeogenes is in people from blood s amples us ing 2H nuclear magnetic res onance s pectros copy. Effects of free fatty acids on gluconeogenes is and autoregulation of glucos e manufacturing in type 2 diabetes. Quantitative contributions of gluconeogenes is to glucos e production during fas ting in sort 2 diabetes mellitus. Abnormal renal, hepatic, and mus cle glucos e metabolis m following glucos e inges tion in type 2 diabetes. Gluconeogenes is takes place in the well-oxygenated peripheral portion of the lobules indicated by the red ring, and glycolys is predominates in the central portion of the lobule. Gluconeogenes is takes place in the well-oxygenated cortex indicated by the purple rectangle. Gluconeogenesis takes place in the well-oxygenated periportal cells o the liver and the cortical cells o the kidneys. The liver and the kidneys are heterogeneous in that some cells produce glucose, while others eat it. The reactions o gluconeogenesis start with lactate, alanine, numerous other amino acids, or glycerol. Several steps in gluconeogenesis require energy in the orm o guanosine triphosphate (G P) or A P. The physiologically irreversible reactions o gluconeogenesis are pyruvate phosphoenolpyruvate (in several steps, two o that are irreversible), ructose 1,6-bisphosphate ructose 6-phosphate, and glucose 6-phosphate glucose. Pyruvate is converted to phosphoenolpyruvate in a number of enzyme-catalyzed steps that take place within the mitochondria and the cytosol. Pyruvate enters the mitochondria, where pyruvate carboxylase carboxylates it to oxaloacetate. Further details concerning the amino acids that give ris e to pyruvate or feed into the citric acid cycle are s hown in. Gluconeogenes is and Fas ting Hypoglycemia 267 cycle with oxaloacetate (see Section 3 in Chapter 22). Hence, oxaloacetate is converted to both aspartate or malate, which could be exported into the cytosol. La cta the (~115 g/da y) Glucos e (~20 g/da y) Glucos e from lume n of inte s tine Co ri c yc le 2. Lactate stems rom red blood cells, the pores and skin, the gut, and exercising muscle. Alanine, glutamine, and other glucogenic amino acids are derived rom skeletal muscle protein or the diet. Glycerol outcomes rom the hydrolysis o adipose tissue triglycerides, which also yields atty acids.
Generic 10mg aricept free shippingThe mutation is ound in 1 in 500 to 15,000 folks, depending on the population, with many patients remaining undiagnosed. There is a lowered capability or oxidative phosphorylation, but the function o this de cit within the total disease process is unclear. Frataxin de ciency also leads to iron overload o the mitochondria, which can improve oxidative stress. Friedreich ataxia is related to the degeneration o the peripheral nervous system, central nervous system, heart, and pancreatic -cells. Linezolid decreases protein synthesis in mitochondria and should lead to lactic acidemia and even peripheral and optic neuropathy. The electron transs port chain reduces oxygen to water and thereby pumps protons into the intermembrane space. The electron transport chain consists o our multisubunit complexes (three o which pump protons), and the 2 electron carriers ubiquinol and decreased cytochrome c. Chie y in muscle and the mind, creatine and phosphocreatine acilitate the transport Oxidative Phos phorylation and Mitochondrial Dis eas es 253 o chemical power rom the mitochondria to websites o consumption within the cytosol; phosphocreatine is also an power reserve. Inhibitors o oxidative phosphorylation lower oxygen consumption, and uncouplers increase it. Clinically relevant inhibitors o oxidative phosphorylation are met ormin, cyanide, carbon monoxide, sodium azide, and hydrogen sul de. Impaired oxidative phosphorylation performs a role within the pathogenesis o most mitochondrial ailments. Mitochondrial ailments pre erentially involve tissues that have excessive calls for or vitality and rely upon mitochondria or proper unction. Af ected sufferers o en present with dys unction o the nervous system, musculature, auditory perception, or pancreatic -cells. Antimicrobial medicine such as aminoglycosides, chloramphenicol, and linezolid impair the unction o mitochondria and have to be administered with appropriate precautions. Friedreich ataxia is due to de ective iron metabolism in mitochondria caused by mutant nuclear-encoded rataxin. Huntington disease is due to mutant, nuclear-encoded huntingtin, and impaired oxidative phosphorylation performs a job within the loss o motor control. Parkinson disease is most o en an idiopathic or acquired disease with multi aceted dys unction o mitochondria. The glucose residues are mostly linked in (14) ashion, and sometimes in (16) ashion to create department factors. The smallest particles include about 2,000 glucosyl residues, the largest about 60,000. The iodine binds into the le handed helices o glucose moieties in the linear parts o glycogen. Muscle and liver store the most important amounts o glycogen; most different cells retailer only a small quantity o glycogen. I a person exercises to exhaustion after which consumes a meal very rich in carbohydrates, the exercised muscular tissues can include as much as 5% o their moist weight as glycogen. Glycogen in liver and muscular tissues is synthesized chie y in the course of the rst ew hours a er a meal. In the next asting period, when glucose use exceeds glucose in ux rom the gut, liver glycogen is degraded to glucose, which is launched into the blood; this helps preserve a traditional asting focus o glucose in the blood. During train, muscle degrades its glycogen for its own use, and the liver degrades a few of its glycogen to provide muscle with glucose. During an overnight quick, the liver degrades a few of its glycogen and releases glucose into the blood for the bene t of other tissues. Glycogen storage ailments (glycogenoses) are quite uncommon; their mixed incidence is about 1: 20,000. Affected patients may be glucose illiberal (and thus at an elevated threat of developing diabetes), have fasting hypoglycemia, develop a myopathy, or have seizures. Compare and contrast how feeding, fasting, and exercise in uence glycogen synthesis and glycogenolysis within the liver and skeletal muscle. Explain the contribution of glycogenesis and glycogenolysis to blood glucose homeostasis in the course of the fed state, the fasting state, and train. List the enzyme de ciencies that give rise to the most typical hereditary glycogenoses and predict their results on blood glucose focus, the quantity of tissue glycogen, and damage to tissues. Compare and contrast the pathogenesis and pathology of Pompe illness (lysosomal acid maltase de ciency) and Lafora illness. Under most circumstances o glycogen synthesis, an current glycogen particle is enlarged. Glycogen is synthesized in the liver and muscle a er a carbohydrate meal and in muscle additionally a er train. Impaired internet hepatic glycogen s ynthes is in ins ulin-dependent diabetic s ubjects throughout mixed meal inges tion; a 13C nuclear magnetic res onance s pectros copy s tudy. Direct as s es s ment of liver glycogen s torage by 13C nuclear magnetic res onance s pectros copy and regulation of glucos e homeos tas is after a mixed meal in normal s ubjects. The glycogen branching enzyme (recommended name: 1,4-glucan branching enzyme) introduces (16) branches. The branching enzyme cuts a stretch o linear, (14)-linked terminal glucose residues and hyperlinks carbon-1 o this stretch to carbon-6 o an upstream glucose residue, thus generating an (16) glucosidic linkage that starts a new branch. Skeletal muscle synthesizes glycogen in response to depleted glycogen shops; this synthesis is strongly enhanced by insulin. Antecedent train and an elevated concentration o insulin every increase both the number o glucose transporters in the plasma membrane and the activity o glycogen synthase within the cytosol. As a end result o these control mechanisms, postexercise glycogen synthesis proceeds at a comparatively low fee in the asting state, and at a markedly higher rate a er a carbohydrate-containing meal. During prolonged train, an elevated concentration o epinephrine prevents glycogen synthesis. The greater the carbohydrate content o the food plan, the upper the muscle glycogen shops. In the short time period, a food plan with larger than 90% o calories rom carbohydrate can lead to three- to our old larger muscle glycogen stores than a food regimen o lower than 10% carbohydrate. In the long term, dif erences between low- and high-carbohydrate diets are smaller. Such a routine results in roughly double the conventional glycogen stores, a phenomenon referred to as supercompensation. In the guts, glycogen depletion as a outcome of an acute increase in workload or due to ischemia subsequently stimulates glycogen synthesis. Filled glycogen shops have a avorable ef ect on maximal power output and hypoxia tolerance. Dietary ructose, glucose, and insulin receptor signaling activate glucokinase, which leads to an elevated focus o glucose 6-phosphate. Glucose 6-phosphate and insulin signaling enhance glycogen synthase exercise, which is the primary determinant o the speed o glycogen synthesis.
Discount 5mg aricept overnight deliveryAfter approximately 2 weeks, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay can detect the antibodies in some patients. Ingestion of the vegetation leads to the encystment of larvae and the formation of mucosal abscesses within the small intestine. Diagnosis is made by finding the eggs in the stool, and the remedy of alternative is praziquantel. If signs are severe, corticosteroids may be useful in decreasing inflammation. Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus Taenia Hymenolepis Hymenolepis Undeveloped In growth saginata, nana diminuta Diphyllobothrium latum Taenia solium Heterophyes Metagonimus heterophyes yokogawai Fasciolopsis buski Echinostoma spp. They could trigger liver enlargement and every sort of biliary situation, together with adenomas, fibrosis, and stricture of the bile ducts. Diagnosis and Treatment the prognosis of fluke infection is made by figuring out ova in the stool or in bile obtained by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. The initial focus was subSaharan Africa, the place estimates point out that as many as 25% of the population are infected. Initially, transmission had been by homosexual, orogenital, or anogenital contact, however the major mode of transmission is now heterosexual contact. Odynophagia may be severe and forces sufferers to limit their meals consumption, inflicting additional debilitation. The presence of belly pain necessitates the differential diagnosis of hepatobiliary and pancreatic issues. Cryptosporidium, Microsporidia, Isospora belli, and Cyclospora are the commonest parasitic infections. The cause of the diarrhea should be decided from stool evaluation and biopsy specimens. Lesions in the esophagus vary greatly however may seem as deep ulcerations and presumably as neoplasms. Careful endoscopic examination and histologic examination of biopsy specimens are wanted to make the analysis. Lesions within the colon could be patchy and should involve solely the best colon, underscoring the significance of colonoscopy. Anorectal signs require special differential analysis and are included in the evaluation of specific anal symptoms. Symptoms of acute diarrhea happen in as many as 90% of sufferers 1 to four weeks after an infection and may last for 1 to 3 weeks. Diarrhea could additionally be mild or severe, and it may be associated with a full-blown image of cramps, anorexia, fever, weight loss, and wasting. Ongoing infections appear to be resolved due to the repopulation of peripheral T cells. Treatment of specific causes of diarrhea, either protozoan or infectious, is described within the chapters for these organisms. Although efficient in 63% to one hundred pc of sufferers, ganciclovir is virustatic (inhibits replica- tion), not virucidal, and most patients have recurrences. Unfortunately, in components of the world the place therapy is less out there, the illness runs its course and will increase mortality. A main challenge is to convey improved remedy to sufferers in underdeveloped nations. Pitchumoni 187 ne of the earliest references to the pancreas as a definite organ happens in the Talmud, which refers to the organ as "the finger of the liver. Herophilus of Chaldikon, in the third century bc, made some initial anatomic descriptions. Almost 200 years later, Rufus of Ephesus used the term "pancreas" (pan, all; kreas, flesh). George Wirsung described the structure of the major pancreatic duct in humans in 1642. About a hundred years later, Giovanni Santorini described the accessory pancreatic duct. The pancreas arises from two diverticula of the foregut, in a region that later becomes the duodenum. Early within the fifth week of gestation, a larger dorsal bud develops proximally just above the level of the hepatic diverticulum. Growing fairly rapidly and lengthening into the dorsal mesentery of the duodenum close to the growing omental bursa, the dorsal pancreatic bud passes in entrance of the developing portal vein. When the rotation is completed, the original ventral bud involves lie close to, under, and somewhat behind the dorsal pancreas, and ultimately its tip lies behind the superior mesenteric vein and the foundation of the portal vein. From the bigger dorsal bud originates the cephalad part of the pinnacle, as nicely as the neck, body, and tail of the pancreas, whereas the caudate part of the pinnacle and the uncinate course of derive from the smaller ventral bud. During the seventh week, the dorsal and ventral buds fuse, enclosing the vena cava. The secretions of the neck, physique, and tail are subsequently shunted into the duct of the smaller ventral pancreas, which thus turns into the principal pancreatic duct of Wirsung. Only the higher portion of the top is finally drained by the unique duct of the dorsal pancreas, the accessory duct of Santorini. The pancreas is 10 to 15 cm (4-6 inches) long and extends transversely throughout the stomach from the concavity of the duodenum to the spleen. Located deep within the epigastrium and the left O hypochondrium behind the lesser omental sac, roughly on the level of the first and second lumbar vertebrae (L1-L2), the gland escapes bodily examination. The head is globular and has an inferior extension, and the lingula (uncinate process) tasks hooklike to the left and is crossed anteriorly by the superior mesenteric vessels. The posterior surface of the pinnacle touches the inferior vena cava, left renal vein, and aorta. Its anterior surface, covered by serosa, is separated by the omental bursa from the posterior wall of the stomach. The inferior floor, under the attachment of the transverse mesocolon, is expounded to the duodenojejunal junction and to the splenic flexure of the colon. The posterior floor is involved with the aorta, splenic vein, and left kidney, where the body tapers off into a short tail. The lymphatics of the pancreas come up as fine periacinar and perilobular capillary networks extending alongside the blood vessels to the floor of the gland. Direct lymphatic connections exist wherever the pancreas is attached to different organs. The arterial blood provide to the top of the pancreas, along with the duodenum, is by an anterior and posterior pancreaticoduodenal arcade shaped by the union of anterior and posterior branches of the superior and inferior pancreaticoduodenal arteries. The splenic artery supplies the tail and physique of the pancreas by way of several branches.
References - Zhong P, Tong HL, Cocks FH, et al: Transient oscillation of cavitation bubbles near stone surface during electrohydraulic lithotripsy, J Endourol 11:55n61, 1997.
- Seki S, Sasaki K, Fraser MO, et al: Immunoneutralization of nerve growth factor in lumbosacral spinal cord reduces bladder hyperreflexia in spinal cord injured rats, J Urol 168(5):2269n2274, 2002.
- Weil A, Reyes H, Bischoff P, et al: Modifications of the urethral rest and stress profiles after different types of surgery for stress incontinence, Br J Obstet Gynaecol 91:46, 1984.
- Goldstein I, Lue TF, Padma-Nathan H, et al: Oral sildenafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Sildenafil Study Group, N Engl J Med 338(20):1397n 1404, 1998.
|
|