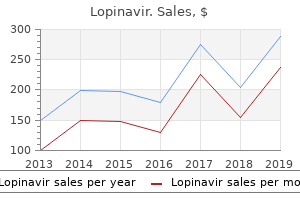
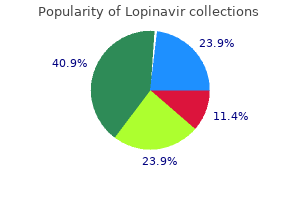
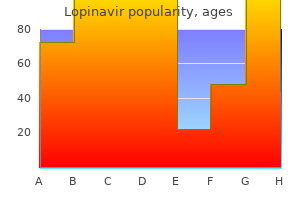
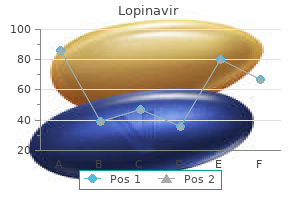
"Buy 250mg lopinavir amex, medicine 524."By: Peter Bartlett Bressler, MD - Associate Professor of Medicine
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/peter-bartlett-bressler-md
Buy discount lopinavir 250mg on-lineThe flexed posture, usually seen within the neurological affected person, is therefore produced by way of increased exercise of the extrinsic muscular tissues which management the hand. Changes in orientation of the hand to the supporting surface will facilitate the maintenance of range of movement. Frequent adjustments to the immediate sensory setting of the hand can present novel expertise. The provision of a scientific programme of sensory stimulation and heightened awareness of the hemiparetic hand is very important if there are optimistic indications for functional restoration. Early recovery of localisation of contact and two-point discrimination may be very constructive and should require an alteration of the direction of the therapy programme to include activation of the hand in facilitation of reaching for standing and locomotion. All members of the rehabilitation group including relatives and carers play an important position in actively selling sensorimotor alternatives for the affected person (see Chapter 8). Assessment of the hand It must be recognised that for a number of causes, not all sufferers will have the ability to recover perform in their hand after neurological pathology, particularly if the sensorimotor integration within the brain and the summation for the areas supplying the corticospinal system are broken. Accurate assessment is required to select acceptable patients for intensive coaching, which is required to overcome the dysfunction. Assessment of sensation is optimally carried out when the affect of the extrinsic wrist flexors is reduced by taking the muscles off stretch. Localisation of touch and two-point discrimination are essential for stereognosis and manipulation and, due to this fact, are the inspiration of the assessment and remedy process. However, stimulation of the hand may be required earlier than sensory testing may give an accurate image. Selective strength coaching of the intrinsic muscle tissue of the hand the human hand is each powerful and dextrous. As previously said, it may be very important recognise the role of depth in promoting restoration of function within the hand which includes the intensity of: Sensory stimulation to result in summation and integration. Strength coaching of key muscular areas of the hand for selectivity of motion, dexterity and energy. Research evidence shows that depth of apply is underpinned by enough motivation on the a half of the patient, carer and therapist (Winstein et al. Practice may must be augmented by a programme of extrinsic stimulation and mental imagery. Motor imagery alone seems to be sufficient to promote the modulation of neural circuits, as the sensorimotor cortex has been associated to both execution and imagination of movements, leading to the same plastic changes in the motor system as these following repeated physical apply (Jackson et al. Yue and Cole (1992) report a rise in muscle energy via imagined energy training, and Rogers (2006) showed that efficiency improves even when imagery is used concurrent to intensive physical training. Patients educated and familiarised with the technique are extra doubtless to practise in general and correctly by themselves, and subsequently they want the continued 24hour-concept support of the interdisciplinary staff with this follow programme (Braun et al. The intrinsic muscles of the hand, lumbricals and interossei contribute to the shaping of the hand and the strength of the grasp. The postural stabilisation provided by the intrinsic muscles of the hand offers the premise for particular person digit motion. The muscle tissue that kind the hypothenar and thenar eminence work in both synchrony and asynchrony to produce a great number of grips and postures for functional activities. Pincer and energy grips involve the necessary muscular control of abductor digiti minimi, first dorsal interosseus and abductor pollicis, and extensor and flexor pollicis longus. Strengthening of the thumb musculature is crucial for each the operate of the hand and the motion of supination and pronation of the forearm. These components have to be obtainable for lively wrist extension and development into task practice. In conjunction with a strengthening programme, consideration should be given to enough repetition of the muscle exercise at variable speeds and velocities. Therapeutic stretch could additionally be required to facilitate exercise and enhance range which may be included into task practice. Consideration of whether the task should start intrinsically with self-ideation or extrinsically in response to exterior stimuli (for example, catching an object) is important. There are a number of key elements which need to be considered in relation to the selection of the duty: available motion parts and power of the hand; supporting postural management components; 174 Recovery of Upper Limb Function. In abstract, there are three key areas underpinning selective power coaching: patient choice, depth of follow and choice of task. Summary this chapter has given an outline of how practical restoration of the higher limb is addressed utilizing the Bobath Concept. This is a particularly tough space to handle due to the inherent instability of upright bipedal stance and the involvement of 177 Bobath Concept: Theory and Clinical Practice in Neurological Rehabilitation the upper limbs in fixation methods. The hyperlink between motor management and useful recovery together with an understanding of the systems concerned has been highlighted. An understanding of how stereotypical patterns of exercise that turn out to be established can intrude with this course of is essential. The importance of afferent data acquired particularly via the arms is a key part in improving physique consciousness. Key Learning Points Understanding the coordinated interaction of the upper limbs with the the rest of the physique is essential to be able to achieve the total potential for higher limb recovery. Understanding the hyperlink between postural management and goal-orientated upper limb exercise and in particular the appropriate alternative of aim. Identifying the parts of motion needed for proximal and distal interactions and the neural foundation. Importance of the relationship between exercise and sensation in any respect phases of rehabilitation. Rehabilitation of reach, grasp and manipulation requires follow within useful duties. A high level of skilled supply and practice throughout the staff will require academic data, coaching and expertise follow. The team must be motivated to work intently together, be taught collectively and spend money on protected instructional time, enabling a dynamic, specialist and productive workforce to facilitate the patient all through the rehabilitation process. Throughout the continuum of recovery, reaching the most environment friendly posture, movement and performance will be the accountability of the partnerships fashioned between the staff members. These partnerships ebb and circulate between completely different members of the group, relying on the place throughout the journey of restoration the patient lies. For instance, with the minimally conscious or the acute affected person, the partnership between the affected person, relatives, nurse and doctor may be the strongest. Through interactions in this partnership the promotion of maximum participation is explored. The shifting bias that exists throughout the rehabilitation process creates adjustments inside these partnerships. As properly as delivering therapeutic intervention and enabling the patient to study within their environment, the therapist will also be required to supply steerage about different partnership interventions, facilitating the most effective consequence of the rehabilitation course of. Opportunities to practise software of abilities into perform ought to be underpinned by the partnerships between the affected person and the related members of the interdisciplinary team. The key members throughout the rehabilitation staff are nurses and assist staff, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech and language therapists, neuro-psychologists, stroke coordinators, medical employees, and household and friends. They need to learn and supported through the rehabilitation course of and each time potential involved in decision-making. Application of the Bobath Concept seeks to enable the patient to work together inside their environment, producing an effective, fascinating and acceptable response to their surroundings.
Generic lopinavir 250mgWe focus here on the physical findings, which can no much less than give a hint as to the supply of the again pain. Further diagnostic checks are wanted to differentiate between symptomatic and asymptomatic morphological alterations. Degenerative Lumbar Spondylosis Chapter 20 549 Imaging Studies Debate continues in regards to the need for normal radiographs for the initial evaluation of sufferers with predominant back ache. However, lumbosacral transitional anomalies could be missed when only sagittal and axial views are obtained. There are only very few alterations that are uncommon in asymptomatic individuals youthful than 50 years [272], i. She was admitted to an intensive rehab program with emphasis on stabilizing exercises which resolved her signs. Computed tomography Computed tomography is the imaging modality of alternative for the evaluation of spinal fusion. A detailed description of the energy and weaknesses of these diagnostic research is included in Chapter 10. Currently, discography predominantly serves as a ache provocation test to differentiate symptomatic and asymptomatic disc degeneration. However, cautious interpretation of the findings continues to be obligatory with reference to the clinical presentation [43]. We suggest using distinction injection to document the correct needle position and filling of the joint capsule (Case Study 1). It is therefore obligatory to carry out repetitive infiltrations to improve the diagnostic accuracy [239]. Stabilization of the putative abnormal segments by an exterior transpedicular fixator has been suggested by several authors [74, 237, 254] with mixed results by method of outcome prediction. Nonetheless, in the presence of chosen factors (see Chapter 7), surgery should no less than be delayed until attempts have been made to modify risk elements which would possibly be amenable to change and all potential conservative means of therapy are exhausted. The first important side is a multidisciplinary practical restoration program and psychological interventions to influence affected person behavior (see Chapter 21). The longer pain and functional limitations persist, the less likely is ache reduction, useful restoration and return to work (see Chapter 6). These patients should promptly be included in a multidisciplinary practical work conditioning program. Favorable indications for non-operative therapy include (Table 4): Cognitive behavioral interventions are necessary to tackle fears and misbeliefs Table four. Since its introduction in 1911 by Albee [3] and Hibbs [127], spinal fusion was initially solely used to treat spinal infections and high-grade spondylolisthesis. Today roughly seventy five % of the interventions are accomplished for painful degenerative disorders [66]. Despite its frequent use, spinal fusion for lumbar spondylosis remains to be not solidly primarily based on scientific evidence when it comes to its clinical effectiveness [66, 102, 103, 264]. For a very lengthy time it was hoped that consequence of spinal fusions could presumably be significantly improved when the fusion charges come near a hundred %. If a pathomorphological alteration in concordance with the scientific symptoms could be found, the patient should be chosen for potential surgery. As outlined above, the period of symptoms ought to be quick to keep away from the antagonistic effects of a chronic ache syndrome. Biology of Spinal Fusion A basic understanding of the general rules of bone development and bone healing as well as the biologic requirements for spinal fusion in the lumbar spine are a prerequisite to selecting the optimal fusion technique [13]. Spinal arthrodesis can be generated by a fusion of:) adjoining laminae and spinous processes) side joints) transverse processes) intervertebral disc space An osseous fusion of the transverse processes is the most typical kind of fusion carried out in the lumbar spine [16]. MacNab was one of the first to realize that the success of intertransverse fusion over posterior fusion. The prerequisite of successful backbone fusion is three distinct properties of the applied graft material, i. Particularly cancellous bone with its porous and highly interconnected trabecular architecture permits straightforward ingrowth of surrounding tissues. Osteoconduction is also observed the optimal graft material should be osteogenic, osteoconductive and osteoinductive Vascular supply to the fusion area is important 556 Section Degenerative Disorders in fabricated materials which have porosity similar to that of bone construction. Osteoinduction indicates that primitive, undifferentiated and pluripotent cells are stimulated to develop into bone-forming cells [4]. Autologous bone for spinal fusion is harvested from the anterior or posterior iliac crest as cancellous bone, corticocancellous bone chips or tricortical bone blocks. The drawback of autologous bone is said to the limited quantity and potential donor site pain [63, 80, 125]. These drawbacks have led to using allograft bone early in the evolution of spinal fusion. Fresh allografts elicit each local and systemic immune responses diminishing or destroying the osteoinductive and conductive properties. Gamma irradiation of a minimal of 34 kGy is recommended to considerably scale back the infectivity titer of enveloped and non-enveloped viruses [220]. Femoral ring allografts for anterior interbody fusions have gained increasing reputation because of their capability for an initial structural support [191]. Bone Graft Substitutes Bone graft substitutes are increasingly getting used for spinal fusion because of the minimal however inherent danger of a transmission of infectious illness with allografts Degenerative Lumbar Spondylosis Chapter 20 557 [115]. These pure ceramics are derived from sea corals and are structurally similar to cancellous bone. These materials are available in various preparations together with putty, granular material, powder, pellets or injectable calcium phosphate cement [20]. However, solely rising experience and long term follow-up will show whether or not these new fusion strategies will surpass the level of safety and medical feasibility and could be established as a cost-effective therapy. So far, no proof has been reported to reveal that these new strategies are superior to spinal fusion. The scientific literature reveals a plethora of articles covering the finish result of surgical therapy. These details tremendously limit treatment recommendations on degenerative lumbar spondylosis. The scientific proof for spinal fusion in lumbar spondylosis is poor Degenerative Lumbar Spondylosis Chapter 20 559 Non-instrumented Spinal Fusion Lumbar arthrodesis can be achieved by three approaches. The so-called combined or 360 diploma fusion is the mixture of each strategies. Posterolateral Fusion Posterolateral fusion was first described by Watkins in 1953 [270] and remains the gold commonplace for spinal fusion. This method has been modified by Truchly and Thompson [255], who used multiple skinny iliac bone strips as graft materials instead of a single corticocancellous bone block due to frequent graft dislocation [255]. In 1972, Stauffer and Coventry [245] introduced the approach nonetheless used today by most surgeons, which consisted of a single midline approach. Furthermore, graft insertion necessitates a substantial retraction of the nerve roots which carries the chance of nerve root injuries and significant postoperative scarring. Based on an evaluation of 1 372 circumstances reported in eight studies [53, fifty six, one hundred thirty, 131, 165, 171, 194, 219], mean fusion fee was 89 % (range, eighty two � 94 %) and the common fee of satisfactory consequence was eighty two % (range, 78 � 98 %) [24].
Buy 250mg lopinavir amexThe retina or innermost layer of the eyeball incorporates microscopic receptor cells, called rods and cones due to their shapes. Dim gentle can stimulate the rods, however fairly brilliant 185 Human Anatomy and Physiology gentle is critical to stimulate the cones. In different phrases, rods are the receptors for night vision and cones for daytime vision. There are three kinds of cones; every is delicate to a different colour: red, green, or blue. Scattered all through the central portion of the retina, these three kinds of cones permit us to distinguish between totally different colors. Aqueous humor is the name of the watery fluid in entrance of the lens (in the anterior cavity of the eye), and vitreous humor is the name of the jellylike fluid behind the lens (in the posterior cavity). Aqueous humor is constantly being shaped, drained, and changed within the anterior cavity. Visual Pathway Light is the stimulus that results in vision (that is our ability to see objects as they exist in our environment). Refraction happens as mild passes through the cornea, the aqueous humor, the lens, and the vitreous humor on its approach to the retina. Nervous alerts finally leave the retina and exit the eye via the optic nerve on the posterior surface of the eyeball. After leaving the attention, the optic nerves enter the mind and journey to the visible cortex of the occipital lobe. In this space of the mind, visible interpretation of the nervous impulses that 187 Human Anatomy and Physiology had been generated by mild stimuli within the rods and cones of the retina result in "seeing". As we will later see, the stimulation or "trigger" that activates receptors concerned with hearing and equilibrium is mechanical, and the receptors themselves are known as mechanoreceptors. Physical forces that 188 Human Anatomy and Physiology contain sound vibrations and fluid movements are responsible for initiating nervous impulses ultimately perceived as sound and balance. A giant part of the ear, and by far its most important part, lies hidden from view deep inside the temporal bone. The auricle is the appendage on the facet of the top surrounding the opening of the external auditory canal. It extends into the temporal bone and ends on the tympanic membrane or eardrum, which is a partition between the exterior and middle ear. The skin of the auditory canal, especially in its outer one third, accommodates many quick hairs and ceruminous glands that produce a waxy substance referred to as cerumen which will acquire in the canal and impair listening to by absorbing or blocking the passage of sound waves. Sound waves travelling by way of the external auditory canal strike the tympanic membrane and cause it to vibrate. Middle Ear the center ear is a tiny and really thin epithelium lined cavity hollowed out of the temporal bone. The names of those ear bones, called ossicles, describe their shapes - malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup). The "handle" of the malleus attaches to the inside of the tympanic membrane, and the "head" attaches to the incus. When sound waves trigger the eardrum to 190 Human Anatomy and Physiology vibrate, that motion is transmitted and amplified by the ear ossicles as it passes via the middle ear. A level price mentioning, because it explains the frequent unfold of an infection from the throat to the ear, is the truth that a tube- the auditory or eustachian tube- connects the throat with the middle ear. The epithelial lining of the center ears, auditory tubes, and throat are extensions of one continuous membrane. Consequently a sore throat might unfold to produce a center ear infection called otitis media. Inner Ear the activation of specialised mechanoreceptors in the internal ear generates nervous impulses that result in listening to and equilibrium. Anatomically, the internal ear consists of three spaces within the temporal bone, assembled in a posh maze known as the bony labrynth. This odd shaped bony space is full of a watery fluid referred to as perilymph and is divided into the next parts: vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea. Within every canal is a specialised receptor called a crista ampullaris, which generates a nerve impulse if you move your head. The sensory cells in the cristae ampullares have hair like extensions which might be suspended within the endolymph. The sensory cells are stimulated when motion of the head causes the endolymph to transfer, thus causing the hairs to bend. The organ of listening to, which lies within the snail shaped cochlea, is the organ of Corti. It is surrounded by endolymph filling the membranous cochlea or cochlear duct, which is the membranous tube throughout the bony cochlea. The Taste Receptors the chemical receptors that generate nervous impulses ensuing in the sense of style are called taste buds. About 10,000 of those microscopic receptors are found on the sides of much larger structure on the tongue referred to as papillae and likewise as parts of other tissues in the mouth and throat. Nervous impulses are generated by specialized cells in taste buds, referred to as gustatory cells. All different flavors result from a mixture of taste bud and olfacctory receptor stimulation. For this purpose a chilly that interferes with the stimulation of the olfactory receptors by odors from meals in the mouth markedly dulls taste sensations. The location of the olfactory receptors is somewhat hidden, and we are sometimes forced to forcefully sniff air to smell delicate odors. Each olfactory cell has a number of specialized cilia that sense completely different chemical compounds and cause the cell to reply by generating a nervous impulse. To be detected by olfactory receptors, chemicals must be dissolved in the watery mucus that lines the nasal cavity. After the olfactory cells are stimulated by odor-causing chemical compounds, the ensuing nerve impulse travels via the olfactory nerves within the olfactory bulb and tract after which enters the thalamic and olfactory facilities of the brain, where the nervous impulses are 197 Human Anatomy and Physiology interpreted as particular odors. The pathways taken by olfactory nerve impulses and the realm the place these impulses are interpreted are closely associated with areas of the brain essential in memory and emotion. For this cause, we could retain vivid and long-lasting reminiscences of explicit smells and odors. Temporary discount of sensitivity to smells often results from colds and other nasal infections. Progressive reduction of the sense of smells usually seen in smokers because of the damaging results the pollution in tobacco smoke. In olfaction, as with all of the special senses, advancing age usually brings a structural degeneration that lead to decreased perform. Caring health professionals acknowledge these indicators of growing older and supply help needed by their aged sufferers to take pleasure in life. General Sense Organs Groups of highly specialised and localized receptors are sometimes associated with the special senses. In the sense organs, nonetheless, receptors are found in nearly every part of the physique.
Purchase lopinavir usBecause propranolol reduces the ratio of oxygen demand to oxygen provide, arrhythmias brought on by myocardial ischemia may also be relieved. Blockers have been shown to scale back the incidence of heart attack and demise in patients with previous myocardial infarction. Despite their selectivity for 1-adrenergic receptors, these medicine in addition to different blockers should be avoided if possible in asthmatic patients. This drug is primarily utilized by anesthesiologists to give short-acting beta blockade in patients undergoing basic anesthesia. Sotalol is nicely absorbed when taken orally, with a bioavailability of almost 100%. Sotalol is useful in supraventricular arrhythmias corresponding to atrial fibrillation and in sure circumstances of ventricular tachycardia. It has been proven to be effective in stopping recurrences of ventricular tachyarrhythmias. It has an fascinating mixture of blocking a number of ion channels, together with sodium, potassium, and calcium. Repolarization is slowed in the His-Purkinje system and in ventricular and atrial myocardium. Inhibition of these latter channels most likely prevents a lot of the inward depolarizing current that can set off early afterdepolarizations. Conduction velocity in the His-Purkinje system and ventricular muscle is also slowed. Amiodarone has an energetic metabolite, desethylamiodarone, which additionally contributes to the antiarrhythmic impact. Desethylamiodarone binds to mobile thyroid hormone receptors, inhibiting thyroid Absorption, destiny, and excretion Propranolol is instantly absorbed after oral administration, but greater than two-thirds of the drug is destroyed in its first move by way of the liver. Propranolol is metabolized by hydroxylation, deamination, and glucuronide conjugation. Of the numerous genes usually induced by thyroid hormone, a quantity of assist the synthesis of certain K+ channels. Short-term therapy is extra prone to restrict effects to Na+ channels, Ca2+ channels, and -adrenergic receptors. The resulting cardiac effects with short-term use seem to be different from the results of long-term therapy and avoid most of the adverse effects seen with long-term administration, such as pulmonary fibrosis and hypothyroidism. Amiodarone is a vasodilator, noncompetitively inhibiting the vascular impact of catecholamines. The cardiac results of catecholamines are likewise inhibited, and coronary arterial resistance is decreased, resulting in elevated coronary blood flow. Amiodarone is used for various arrhythmias, together with ventricular extrasystoles, tachycardia, and fibrillation. It can be efficacious in some atrial arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation and flutter, in which it may have unique effects on the adverse remodeling modifications within the atria, which are thought to be partly liable for the genesis of atrial fibrillation. Changes in thyroid operate (hyperthyroidism and especially hypothyroidism) have been reported, and these could also be associated to the aforementioned facts that amiodarone resembles thyroid hormone and influences thyroid hormone actions. Amiodarone can scale back the action of thyroid hormone by binding to the thyroid hormone receptor and blocking its cellular results. It has additionally been shown that amiodarone can inhibit the action of thyroid-stimulating hormone, which may additionally contribute to a hypothyroid impact by amiodarone. The drug inhibits the conversion of thyroxine to triiodothyronine in peripheral tissues and causes the buildup of reverse triiodothyronine (see Chapter 29). Finally, amiodarone inhibits a number of cytochrome P450 enzymes and might cause a variety of drug�drug interactions. Dronedarone Dronedarone is structurally just like amiodarone, but it lacks the iodine atoms and is extra water-soluble, giving it a half-life of about 20 hours. A highly lipophilic drug, amiodarone is sequestered in tissues, yielding an apparent quantity of distribution of roughly 60 L/kg. Because the drug would normally take weeks to attain a steady-state focus after the initiation of remedy, loading doses are routinely used. Amiodarone is extensively metabolized by the liver; a desethyl by-product, which has antiarrhythmic properties as indicated previously, has been recognized. When the drug is withdrawn, the tissue concentrations decrease solely progressively because the drug is eliminated. It blocks Kr channels and causes the opening of Ca2+ channels, which promote Na+ influx through gradual channels, extending section 2 of the motion potential. The drug is administered intravenously for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. It can be used to convert these arrhythmias, especially of current onset, to regular sinus rhythm. It is used for acute conversion of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter and for short-term upkeep of normal sinus rhythm. Because amiodarone has adverse inotropic properties, its use could also be associated with a lower in cardiac operate. The primary considerations are pulmonary fibrosis and pneumonitis, which may turn out to be clinically evident in a significant percentage of patients with long-term use, and could be lethal. Verapamil and diltiazem are prescribed primarily for their antianginal (see Chapter 21) and antiarrhythmic results. The drug is helpful for short-term therapy of supraventricular tachycardia involving reentry with fast ventricular response. In every case, the drugs are selective for potential-dependent Ca2+ channels somewhat than receptor-operated channels. These channels are distinguished by their electrical properties and anatomic location. Verapamil and diltiazem are useful in treating supraventricular arrhythmias corresponding to atrial fibrillation and flutter. This helps indirectly to management ventricular price, which could be affected by the aberrant supraventricular activity. Both medicine have additionally been used successfully in stopping attacks of atrial tachycardia. Other elements of the pharmacologic features of the Ca2+ channel blockers are discussed in Chapters 21 and 23. Adverse effects Adenosine should be injected intravenously as a fast bolus with a saline flush behind it because of its extraordinarily brief plasma half-life, due to its fast transport into tissues. Arrhythmias, together with coronary heart block and transient asystole, can also occur immediately after injection. Patients are warned they may feel a metallic style and will turn into dizzy or black out because the drug is injected. Adenosine the endogenous purine nucleoside, adenosine, is approved for terminating attacks of supraventricular tachycardia. Magnesium Magnesium sulfate is used intravenously to overcome drug-induced torsades de pointes.
Order lopinavir online nowPosture may be assessed in steady and dynamic situations to have the ability to analyse functional activity. There are core postural units that are part of useful actions, which include standing, supine, sitting, sidelying, stepstanding and inclined. The management of the suitable level of neuromuscular activity in relation to a given posture and practical goal requires the nervous system to adjust postural tone appropriately. This is expounded to the impact of gravity and the base of support, and constantly adapts with respect to changing environmental calls for to find a way to counteract the drive of gravity. Descending spinal activity normally adapts the postural muscle tone by way of its influences on the spinal cord circuitry. This permits the muscle tissue to be more or less appropriately stiff or compliant to enable each applicable alignment for stability and motion. The base of assist acts as a reference level for motion inside a posture and for movement from one place to another. Balance methods Balance strategies allow for the organisation of motion in a framework of postural control. They are patterns of movement or variations in muscular tissues, resulting from feed-forward and suggestions mechanisms which are influenced by learning, experience and sensory inputs. Reactive balance methods enable the body to reply to sudden displacements. They happen in muscles, simply earlier than or alongside focal movements, so as to stabilise the physique or its segments during the execution of the movement (Schepens & Drew 2004). They are expertise dependent and are therefore learned responses modified by suggestions (Mouchnino et al. For instance, it has been shown that acceptable core muscle recruitment can increase the capacity of muscle activation in the extremities (Kebatse et al. Following nervous system harm and the subsequent disruption of postural activity, steadiness responses generally turn out to be extra response based mostly rather than anticipatory, because of lack of acceptable feed-forward mechanisms. Postural strategies include the ankle and hip strategy, stepping reactions, grasp with hand and protective extension of the higher extremities. The ankle and hip strategies are used in order to maintain a set base of support, whereas the others relate to changing the bottom of assist. They can be used interchangeably depending on the surroundings, but usually sufferers with neurological dysfunction will over-rely on the hip technique (Maki & McIlroy 1999). Also, the change-in-support strategies are sometimes used prematurely because of a lack of applicable antigravity activity and feed-forward controls. Patterns of motion All actions happen in patterns which are coordinated and comply with an appropriate trajectory with respect to the task and the surroundings. Muscles are connected to the skeleton in such a method as to promote actions that combine flexion, extension 33 Bobath Concept: Theory and Clinical Practice in Neurological Rehabilitation and rotation. Rotation is especially important when considering the interplay of the different body segments with one another and in relation to the midline. Patterns of movement relate to the timing and sequencing of motion, on an appropriate background of postural stability, and can be described as optimum muscle firing patterns for motor activity. Mrs Bobath described patterns of movement as sequences of selective motion for perform (Bobath 1990). They are described in the literature as having considerable flexibility and are primarily expressed in extrinsic muscles requiring a background of postural stability (Carson & Riek 2001). The sequence, timing and flow of actions are all have to be taken into consideration in the re-education of appropriate patterns of movement. All muscles need to work from a steady base to permit them to be used to produce selective motion which is appropriate for the duty and not be diverted to try to stabilise the body. The achievement of a useful vary of movement, produced towards a background of postural stability, is especially necessary particularly with respect to reach and grasp and stepping. The energy of acceptable muscle recruitment in functional patterns is an important aspect of motor management and motor studying. It is also recognised that the flexibility of muscles to generate appropriate torque at one joint will be greatly affected by the torques produced at different joints (Mercier et al. Thus, the manufacturing of selective motion in patterns depends on stability at adjoining joints. Patients who use sub-optimal movements for objective success alone could possibly carry out tasks in the quick term, but the presence of compensatory exercise is associated with long-term problems similar to pain, discomfort and joint contractures (Cirstea & Levin 2007). Clinically, sufferers with neurological dysfunction usually current with extreme co-activation of antagonistic muscular tissues, leading to co-contraction, poor recruitment of motor neurones and biomechanical adjustments in muscular tissues, which all affect the manufacturing of selective motion in applicable patterns. Muscle energy and endurance the necessity to integrate specific power training as a half of gaining environment friendly movement is seen by Bobath therapists as a key element of regaining environment friendly useful movement (Raine 2007). It is now recognised that weakness is an important factor limiting the recovery of motor performance following mind injury. A higher understanding of the neural mechanism of muscle recruitment and of muscle and nervous system plasticity has led to a larger consciousness of the inevitable secondary weak point that can happen in muscle tissue following nervous system harm. Disordered recruitment 34 An Understanding of Functional Movement as a Basis for Clinical Reasoning that occurs with nervous system damage will inevitably have an result on selective muscle operate with plastic adjustments occurring shortly. To appropriately carry out functional duties, muscle tissue must be in a position to generate enough force and pressure to overcome the resistance of the activity and likewise be in a position to create applicable tensions, at particular lengths, so selective functional movements can be performed. Functional activities may involve production of a one-off exercise, such as standing up from a chair, or a series of sub-maximum efforts over time, similar to strolling, going upstairs or working. The former will involve muscle energy, whereas the latter will contain both features of energy and endurance or stamina (Trew & Everett 2005). In order to strengthen muscles within a rehabilitation programme, they need to be labored to fatigue with a load positioned on them. Muscles that normally stabilise body elements such as multifidus, transversus, soleus, serratus anterior need to be appropriately recruited to obtain active stabilisation of body parts during energy coaching. This will ensure ongoing preservation of applicable length�tension relationships, which is crucial for the preservation of efficient alignment and motion. Use of eccentric muscle work could lead to enhancements in each concentric and eccentric power and creates a higher technology of rigidity inside the muscle. Muscle power may be improved by rising the pace and explosiveness of the activity. It is thought that coaching results of any exercise is the results of many physiological sub-systems and entails appropriately ordered neural instructions, as well as applicable pressure responses of the muscle structure. It is felt, the place potential, that remedy routines should match the actions of every day living. If energy routines may be achieved in practical situations corresponding to throughout stand to part sit to stand, it will have the best influence on both appropriate recruitment and appropriate stress and cargo on the muscle structure to induce the required plastic adaptation for enchancment of operate (Lieber 2002; Yang et al. Grading and growing of applicable loads are necessary sources of afferent information that may help increase recruitment of applicable muscle exercise within functional ranges of management. Repetition to enhance stamina, changing speeds and extra loading are variables that can add rising stress, provided that the ability of the muscular tissues to reply appropriately is rigorously monitored. Considerations of strength and stamina elements of training are necessary within the design and progression of home programmes, making certain that enough and applicable recruitment occurs alongside 35 Bobath Concept: Theory and Clinical Practice in Neurological Rehabilitation the strengthening exercise.
Plant Sterolins (Beta-Sitosterol). Lopinavir. - What is Beta-sitosterol?
- Burns, prostate infections, sexual dysfunction, preventing colon cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, allergies, cervical cancer, fibromyalgia, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), asthma, baldness, migraines, chronic fatigue syndrome, menopause, and other conditions.
- Trouble urinating from an enlarged prostate, or "benign prostatic hyperplasia" (BPH).
- Dosing considerations for Beta-sitosterol.
- High cholesterol.
- Gallstones.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96902
Cheap lopinavir 250 mg on lineWhere illustration of an space has not completely been lost, the representation of the peri-infarct tissue and areas in axonal communication with the lesioned area, via axonal sprouting, have been found to take on representation and subsequently function of the lesioned area (Rapisarda et al. Reorganisation has been seen in areas of the visual cortex which turns into associated with tactile duties in blind subjects who learn Braille (Sadato et al. The Bobath Concept explores this potential for cortical reorganisation through selective afferent enter to optimise internal illustration and affect motion control. Selective motor training or manipulation of the task, surroundings, or aspects of the individual as a part of motion re-education additionally goals to promote plastic 6 Bobath Concept: Developments and Current Theoretical Underpinning modifications. This has been seen within the cortical representation of the left hand, in a left handed string instrument participant which when scanned reveals larger cortical representation in contrast with the left hand of a non-string participant (Elbert et al. Enriched environments giving subjects higher than normal stimulation have been shown, at the right time, to promote vital neuroplastic changes and improvement in practical outcomes (Ohlsson & Johansson 1995; Johansson 1996). Emergent properties of every cortical area are constantly formed by behavioural calls for, pushed largely by repetition and temporal coincidence (Nudo 2007). Such repetition drives motor cortical areas to form discrete modules by which the conjoint exercise is represented as a unit, quite than fractionated and particular person muscle contractions (Nudo 1998). Skilled motor actions requiring exact temporal coordination of muscle tissue and joints should be practised many times over and applied into on an everyday basis meaningful activities for optimal carry-over. Muscle plasticity Like neuroplasticity, the adaptability of muscle has been investigated extensively. Virtually each structural aspect of muscle, similar to its structure, gene expression, fibre type distribution, number and distribution of alpha motor items and motor end plates, variety of sarcomeres, myosin heavy chain profile, fibre size, mitochondrial distribution, tendon size, capillary density and muscle mass, has the potential for change with the appropriate stimulus (Dietz 1992; Pette 1998; Mercier et al. Skeletal muscle can be either conditioned or deconditioned depending upon the demands put on the muscle, and these can influence properties such as energy, pace and endurance of the muscle. The vary of muscle fibre sorts allows for the varied position and function of muscle wanted to support human movement (Scott et al. It is the adaptability of the proteins and the design of sarcomeres and myofibrils which provides the basis for the modelling and remodelling of a large spectrum of fibre sorts to match the specific necessities and altered practical demands (Pette 1998). Muscle fibre phenotype is pushed by neural exercise and mechanical factors, a mix of stretch and exercise (Goldspink 1999). This atrophy is more fast in gradual oxidative, postural and biaxial muscular tissues with a slow to fast shift in fibre sort and a discount in the capillary density (Mercier et al. Inactivity in a shortened position results in an increase in connective tissue, a rise in stiffness and resistance to passive stretch (Williams & Goldspink 1973). Muscles immobilised 7 Bobath Concept: Theory and Clinical Practice in Neurological Rehabilitation in a shortened place have been found to lose sarcomeres, with the remaining sarcomeres increasing in length to maximise tension on this shortened place (Grossman et al. Neurological lesions and the resultant neuroplastic adjustments have a big impression on the demands positioned upon muscle. Early stages show an incapability to obtain the execution of a voluntary command and depart the muscle in a position of inactivity and immobility (Gracies 2001). Muscles might obtain an increase or loss of drive to the alpha motor neuron and its motor finish plate, which can result in a posh combination of conditioning and deconditioning. Where hypertonic muscular tissues are immobilised in a shortened position the potential for a contracture develops with muscle atrophy, loss of sarcomeres, failure of actin and myosin cross-bridges to disengage, and accumulation of connective tissue (Watkins 1999; Gracies 2001). It has been found that even in the case of increased drive, however, muscles have been found to weaken as a outcome of insufficient motor unit synchronisation and decreased torque generated by the muscle (Gracies, 2001). Muscle imbalance in compliance, length and energy will all influence coordination for selective motion management. This highlights the significance of discovered non-use in both hemiparetic and non-hemiparetic sides and highlights additional the need for an individualised, holistic approach to the therapy of patients with neurological dysfunction (Hachisuka et al. The levels describe a development via cognitive to automatic ranges whereby the performance is refined and reveals carry-over of studying (Wishart et al. This process demonstrates the developments in cortical representation for the educational of the new skill. Motor studying theories suggest that active participation, apply and significant goals are all essential for studying (Schmidt 1991; Winstein et al. There are quite a few variables which may be considered to be necessary determinants in motor learning which have been investigated utilizing healthy people studying novel motor expertise (Winstein 1991; Marley et al. These embody: apply (amount, variability, contextual interference [order of repetitions similar to blocked or random]); part or complete task; augmented feedback (frequency, timing, bandwidth [level of efficiency to be reached before feedback provided]); psychological follow; modelling; steering; attentional focus (goal attainment) and contextual variety. One of the key features that wants consideration in all features of practice is to guarantee a state of affairs is created that allows the person to engage in a problemsolving course of to enable them to achieve the duty (Marley et al. Varied circumstances and random apply are more effective for motor studying (carry-over in performance), whereas static circumstances and blocked follow are more effective for improvements within the instant motor performance (Wishart et al. Whole task follow is recommended when duties are continuous (reach and grasp) or reciprocal (walking) in nature (Dean & Shepherd 1997). Part tasks are useful when an exercise may be broken down into a variety of separate discrete duties. Augmented feedback shares information about the traits (knowledge of the performance) or the result (knowledge of the results) of the movement. Although efficiency could also be improved with steady suggestions, motor studying has been shown to be better with rare feedback and/or abstract of results (Saladin et al. Feedback offered once a set degree of failure has been passed (bandwidth) has also been found to be useful for learning (Ezekiel et al. Feedback can be essential in motivating the person which is seen as essential in the rehabilitation course of. Mental follow, defined as the rehearsal of a task with out overt physical exercise, has proven a optimistic studying impact, particularly when used along side physical follow. It can be helpful when there are limitations in the period of time or power for engagement in exercise, or when physical practice outdoors the remedy session could be hazardous or detrimental to the rehabilitation process (Lehto et al. Physical demonstration of the duty (modelling) and activities designed round significant goal-directed duties have been found to be helpful (Wulf et al. Without context of a task, motion patterns could exist but they will be devoid of methods (Majsak 1996). Guidance should be selective, graded and must problem the individual to problemsolve their movement difficulties. They have to be chosen and facilitated appropriately to enable the individual to be actively concerned to find solutions for his or her motor issues. Motor learning is commonly demonstrated not just by elevated precision in the acquisition of the motor performance but the variability with which the person is ready to obtain the activity (Majsak 1996). The importance of giving the individual movement decisions or diversity in motion methods will also enable them to transfer their expertise to quite a few tasks and environments. Opportunities have to be made the place the person is problem-solving and error correcting their very own motion in preparation for the switch of abilities and software of skills for achievement of significant motor activities. Following stroke, the individual will present with numerous musculoskeletal (biomechanical), neuromuscular, sensory-perceptual and cognitive constraints which may limit or problem the potential for the achievement of motor learning in sure motor abilities. There needs to be a stability between the period of time in preparation and the amount of time utilized in selective half or complete task practice. Interactions between the constraints of the individual, the setting and the task are advanced and continuous (Majsak 1996). Upper motor neuron syndrome Following a mind damage an individual will usually have a posh presentation impacting not only on the neuromuscular system but also on the musculoskeletal, sensory-perceptual and cognitive systems (Cohen 1999).
Syndromes - Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
- Depression (depression is a common cause of sleep problems in people of all ages)
- Keep your blood from clotting
- Is it clear or cloudy?
- Traumatic injury of the bladder and urethra
- Have you been checked for osteoporosis?
- Basic metabolic panel
- Frequent thirst
- Where is the lump located?
Generic lopinavir 250mg lineOther nutrients are also actively transported into the blood of capillaries within the intestinal villi. Table 11-1 Chemical Digestion Digestive juices and enzymes Saliva Amylase Gastric Juice Protease (Pepsin) Proteins (intact of plus hydrochloric acid Pancreatic Juice Protease (trypsin) and Lipase Amylase Intestinal Juice Peptidases Sucrase Lactase Maltase Peptides Sucrose (cane sugar) Lactase (Milk sugar) Maltase (malt sugar) Peptides Fatty Maltose Amino acids Glucose and fructose (simple sugars) Glucose and galactose (Simple sugars Glucose acids, amino acids and glycerol partially digested) Fats emulsified by bile Starch Proteins Partially proteins digested Substance Digested (or hydrolysed) Starch (Polysaccharide) Maltose (disaccharide) Resulting Products* *Substances underlined are finish products of digestion (that is, completely digested meals ready for absorption) 333 Human Anatomy and Physiology Review Questions 1. If you inserted 9 inches of an enema tube by way of the anus, the tip of the tube would in all probability be in what construction Differentiate between deciduous and permanent enamel with respect to varieties and numbers. The urinary system consists of: Two kidneys: this organ extracts wastes from the blood, balance body fluids and form urine. The urinary bladder: this reservoir receives and stores the urine delivered to it by the 2 ureters. The urethra: this tube conducts urine from the bladder to the out side of the body for elimination. They 338 Human Anatomy and Physiology are protected no much less than partially by the last pair of ribs and capped by the adrenal gland. On the medial concave border is the hilus (small indented area) where blood vessels, nerves & ureters enter and depart the kidney. Covering and supporting every kidney are three layers of tissue: � � � Renal capsule � innermost, powerful, fibrous layer Adipose capsule � the center layer composed of fat, giving the kidney protective cushion. The renal pelvis is the massive collecting house with in the kidney formed from the expanded higher portion of the ureters. The pelvis department to two cavities, these are 2-3 major calyces and 8 to 18 minor calyces. It consists of eight to 18 renal pyramids, that are longitudinally striped, one cone shaped area. It is divided in to two region the outer cortical and the inside juxtamedullary region. Filters (by hydrostatic presure) water, dissolved substances (minus most plasma proteins, blood cells) from blood plasma. Actively secretes substances such as penicillin, histamine, organic acids, organic bases. Glomerular capsule Proximal convoluted tubule Descending loop of the nephron Ascending loop of the nephron Distal Convoluted tubule Collecting duct the major functions of the kidneys are: 343 Human Anatomy and Physiology All the features are directly or indirectly related to the formation of urine. The sequence of events results in: To the elimination of wastes Regulation of whole body water balance. Control of the chemical composition of the blood and other physique fluid Control of acid base stability the processes in urine formation are: 1. Tubular secretion Average Comparison of filtration, re-absorption and excretion, right here variation in urine composition will happen throughout variation in the daily food plan, fluid consumption, climate and exercise. The ureters pass between the parietal peritoneum and the body wall to the pelvic cavity, where they enter the pelvic cavity. The lumen of the ureters is composed of three layers: Innermost, Tunica Mucosa the center, Tunica Muscularis (made of smooth muscle) the outer, Tunica Adventitia 12. It is located on the floor of the pelvic cavity and 346 Human Anatomy and Physiology just like the kidneys and ureters. The opening of ureters and urethra within the cavity of the bladder outline triangular space known as the trigone. At the positioning where the urethra leaves the bladder, the smooth muscle in the wall of the bladder forms spiral, longitudinal and circular bundles which contract to stop the bladder from emptying prematurely. These bundles operate as a sphincter called Internal Urethral Sphincter (Involuntary). Far there alongside the urethra within the center membranous portion a circular sphincter of voluntary skeletal muscle type the external urethral sphincter. It joins the bladder at its inferior floor and transport urine out aspect the physique during urination. In male it pass by way of prostate, membranous portion (pelvic diaphragm muscle), spongy portion (that move through corpus spongosus) and open on the tip of penis. The spongy portion joined by ducts from bulbo-uretheral gland (Mucus secreting gland). Proteins, glucose, casts (decomposed blood) and calculi from minerals are irregular if present in urine. To keep the proper osmotic focus of the extra cellular fluid to excrete wastes and to maintain proper kidney function the physique must excrete a minimum of 450ml of urine per day. The volume and concentration of urine is managed by: Antidiuretic hormone Aldestrone the Renin � angiotensin mechanism 349 Human Anatomy and Physiology 12. Steps of urination are: Conscious desire to urinate Pelvic diaphram muscle relax Urinary bladder neck Moves down, stretch, outlet and Opens, wall wall stretch Smooth Urinary Contracts ejects muscle & of urine bladder Receptors are stimulated 350 Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Questions 1. The internal most layer of the ureters is the a) Mucosa c) Adventitia e) Circular layer three. The kidney perform in all of the following besides a) Acid � base steadiness b) An endocrine organ c) By eradicating metabolic waste d) By removing excess carbon dioxide e) By sustaining osmotic concentration four. An elevated quantity of urine formation would observe:a) Inhibition of tubular sodium re-absorption b) A fall in plasma osmolarity c) A fall in plasma quantity d) a and b e) a, b and c 5. The volume or chemical make-up of those fluids whenever deviates even barely from regular, disease outcomes. The appropriate proportion of water and electrolytes in the water and proper acid base steadiness are necessary for life to exist. Loss of 10% of complete physique water normally produce lethargy, fever and dryness on mucous membrane and a 20% loss is deadly. Extra cellular fluids found as interstitial fluid (the immediate environment of physique cells), blood plasma and lymph, cerebrospinal, synovial, fluids of the eye & ear, pleural, pericardial, peritoneal, gastrointestinal and glomerular filtrate of the kidney. The concentration of water in the interstitial fluid is slightly larger than the focus of water in plasma. Osmotic stress: Is the strain that should be utilized to a solution on one facet of a selectively permeable membrane to forestall the Osmotic move of water across the membrane from a compartment of pure water. Such accumulation of water produces distention of the tissue which seems as puffiness on the floor of the physique. Causes of edema may be plasma protean leakage decreased protein synthesis, increased capillary or venous hydrostatic strain, obstructed lymphatic vessels and inflammatory reaction. The important mineral solutes (electrolytes) of the body enter the physique through meals or drink. Under regular situation water is taken in to and excreted from the body, so it matches to maintain homeostasis. Drinking of water is regulated by nervous mechanism (thirst center within the brain) along with hormonal mechanism (Antidiuretic hormone). Facilitate motion of water between the physique compartments Together with the soluble proteins, they maintain the hydrogen ion Concentration (acid-base balance) Sodium, potassium, chlorides and magnesium are essential to the manufacturing and maintenance of membrane potentials (nerve & muscle potentials) Sodium, potassium and chloride ions present within the highest concentration in the physique. These three electrolytes are notably important in sustaining physique perform and normal water distribution among the many fluid compartment. Any molecule that dissociates in answer to launch a hydrogen (H+) ion is called an acid. Enzymes, hormones and the distribution 360 Human Anatomy and Physiology of ions can all be affected by the concentration of hydrogen ion. Specific chemical buffer system of the physique fluids (react very rapidly, in minutes) 3.
Cheap lopinavir genericA gyrus (plural = gyri) is the ridge of one of those wrinkles, and a sulcus (plural = sulci) is the groove between two gyri. The pattern of those folds of tissue can be utilized to point out particular areas of the cerebral cortex. The folding of the cortex maximizes the quantity of gray matter within the cranial cavity. During embryonic improvement, the telencephalon is a structure that finally develops into the cerebrum. The floor of the brain could be mapped based mostly on the places of enormous gyri and sulci. The lateral sulcus that separates the temporal lobe from the opposite regions is one such landmark. Superior to the lateral sulcus are the parietal and frontal lobes, which are separated from one another by the central sulcus. The posterior area of the cortex is the occipital lobe, which has no obvious anatomical border between it and the parietal or temporal lobes on the lateral floor of the mind. From the medial surface, an apparent landmark separating the parietal and occipital lobes known as the parieto-occipital sulcus. The frontal lobe is liable for complex capabilities together with motor capabilities (planning and executing movements through instructions despatched to the spinal twine and periphery) and, inside the prefrontal cortex, aspects of character through influencing motor responses concerned in decision-making. The occipital lobe is where visual processing begins, although the other parts of the mind can contribute to visual function. The temporal lobe contains the cortical space for auditory processing and in addition has regions crucial for reminiscence formation. Located deep within the lateral sulcus is a fifth lobe of the brain referred to as the insular lobe. Subcortical grey matter Beneath the cerebral cortex are sets of nuclei often known as subcortical nuclei that increase cortical processes. The nuclei of the basal forebrain modulate the general exercise of the cortex, possibly leading to larger consideration to sensory stimuli. The hippocampus and amygdala are medial-lobe constructions that, along with the adjacent cortex, are concerned in long-term reminiscence formation and emotional responses. The basal nuclei are a set of nuclei within the cerebrum liable for evaluating cortical processing with the final state of activity within the nervous system to influence the chance of movement taking place. The main buildings of the basal nuclei that control motion are the caudate, putamen, and globus pallidus, that are positioned deep in the cerebrum. The caudate is a long nucleus that follows the essential C-shape of the cerebrum from the frontal lobe, via the parietal and occipital lobes, into the temporal lobe. The putamen is mostly deep in the anterior regions of the frontal and parietal lobes. The globus pallidus has two subdivisions, the exterior and inner segments, that are lateral and medial, respectively. Diencephalon the diencephalon is the connection between the cerebrum and the practically the entire nervous system and has two main regions: the thalamus and the hypothalamus. The single exception is the system associated with olfaction, or the sense of smell, which connects immediately with the cerebrum. The thalamus is a group of nuclei that relay data between the cerebral cortex and the periphery, spinal twine, or brain stem. All sensory info, except for olfaction, passes by way of the thalamus earlier than processing by the cortex. The cerebrum and basal nuclei additionally send motor info to the thalamus which normally entails interactions between the cerebellum and different nuclei within the brain stem as properly. Inferior and slightly anterior to the thalamus is the hypothalamus, the other major region of the diencephalon. The hypothalamus is a collection of nuclei which may be largely concerned in regulating homeostasis. The hypothalamus is the manager region in command of the autonomic nervous system and the endocrine system via its regulation of the anterior pituitary gland. Other components of the hypothalamus are concerned in reminiscence and emotion as part of the limbic system. The hypothalamus is inferior and anterior to the thalamus, culminating in a pointy angle to which the pituitary gland is connected. The structure emerges from the ventral surface of the forebrain as a tapering cone that connects the brain to the spinal wire. Attached to the mind stem, but thought-about a separate region of the grownup brain, is the cerebellum. The midbrain coordinates sensory representations of the visual, auditory, and somatosensory perceptual data. The pons and the medulla regulate a quantity of crucial features, together with the cardiovascular and respiratory methods and charges. The cranial nerves (described below) join via the brain stem and supply the mind with the sensory input and motor output associated with the head and neck, together with most of the special senses. The major ascending and descending pathways between the spinal twine and brain, particularly the cerebrum, pass by way of the mind stem. The higher portion of the midbrain is composed of 4 bumps generally identified as the colliculi (singular = colliculus), which suggests "little hill" in Latin. The inferior colliculus is the inferior pair of those enlargements and is a half of the auditory mind stem pathway. Neurons of the inferior colliculus project to the thalamus, which then sends auditory data to the cerebrum for the conscious notion of sound. The superior colliculus is the superior pair and combines sensory details about visual house, auditory house, and somatosensory area. Activity within the superior colliculus is related to orienting the eyes to a sound or touch stimulus. The mind stem comprises three regions: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla Cerebellum the cerebellum, because the name suggests, is the "little brain" and accounts for about 10 % of the mass of the brain. The cerebellum is basically responsible for evaluating data from the cerebrum with sensory feedback from the periphery through the spinal wire. Descending fibers from the cerebrum have branches that connect to neurons within the pons. Sensory data from the periphery, which enters via spinal or cranial nerves, also initiatives to a nucleus in the medulla generally identified as the inferior olive. Fibers from this nucleus enter the cerebellum and are in contrast with the descending instructions from the cerebrum. For example, if the cerebrum sends a command all the method down to the spinal cord to initiate walking, a duplicate of that motor command is shipped to the cerebellum. Sensory suggestions from the muscular tissues and joints, proprioceptive details about the movements of walking, and sensations of balance are sent to the cerebellum via the inferior olive and then the cerebellum integrates all of that data. The output of the cerebellum is into the midbrain, which then sends a descending input to the spinal cord to appropriate motor info going to skeletal muscular tissues. It is also liable for lifting the higher eyelid when the eyes point up, and for pupillary constriction.
Order 250mg lopinavir with visaWhen the trapezius contracts, the head is drawn back and to the aspect and the scapula is rotated. The latissimus dorsi originating in the thoracic, lumbar and sacral vertebrae and the iliac crest insert into the groove below the biceps on the humerus for adduction and rotation of the arm. These muscles insert into the greater trochanter of the femur permining thigh movement. Major muscles associated with the anterior aspect of the thigh are the quadriceps femoris (L quadri = 4 + ceps from caput = head, thus a 4 headed muscle) originating within the iscbial tuberosity on the pelvis and inserting into the femur. In the posterior part of the thigh are the hamstring muscles, including the gTacilis, sartorius, biceps femoris, and semitendinous muscles which cause flexion of the thigh. There are 4 units of stomach muscle tissue: (a) the internal oblique muscle ascending; (b) the external indirect muscle descending; (c) the transversus abdominus - throughout the abdomen; (d) the rectus abdominus muscle - vertically. These are locations the place blood vessels and other structures normally lengthen by way of the muscle tissue. Originating on the pelvis, it inserts into the medial surface of the shaft of the tibia. The calf of the leg incorporates the gastrocneinius, the biggest muscle which extends the foot and helps to flex the knee or the thigh. Originating on the femur, this muscle inserts by the Achilles tendon into the calcaneus. It has two sources of origin, the quick head rising from the coracoid strategy of the scapula and the long head from the scapula above the glenoid fossa. For example, the flexor poilas longus, which permits us to flex our thumb, originates in the radius and inserts into the terminal phalanx of the thumb. The following listing includes some of the more generally used tenus related to ailments of muscular tissues and bones. Achondroplasia is a congenital anomaly resulting in dwarfism as a end result of abnormally short long bones. Dislocation the ligaments on the joint give away fully and the bone is displaced from its socket. Medical Terminology Course 15 Myasthenia gravis is exhibited by speedy fatigue of muscular tissues without pain. Sprains the ligaments that support joints are stretched or Tenosynovitis inflammation of a tendon sheath. Myositis is irritation of muscle tissue, Osteitis deformans (Pagets disease) the enlargement and distortion of bones in older age. It consists of the mind and spinal twine, linked to the peripheral half related with tissues and organs. Sensory nerve fibres carry messages from tissues and organs to the mind and spinal wire. Motor nerve fibres carry messages to tissues and organs, from the mind and spinal wire. Rheumatoid arthritis a chronic disease affecting many joints which ends up in deformity. The bones get out of practice when weight bearing, and eventually harden within the deformed state. Spondylolisthesis spondylos = vertebrae, olithesis = forward slipping, a ahead slipping of the 6. It is made up of two cerebral hemispheres (hemi = half) every of which is divided into lobes. The anterior commissure is made up of nerve fibres linking the two cerebral hemispheres. Deep within the substance of the cerebral hemispheres there are additional lots of grey matter which, together with the cerebrum, type the forebrain: (1) the basal ganglia, involved with the modification and coordination of voluntary muscle motion; (2) the thalamus, an necessary relay centre for sensory fibres on their approach to the cerebral cortex; crude sensation and ache may be felt right here; (3) the hypothalamus, incorporates the centres for the autonomic nervous system. The white matter of the midbrain carnes sensory and motor fibres, linking the red nucleus with the forebrain, the hindbrain and the spinal twine. It contains nerve fibres which link the cerebral cortex with the medulla oblongata and the spinal wire (L. The function of the cerebellum is to coordinate groups of muscular tissues so that they work together smoothly. It flows from the lateral ventricles through the foramen of Monro to the third ventricle. From the third ventricle it flows through the aqueduct of Sylvius to the fourth ventricle. Leaving the fourth ventricle, it bathes the brain and spinal twine within the subara chnoid house between the aracimoid and pia mater. It is absorbed by the great venous durai sinuses, particularly the superior saggital sinus. Facial muscle tissue, sub-maxillary and sublingual salivary glands Transmits ordinary sensations from eye, face, sinuses and teeth. Tactile and taste sensations from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue and the taste bud. Sternomastoid, trapezius and consthctor muscles of the pharynx, larynx and soft palate. Tactile and taste sensations from the posterior 1/3 of the tongue, the tonsils, pharynx and the carotid sinuses. Peripheral nerves are linked to the spinal wire by two roots: the anterior or motor root and the posterior or sensory root (Diagram 9). Diagram 9: the Peripheral nerve Nerve ganglion Posterior root the external ear the pinna (L. It collects the sound which is transmitted via the auditory canal, resulting in the tympanic membrane or eardrum, (Gr. It is related with the nasopharynx by the Eustachian tube, which opens upon swallowing to permit air to enter the center ear, thus equalizing pressure on either side of the tympanic membrane. There are three small bones in the middle ear called auditory ossides that are connected to kind a small lever between the tympanic membrane and the oval window (fenestra cochlea). The auditory ossides are named based on their shapes - the malleus, (Latin = hammer), the incus (Latin = anvil), and the stapes (Latin = stirrup). Two small muscles, the tensor tympani linked to the malleus and the stapethus related to the stapes, contract as a protecting mechanism during excessively loud noise. This amplifies and transmits the sound throughout the center ear in order that the foot plate of the stapes strikes backwards and forwards in the oval window which is in touch with the cochlear fluid, during which vibrations are established. These vibrations stimulate receptors in the Organ of Corti, and nerve impulses are despatched to the sound centre in the brain. It is a spiral canal containing a receptor for listening to referred to as the Organ of Corti to which is connected the cochlear branch of the auditory nerve, it has hair cells which decide up impulses transmitted from the middle ear. The superior, posterior and lateral semicircular canals each connect by an ampulla (L. Anteri�r root the peripheral nervous system is answerable for the innervation of all voluntary muscle tissue (except these controlled by cranial nerves) and the transmission of sensory impulses from the whole of the physique (with the exception of the face). Division, injury or disease of peripheral nerves thus normally results in both sensory and motor loss.
References - Park SO, Ha JH, Hong KY, et al: Usefulness of mapping biopsy in the treatment of penoscrotal extramammary Pagetis disease, Ann Surg Oncol 24(11):3229n 3236, 2017.
- Dieckmann KP, Pichlmeier U: Clinical epidemiology of testicular germ cell tumors, World J Urol 22:2n14, 2004.
- Engel, G. (1959). Psychogenic pain and the pain prone patient. American Journal of Medicine, 26, 899n918.
|
|