"Purchase extra super cialis with a visa, erectile dysfunction statistics singapore."By: Keira A Cohen, M.D. - Co-Director, The Johns Hopkins Center for Nontuberculous Mycobacteria and Bronchiectasis
- Assistant Professor of Medicine
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/10003818/keira-cohen
100mg extra super cialis with amexShe feels ftne and denies palpltatlons, weight loss, warmth Intolerance, and change In bowel movements. What two circumstances account for the majorlty of circumstances of subcllnlcal hyperthyroidism1 C. Clinical evaluation: A evaluation ofthe medical penalties of variation in thyroid operate inside the reference range. Epidemiology, medical options, and therapy of diffuse and multinodular nontoxic goiters. The impact of goitre and its therapy on the trachea, airflow, oesophagus and swallowing perform. Subclinical thyroid dysfunction and the risk for fractures: a systematic evaluate and meta-analysis. Diagnostic potential of ancillary molecular testing in differentiation of benign and malignant thyroid nodules. American Thyroid Association statement on surgical application of molecular profiling of thyroid nodules: present influence on perioperative determination making. Thyroid nodules: pathophysiological perception on oncogenesis and novel diagnostic methods. Management of thyroid nodular disease: present cytopathology classifications and genetic testing. Molecular testing of thyroid nodules: a evaluate of present obtainable tests for fine-needle aspiration specimens. Subclinical hyperthyroidism and cardiovascular manifestations: a reevaluation of the affiliation. Thyroid hormone resistance syndrome attributable to heterozygous A317T mutation in thyroid hormone receptor~ gene: report of 1 Chinese pedigree and evaluate of the literature. Subclinical hyperthyroidism and cardiovascular risk: recommendations for treatment. The glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids are essential fur survival, however no essential position has been detennined for adrenal androgens. The inside adrenal medulla, mentioned in Chapter 12, secretes catecholamines (epinephrine, norepinephri. Mainly because of their potent immunosuppressive and anti inflammatory effects, glucocorticoids are generally used in pharmacologic doses to deal with ailments similar to autoimmune problems. Interestingly, though the deleterious effects of glucocorticoids in states of hypercortisowm and the helpful effects of their use in pharmacotherapy are nicely understood, the actual position of endogenous glucocorticoids in metabolic homeostasis throughout instances of minimal stress remains somewhat enigmatic. The main problems of the adrenal cortex (Table 21-1) are characterised by an excessive or deficient secretion of each type of adrenocortical hormone: hypercortisolism. They are flattened, crescent-shaped constructions, which collectively normally weigh about 8-10 g. The zona glomerolosa is the outermost layer, situated immediately beneath the capsule. Zona fasciculata cells are polyhedral in form and organized in straight cords or columns, one or two cells thick, operating at proper angles to the capsule with capillaries between them. Also proven (turquoise) are extra-adrenal websites at which ccrtlcal and medullary tissues are typically found. Zona reticularis cells are smaller than the opposite two types and are arranged in irregular cords interlaced in a network. These steroid hormones are low-molecular-weight lipid-soluble molecules, derived from cholesterol, and are capable of diffuse freely across cell membranes. Glucocorticoids Glucocortlcold Synthesis, Protein Binding a Metabolism Cortisol and corticosterone are referred to as glucocorticoids as a end result of they improve hepatic glucose output by stimulating A Zona glomerulosa Choleeterol Cholesterol desmolase glucocorticoid secreted by the adrenal cortex is cortisol. Zona reticularis Cholestsrol Cholesterol desmolase Zona fasciculata Cholesterol Cholesterol desmolase! Slmpllfted pathways of steroid synthesis In the totally different zones of the adrenal cortex. Note the differences In the kinds of enzyme needed and the different order of enzymatic reacdcns In the different zones. Protein binding serves primarily to distribute and deliver the hormone to target tissues, however it additionally delays its metabolic clearance and prevents marked fluctuations within the cortisol level during episodic secretion by the gland. Its manufacturing is increased by pregnancy, estrogen or oral contraceptive remedy, hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus, sure hematologi. Because cortisol is protein certain to a greater diploma than corticosterone, its half-life within the circulation is longer (-60-90 minutes) than that of corticosterone (-50 minutes). Because of its avid protein binding and in depth metabolism earlier than excretion, less than 1% of secreted cortisol seems within the urine as free cortisol. The hypothalamus is subject to regulatory influences from different elements of the mind, including the limbic system. The diurnal rhythm is altered additionally by modifications in patterns of sleep (eg, shift work). When extended corticosteroid treatment is stopped, the adrenal is atrophic and unresponsive, and the patient is at risk for acute adrenal insufficiency. Another well-accepted method of stopping adrenal insufficiency following glucocorticoid remedy is to slowly taper the dosage ofexogenous glucocorticoids. A short-term taper (days to a couple of weeks) of phamw:ologic doses ofglucocorticoids prevents a rebound flare of the underlying treated illness (eg. The mind and heart are spared from this antagonism, and the additional supply of glucose helps these vital organs cope with stress. In diabetics, the insulin antagonism could worsen the control of blood sugar levels, elevate plasma lipid ranges, and enhance the formation of ketone bodies. However, in nondiabetics, the rise in blood glucose levels stimulates a compensatory enhance in insulin secretion that prevents these sequelae. Small amounts of glucocorticoids have to be current for other metabolic processes to occur (permissive action). For example, glucocorticoids must be current for catecholamines to produce their calorigenic, lipolytic. Synt/Nsis-Aldoaterone is the principal mineraloc:ortic:oid secreted by the adrenal. Protein Binding-Aldosterone is sure to plasma proteins (albwnin and corticosteroid-binding globulin) to a lesser extent than glucoc:ortic:oids. Free (unbound) aldosterone makes up 30-40% of the total consequent increase in circulating glucocorticoids after damage are essential to survival. Hypophysectomized or adrenalectomized people treated with solely maintenance doses of glucocorticoids might die when exposed to such stress. What are the hlstologlc layers of the adrenal cortex, and what steroids does each secrete Describe the adverse feedback management of the hypothalamlc-pltultary-adrenal axis. Din is excreted by the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidney in response to decreases in renal perfusion strain and refie:x. Once within the circulation, renin acts on angloteminogen to Conn angiotemin I, a decapeptide. Angiotensin eleven binds to zona glomerulosa cell membrane receptors and stimulates the synthesis and secretion of aldosterone.
Generic extra super cialis 100mg otcMost of the pathologic options of the hereditary hypercoagulable states consist of laboratory abnormalities. In the evaluation of sufferers suspected of having a hereditary hypercoagulable state, there are two basic types oflaboratory abnormalities. Prothrombin levels may additionally be Clinical Manifestations Most thromboembolic occasions encountered in medical practice are secondary, not primary. Patients have blood clots normally within the deep veins of the legs for 2 causes: (1) because of sluggish blood circulate (in high-capacity, low-flow veins) compared with other sites, particularly when inactive (eg, bedridden after surgery or as a result of illness); and (2) because the extremities are extra probably to sustain injury than the trunk. Trauma causes blood vessel compression or injury; thus, two components of the Virchow triad are extra readily noticed in the legs than elsewhere. Because blood return to the central circulation is blocked in these highcapacity vessels, superficial collateral veins just below the pores and skin may be prominent and engorged. The swelling is mechanical, as a end result of normal arterial blood flow continues to the extremity while venous return is compromised, leading to engorgement. Pain happens primarily as a result of the swelling alone however can even occur from lactic acid buildup in the muscles of the legs. This happens when the pressure in the legs increases to the point that it compromises arterial blood flow and enough oxygen supply to those muscular tissues. The clot blocks blood circulate from the heart to a portion of lung, leading to hypoxemia, which may be exacerbated by underlying lung disease. The scientific presentations of all hypercoagulable states are comparable, but there are some fascinating differences. Because of the dominant pattern of inheritance, suspicion is aroused when different relations have had clotting issues, underscoring the significance of taking a household historical past. Despite the distinct coagulation abnormalities, most thromboses still happen in traditional sites (ie, the deep veins of the legs with or without pulmonary embolism). Other unusual sites (eg, the sagittal sinus of the cranium or the mesenteric veins in the abdomen) usually tend to be found in patients with underlying coagulation issues than in those without. Heterozygotes who develop thrombosis normally present in the setting of a "t;ypical" threat issue: sustaining an injury. Homozygous protein C or protein S deficiencies present the highest probability of inflicting sickness. Both conditions usually end in thrombosis, which is fatal in youth (neonatal purpura fulminans), though some sufferers might not present until their teenagers. Heterozygotes for protein S deficiency have a 1- to 10-fold increased relative threat of thrombosis. These patients have a lifetbne 5- to 10-fold elevated relative threat for thrombosis. Families during which homozygous females have had repeated pregnancies without issue have been rigorously described. What constitutes the Vlrchow triad offactors predisposing to the formation of lntravascular clots Questioning reveals diffuse weak spot and feeling winded when strolling uphill or climbing multiple flight of stairs. The patient has no slgnlflcant medical historical past, socTal history, or family historical past. The physlcal examlnatlon Is unremarkable aside from his rectal examination, which reveals brown, gualac-posltlve stool (suggesting the presence of blood In the stool). She is in need of breath after walking sewral bloch On review of methods, she mentions gentle diarrhea. She has noted intermittent numbness and tingling of her lower extremities and a loss of steadiness while walking. She denies other neurologic or cardiac signs and has no history of black or bloody stools or other blood loss. On bodily examination, she is tachycardic to 11 obpm; different vital indicators are within regular limits. The head-and-neck examination is notable for pale conjunctivas and a beefy purple tongue with loss of papillae. Neurologlc examination reveals decreased sensation to light touch and vibration In the lower extremities. The hematology marketing consultant on name Js requested to see this affected person because of a low hematocrlt stage. What elements of this case presentation support the diagnosis of cyclic neutropenia Assuming that the analysis of cyclic neutropenia is correct, what would one count on the peripheral blood smear to appear to be Current mediations indude morphine for ache and subcutaneous heparin for prophylaxis in opposition to deep venous thrombosis. Consultation with a hematologist is requested due to a dropping platelet depend. On physical e>Cllmination, the affected person has a quantity of bruises, and his lower extremities are cast1! Laboratory tests from the last several days reveal a platelet count that has dropped from a hundred and seventy,000/�L on admission to 30,000/�L 5 days later. Her medical historical past is notable for an episode about 2 years ago of deep venous thrombosis in the right lower extremity while taking oral contraceptives. What are some causes of inherited hypercoagulable states particularly associated with the coagulation cascade How might this girl be evaluated for the presence of an inherited hypercoagulable state An overview of molecular ham of iron metabolism regulation and the associated pathologie1. Hepcidln: a promising therapeutic: goal for iron issues: a systematic: review. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: a scientific review of revealed reports. Unfractionated heparin versus low molecular weight heparins for avoiding heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in postoperative patients. Pregnancy-related venous thromboembolism risk in asymptomatic ladies with antithrombin deficiency: a scientific evaluate. Information is gathered by sensory systems, built-in by the brain, and used to generate signals to motor and autonomic pathways for management of motion and of visceral and endocrine functions. These actions are managed by neurons, that are interconnected to kind signaliDg networks that compose motor and sensory methods. In addition to neurons, the nervous system contains neuroglial cells that serve quite so much of immunologic and help features and modulate the exercise of neurons. Understanding the pathophysiology of nervous system illness requires information of newal and glial cell biology and the anatomy of neural networks.
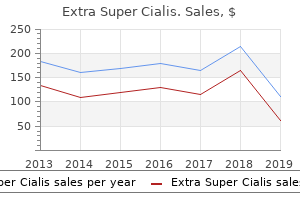
Purchase extra super cialis with a visaIn addition, the rise in temperature and the fall in pH that happen in some metabolically active tissues have a vasodilator effect. The steadiness between platelet thromboxane A, and endothelial prostacyclin could be shifted by the administration of low doses of aspirin. Thromboxane Az and prostacyclin are each produced from arachidonic acid by the cyclooxygenase pathway. Therefore, the chronic administration of small doses of aspirin reduces intravascular clotting for extended intervals and is of value in preventing myocardial infarctions, unstable angina, transient ischemic attacks, and stroke. Nitric Oxide the manufacturing ofa potent vasodilator by endothelial cells was:first suspected when it was famous that removing of the endothelium from rings of arterial tissue converted the normal dilator response to acetylcholine right into a constrictor response. One issue is the myogenic response to stretch of the sleek muscle in arterioles; as pressure inside a vessel rises, its clean muscle is stretched, and its response is to contract. Substances Secreted by the Endothelium the blood vessels are lined by a steady layer ofendothelial cells, and these cells play an important role in the regulation of vascular function. They reply to flow modifications (shear stress), stretch, quite a lot of circulating substances, and inflammatory mediators. In response to these stimuli, they secrete progress regulators and vasoactive substances. The development elements regulate vascular growth and are essential in a selection of illnesses. All are polypeptides related to the sarafotoxins, polypeptides found in snake venoms. All are cleaved from larger prohonnones (big endothelins) by endothelin-converting enzymes. Two G protein-coupled receptors-A and B-that mediate endothelin effects have been identified. The decapeptide lysyl-bradykinin can be converted to the nonapeptide bradykinin by aminopeptidase. These kinin precursor proteins are products of a single gene produced by various splicing. The proteases answerable for the cleavage ofkininogens are the kallikreim, a family of enzymes encoded in humans by three genes situated on chromosome 19. Lysyl-bradykinin and bradykinin are primarily tissue hormones produced, for example, by the kidneys and actively secreting glands, however small amounts are additionally discovered in the circulating blood. Kinins enhance blood move to actively secreting glands by producing vasodilation, and. This leads to the urinary excretion of sodium and water, a discount of intravascular quantity, and a decreased stretch of the atrial myocytes. As all three natriuretic peptides have cardio- and reno-protective properties, their therapeutic potential in persistent heart failure treatment is at present underneath study. Neural Control Via the Sympathetic Vasomotor System Table 11-1 summarizes the components affecting the caliber of the arterioles within the body, and hence peripheral resistance and tissue blood flow. It additionally includes the control of blood stress by noradrenergic and, in some instances, cholinergic sympathetic vasomotor nerves to the arterioles. Discharge of the noradrenergic vasomotor nerves causes constriction of the arterioles innervated by the nerves, and if the discharge is general quite than native. In addition, the discharge of sympathetic noradrenergic nerves innervating the center will increase blood stress by increasing the drive and rate ofcardiac contraction (inotropic and chronotropic effects), growing stroke quantity and cardiac output Noradrenergic stimulation also inhibits the impact of vagal stimulation, which nonnally slows the center and decreases cardiac output. McGraw-Hiii, 2016J Neural management Increased discharge of noradrenergic vasomotor nerves Dl. The baroreceptors are stretch-sensitive nerve endings located within the carotid sinuses and aortic arch on the arterial aspect and within the walls of the great veins and the cardiac atria on the venous facet. From the nucleus, second-order neurons cross to the caudal portion of the ventrolateral medulla and environs. From there, third-order inhibitory neurons cross to the rostral ventrolateral medulla, the situation of the cell our bodies of the neurons that management blood strain. The axons of those neurons descend into the spinal cord and innervate the cell bodies of the blood pressure-regulating preganglionic sympathetic neurons in the intennediolateral gray column of the spinal twine. The axons of the preganglionic neurons leave the spinal cord and synapse on the postganglionic neurons in the ganglionic chain and collateral ganglia, as well as on the catecholamine-secreting cells in the adrenal medulla. This is caused by the inhibitory y-aminobutyric acid-secreting neuron link between the caudal portion of the ventrolateral medulla and the rostral ventrolateral medulla. In addition, an elevated barore<:eptor discharge stimulates afferents from the nucleus tractus solitarius to the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus. Adrenal medullary seaetion is elevated by the discharge of the sympathetic nervous system, although the contributions of circulating catecholamines to the increase in blood strain are comparatively small. The resultant inaease in circulating angiotensin Il not only acts directly on vascular clean muscle to trigger constriction but additionally inaeases aldosterone secretion, which in tum increases Na� retention, increasing intravascular quantity. Moreover, activation of the decrease affinity V1 vasopressin receptor on vascular clean muscle leads to a marked increase in vascular tone. Why does the speed of blood flow lower tremendously ln the capillaries after which increase in the veins It is characterised by localized fibrous thickenings of the arterial wall related to lipid-infiltrated plaques that may ultimately calcify. Old plaques are additionally vulnerable to ulceration and rupture, triggering the formation of thrombi that impede move. It additionally leads to frequent extreme and life-threatening illnesses of the center and brain because of the formation of intravascular clots on the site of the plaques. In the United States and most other developed countries, it has been calculated that atherosclerosis is the underlying reason for about 50% of all deaths. Almost all patients with myocardial infarction-and most of those with stroke resulting from cerebral thrombosis-have atherosclerosis. The incidence of ischemic heart disease and strokes has been declining within the United States since 1963, but atherosclerosis remains to be very common. Thus, atherosclerosis underlies and is essentially answerable for a big portion of the clinical problems seen by physicians caring for adult patient!. The endothelium is subject to shear 1tre11, the tendency to be pulled alongside or deformed by flowing blood this is most marked at factors the place the arteries branch, which can also be the place the lipids accumulate to the best degree. The streaks seem in the aorta in the first decade of life, in the coronary arteries in the second decade, and in the cerebral arteries in the third and fourth a long time. Vascular clean muscle cells in the neighborhood of froth cells are stimulated and transfer from the media to the intima. After vascular Injury, monocytes bind to the endothellum, then cross It to the subendothellal house, and become activated tissue mlaophages. In addition, the "loading" of macrophages with ldl cholesterol may be lipotoxic to the endoplasmic reticulum, resulting in macrophage apoptosis and plaque necrosis.
Purchase 100 mg extra super cialisIn the corpus, postganglionic nerves release acetylcholine, which immediately prompts parietal cells by M3 receptors. Acetylcholine also induces histamine release from enterochromaffin cells, which stimulates H+ ion secretion by parietal cells. In the antrum, vagal stimulation induces the discharge of gastrinreleasing peptide from postganglionic fibers, which stimulates gastrin launch and thus indirectly stimulates H+ ion secretion. Acetylcholine additionally inhibits somatostatin launch from D cells in the corpus and pylorus to stimulate H� ion secretion. The gastric section (-70% of response) of secretion is induced by stimuli throughout the abdomen. Vagal sensory nerves detect gastric distension with meals and set off a vagovagal reflex throughout which vagal motor nerves launch acetylcholine within the abdomen to promote acid secretion. Partially digested proteins and amino acids stimulate gastrin release from G cells in the pylorus. G cells, like D cells, are open-type endocrine cells that instantly sense the contents of the abdomen. Acidification of the pylorus stimulates the discharge of somatostatin, which inhibits acid secretion by a negative-feedback loop as described. During the intestinal section, the products of protein digestion, on getting into the small intestine, can stimulate gastrin launch from G cells within the duodenum. Many substances, most notably fat and acid, stimulate the secretion of hormones from the small gut that inhibit gastric acid secretion. Helicobacter pylon is a bacterium that lives in the mucous layer of the stomach the place the enzyme urease is active, changing urea to col and ammonia. H pylori also secretes proteins, such as CagA and VacA, that modulate immune responses and directly aher mucosa! In some individuals, nevertheless, the infection remains confined to the antrum but leads to elevated acid secretion and symptomatic inflammation that causes ulceration of the stomach or duodenum. During the gastric phase of digestion, rood within the stomach triggers vagovagal reflexes and stimulates gastTin secretion. Acidification of the gastTic antrum stimulates the discharge of somatostatin, which inhibits gastrin launch and thus acid secretion; vagal acetyk:holine (Ach) inhibits somatostatin launch. In some sufferers, chronic H pylori an infection can spread to the corpus and lead to continual irritation that triggers the demise (atrophy) of parietal cells and altered mucosa! In certain geographical areas (eg, East Asia and elements of Central and South America). Other Gastric Secretions Chief cells within the glands of the gastric corpus secrete pepslno- gen, an inactive pre<:Ursor (zymogen) of the energetic protease pepsin. Acetylcholine is the principle stimulant of pepsinogen secretion, though other factors (eg, gastrin) also stimulate secretion. Once released into the lumen of the abdomen, gastric acid and pre-existing pepsin convert pepsinogen to pepsin. It is an endopeptidase that begins the degradation of dietary proteins into peptides. Mudns are high-molecular-weight glycoproteins secreted by mucous cells of gastric glands in the corpus and annum. The peptide spine of mucins is densely populated with carbohydrate facet chains enriched with sulfate groups. Mucins combine with phospholipids, bicarbonate, and water to kind the mucous gel layer that adheres to the floor of stomach epithelial cells. Feeding disrupts the migrating myoelectric complex, and now the antrum contracts regularly at a rate of about three contractions per minute. These slow waves of peristaltic contraction originate from spontaneously energetic interstitial cells of Cajal within the pacemaker zone in the course of the physique of the stomach, and so they sweep towards the antrum. When the membrane potential of muscle cells depolarizes to attain threshold, motion potentials frre. Gastrin and acetylcholine stimulate contraction by increasing the magnitude and duration of the action potentials. Intrinsic issue is a glycoprotein secreted by parietal cells required for vitamin B12 absorption. The acidic setting permits the binding of B12 to haptocorrin (R factor), a glycoprotein produced by salivary and gastric glands. The B12-haptocorrin complicated enters the duodenum, the place pancreatic proteases digest the haptocorrin. Intrinsic factor combines with B12 in the much less acidic environment of the small gut, forming a degradation-resistant complicated for transport to the ileum. Specific receptors on epithelial cells lining the ileum bind the vitamin B12-intrinsic issue complicated, which is taken into cells by endocytosis. In autoimmune gastritis, parietal cells are destroyed, leading to a lack of intrinsic factor secretion, which may result in vitamin B12 deficiency and pernicious anemia. This anemia is caused by the impaired synthesis of purines and thymine for which vitamin B12 is required. Gastric Emptying Immediately after a meal, the stomach may include up to 1 L of fabric, which empties slowly into the small gut. Regulation of gastric emptying occurs by alterations within the motility of the proximal and distal stomach, pylorus, and duodenum. Gastric emptying is brought about by a rise in tone (intraluminal pressure) within the proximal stomach, an increase within the strength of antral contractions, the opening of the pylorus, and the inhibition of duodenal segmental contractions. The fee of gastric emptying is dependent upon the chemical and physical composition of chyme that enters the duodenum by way of the stimulation of both neural and hormonal pathways. Solids and liquids empty at totally different rates: Liquids empty quickly, and solids empty solely after a lag section. Acid, fats, and hyperosmolar options entering the duodenum sluggish gastric emptying via the stimulation of neuronal and hormonal mechanisms. Sensory neurons within the duodenum, each vagal and spinal, respond to nutrients, H+ ions, and the hyperosmolar content of chyme. Vagal motor nerves lower antral contractions, contract the pylorus, and decrease proximal gastric motility. Many hormones launched by endocrine cells in the small gut have been implicated within the suggestions inhibition of gastric emptying. Secretin, the release of which is stimulated by acid, inhibits antral contractions and stimulates pyloric sphincter contraction to gradual emptying. Cholecystokinin, the discharge of which is stimulated by fats, acts on vagal sensory nerve receptors to produce a vagovagal reflex that decreases gastric emptying. Patterns of Gastric Motility In phrases of motility, the proximal and distal areas of the stomach are distinct. During every swallow, the stretch of the esophagus induces a vagovagal reflex that causes the gastric corpus to loosen up in preparation to receive the meals, a phenomenon generally recognized as receptive leisure. The antrum of the abdomen is extremely muscular, and right here contractions serve to break meals into smaller items, thereby facilitating digestion. The pyloric sphincter controls the speed at which the antral contractions propel partially digested meals, or chyme, into the duodenum. During fasting, the antrum is relatively quiescent, with occasional forceful contractions occurring each 75-90 min.
Buy extra super cialis online pillsA palpable gallbladder in the proper higher quadrant is referred to as the Courvoisier law. A palpable gallbladder makes gallstones of the frequent bile duct much less likely than carcinoma of the pancreas as a result of gallstones typically end in irritation and subsequent scarring, resulting in a shrunken, not distended, gallbladder. Adenocarcinomas of the pancreas might current with anemia, migratory thromboembolic illness, or disseminated intravascular coagulation. The coagulopathies may be related to thromboplastins launched throughout the mucinous secretions of the adenocarcinoma. Clinical prognostic elements include tumor measurement, site, medical stage, lymph node metastasis, type of surgery, anemia requiring blood transfusion, performance status, and adjuvant radiation remedy. The poor total prognosis 5-year survival of <5%, and solely 15-20% of sufferers undergoing healing tumor resections residing >5 years) may be attributed primarily to the advanced stage of the disease by the time it presents clinically, the rapid rate oflocal tumor expansion, and the early systemic dissemination. This patient in all probability suffers from osteoporosis, accelerated by her underlying renal failure. Calcium is poorly absorbed from the gut because of decreased renally generated vitamin 1,25-0H)2D3 levels. Hypocalcemia results and is additional exacerbated by high serum phosphate ranges from impaired phosphate excretion by the kidney. Also implicated are the diminished responsiveness of bone to vitamin D3 and chronic metabolic acidosis. Easy fatigability is commonly attributable to a worsening normochromic, normocytic anemia seen in persistent kidney illness. This occurs primarily because of impaired erythropoietin synthesis by the kidney and thus decreased erythropoiesis. To enhance signs, exogenous erythropoietin is began to raise the hematocrit of25-28%, typically seen in chronic kidney disease patients. This is assumed to occur from uremic toxins that irritate and inflame the pericardium. Crush accidents release myoglobin into the bloodstream that precipitates within the renal tubules, inflicting intrarenal toxicity and subsequent failure. The abrupt onset of hematuria ("cola-colored" urine), edema, and variable levels of hypertension most commonly happen 7-14 days after streptococcal pharyngitis or impetigo and might occur sporadically or in clusters. Significant glomerular harm can result in rapid development to oliguria and acute kidney injury. Immobilization from a protracted hospital stay puts this affected person at additional danger for deep venous thrombosis. At least 75% of stones are calcium containing and reflect idiopathic hypercalciuria. Hyperparathyroidism and hyperuricosuria are other necessary causes of calcium stones. If the affected person is ready to gather a handed stone, an evaluation of its composition can be useful in diagnosing the subtype and tailoring treatment. After efficient pain control is achieved, the patient could return home, and the necessity for adequate hydration with at least 2 L/day should be reinforced Hydration could dilute unknown substances that predispose to stone formation and minimize the probability of Ca2+ precipitation in the nephron. High-protein diets in recognized stone formers are inadvisable since they predispose to recurrent calcium nephrolithiasis. A high-sodium food regimen must be prevented as a result of Na+ predisposes to Ca2+ excretion and will increase the saturation of monosodium urate, which acts as a nidus for calcium oxalate stone formation. Finally, citrate supplementation could also be thought of because of the flexibility of citrate to chelate calcium in answer, forming soluble complexes versus calcium oxalate or phosphate. Bacterial infections may cause glomerular harm tluough the deposition of antibody-antigen complexes. Rather, the subendothelial deposition of immune complexes is required to damage highly vascularized nephrons by fixing complement (this explains the serum levels measured) and by activating myelomonocytic cells. Deposition of those complexes can occur solely in the presence of excess antigens to make the complexes soluble, allowing them access to the subendothelial house and enabling them to trigger damage. This disorder is often self-limited; 95% of individuals get well regular renal perform inside 2 months after onset. Treating underlying infectious substrates might hasten the resolution of the glomerulonephritis. Patients with nephrotic syndrome have hypoalbuminemia and profoundly decreased plasma oncotic pressures because of the loss of serum proteins in the urine. This leads to intravascular volume depletion and the activation of the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system and the sympathetic nervous system. Despite indicators of volume overload such as edema or anasarca, patients may develop indicators of intravascular volume depletion, together with syncope, shock, and acute kidney damage. Minimal change disease, because the name suggests, is associated with few or no changes obvious on light microscopy, as opposed to other subtypes of glomerulonephritis associated with various levels of segmental sclerosis or basement membrane thickening. Immunofluorescence staining is mostly unremarkable, whereas membranous glomerulonephritis is characterised by IgG and C3 deposited uniformly along capillary loops. However, the pathologic changes are most evident on electron microscopy, which reveals the obliteration of epithelial foot processes and slit diaphragm disruption. Minimal change illness is typically seen in children, however when present in adults it can be idiopathic or can follow an upper respiratory tract an infection, may be associated with tumors similar to Hodgkin illness, or may be associated to hypersensitivity reactions. Hypercoagulability is a clinically significant manifestation of nephrotic syndrome and is attributable to renal losses of proteins C and S and antithrombin, as nicely as elevated serum C. Fragments of renal pelvis stones that break off and travel down the ureter produce the pain syndrome often known as renal colic. In the setting of acute obstruction, distention at the degree of the renal pelvis, ureter, or renal capsule can produce ache that may become quite intense. Primary hyperparathyroidism accounts for most circumstances of hypercalcemia within the outpatient setting. However, notably in older individuals, hypercalcemia of malignancy is one other important trigger to consider. Medications, particularly lithium and the thiazide diuretics, also trigger hypercalcemia. Other causes embody familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia, thyrotoxicosis, granulomatous diseases, milk-alkali syndrome, and adrenal insufficiency. A mixture ofthese mechanisms is answerable for the hypocalcemia seen in hypoparathyroidism. The increased stress on her parathyroid glands due to her pregnancy has most likely precipitated her symptomatic hypocalcemia. A optimistic Trousseau sign is demonstrated by inflating the sphygmomanometer above the systolic blood pressure for three min. A uncommon, severe kind that manifests in infancy is called neonatal extreme primary hyperparathyroidism. Hypercalcemia is mostly seen in strong tumors, primarily squamous cell carcinomas, renal cell carcinoma, and breast carcinoma. The secretion of serotonin, prostaglandins, or calcitonin probably causes the watery (secretory) diarrhea this affected person has. Flushing is usually caused by the tumor producing either substance P or calcitonin generelated peptide, both of that are vasodilators. The prognosis can be made most effectively by fineneedle aspiration of the thyroid nodules.
Order extra super cialis 100 mg without prescriptionAn example of the latter is decompensated heart failure with poor cardiac output and diminished renal perfusion (termed cardiorenal syndrome). Prarenal Causes As demonstrated by the Starling equation, filtration across a glomerulu. Notable amongst intrarenal causes are the toxic effects of aminoglycoside antibiotics and rhabdomyolysis, during which myoglobin, released into the bloodstream after a crush injury to muscle, precipitates within the renal tubules. Drug toxicity may be mitigated by carefully monitoring renal function during antibiotic remedy, particularly in elderly sufferers and those with some degree of underlying renal compromise. Rhabdomyolysis may be detected by obtaining a serum creatine kinase level in sufferers admitted to the hospital with trauma or altered psychological standing and may be mitigated by sustaining a vigorous alkaline diuresis to forestall myoglobin precipitation in the tubules. The prerenal issue is renal hypoperfusion owing to the hypotensive, low syrtemic vascular resistance of the septic state. Patients with sepsis are sometimes additionally exposed to nephrotoxic medication similar to aminoglycoside antibiotics or iodinated intravenous contrast for computed tomography imaging. The precise molecular mechanisms answerable for the event of acute tubular necrosis stay unknown. According to the tubular concept, mobile debris occludes the tubular lume:n, forming a cast that increases intratubular strain sufficiently to offset perfusion strain and decrease or abolish internet filtration stress. The vascular principle proposes that decreased renal perfusion pressme from the mixture of afferent arteriolar vasoconstriction and efferent arteriolar vasodilation reduces glomerular perfusion pressure and, therefore, glomerular filtration. Postrenal causes the posb:enal causes of acute kidney injury are those leading to winary tract obstruction, which can occur at any degree of the urinary tract. Obstruction can be both intrinsic (eg, nephrolithiasis inflicting u:reteral obstruction) o. For obstruction occurring above the level of the bladder, bilateral obstruction is often required to trigger acute kidney harm unless the patient has only one functioning kidney. Mild or uncompllcated medullary hypoxia results In tubulcglomerular reflex adjustments that restore medullary oxygen sufficiency at the prtce of diminished renal operate. However, In the occasion of extreme renal medullary hypoxia or when associated with complicating factors similar to these Indicated In the determine. Whether acute kidney Injury Is reverslble er lrrever:slble depends en a stability of reparatlve and complicating factors. However, the overlap in scientific presentation alongside the continuum between prerenal azotemia and acute tubular necrosis is such that the results ofany one ofthese tests must be interpreted in the context of different findings and the clinical historical past. If the affected person proceeds to acute tubular necrosis, this ratio could return to regular however with a progressively elevated serum creatinine. Urinalysis is a simple and cheap take a look at that serves as an necessary software in the initial evaluation of the patient with acute kidney injury. Casts are shaped when particles within the renal tubules (protein, pink c:ells, epithelial cells) takes on the cylindrical, smooth-bordered shape of the tubule. Likewise, as a outcome of hypovolemia is a stimulus to vasopressin release (see Chapter 19), the urine is maximally concentrated (up to 1200 mOsm/L) in prerenal azotemia. However, with progression to acute tubular necrosis, the power to generate a concentrated urine is largely misplaced. Another consequence could also be a dysregulation of elements that seeure tubular cells together, leading to a leak of filtrate out of the tubular lumen and an abnormal sorting of mobile transmembrane channels required for the traditional function of the nephron. It appears that these merchandise, along with the activation of complement and neutrophils, will increase vasoconstriction in the already ischemic renal medulla and, in that means, exacerbate the degree of hypoxic harm occurring in acute kidney harm. Clinical Manifestations Acute kidney damage can contribute to vital morbidity and is an impartial predictor of mortality. Thus, lately, significant research effort has been focused on figuring out particular biomarkers of acute kidney damage earlier within the hospital course, before the serum creatinine is elevated or urine output is decreased. The initial symptoms of kidney damage are typically fatigue and malaise, most likely early penalties of the loss of the power to excrete water, salt, and wastes by way of the. Later, more profound signs and indicators of the loss of renal water and salt excretory capacity develop: dyspnea, orthopnea. Altered psychological standing displays the toxic impact of uremia on the brain, with elevated blood ranges of nitrogenous wastes and glued acids. The medical manifestations of acute kidney damage rely not solely on the cause but also on the stage in the pure historical past of the illness at which the affected person involves medical attention. Recovery from acute tubular necrosis, ifit occurs, will then follow a more protracted course, probably requiring supportive dialysis before sufficient renal operate is regained. A selection ofclinical checks can help decide whether or not a affected person with signs ofacute kidney damage is within the early part of prerenal is a vital indicator in oliguric acute kidney injury to determine whether or not a patient has progressed from easy prerenal azotemia to frank acute tubular necrosis. With the progression of prerenal azotemia to acute kidney harm with acute tubular necrosis, this ability of the kidney to avidly retain sodium is usually lost However. What are the features that distinguish prerenal, intrare- nal, and postrenal causes of renal failure What clues are helpful in figuring out whether or not newly identified renal failure is acute or persistent This replicate"$ the long-standing and progressive nature of their renal disease and iu systemic effect$. A clinical pearl is to all the time assume that renal failure is acute-this gives clinicians the chance to establish and deal with acute kidney injury in a well timed style while it still has the potential to reply to therapy. As a end result, a higher practical burden is borne by fewer nephrons, leading to a rise in glomerular filtration strain and hyperfiltration. The kidneys have an incredible functional reserve-up to 50% of nephrons may be misplaced without any short-term evidence of useful impairment. This is why people with two healthy kidneys are capable of donate one for transplantation. However, even at this apparently secure stage of renal perform, hyperfiltration-accelerated evolution to endstage persistent kidney disease is in progress. Pathogenesis of Uremla the pathogenesis of urelnia derives partly from a combination of the toxic results of (1) retained merchandise normally excreted by the kidneys (eg, nitrogen-containing products of protein metabolism); (2) regular merchandise such as hormones Pathology Ii Pathogenesis A. Excretory failure additionally results in fluid shifts, with increased intracellular Na+ and water and decreased intracellular K+. These alterations could contribute to subtle alterations in the function of a number of enzymes, transport methods, and so forth. The fall in blood pH in these individuals can often be corrected with 20-30 mmol (2-3 g) of sodium bicarbonate by mouth every day. However, these patients are extremely prone to acidosis within the event of either a sudden acid load (eg, ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis, poisonous ingestions) or bicarbonate loss (eg, diarrhea). A average degree of Na+ and water retention might happen without objective indicators of extracellular fluid excess. However, continued excessive Na+ ingestion (as present in a typical Western diet) leads to additional fluid retention and contributes to heart failure, hypertension, peripheral edema, and weight acquire. A common recommendation for the patient with continual kidney disease is to limit sodium to 2 g/d or much less and to prohibit fluid intake in order that it equals urine output plus 500 mL (to compensate for insensible losses). Further adjustments in volume standing may be made both through using diuretics (in a affected person who nonetheless makes urine) or at dialysis. Dry mucous membranes, tachycardia, hypotension, and dizziness all recommend volume depletion. Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Abnormalities Heart failure and pulmonary edema can develop within the context of volume and salt overload.
Extra super cialis 100 mg cheapOn one hand, the desire to keep away from atrial fibrillation and serious fractures, mentioned above, may drive the clinician to recommend therapy. Additional features of Cushing syndrome embrace hirsutism (82%), muscular weak point (58%) and muscular atrophy (70%), again pain (58%), pimples (40%), psychological symptoms (40%), edema (18%), headache (14%), polyuria and polydipsia (10%), and hyperpigmentation (6%). It may be associated to salt and water retention from the mineralocorticoid results of the surplus glucocorticoid, the elevated secretion of angiotensinogen or deoxycorticosterone, or a direct impact of glucocorticoids on blood vessels. The reason for the weight problems and redistribution of body fats seen in Cushing syndrome can additionally be somewhat unclear. It could additionally be explained by the increase in urge for food or by the lipogenic effects ofhyperinsulinemia caused by cortisol extra. The striae outcome from increased subcutaneous fat deposition, which stretches the skinny skin and ruptures the subdermal tissues. These striae are depressed under the skin surface due to the loss of underlying connective tissue. An incidentally discovered adrenal mass is commonly referred to as an adrenal incidentaloma. The evaluation of an adrenal mass requires each a practical and an anatomic workup. The functional evaluation is to determine whether or not the mass is producing excess adrenal hormone by performing a dexamethasone suppression take a look at (or 24-hour urine free cortisol) to exclude hypercortisolism, by measuring the plasma or urinary metanephrines to exclude pheochromocytoma, and by measuring the serum potassium and aldosterone-to-renin ratio to exclude hyperaldosteronism. Anatomically, the lesion must be evaluated to decide degree of concern for malignancy. Lesions which are massive (>6 cm), heterogeneous, and never low in sign intensity can be malignant. Clinical and/or hormonal re-evaluation can be repeated periodically if the affected person develops signs in maintaining with a hyperfunctional adrenal tumor since nonfunctioning adenomas may (rarely develop hormone overproduction at a later time. The major consequences of chronic aldosterone excess are sodium retention and potassium and hydrogen ion wasting by the kidney. One of the genes activated by aldosterone is the gene for serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase (sgk), a serine-threonine protein kinase. Aldosterone also binds on to distinct membrane receptors with a high affinity for aldosterone and, by a rapid, nongenomic action, increases the activity of membrane Na+-K+ exchangers to increase intracellular Na+. In the distal renal tubules and collecting ducts, aldosterone acts to promote the exchange of Na+ for K+ and H+, inflicting Na+ retention, K+ diuresis, and elevated urine acidity. Elsewhere, it acts to enhance the reabsorption of Na+ from the colonic fluid, saliva, and sweat. The internet impact in major aldosteronism is the delicate hypematremia, hypokalemia, and acidosis seen on this affected person. Hypertension outcomes from the underlying sodium retention and subsequent enlargement of plasma quantity. The prolonged potassium diuresis produces signs of potassium depletion, together with muscle weak spot, muscle cramps, nocturia (frequent nighttime urination), and lassitude. A blunting of baroreceptor function, manifested by postural falls in blood strain without reflex tachycardia, may develop. Prolonged potassium depletion damages the kidney (hypokalemic nephropathy), causing a resistance to antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin). Patients may be unable to concentrate urine (nephrogenic diabetes insipidus), leading to signs of thirst and polyuria and the discovering of a low urine specific gravity (<1. Urinary electrolytes present an inappropriately large amount of potassium within the urine. Other signs of chronic adrenal insufficiency include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, hypoglycemia, and personality changes. The examiner also wants to look for orthostatic changes in blood pressure and pulse, hyperpigmentation of the mucous membranes and other areas, vitiligo, and loss of axillary and pubic hair. In Addison disease, the deficiency of cortisol is related to a deficiency of aldosterone, resulting in an unregulated renal lack of sodium and a retention of potassium. Additional blood chemistry findings suggesting Addison disease include delicate acidosis, azotemia, and hypoglycemia. At a specificity of 95%, the sensitivity of the 250 �g cosyntropin stimulation check is 97% for main adrenal insufficiency. Hypotension, including recumbent hypotension, happens in about 90% of patients with Addison illness and may cause orthostatic signs and syncope. These symptoms are related to the volume contraction ensuing from unregulated renal sodium losses. During the new child interval, there are two traditional shows of congenital adrenal hyperplasia resulting from basic 21~-hydroxylase deficiency: salt wasting and non-salt losing (also known as "simple virilizing"). Neonates with the salt-wasting kind have severe cortisol and aldosterone deficiencies and, if undiagnosed and untreated, will develop doubtlessly deadly adrenal disaster and salt losing at 2-3 weeks of age. Currently, one of the best screening check for main aldosteronism includes determining the plasma aldosterone concentration (normal: 1-16 ng/dL) and plasma renin exercise (normal: 1-2. Subsequent workup entails measuring the 24-hour urinary aldosterone excretion and the plasma aldosterone stage with the affected person on a diet containing greater than 120 mEq of Na+ per day. The urinary aldosterone excretion exceeds 14 �g/d, and the plasma aldosterone is often more than ninety pg/mL in primary aldosteronism. The gold commonplace for prognosis is bilateral adrenal venous sampling, which is more delicate and specific than imaging, to identify a unilateral trigger, particularly an adrenal adenoma causing the primary aldosteronism. The syndrome is thought to be due to an impairment of renin manufacturing by the juxtaglomerular equipment, associated with underlying renal illness. Chronic kidney illness is often not severe sufficient by itself to account for the hyperkalemia. The impaired secretion of both potassium and hydrogen ion within the renal tubule causes the noticed hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis. More than 90% ofcases are as a outcome of a deficiency ofthe enzyme steroid 21~-hydroxylase. Causes of hypothalamic or pituitary dysfunction include prolactin-secreting tumors, hypothyroidism, extreme stress and train, and weight loss. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a comparatively frequent illness, occurring in 1 in 5000 to 1 in 15,000 births. The high androgen levels impede creating follicles and disrupt the feedback relationships that usually end result within the choice of a dominant follicle for ovulation. The resulting anovulation is associated with amenorrhea and estrogen-induced endometrial hyperplasia with consequent breakthrough bleeding. The elevated estrogen ranges are also implicated within the development of endometrial cancer. In an effort to standardize the nomenclature used to describe the causes of irregular uterine bleeding, the International Federation ofGynecology and Obstetrics proposed a model new classification system in 2011. This system encompasses the most common pathologies associated with abnormal uterine bleeding. It consists of uterine Polyp, Adenomyosis, Leiomyoma, Malignancy (and endometrial hyperplasia); Coagulopathy; Ovulatory dysfunction; and Endometrial, Iatrogenic, and Not yet categorized causes. Unopposed estrogen exposure without progesterone in the perimenopausal or postmenopausal interval can lead to endometrial hyperplasia. With continued estrogen extra, this endometrial hyperplasia can progress to endometrial most cancers.

Order extra super cialis 100mg on lineIn neoplasia, these mechanisms can fail, leading to abnormalities in the construction or number of chromosomes, which is referred to as chromosome instability. Errors in orchestrating replication or in correctly separating and allocating chromosomes throughout mitosis results in an uneven distribution to daughter cells, producing cell progeny which have increased numbers of some chromosomes and reduced numbers ofother chromosomes. While losses of entire chromosomes may be deadly to cells, gains are sometimes tolerated and selected for throughout repeated proliferative cycles. As a consequence, tumor cells regularly have many greater than the forty six chromosomes of regular cells, an attribute known as aneuploidy. In the scenario of chromosomal translocation, part of one chromosome is fused with a part of another chromosome, and the resulting abnormal hybrid chromosome is passed on to all tumor cell progeny thereafter. A chromosomal translocation is often a random occasion seen in a single most cancers only, or it can be a particular and recurring event seen in multiple cancers. In reality, a really particular chromosomal translocation can be the deBning attribute of some forms of most cancers. Defects In Protecting Chromosome Ends the truth that the diploid human genome is fragmented into 46 chromosomes implies that there are 92 ends within the human What regulates chromatin construction Genes that confer a bonus to tumor cells by way of a loss-of-function alteration are named tumor suppraso. Genes that confer a bonus through a gain-of-function alteration are named proto-oncogenet, and their altered counterparts are named oncogene&. Tumor suppressor genes are far more frequent as a result of many kinds of gene mutation could cause loss of function or loss of expression of the protein product. Alternatively, the gene could be silenced by promoter methylation or can be totally or partially misplaced by deletion. In certain circumstances, lack of one allele can outcome in a reduction of gene expression. For some genes, this gene-dosage reduction is adequate to promote tumorigenic growth. The diploid human genome naturally accommodates defective alleles of many genes, and though defective alleles are for essentially the most half biologically silent, in the case of tumor suppressor genes, a faulty allele can confer significant most cancers threat to an individual and all family members harboring such an allele. The loss of function of a gene in adult tissues is statistically rather more possible when only one functional allele exists in all cells from the start of. In households with these syndromes, a faulty allele of the responsible tumor suppressor gene is handed in the germline, and members who harbor this heterozygous genotype inherit a excessive threat for tumors by which the second allele has also been misplaced. What are the genetic mechanisms by which oncogenes are activated and tumor suppressor genes are inactivated What is the molecular foundation for many inherited susceptibilities to certain cancers Families carrying these alleles are noticeable for his or her excessive incidences of cancers associated with these genes. Many of those capabilities could also be altered simultaneously through deregulation of transcription components that regulate many genes. Examples of tumor suppressor proteins embody both the retinoblastoma protein and the pl6 cell cycle inhibitor, which perform in restricting proliferation on the G1 checkpoint of the cell cycle. Loss of the genes encoding these proteins can result in unchecked progression via the G l/S checkpoint. This protein underlies many mobile capabilities and reconciles the proliferative, metabolic, and artificial actions of the cell with inputs together with nutrient and vitality supply and growth factor indicators; thus, it could enable cells to survive periods of stress or starvation. When all human tumor suppressor genes have been fully recognized, the record will be a lot larger. Proto-oncogenes embrace proteins concerned in varied steps of the extracellular development issue signaling pathway from the membrane receptors to the membrane intermediates to the proteins mediating the cytoplasmic signaling cascades. These are highlighted In the purple callouts; when mutationally activated In cancers, they promote excessive slgnallng. Some of the genes that negatively regulate the pathway are tumor suppressor genes. Ras proteins are a household of membrane-bound signaling switches that perform instantly downstream of membrane receptors at a key department level of cytoplasmic signaling. Mutational activation of Ras proteins causes overactive cytoplasmic signaling and deregulation of proliferative and apoptotic pathways. Raf proteins are a family of serine-threonine kinases that function downstream of Ras proteins. Since the inactivation of a single tumor suppressor gene or the activation of a single oncogene is inadequate for the event of most types of human tumors, the process of tumorigenesis entails the sequential acquisition of a number of "hits" over time resulting in sequential cellular phenotypic changes-from atypia to dysplasia to hyperplasia to in situ most cancers to invasive most cancers, and in the end to metastatic most cancers. The largest body of evidence to assist this theory has been generated from the molecular examine of colon cancer and identifiable pre-neoplastic lesions, including colonic polyps and adenomas. In this mannequin, the progressive development of neoplasia from premalignant to malignant to invasive lesions is associated with an increasing number of genetic abnormalities, together with each oncogene activation and tumor suppressor gene inactivation. This principle of tumorigenesis is further supported by the identification of inherited abnormalities of several tumor suppressor genes, all associated with a strong familial tendency to develop colon most cancers at a younger age. The expression of this oncogene in hematopoietic cells of animal fashions reproduces the disease. This oncogenic occasion is seen in virtually 100 percent of cases of this disease, and a therapy that inhibits the kinase activity of this oncoprotein produces remissions in practically I 00% of affected patients. The identification of tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes as the elemental enablers of tumorigenesis has led to the speculation that cancer may be successfully treated by therapies that counteract the biochemical sequelae of those molecular abnormalities. This speculation has fueled makes an attempt to develop therapeutic agents that may inhibit the operate of activated oncoproteins or restore the function of inactivated tumor suppressor proteins. Current pharmaceutical applied sciences have enabled the development of drugs focusing on gain-of-function mutations, and heaps of oncogenes can now be inhibited by such drugs. But since regular cells could use different pathways to compensate for the loss of a tumor suppressor gene, activating the functions of such different pathways is a roundabout method to kill cancer cells. Such collateral target genes utilized for therapeutic functions are known as synthetic lethal genes. The oncogenic process may be driven by way of abnormalities in signaling of all types: abnormal time, length, or intensity; irregular tissue expression; or abnormal subcellular compartment localization. The regulation of progress in advanced organisms requires specialized proteins for the traditional growth, maturation, improvement, and function of cells and specialized tissues. The complexity of the human organism requires that these proteins be expressed at precisely coordinated factors in area and time. An essential element of this regulation is the system of hormones, development components, and progress inhibitors. On binding to particular receptor proteins on the cell floor or in the cytoplasm, these factors lead to a posh set of indicators that can end result in quite a lot of mobile effects, together with mitogenesis, development inhibition, modifications in cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, differentiation, and induction of a secondary set of genes. The actual end results depend not only on the particular type of interacting issue and receptor, but additionally on the cell kind and milieu in which factor-receptor coupling occurs. This system permits for cell-to-cell interactions, whereby an element secreted by one cell or tissue can enter the bloodstream and influence one other set of distant cells (endocrine action) or act on adjacent cells (paracrine action).
References - Signoretti S, Waltregny D, Dilks J, et al: p63 is a prostate basal cell marker and is required for prostate development, Am J Pathol 157(6):1769n1775, 2000.
- Aalia Sachedina MD, Chan M F Kiri, MacGregor M F P Duncan, et al: More than grapes and bleeding: an updated look at pelvic rhabdomyosarcoma in young females, J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 1-17, 2018.
- Rofeim O, Gilbert BR: Long-term effects of cryopreservation on human spermatozoa, Fertil Steril 84:536n537, 2005.
|
|

