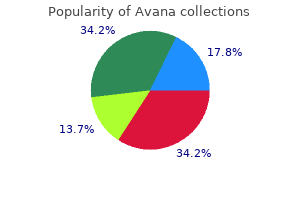
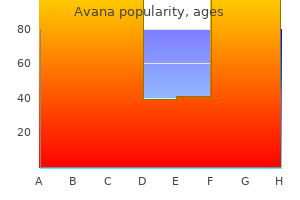
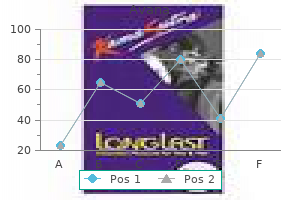
"Generic avana 50 mg online, impotence therapy."By: Joshua C Briscoe, MD - Medical Instructor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences
- Medical Instructor in the Department of Medicine
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/joshua-c-briscoe-md
Discount 100mg avana visaA baby with acute laryngotracheobronchitis should be assessed for severity of illness on basis of common appearance, stridor (audible with or with out stethoscope), oxygen saturation and respiratory misery (Table 14. Mild circumstances could be managed on ambulatory basis with symptomatic treatment for fever and inspiring the kid to take liquids orally. Parents could additionally be explained in regards to the progression of illnesses and to convey the child back to hospital in case of worsening of signs. A affected person with reasonably severe illness might have hospitalization and remedy with nebulised epinephrine (1:a thousand in doses of zero. While epinephrine acts rapidly to lower vascular permeability, airway edema and improves Laryngitis and Laryngotracheobronchitis (Infectious croup) these circumstances are almost always brought on by viral infections, often with parainfluenza type l. Other viruses incriminated embrace respiratory syncytial and parainfluenza types 2 and 3, influenza virus, adenovirus and rhinovirus. As the obstruction increases, the stridor becomes more marked and the suprasternal and sternal recession with respiration turn out to be manifest. Severe croup might have hospitalization, preferably in intensive care, with oxygen inhalation and need for steroids (similar to reasonable severity). Pneurnocystis jiroveci, his to plasmosis and coccidioidomycosis might trigger pneumonia in immunocomprornised children. Other causes of pneumonia include ascaris, aspiration of food, oily nose drops, liquid paraffin and kerosene poisoning. Clinical Features Risk components for pneumonia include low delivery weight, malnutrition, vitamin A deficiency, lack of breastfeeding, passive smoking, large household size, household history of bronchitis, superior start order, crowding, younger age and air pollution. Indoor air air pollution is among the main risk issue for acute lower respiratory tract an infection in kids in creating countries. Onset of pneumonia may be insidious starting with upper respiratory tract an infection or could additionally be acute with excessive fever, dyspnea and grunting respiration. Pneumonia Pneumonia may be categorised anatomically as lobar or lobular pneumonia, bronchopneumonia and interstitial pneumonia. In the primary 2 months, the common agents embrace gram-negative micro organism similar to Klebsiella, E. After 3 yr of age, frequent bacterial pathogens include pneumococci and staphy lococci. Gram-negative organisms cause pneumonia in early infancy, severe malnutrition and immunocompro rnised kids. Overcrowding and diminished host resistance predis poses the kids to an infection with pneumococci. Scattered areas of consolidation occur, which coalesce around the bronchi and later turn into lobular or lobar in distribution. Pathological course of passes from the stage of congestion to purple and grey hepatization before the final stage of resolution. In severe circumstances there may be grunting, chest indrawing, problem in feeding and cyanosis. Percussion observe is impaired, air entry is diminished, crepitations and bronchial respiration may be heard over areas of consolidation. The analysis relies on historical past, bodily examination, X-ray findings of lobar consolidation. While the remedy of alternative for pneumococcal pneumonia is penicillin (penicillin V 250 mg q 8-12 hr orally, penicillin G 0. The want for oxygen administration should be guided by indicators of respiratory distress (rapid breathing, chest retractions, nasal flare), presence of cyanosis or hypoxernia on pulse oximetry. In infants, the pneumonic process is diffuse initially, but soon the lesions suppurate, leading to bronchoalveolar destruction. The pneumatoceles fluctuate in size and at last resolve and disappear inside a interval of few weeks to months. Staphylococcal abscesses might erode in to the pericardium causing purulent pericarditis. Empyema in a toddler below two yr of age is kind of at all times secondary to staphylococcal infections. The sickness often follows higher respiratory tract infection, pyoderma or a purulent illness. Pulmonary infection may occasionally be difficult by disseminated illness, with metastatic abscesses in joints, bone, muscular tissues, pericardium, liver, mastoid or mind. The diagnosis of staphylococcal pneumonia is suspected in a new child or an infant with respiratory infection who has evidence of staphylococcal an infection elsewhere in the body. The attribute complications of pyopneumothorax and pericarditis are extremely suggestive. The baby must be hospitalized and isolated to stop the spread of resistant staphylococci to the other patients. Note a number of pneumatoceles Disorders of Respiratory System Empyema is aspirated and the pus is sent for tradition and sensitivity. Prompt antibiotic remedy ought to be initiated with coamoxiclav, or a combination of cloxacillin and a 3rd generation cephalosporin. Therapy should proceed till all proof of the illness disappears each clinically and radiologically, which usually takes 2 weeks in uncomplicated instances. The onset is abrupt with fever, chills, dyspnea, speedy respiration, blood streaked sputum, cough and excessive prostration. Signs of bronchopneumonia are generally much less pronounced, because the pathology is usually interstitial. X-ray movie reveals interstitial pneumonia, seg psychological involvement, diffuse peribronchial densities or an effusion. Therapy for streptococcal pneumonia is carried out as outlined for pneumococcal pneumonia. Empyema and pyopneumothorax are handled by intercostal drainage under water seal or low strain aspiration. Significant pleural thickening that stops complete expansion of the underlying lung might require decor tication. Installation of streptokinase or urokinase in pleural cavity or loculated pleural effusion may be helpful. Haemophilus influenzae infections occur often between the Primary Atypical Pneumonia the etiological agent of main atypical pneumonia is Mycoplasma pneumoniae. The illness is rare in kids beneath the age of 4 yr, although subclinical and delicate infections are reported in infants. Primary atypical pneumonia entails the interstitial tissue with spherical cell infiltration. The alveolar septae are edematous and mucosa of the broncl1ioles is inflamed and ulcerates. Haemophilus Pneumonia age of three months and three years and are practically at all times related to bacteremia. Infection normally begins within the nasopharynx and spreads domestically or by way of the blood stream.
Purchase avana 200 mg without a prescriptionSeparate the anvil and staple cartridge, and take away the anvil and the plastic ring. When you remove the pack from the upper stomach, bleeding is probably not absolutely controlled. If so, fastidiously examine the anastomosis to identify where the transection is incomplete, or decide the site of bleeding. In each instances insert some additional mattress sutures of Vicryl via the whole thickness of the oesophageal wall to control bleeding from any remaining vessels and seal the anastomosis. Identify, dissect, ligate and divide all the quick gastric vessels between the greater curvature of the stomach and the spleen. Check the rest of the greater curvature of the abdomen and dissect, ligate and divide any remaining vessels between it and the diaphragm. On the lesser curve of the abdomen establish, ligate and divide any vessels passing to it from the lesser omentum. The whole proximal abdomen should now be separated from any feeding vessels alongside its greater and lesser curves. Fortunately, the interior vascularization of the abdomen is almost all the time adequate to prevent any avascular necrosis. Devascularization of the belly oesophagus is performed near the oesophageal wall by ligating and dividing all perforating veins which run transversely. Division of the vagii facilitates the devascularization; due to this, carry out a pyloroplasty. Duodenum Postoperative 1 n Since the stomach has been opened give antibiotics for 48 hours. The goal of the shunt is to obtain profound decompression of the portal system and decrease portal pressure, thereby stopping the variceal bleeding. Oesophageal varices Short gastric veins Portal vein Splenic vein Coronary vein Superior mesenteric vein Left renal vein C. Appraise 1 n Portal decompression may be portacaval, which may be end-toside or side-to-side. In poor-risk sufferers perioperative mortality is 50%; in good-risk sufferers, round 5%. Investigate liver operate, determine the nature of the liver pathology and the vascular anatomy. Patients who tolerate this operation properly with minimal encephalopathy are these with good liver operate, such as sufferers with portal vein occlusion, major biliary cirrhosis or hepatic fibrosis. Therefore the outline might be limited to the normal end-to-side portacaval shunt. There are often dilated portal-systemic venous anastomotic vessels in this tissue, which may require cautious, individual suture ligation. It shunts all of the portal blood in to the infrahepatic vena cava, reduces the portal hypertension and stops bleeding from oesophageal varices. During this dissection retract the common bile duct anteriorly and to the left, taking care to not injury the blood provide to its wall. Be cautious of preserving an aberrant proper hepatic artery if it exists, as it lies behind the bile duct and on high of the portal vein. Flush the now collapsed section of portal vein distal to the clamp with an answer of heparin 1:500 000 in physiological saline. Access n 1 Place the affected person supine on the working table with slight rotation in the direction of the left. Check 1 n Confirm an excellent move through the shunt by feeling for a venous thrill or preferably by observing a measured fall in portal stress (using a Doppler flow probe or measure portal strain by manometer) when the clamps are removed. Monitor progress by weighing the affected person daily, measuring urine quantity and checking for electrolyte imbalances, azotaemia and encephalopathy. This includes placement of a tube extending from the peritoneal cavity to the jugular vein via a subcutaneous track within the anterior chest wall. Interposed within the tube is a one-way valve that opens only to stress exceeding 2�4 cmH2O and permits drainage of ascitic fluid in to the circulation. A peritoneovenous shunt is indicated solely in cirrhotic sufferers with intractable ascites unresponsive to medical therapy. Contraindications embody very poor liver perform with encephalopathy, contaminated ascites, coagulopathy and cardiac failure. Complications are widespread with peritoneovenous shunts, and embody shunt blockage, infection, thrombocytopenia and, often, disseminated intravascular coagulation. Closure 1 n Close 2 n For the stomach wall in a normal manner, with out drainage. To anticipate and handle this: n Manage the affected person initially within the intensive care unit with help from an expert medical hepatologist n Maintain accurate fluid balance and correct irregular clotting n Take steps to forestall or management hepatic encephalopathy. In session with the hepatologist prescribe twice-daily phosphate enemas to hold the colon empty, and oral lactulose or lactitol when gastrointestinal activity returns, at a dose producing one or two delicate motions a day. Restrict protein consumption, beginning at 20 g/day and rising by 10 g every second day. Patients with continual encephalopathy will most likely tolerate no extra than 40�60 g/day of protein per day. Haemorrhage is the commonest reason for conversion, followed by issue in mobilizing the spleen as a outcome of adhesions or spleen measurement and injury to adjacent organs. Appraisal n 2 n Elective splenectomy is most commonly carried out for idio- 1 the spleen is a vital organ, with each haematological and immunological features. Its haematological functions embrace the storage, maturation and destruction of pink blood cells. Immunologically it produces peptides needed for the phagocytosis of encapsulated micro organism (Streptococcus pneumonia, Neisseria meningitidis and Haemophilus influenza). It is a web site of antibody synthesis and may be a reservoir for monocytes which are mobilized following tissue harm. When potential, preserve a minimal of a half of the spleen, as opposed to total splenectomy. Splenectomy is also required sometimes for different types of splenomegaly with hypersplenism and infrequently for circumstances such as cyst, abscess, haemangioma or splenic artery aneurysm. Splenectomy is sometimes carried out as part of other operations, corresponding to total gastrectomy and distal pancreatectomy. Classically, sufferers are shocked, with pain within the left hypochondrium and shouldertip and evidence of left lower rib fractures. Urgent laparotomy is required to management bleeding if the affected person remains unstable after preliminary resuscitation. Lesser splenic accidents may be managed conservatively with vigilant medical observation and blood transfusion. Massive splenomegaly presents difficulties in access, vision and manoeuvring the spleen.

Generic avana 50 mg onlinePyloroplasty can be revised so that the pylorus is restored to anatomical normality but reviews are diversified on the success of the process. The trigger is probably excessive bile reflux on to the gastric mucosa following Polya gastrectomy or gastroenterostomy with vagotomy. The detergent bile breaks the protective mucosal barrier, which can present access to the mucosa for ingested carcinogens. A food regimen poor in vitamins and antioxidants, together with hypoacidity within the abdomen, may be other predisposing components. The reassurance that critical disease has been excluded usually results in an improvement in the symptoms. Gastric carcinoma is usually proof against radiation therapy, but responds to chemotherapy. Early gastric eleven n Occasionally, gastric retention develops from stomal obstruction 172 associated with adhesions trapping the efferent bowel, intussusception of the afferent loop in to the stomach or prolapse of two n Unfortunately, most tumours current late. They embody these with a household historical past of the illness, pernicious anaemia and gastric atrophy, hypergammaglobulinaemia, atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, polyps and former gastric surgery. Barium meal X-ray is usually now deprecated if endoscopic prognosis has been made, but in expert hands it might possibly generally give priceless data. For instance, gastric rigidity and lack of peristalsis recommend extensive submucosal spread. Endoluminal ultrasound is a useful technique of assessing infiltration and local nodal involvement. Laparoscopy is helpful for figuring out tumour unfold within the peritoneal cavity and assessing any fixation of the tumour to surrounding organs. The first is intestinal in sort, creating in areas of intestinal metaplasia and tending to be localized. Nevertheless, gastric cancer should be primarily regarded as a locoregional disease which is probably curable by classical oncological surgery that removes the first tumour and its draining lymph nodes. Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis Serosa Type 1 Polypoid Type 3 Infiltrating Type four Diffuse. Local nodes within three cm of the primary tumour are designated N1, the subsequent nodes to be affected are N2, the third tier is N3 and distant spread is N4. If the tumour has not spread in to unresectable native structures, or been metastasized by the blood stream, healing resection may be attempted. En bloc resection of the tumour with the N1 nodes is designated a D1 resection, with the N1 and N2 nodes a D2 9 n Other structures may be removed in continuity with the abdomen, together with the parietes, the spleen, transverse colon or pancreas. Overall, 5-year survival in Britain is now about 40% after probably healing D2 resection. For diffuse distal growths and people within the body of the stomach a radical whole gastrectomy is required. This is typically carried out through a left thoracoabdominal incision however can typically be performed satisfactorily through the stomach. Greater curve 12 When resection is impracticable, try to relieve current or impending obstruction. For a proximal obstruction think about dilating a stricture with bougies or inflatable balloons followed by the insertion of a stent. It resembles radical total gastrectomy except that a fringe of proximal abdomen is retained; its measurement is set by the extent of proximal unfold of the tumour because the resection margin must be 5 cm clear of detectable tumour. Preservation of the proximal abdomen permits gastrojejunostomy to be completed via the stomach. Any native invasion of contiguous structures should be resectable with the abdomen, such as proximal duodenum, a segment of small bowel, transverse colon, pancreas or spleen. If there are intensive metastases, palliative resection is probably inappropriate. In the lower diagram the body of the stomach has been eliminated to display the deeply placed nodes. Start your full exploration from the pelvis and work in the course of the abdomen so as not to disperse malignant cells. Examine the higher omentum for deposits after which elevate it to really feel the para-aortic nodes and people around the root of the mesentery, and the right colic and middle colic arteries. Examine the full length of the small and then large gut, looking for peritoneal deposits on the bowel wall, the mesentery and the parietal peritoneum. Throughout the examination verify pulsation in the arteries, noting atheromatous rigidity, aneurysms and venous or lymphatic obstruction. Feel each lobes of the liver and adjoining diaphragm, gallbladder and free edge of the lesser omentum, the spleen, kidneys and adrenal glands. Starting at the oesophageal hiatus and dealing distally, look and feel for tumour involvement, fixity, glands and likewise incidental disease. Systematically transfer distally, avoiding dealing with or squeezing the tumour if attainable. Now palpate the body and tail of the pancreas via the lesser omentum and transverse mesocolon, then the area of the coeliac axis simply above the neck of the pancreas. None of these manoeuvres commits you to proceed with radical resection if you discover unsuspected unfold. Carefully dissect out the lymph nodes at the origin of the left gastroepiploic artery, then doubly ligate and divide the artery and vein. Carefully isolate them and the subpyloric lymph nodes before doubly ligating and dividing them at their origins. Therefore, stay vigilant and raise the peritoneum off the anterior surface of the pancreas, which is in a position to lead to the coeliac axis and its branches. Carefully make a transverse incision within the anterior leaf above the pylorus to reveal the best gastric vessels and the suprapyloric lymph nodes. Look for and divide between ligatures the accessory hepatic artery crossing from the left gastric artery. In order to keep away from damaging the pancreas, apply fine haemostasis forceps on the vessels a couple of millimetres from the duodenal wall, divide the vessels between the tips of the forceps and the duodenal wall, then choose up the short duodenal cut ends to ligate them. There is a cold airplane of fusion between the folded omentum, which was part of the dorsal mesogastrium, and the anterior leaf of mesocolon. Gently peel off the omentum, taking care to not injury the anterior leaf of mesocolon or the middle colic and marginal vessels. In the free edge of the fold lies the left gastric vein; identify, doubly ligate and divide this primary. Now extend the dissection of the hepatic artery to the coeliac artery, so as to dissect all of the glands from this area, including those around the origin of the splenic artery and look out for the left adrenal gland. Elevate the gland mass in to the column of tissue around the now cleaned origin of the left gastric artery.
Buy discount avana lineHowever, such instruments traumatize the move surface and are expensive and for these causes have been largely abandoned. It is true that the smooth muscle of arteries contracts protectively in response to damage in order that an necessary vessel could appear fairly small both angiographically and on direct inspection. In the case of limb injuries that is both the unique arsels distal to the site of harm. The process should embody measures to cope with this drawback (see below), in any other case the run-off vessels are normally regular. Since only brief segments are required, problems are not often encountered to find a vein of suitable quality and calibre. If there was in depth injury to both artery and main veins think about harvesting a segment of vein from the opposite leg or upper limb. Repair of broken major arteries at all times takes precedence over orthopaedic fixation of fractures. In these circumstances it might be advisable to restore vascular continuity initially by inserting a temporary intraluminal plastic shunt, and finishing the restore as soon as the fractures have been stabilized, when the length of the arterial defect could be accurately measured. Attempt direct end-to-end anasto- 5 n If the artery is in continuity there may be bruising of the adven- mosis provided that there shall be no pressure. The intima and inner layers of the media cut up transversely and the sides roll back to type a flap, which obstructs move, inflicting secondary thrombosis. Excise the broken segment fully, cutting back every end of the artery as earlier than to find wholesome intima. If either is inadequate move a Fogarty catheter distally and proximally to withdraw any propagated clot and then instil heparinized saline. Prepare 1 n Once the presence of main arterial damage has been established, n undertake surgical exploration without delay. Inform the blood bank of major haemorrhage in order that applicable merchandise could be made obtainable. This requires a pores and skin incision that extends well beyond the confines of the injury. Remember to reverse the vein to keep away from obstruction to blood circulate by competent valves. Complete the proximal anastomosis first, in end-to-end fashion, utilizing the triangulation approach with interrupted sutures for small or inaccessible vessels or the indirect overlap method for larger vessels. Apply a clamp to the distal finish of the graft and permit arterial strain to distend it in order to determine the optimum length to keep away from each excessive pressure and kinking. Technical difficulty could additionally be encountered in effecting passable end-to-end anastomoses, normally because of awkward entry. Under these circumstances the ends of the artery could additionally be ligated and the area of trauma bypassed with end-to-side anastomoses at distant, extra accessible, websites. Recurrent thrombosis regardless of a technically satisfactory repair warrants immediate systemic heparinization. It could also be difficult to resolve whether or not or to not repair related injury to veins. As a rule, repair main axial veins such as the femoral vein and, in the case of nearamputation of a limb, restore continuity to two veins for each artery repaired. Where major closure is either not possible or inadvisable, always cowl the arterial restore with wholesome viable tissue, which in follow often means a muscle flap. Prepare 1 n the urgency of the scenario dictates that preoperative preparation should be restricted. Aftercare n 2 n Arrange common half-hourly statement of the distal circulation 1 Except in circumstances the place continued bleeding is a major problem, keep anticoagulation with heparin for a quantity of days. Access 1 n For lower limb emboli, expose the common femoral artery (see 2 n For higher limb emboli, expose the brachial artery within the antecubital fossa (see above). Complications 1 n Early thrombosis or bleeding on the website of the restore demands im2 n A false aneurysm may result from a contained anastomotic leak three n the risk of related deep venous thrombosis is excessive, so take apand this additionally requires early re-exploration and repair. In the case of the femoral 2 n Select an embolectomy catheter of a size appropriate to the vessel: 3 n A variety of totally different makes of embolectomy catheter are avail3F for axillary and brachial arteries, 4F for the superficial and profunda femoral arteries and 5F for the aortic bifurcation. Choose one with a central irrigating lumen that permits injection of heparinized saline or X-ray contrast medium in to the vessels past the balloon. Inflate the balloon and withdraw the catheter slowly while adjusting the strain within the balloon to accommodate adjustments within the diameter of the vessel. Avoid extreme friction between the balloon and the arterial wall since this could trigger intimal damage to the vessel. Directly suture the widespread femoral artery; think about using a small vein patch for the brachial artery. Haemorrhagic pathologies, bleeding tendency, current surgery and intracardiac thrombus are a quantity of of the contraindications. This could be because of pre-existing arterial illness or to the catheter having been launched in a subintimal airplane. Avoid direct aorto-iliac reconstruction beneath these circumstances if in any respect potential and carry out either a femoro-femoral crossover or an axillofemoral bypass. This could show embolus impacted on the popliteal bifurcation and within the tibial arteries, or proof of atherosclerotic occlusion. Alternatively, expose the infrageniculate popliteal artery to allow Fogarty catheters to be launched immediately in to the tibial vessels. However, if distal perfusion remains poor, then proceed to femoropopliteal bypass. Where services for intra-operative fluoroscopy exist, as an various selection to exposure of the popliteal artery for retrieval of emboli from the tibial arteries, move the embolectomy catheter over a guide-wire negotiated in to each vessel in flip. Action 1 n Puncture the common femoral artery with a Potts-Cournand nee- n 3 n Under X-ray management advance a long guide-wire via the vessel past the embolus. Because the agent is infused domestically in to the thrombus relatively small amounts are required. The excessive incidence of significant bleeding complications related to systemic administration is thereby decreased. This entails pulsed high-pressure injection of the thrombolytic agent by way of a catheter with multiple facet holes. Lysis might happen over a period of hours or might have to proceed for 24�48 hours, with repeated angiography to assess progress and repositioning of the wires. This requires close nursing supervision of the patient, with fastidious care of the intraarterial traces and infusions. This avoids haemorrhagic complications and is associated with a decreased danger of embolization of fragmented thrombus in to the peripheral vascular bed. The most effective system employs the Bernouilli impact to break up and aspirate the thrombus. In most instances adjuvant percutaneous angioplasty will be necessary to deal with causative stenotic lesions due to anastomotic intimal hyperplasia or progressive atheroma. Ensure a graft takes its blood supply from an area of the aorta with sufficient inflow and assess and consider the position of the proximal clamp, especially within the presence of calcified plaque which can be at risk of rupture. Further administration of the thrombolytic agent could additionally be effective but it have to be infused instantly in to the clot. Alternatively, small fragments could additionally be eliminated by suction utilized to a bigger catheter (suction embolectomy).
Diseases - BOD syndrome
- Ichthyosis, keratosis follicularis spinulosa Decalvans
- Illyngophobia
- Cataract cardiomyopathy
- Gangliosidosis
- Sclerotylosis
- Ankyloblepharon ectodermal defects cleft lip palate
- Pheochromocytoma
- Watermelon stomach
- Osebold Remondini syndrome
Order avana 100mg otcIf epiglottitis is suspected, speedy airway management is important and includes intubation by skilled personnel. Bacterial tracheitis is often seen in younger children following viral higher respiratory tract infection. Bronchos copy is each diagnostic and therapeutic, because the purulent tracheal secretions can be visualised, cultured and mechanically debrided. Bacterial tracheitis is a relative medical emergency, as life-threatening obstruction might develop from these tracheal secretions. Retropharyngeal abscess is a potential suppurative complication of bacterial pharyngitis that will present with strider. Flexible endoscopy reveals partial collapse of a flaccid supraglottic airway with inspiration. Laryngomalacia is generally benign and self limited, as most cases resolve by 18 months of age. Surgical intervention is advised for either respiratory misery or failure to thrive. Bilateral vocal twine paralysis usually presents with a high-pitched inspiratory stridor and cyanosis. Unilateral vocal wire paralysis, in distinction, could present with a gentle stridor or with signs of aspiration.
[newline]Iatrogenic harm during ligation of patent ductus arteriosus is a frequent trigger. Congenital subglottic stenosis is the third most common congenital laryngeal anomaly. It results from incomplete recanaliza tion of the laryngotracheal tube during embryonic improvement. Many circumstances resolve spontaneously as the youngster grows, whereas extreme cases usually require tracheostomy. Surgical excision of the stenosis could also be necessary to relieve the obstruction in these cases. Vascular ring is a good vessel anomaly that causes extrinsic compression of both the trachea and the esophagus. The youngster with vascular ring anomaly normally presents with dysphagia in addition to stridor. Treatment Congenital Causes Congenital saccular cyst, laryngeal internet and laryngeal atresia are rare laryngeal anomalies. It most often outcomes from longterm endotracheal intubation and subsequent scar formation. Minor stenosis may be noticed, whereas more severe stenosis could also be handled by a wide selection of surgical strategies including tracheostomy, widening of the stenosis with cartilage grafts, and excision of the stenotic phase. Recurrent respiratory papilloma is the most typical benign laryngeal tumor and presents with gradual airway obstruction. Endoscopy reveals single or a quantity of irregular, wart-like lots in the larynx or pharynx. Transmission is believed to be vertical, from the passage of the fetus via an infected delivery canal. Multiple surgical procedures are usually needed as the illness usually recurs. Foreign Body Aspiration Neoplasms Iatrogenic Causes Foreign physique aspiration ought to at all times be thought-about as a possible reason for stridor and airway obstruction in kids. Conforming objects such as balloons pose the greatest danger of choking demise, followed by round objects corresponding to balls or marbles. After establishing airway patency, pressing endoscopic visualization and elimination by an experienced surgeon are needed. Hoarseness Vocal nodules are the most typical cause of hoarseness in kids and are generally caused by vocal abuse. They are seen more frequently in habitually shouting or screaming youngsters, often boys with siblings. The severity of hoarseness fluctuates, worsening with vocal abuse and enhancing with relaxation. Endoscopy reveals small, bilateral, opposing nodules on the junction of the anterior and middle-thirds of the vocal twine. Reflux has been implicated in numerous ailments of the head and neck, starting from laryngitis and subglottic stenosis to persistent sinusitis and otitis media with effusion. Medical management is often effective, although surgical fundoplication could also be wanted in severe circumstances. Reflux laryngitis might end result from gastric secretions spilling Drooling Drooling (sialorrhea) is a typical, self-limited discovering in young kids. However, in youngsters with neuromuscular problems, dysphagia and poor lip closure may result in continual drooling. If the swallowing mechanism is also irregular, pooled secretions might allow chronic aspiration, resulting in pneumonia or different problems. Medical therapy for drooling not controlled with speech therapy consists of drying brokers corresponding to glycopyrrolate and antihistamines. At present, the preferred surgical remedy is bilateral submandibular gland excision with parotid duct ligation. Tracheostomy or separation of the trachea from the upper airway is reserved for profound and life-threatening persistent aspiration. Hypothyroid myxedema may often cause a rise in vocal fold edema and current as hoarseness or stridor. Thyroid operate exams should be conducted within the hoarse baby with a scientific historical past suggestive of hypothyroidism. In its mildest type, kids with this process may experience feeding diffi culty, recurrent respiratory tract an infection or hoarseness. In its more severe varieties, the cleft could lengthen inferiorly between the entire trachea and esophagus. Severe clefts often cause vital aspiration pneumonias and are sometimes not compatible with life. The situation could additionally be associated with hereditary conditions similar to Opitz-Frias or Pallister-Hall syndromes. Laryngotracheal cleft Suggested Reading Diseases of the Enr American Academy of Pediatrics and American Academy of Family Physicians. Antibiotics for the prevention of acute and chronic suppurative otitis media in kids. Purulent material could also be expressed from the parotid duct intraorally with parotid massage. Treatment includes oral antibiotics as nicely as hydration, sialogogues, therapeutic massage and warm compresses. Infections Bacterial parotid sialoadenitis Viral parotitis is triggered most frequently by the mumps virus. They may also present with an acute unilateral hearing loss or vestibular weak point. Systemic manifestations corresponding to meningoencephalitis, pancreatitis and orchitis can also be current. A number of laboratory tests and radiological research including chest radiograph support the prognosis.
Order genuine avana lineThe appendix base is all the time found on the confluence of the three taenia coli on the caecum. The four n Introduce a Vicryl Endoloop (Ethicon) by way of the umbilical mesoappendix immediately adjoining to the appendix base is skinny and usually solely consists of a layer of peritoneum. This window is a useful place to begin separating the mesentery with a diathermy hook. Vessels near the appendix are small and can be divided using diathermy alone, with minimal bleeding. An assistant can hold the mesentery whilst you maintain the appendix, so facilitating the separation. Place two ties near the caecum and the third tie roughly 1 cm distal to the first two. If the appendix base is friable and oedematous, divide it using a stapler, together with some caecal wall if necessary. If the appendix is fixed or lying retrocaecally, place a port in the right higher quadrant of the stomach to help mobilization and dissection. Be keen to transfer the telescope between ports to improve your view of the base of the caecum. Do not hesitate to convert the procedure in to an open operation if dissection is unimaginable, if bleeding is uncontrollable, and when you determine or suspect visceral injury. If the appendix is perforated, as quickly as attainable apply an Endoloop beneath the perforation, so lowering contamination from leakage of bowel content material in to the peritoneal cavity. The appendix may be friable and disintegrate if held by forceps: place it in a retrieval bag to scale back contamination. Use liberal irrigation and suction to take away all purulent fluid from the pelvic, subhepatic and subphrenic spaces. Insert a small tube drain by way of one of the 5-mm ports, which can usually be eliminated on the subsequent day. In such circumstances, take special care to avoid inadvertently injuring the gut, blood vessels or ureter. Reduce the danger through the use of lowmolecular-weight heparin prophylaxis, anti-thromboembolic stockings and intermittent pneumatic calf compression gadgets intra-operatively. Closure 1 n Withdraw the ports beneath imaginative and prescient and attempt to allow the entire 2 n Close insufflation fuel to escape. Laparoscopic vs conventional appendectomy: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. A potential randomized comparison of laparoscopic appendectomy with open appendectomy. Postoperative 1 n In the absence of common peritonitis enable oral fluids and food n once the affected person is absolutely awake. Most sufferers could be discharged on the primary postoperative day and almost all by the second. Possible sources embody the inferior epigastric artery, appendicular artery, retroperitoneal vessels or the staple line. You can injure the inferior epigastric artery when introducing the left iliac fossa port. Attempt to identify and management the source of bleeding by re-laparoscopy if potential, before changing to open surgical procedure. More usually the appendix has ruptured and an abscess has shaped, its partitions comprising the fibrin-lined omentum and adherent viscera. Conventionally, the patient is re-admitted for interval appendicectomy after 1�2 months. You could encounter oedema as three n Alternatively, you could enter the abdomen and discover the mass on the posterior wall. It may result from a retained foreign physique, necrotic tissue, insufficient drainage of blood or contaminated fluid, or an anastomotic leak. The abscess may develop above the liver (subphrenic), below the liver (subhepatic), alongside both paracolic gutter, between loops of bowel in the mid-abdomen or in the true pelvis. On the proper it lies above the proper lobe of the liver, on the left it lies above the left lobe of the liver, gastric fundus and spleen. Right subhepatic collections could additionally be anterior (paraduodenal) or posterior (suprarenal. Left subhepatic collections may lie anterior to the abdomen and transverse colon or posteriorly in the lesser sac. In the presence of a subphrenic abscess the hemidiaphragm could additionally be elevated, as demonstrated on a chest X-ray, and a reactive pleural effusion often develops above the diaphragm. You might even see a fluid stage with gasoline above if leakage from a viscus or anastomosis has developed, or within the presence of gas-forming organisms. Aspirate a specimen of pus for tradition and determination of antibiotic sensitivity. Take a specimen of the contents of the cavity for bacterial culture and to decide the antibiotic sensitivity of the contained organisms. This is the stump left after the distal half has dropped off after a perforation and is mendacity within the abscess cavity. Remember, inflamed tissues are friable; reply to the findings and be willing to cease if you encounter problem. A bevel-tipped catheter is passed over the guidewire in to the cavity and the guidewire is then withdrawn. This kind of posterior assortment could additionally be drained by a posterior extra-peritoneal method, through the mattress of the twelfth rib, or from an anterolateral course. This is to keep away from the necessity to carry out an exploration after opening the abscess and risking basic contamination. Explore the right and left subphrenic and sub-hepatic areas, and enter the lesser sac via an avascular part of the hepatogastric omentum. Ideally, an extrapleural, extra-peritoneal method avoids the potential for contaminating the peritoneal or pleural cavities. As a rule that is potential only for posterior collections, though a right anterior subphrenic abscess can sometimes be approached extra-peritoneally. Recurrent belly abscesses: incidence, outcomes of repeated percutaneous drainage, and underlying causes in 956 drainages. Prepare Start antibiotic cover towards the probably organisms earlier than embarking on operation. Take recommendation from a medical microbiologist, particularly when you have managed to ship a specimen of pus for examine. Appendicectomy: evaluation of stump invagination versus simple ligature: a prospective, randomised trial. Incise the mattress of the rib cephalad to the middle, to keep away from coming into the pleural cavity. To drain a subphrenic abscess, separate the peritoneum from the undersurface of the diaphragm.
Order 200mg avana overnight deliveryMobilize the upper half of the gastric larger curve by dividing no much less than half the quick gastric vessels. Insert stitches to produce a wrap no more than three cm long, across the decrease oesophagus. Each of usually two or three stitches picks up gastric fundus on the proper and the oesophagus. A second set of two or three stitches picks up the oesophagus and the left higher stomach, leaving the anterior 90 of oesophagus bare. Take care to not 4 n Now gently fold the gastric fundus behind the decrease oesophadamage the anterior vagus when doing this. The posterior vagus nerve may be included in the wrap or the wrap could additionally be placed between the posterior vagus and the oesophagus. Leave a space between the hiatus and the stented oesophagus that will admit a finger. However, the technique is different because of the completely different access to the organs and because laparoscopic devices have a special set of disadvantages from these encountered throughout a traditional strategy. Take your dissection over the top of the oesophagus and down the left crus dividing attachments between the angle of His, fundus and diaphragm. When the crural muscular fibres are absolutely uncovered, blunt dissection of the oesophagus may be safely achieved from the lateral and anterior elements. Access 1 n Place the patient supine with the legs in Lloyd-Davies stirrups as n three n Have the anaesthetist cross a nasogastric tube to aspirate the stom2 Tilt the working table 30 head up. Most surgeons now keep away from using a 50 F Maloney dilator because of the risk of perforation. First make sure that the posterior left crus is totally dissected; it Action 1 n First expose the distal oesophagus by dividing the gastrohepatic 2 n Divide the ligament with a harmonic scalpel taking care to idenligament from in regards to the degree of the left gastric artery to the hiatus. You 5 mm Nathanson retractor 5 mm working port 5 mm working port 10 mm retractor 10 mm camera 118. In thinner patients the posterior crus presents as a visual ridge of tissue covered by para-oesophageal fat, supplied retraction is appropriate. The left crus may also be recognized by on the lookout for the posterior vagus nerve because it curves over the construction. Although posterior closure of the crura is easily completed in the case of small hernias, it could be troublesome in a affected person with a large para-oesophageal hiatal hernia. If needed, perform anterior restore with mesh reinforcement or suture the wrap to the right crus. Fundoplication could be carried out to stop reflux after widely mobilizing the oesophagus. Use a sweeping chopstick movement with two forceps to open a window, making certain this is under the left crus seen from the best. Attempt to make the window behind the posterior vagus, keeping it next to the oesophagus. Have the primary assistant use an atraumatic, finely serrated 5-mm grasping forceps, so as to avoid tearing fatty tissue or the brief gastric vessels. Grasp the higher curve of the abdomen approximately 5�7 cm from the angle of His and draw it to the right behind the oesophagus. If crural restore is difficult, suture the wrap with two nonabsorbable sutures to the best crus to forestall wrap migration. Peri-oesophageal scarring, secondary to penetrating ulcers, and stricture formation are often, however not always, predictable. Elevate the oe- n 10 In order to safe the wrap in the stomach, you should close the hiatus by suturing the crura together. Take care to avoid injuring the posterior wall of the oesophagus whenever you place sutures within the left crus. Delayed larger curve perforation at the angle of His could observe extreme use of diathermy. Evade the possibility through the use of the most up-to-date ultrasonic dissector available for dissection on this space. If damage to the oesophagus is suspected, endoscope the patient on the table and look for harm or inflate the oesophagus/stomach beneath water. A nasogastric tube could be left in place for 12 hours till the affected person demonstrates regular swallowing. Postoperative 1 n Order a postoperative Gastrografin swallow if you encountered 2 n Encourage the affected person to drink fluids after 6 hours. The fundus may prolapse through a congenital or acquired defect within the diaphragm close to the hiatus. If the affected person develops ache, vomiting from entrapment, obstruction or volvulus, operative restore must be performed as a matter of urgency. Incorporation of the oesophageal suture is necessary as a result of it helps to safe the wrap. Avoid the danger of perforation by refraining from making use of excessive traction on the anterior abdomen. If it does happen, repair it by inserting laparoscopic sutures, offered the extent of injury is clearly seen. Direction of opening peritoneum on margin of crura Action 1 n Elevate the left lobe of the liver and establish the hiatus and the n three n the operation is tremendously facilitated by early excision of the hernial 2 Gently reduce the abdomen in to the stomach. The sac is then excised and the entire circumference of the oesophagus is carefully examined by rotating it. Divide the sac at the hiatal margin, pull down and excise the sac, taking care to not harm the vagi. Interrupted sutures attach gastric fundus to diaphragm three n Gently scale back the stomach in to the abdomen. Take a generous seromuscular chew of the higher stomach at a point that will preserve reduction of the stomach and allow it to be drawn as a lot as the port website when the suture is tied. Bring the needle out of the port and leave the ends lengthy and leave the needle in place. Interrupted non-absorbable sutures anchor the fundus and greater curve to the diaphragm and anterior belly wall. This may be achieved both by performing a limited myotomy with minimal disturbance of the hiatal anatomy or by a extra intensive process together with an antireflux process. However, if a revision process is required, extra intensive dissection and an antireflux operation might be wanted. Retention of contents within the oesophagus produces oesophagitis, and if the retained meals is aspirated the affected person might develop respiratory problems, including pulmonary fibrosis. The goal must be to make the prognosis at an early stage earlier than the typical X-ray adjustments appear. Since myotomy is a restricted technical manoeuvre, minimal entry strategies are notably appealing. Laparoscopic cardiomyotomy might be the process of selection, provided expertise can be maintained by a sufficient quantity of those uncommon cases. The process should be carried out beneath fluoroscopic control whether by an endoscopist or interventional radiologist.
Discount 200 mg avana overnight deliveryThe child presents with sudden appearance of bruises and mucosal bleeding, epistaxis, oral oozing and extended bleeds with superficial trauma. It is essential to accurately diagnose this entity and differen tiate it from severe situations like leukemia. Liver and renal operate checks and lactate dehydrogenase levels are carried out to rule out hepatitis, occult malignancy, hemolysis and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Screening checks for disseminated intravascular coagulopathy are carried out if sepsis is suspected. Bone marrow examination reveals elevated megakaryocytes and excludes marrow infiltration, leukemia or bone marrow failure. Postnatal management requires transfusion of washed maternal platelets (preferably irradiated) and close monitoring until the platelet counts normalize. The risk for neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia will increase in subsequent pregnancies. Hemophilia Hemophilias are the commonest hereditary clotting defects, occurring as X-linked recessive disorders. The scientific manifestations of hemophilia A and B are indistinguishable and the presentation is dependent upon the level of issue current. In gentle cases, the issue level is adequate to forestall spontaneous bleeds and bleeding manifests solely with surgery or extreme trauma. Children with hemophilia ought to be managed at specialized facilities geared up for their wants. The dose of factor replaced is focused to the severity of bleeding manifestations. Minimizing the danger of hemorrhage and decreasing the lengthy run unwanted effects of remedy are the objectives of therapy. Corticosteroids can be administered after the possibility of hematological malignancy has been ruled out on bone marrow examination. If critical hemorrhage occurs, platelet transfusions could also be used under cover of steroids. Successful management of re fractory persistent immune thrombocytopenia with intracranial hemor rhage by emergency splenectomy. Almost half the circumstances happen with the primary pregnancy, without historical past of sensitization. While patients with mild thrombocytopenia remain asymptomatic, hemorrhagic complications, including intracranial hemorrhage, might happen within hours of birth. As particular tests are limited, the condition is primarily recognized by exclusion of other etiologies of. E-aminocaproic acid or tranexamic acid may be effective as adjunct remedy in mild instances of hemophilia. Genetic counseling is required and families must be knowledgeable of the availability of prenatal diagnosis. The prevalence of late vitamin K deficiency bleeding in breastfed infants not given prophylaxis is 20 instances per 100,000 stay births. Deficiency of vitamin K dependent elements results in prolonged prothrombin and activated partial thromboplastin time. Vitamin K is run as a single subcutaneous dose of 1 mg at start to forestall hemorrhagic disease of the new child. The presentation ranges from an isolated derangement of laboratory parameters to extreme bleeding from multiple websites, associated with excessive mortality. Vitamin K is present in green leafy vegetables and oils (soyabean, canola) and is synthesized by colonic micro organism. Deficiency is frequent in newborns due to poor transmission of vitamin K across the placenta, its paucity in breast milk, lack of intestine bacteria and prematurity of liver function. Later in life, vitamin K deficiency might comply with prolonged antibiotic use, parenchymal liver illness. The tissue factor accumulates on activated platelets by binding to platelet P-selectin which ends up in thrombin generation. Causes the principle illnesses inflicting disseminated intravascular coagulopathy are listed in Table 12. Screening tests Peripheral blood film examination and hemogram present schistocytes and thrombocytopenia. Prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time and thrombin time are prolonged. Supportive checks Increase in fibrin degradation merchandise or D-dimers is attribute. Tissue per fusion and respiratory operate have to be maintained by alternative with intravenous fluid and provision of oxy gen to appropriate hypoxia. Coagulopathy may be compounded by vitamin K deficiency, which requires correction. Monitoring is crucial for guiding administration and checking adequacy of alternative element assist. Replacement therapy could be halted when stabilization in platelet counts and fibrinogen ranges and a fall in fibrin degradation merchandise is observed. Specific indications for such therapy embrace the presence of arterial or massive vessel venous thrombosis. These sufferers ought to proceed to obtain substitute remedy with heparin during steady monitoring of platelet counts and fibrinogen levels and prothrombin, activated partial thromboplastin and thrombin time. Towards definition, medical and laboratory standards, and a scori11g system for disseminated i. Protein S stage approaches grownup worth by the age of 3-6 months, but protein C levels stays low during childhood. In newborns compared with adults, thrombin technology is delayed and decreased, in all probability due to low prothrombin level. Other predisposing factors for arterial or venous thrombosis embody latest surgery, trauma, use of central venous catheter, nephrotic syndrome, dehydration, sepsis and collagen vascular issues (Table 12. Limb edema, erythema and tenderness on dorsiflexion of the foot (positive Homan sign) recommend deep vein throm bosis. Signs of arterial thrombosis include diminished or absent peripheral pulses and cool extremities. Manifes tations of pulmonary embolism include nervousness, breathlessness, pleuritic chest ache, fever, tachypnea and cough, and a excessive index of suspicion is required to make the diagnosis. Symptoms of central nervous system thrombosis embody vomiting, lethargy, seizures or weakness in an extremity. Laboratory Evaluation Many clotting factors are consumed in acute thrombosis and factor ranges may be fallaciously low in the acute part. The child must be evaluated to rule out disseminated intravascular coagulopathy with full blood rely, peripheral blood smear, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time and fibrinogen level.
References - Buffington CA, Chew DJ, DiBartola SP: On the definition of feline interstitial cystitis, J Am Vet Med Assoc 215(2):186n188, 1999.
- Nesbit RM: Diagnosis of intermittent hydronephrosis: importance of pyelography during episodes of pain, J Urol 75:767, 1956.
- Raassen TJ, Ngongo CJ, Mahendeka MM: Iatrogenic genitourinary fistula: an 18-year retrospective review of 805 injuries, Int Urogynecol J 25(12):1699n 1706, 2014.
- North American Pediatric Renal Transplant Cooperative Study (NAPRTCS), 2004.
|
|