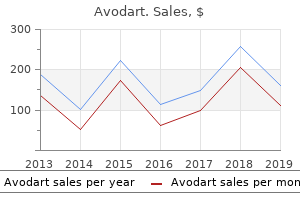
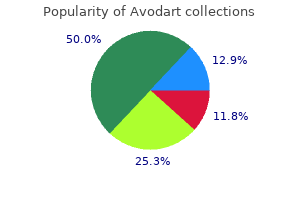
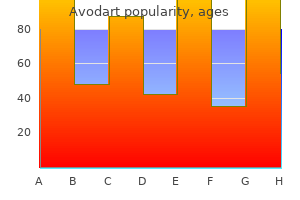
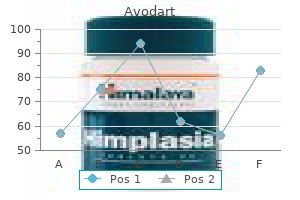
"Order avodart 0.5mg fast delivery, treatment with chemicals or drugs."By: Jonathan Tze-Wei Ho, M.A., M.D. - Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/10003132/jonathan-ho
Buy avodart 0.5mg amexLarger portals are likely to leak fluid during surgery and therefore must be made as late as is possible within the surgical procedure. The use of commercially obtainable portal plugs can even assist in lowering fluid extravasation from these portals. Surgical Treatment Arthroscopy is the most accepted means of tackling a case of unfastened bodies. Not solely does it permit simple removal of free bodies, but it also allows a detailed analysis of the anterior as nicely as the posterior compartments of the knee joint with minimal morbidity. A variety of arthroscopic graspers should be out there for gasping unfastened bodies of various dimension, consistency and shape. Cupped, serrated and low profiles are the assorted suggestions obtainable for grasping round, slippery or thin flat loose bodies respectively. Having a ratchet handle additionally allows the surgeon better freedom in maneuvering the free physique once engaged within the grasper. It is important to perform an in depth arthroscopic analysis of the entire joint in each case of unfastened body removal. Occasionally they may be hidden behind synovial folds and hence it is essential to visualize in addition to probe all corners of the knee. Occasionally one might have to resort to making accent portals along with the standard anterolateral and the anteromedial portals. The posteromedial compartment can alternatively be visualized by performing a modified Gillquist maneuver. To stop injury to the arthroscope, the telescope is changed by the blunt obturator and gently coaxed into the posteromedial compartment. Once the obturator is changed by the arthroscope, use of a 70� arthroscope as opposed to a standard 30� arthroscope can also enable a wider space to be examined. A large number of research have been published indicating advantages, and an equally large number of research point out in any other case. The fact lies somewhere in between, and affected person choice is crucial think about success of this process. The minimally invasive nature of this operation makes it a pure selection for the patient. Overall, it has been proven that arthroscopy has no significant position in osteoarthritis. They must know that arthroscopy, in their case, is primarily diagnostic, and any profit may be a bonus. Sometimes, one does arthroscopy as an investigation prior to deciding whether the patient is suitable for a unicondylar or complete knee alternative. Arthroscopy will treatment his signs: this will likely occur where locking because of a free physique is the primary complaint. On the other hand, an analogous affected person with synovitis and mechanical symptoms as the main grievance will benefit from arthroscopic surgical procedure. In common, patients with regular limb alignment and wellpreserved joint house on a standing X-ray, would do properly. Osteophytes: Large osteophytes from femoral condyles and people from patella make movement of the arthroscope tough. One have to be careful, as forceful movement of the scope might harm the knee or the scope. One have to wash the joint a few instances and enhance intra-articular pressure to get a clear view. Difficult judgment: It is usually exhausting to decide what may be causing signs, and which out of so many procedures could assist. This wants years of expertise, however in general, a pathology inflicting mechanical disturbance ought to be attended to . If mechanical symptoms and never ache is his major complaints, one may still think about arthroscopy primarily for aid in mechanical signs. Such patients will need realignment osteotomy or joint alternative for ache aid. One needs to be careful while applying tourniquet, as in these patients with bulky and short thigh, the tourniquet could also be slide down, practically to the knee. One might need to do arthroscopy with out tourniquet, but irrigation fluid in such case has to be under sufficient strain to maintain readability of vision. This makes entry into the suprapatellar pouch troublesome; one might have to make an additional, supero-lateral portal for proper analysis of supra-patellar pouch and patello-femoral joint. Diagnostic arthroscopy: Particular attention is paid to unfastened bodies, chondral flaps, meniscus flaps and impinging osteophytes. Subchondral drilling: Popularly known as Pridie procedure, in this procedure multiple drill holes are made in the subchondral bone with the help of two mm K-wire. Joint debridement: this consists of removing of loose, hanging flaps of cartilage and synovial tissue. Removal of osteophytes, hypertrophic synovium and unstable meniscal flap is an integral part of joint debridement. Abrasion arthroplasty: In this operation, a superficial layer of subchondral bone, roughly 1�3 mm thick is eliminated to expose the interosseous vessels. Theoretically, the ensuing hemorrhagic exudates kind a fibrin clot and allows for formation of fibrous repair tissue over the eburnated bone. Microfracturing: this can be a method in which arthroscopic awl is used to create a number of perforations in the subchondral bone or the bare bone might lead to fibro-cartilage rising over this space. Lateral release of the patella using electrical cautery, in cases with lateral monitoring of the patella. The clarification for symptomatic reduction has been postulated such as removing of cartilage debris, crystals, and inflammatory components. It has proprioceptive senses that help shield the knee joint throughout use, has a bodily configuration of multiple bands with a multi-axial function that guides the knee through its complex helicoid movement, and has broad insertion websites, which allow the traditional kinematics of knee movement to happen with stability. Its predominant source of blood provide is the center genicular artery, which arises from the popliteal artery and pierces the posterior capsule. If a primary restraint has been torn but a secondary restraint stays intact, scientific testing could reveal only slight laxity. However, components apart from final energy will influence performance, such as biologic modifications in graft supplies over time and the results of repetitive loading. The patient might notice that the knee felt too unstable to proceed ambulation and had problem bearing weight. A careful bodily examination of the injured knee as in comparability with the conventional knee will reveal most ligament disruptions if the affected person is relaxed. A average to extreme effusion is normally present, and this will likely limit vary of movement. Lachman Test the knee is placed in 30� of flexion, the femur is stabilized, and an anteriorly directed pressure is applied to the proximal calf.
Purchase avodart ukFactors under the management of surgeon for profitable therapy are: � Good discount � Proper choice of implant � Proper surgical technique, which incorporates availability of modern operation rooms and full set of implants and instrumentations � Availability of picture intensifier and clean air system (laminar air flow) in operation rooms can be essential. The elements most vital for instability and fixation failure are: � Loss of posteromedial or medial cortical assist � Severe comminution � Subtrochanteric extension of the fracture � Reverse indirect fracture � Shattered lateral wall � Bone high quality. There are a lot of articles with meta-analysis and randomized, prospective research; still there are lot of controversies concerning selection of implants and procedures. Screw of sliding in the barrel is decided by: � Fracture geometry � Quality of reduction � Position of screw in the head and neck of femur � Angle of the barrel and plate � Integrity of lateral wall. The shearing force on the femoral head being transferred to the axis of the sliding screw, therefore producing a compressive drive. Note the stress within the aspect plate to compress the fracture of the lateral cortex. For this purpose, the top screw is placed higher to acquire distance inside the proximal fragment. Even if the fracture unites, there could also be thigh pain, shortening of limb and dangerous limp Cutout of implant may occur in severe osteoporotic bone Reverse indirect fracture are unstable fractures. Excessive collapse happens as a result of shearing forces and to highly effective muscular tissues appearing on fragments. Reduction: Patient is positioned in a supine place on a fracture table, ideally under epidural anesthesia. Reduction of the fragments, particularly the anteromedial, is an important prerequisite for good union. Anatomical reduction could be achieved by closed method by applying traction to over distract. Most fractures are decreased by direct traction, slight abduction and normally 10�15% inside rotation. Occasionally slight external rotation could also be required for extra in depth and comminuted fractures. With image intensifier the limb must be rotated internally to obtain satisfactory reduction. It is essential to verify on the lateral projection that the shaft has not sagged posteriorly. Once discount is achieved, most essential step is to preserve it, until definitive fixation is full. With elevation of the sagging shaft, a Steinman is passed from larger trochanter into the pinnacle of femur as provisional fixation to preserve the reduction. The valgus position of the proximal fragment reduces the deforming drive and the incidence of fixation failure, and makes the fracture more stable. In an osteoporotic bone with comminuted fracture, anatomical discount is troublesome if not unimaginable. In comminuted fractures, the larger trochanter fragment is pulled superiorly to permit direct visualization of the fracture. This maneuvers denervates the posterior fiber and is related to higher bleeding. Occasionally, the sharp anteromedial spike of the proximal fragment is entrapped within the overlying rectus femoris muscle tissue. The level of coalescence of the strain and compression trabeculae ends in a dense pattern of cancellous bone in the center of the femoral head. This is where the best purchase in the bone could be obtained for a fixation device. When these trabecular are absent, the surgeon can anticipate a higher rate of failure with use of any gadget. The tip-to-apex distance has been described by Beumgaertner67 as a guide to accurate screw placement, and must be less than 25 mm. Tip-to-apex distance helps outline screw position and threat of cutout and is easily measured intraoperatively. If the screw is positioned inadvertently within the superior half of the top, then a better angled barrel plate (140�) could also be required. If the screw is positioned within the decrease half of the pinnacle, barrel and plate angle is lower than 135�, often 130�. Tapping of the femoral head to cut screw threads prior to insertion of the screw is recommended in all, but the most Advantages of Central Placement of the Implant � the putting of the lag screw in a central place avoids the potential complication of a peripherally placed screw, which can seem to be within the femoral head. This will reduce the torsional stress and thereby the danger of rotation of the proximal fragment throughout insertion of the screw. An various technique of stopping rotation is by putting a supplementary guidewire across the fracture. In a basicervical fracture, the authors always insert a supplementary lag screw to prevent rotation of proximal fragment. The lengthy barrel plate has insufficient shaft of screw to slide to enable enough collapse of the fracture and, once the full length of collapse available has occurred, the screw is pressured to penetrate into the acetabulum. Fixation of the Posteromedial Fragment the posteromedial fragment could additionally be fixed in a younger patient in whom restoration of normal anatomy is a extra important and a fascinating objective. If the posteromedial or medial fragment is massive enough, cerclage wire could additionally be used, using newer cerclage wire fixation system (Synthes, Zimmer). The compression device acts as an intermediate section, capturing the lag screw proximally (similar to a normal plate) and interesting the barrel facet plate distally in a sliding monitor. The barreled aspect plate is connected to the femoral shaft with bone screws directed in two planes. If positioned at a high angle, the screw might be very near the upper cortex of the head and neck. Trochanteric stabilizing plate: When the lateral wall is fractured, the trochanteric stabilizing plate construct buttresses the larger trochanter and prevents lateral displacement of head fragment. The trochanteric stabilizing prevented excessive fracture collapse and consecutive limb shortening in 90% of patients with an unstable fracture pattern. Cement might, nevertheless, be more appropriate for a pathological fracture with a significant bone defect and a limited lifeexpectancy; on this situation, cement could be helpful in bridging the bony gap. They concluded augmentation of femoral heads yielded a significantly superior rotational stability, in addition to an enhanced IntertrochanterIc Fractures oF Femur 1537 � Reduce and compress and stabilize all fragments intraoperatively � Four screws mounted within the distal fragment. Postoperative Management If a affected person has good fixation, full weight-bearing is allowed the very next day of surgery. If the fixation is unstable, as when the bone is osteoporotic, only partial or no weight-bearing is permitted. Unstable fracture in osteoporotic bone seems to require an extra lag screw fixation above or under the screw. The major trochanteric fragment is fastened by the use of a wire pressure band (the screw ought to be considerably more distal); (C) Trochanteric stabilizing plate Pain Management pull-out resistance, compared to the nonaugmented state in osteoporotic bone. Although adults older than 65 years have surgical procedures more frequently than some other group, additionally they have the worst postoperative pain management. Reason for failure to assess for ache, insufficient data about ache evaluation and management, a misperception that pain is a natural and anticipated consequence of getting older. Untreated acute ache has physiologic, economic, and high quality of life penalties, poorer scientific outcomes. The most necessary aspect of ache evaluation is frequent reevaluation and re-assessment.
Order avodart 0.5mg fast deliveryIn the fractures that are considerably comminuted, a single small fragment dynamic compression plate, reconstruction plate, or locking compression plate secured to the fractured column goal of therapy of these accidents is to promote complication-free therapeutic in order to recreate a pain-free, cell, and functional elbow joint. With more extreme accidents, these targets is in all probability not attainable, and the affected person ought to be endorsed about this at an early stage. The risk of functional impairment is very excessive if displaced distal humerus fractures are treated nonoperatively and had high failure fee with older earlier kind of inside fixation. Each surgical step is deliberate which can avoid problems and surgeon is prepared for any surprising problem, as varied choices are well-planned. Depending upon the kind of fracture sample, extra-articular or intra-articular, involving single column, lateral or medial or both column involvements, the surgical treatment is planned. Single column fractures (Type B) are rare, comprising approximately 15% of all distal humeral fractures. The postoperative rehabilitation following surgical reconstruction is essentially the same as for bicolumn fractures. Fractures involving each columns are the most typical sort of distal humeral fracture, accounting for more than one-third of all accidents seen in this space. These fractures happen in the middle-aged and aged females throughout simple falls, and in younger people throughout high-energy sporting injuries or street visitors accidents. They become more comminuted, each within the metaphysis and in the articular phase, continuing from the C1. The Jupiter system makes an attempt to describe the generally encountered articular fracture configurations, and locations particular emphasis on the level of the transverse fracture line across the condyles, distinguishing high (transverse fracture line above the olecranon fossa) from the low (transverse fracture line under the olecranon fossa, usually simply proximal to the trochlea) subtypes. Many publications have now documented passable outcomes utilizing these strategies, when the standard method is adopted. This is as a end result of the interior fixation is commonly unstable, predisposing to fixation failure and nonunion. Surgery should ideally be performed as early as potential, as quickly as the swelling is lowered and patient is medically match. The latter two approaches are more commonly considered if there are doubts about whether the fracture will be reconstructable by inner fixation or would require elbow alternative. Surgical Approach By and large distal humerus intra-articular fractures are accessed by posterior method, which provides the wonderful publicity of the articular fragments of distal humerus. This approach requires reflection of the extensor mechanism, typically by way of a triceps-splitting strategy or an olecranon osteotomy. The transolecranon publicity for distal humerus fractures is a instructed approach for bettering articular visualization, allowing accurate reduction. Significant osteotomy complications corresponding to nonunion and implant prominence have prompted recommendations for alternate exposures. Triceps splitting (Campbell): A longitudinal straight or curvilinear incision is made from the proximal triceps muscle to the distal triceps tendon across its insertion on to the tip of proximal olecranon. Then the full-thickness skin flaps are created medially and laterally by splitting the triceps muscle distally alongside the central tendon as much as the olecranon and peeled subperiosteally. At the top of process, the triceps tendon is repaired with nonabsorbable suture. Subsequently, an apex distal chevron osteotomy is planned which enters the elbow joint at the shallowest part of the trochlear notch. The osteotomy is started initially with oscillating saw as much as articular cartilage and finally completed by two straight osteotomes to crack the remaining subchondral bone. The anconeus muscle flap and olecranon fragment are then elevated off the posterior humerus, which exposes the fracture of distal humerus completely. After repair or reconstruction of the distal humerus, the osteotomy is lowered and internally fixed. Paratricipital: the paratricipital approach has the advantage of maintaining the triceps insertion undisturbed, and it eliminates the danger of postoperative triceps insufficiency. The strategy can be helpful for open discount and inside fixation of distal humerus fractures, particularly transcondylar fractures of distal humerus. Visualization may be compromised by the presence of the intact triceps unit over the elbow joint. A posterior skin incision is made, and the ulnar nerve is recognized and protected. Medially, the tissue aircraft between the medial intermuscular septum and the medial side of the olecranon and triceps tendon is developed. Laterally, the plane between the lateral intermuscular septum and the anconeus muscle, which is in continuity with the lateral side of the triceps, is developed. The dissection between the medial and lateral tissue planes meets at the posterior humeral cortex as the triceps muscle is launched from the humerus. Placing the elbow into an extended place relaxes the triceps and should lead to improved visualization of the posterior elbow. Olecranon osteotomy: Posterior transolecranon exposure by olecranon osteotomy affords optimum visualization of the distal humerus articular surface and both columns of the distal humerus for the remedy of intra-articular fractures. A posterior skin incision is used, and full-thickness pores and skin flaps are created medially and laterally. Following identification and safety of the ulnar nerve, which is either retracted and kept away from the operative field or transposed anteriorly. A capsulotomy is completed on each the medial and the lateral sides of the olecranon at the mid-portion of the larger sigmoid notch after the medial triceps and the anconeus muscle are divided. A transverse intra-articular osteotomy is inherently unstable and could be difficult to reposition accurately. Commonly the osteotomy is created with an oscillating noticed in a chevron configuration, usually with the apex pointed distally. An osteotome is used to complete the process so that a portion Triceps-reflecting (Bryan-Morrey): In this process, the extensor mechanism comprising of triceps tendon, forearm fascia and periosteum is mirrored as one unit from the medial to lateral of the olecranon. The ulnar nerve is identified and guarded, after which a periosteal elevator is used to dissect the triceps muscle from the posterior humeral cortex. With a scalpel, the forearm fascia, periosteum, and triceps tendon are reflected directly of the olecranon from medial to lateral as a continuous sleeve. Now the complete triceps muscle with posterior capsule is reflected upwards and laterally, and elbow is flexed to expose the joint. At the end of process, triceps tendon is repaired back to the olecranon by means of unabsorbable sutures handed by way of the transosseous drill holes within the olecranon. The triceps restore wants safety for 4�6 weeks postoperatively and may keep away from energetic elbow extension against resistance. Triceps-reflecting anconeus pedicle (Driscoll): this strategy displays the triceps in continuity with anconeus. It normally begins laterally by preserving the lateral collateral and annular ligament the place anconeus is elevated subperiosteally from proximal ulna, which is separated from the capsule. To start, anconeus is exposed distally and publicity developed proximally and muscle reflected upwards by developing the interval between extensor carpi ulnaris and anconeus. The origins of widespread extensors, extensor carpi radialis longus and brachioradialis are left undisturbed on the humerus. The anconeus tendon and muscle is then separated from annular ligament and lateral collateral ligament advanced, that are preserved, and dissection continued proximally beneath the triceps muscle.
Buy avodart 0.5mg overnight deliveryIt is important not to do overzealous testing for stability, lest one may dislodge a clot. A fast look to assess the limb length, comparative position of limbs, areas of apparent pores and skin and gentle tissue breach, and inner degloving will give fair idea. It is necessary to turn the affected person, even though painful, to assess the posterior gentle tissues. Presence of blood at the urethral meatus or bleed per vagina or rectum should ring a warning bell. In absence of basic surgical colleague, an orthopedic surgeon could must carry out per rectal examination to assess the injury to decrease gut and the prostate in males. Bleeding per vagina could require evaluation by gynecologist, but of their absence, discover out the cause by doing a per vagina examination to assess the cause for bleeding and see if you feel any bony spicules. Bleeding through the orifices makes the harm compound, except proved in any other case and compound pelvic damage carries larger mortality, due to speedy unfold of an infection in area with wealthy supply of blood products. Radiology A quick anteroposterior view of pelvis with each hips is helpful in diagnosing many of the pelvic fractures including that of sacrum, offered, the eyes know what to look for and the brain is skilled to interpret what the eyes see. Look for following: � Anterior lesions in form of separation of symphysis pubis or fractures of pubic rami � Sacral fracture-especially examine the shape of sacral foramina on either side � Sacroiliac dislocation � Fracture by way of iliac wing � Avulsion of L5 transverse process, ischial backbone, ischial tuberosity or sacral attachment of sacrospinous ligament � Also compare the levels of highest points of iliac wing and levels of ischial tuberosities. Careful examine of this view offers wealth of data regarding harm pressure vector and stability. Young and Burgess Classification Pennal described the harm patterns according to the force vector. Young and Burgess further subclassified these accidents, describing varied damage patterns as the force progressed. Lateral Compression Injury Here the drive acts either instantly on the pelvis or not directly thorough the femur. This harm, inner rotation of hemipelvis on the aspect of injury and exterior rotation of the alternative facet can be described as "windswept" pelvis. Very hardly ever they may be treated by external fixation if the internal rotation of pelvis requires disimpaction and correction. Only if the affected person is hemodynamically unstable, and different associated injuries require stabilization, then one might think about external fixation in early phases. Open reduction and fixation of iliac wing may not be accomplished primarily usually because of poor general well being of the affected person or poor local pores and skin and soft tissue condition. It is taken with affected person supine on X-ray table and X-ray beam directed 60 degrees towards the toes. This is a superb view, that shows anterior, or posterior displacement of the pelvis, higher than another view. One can also see medial displacement of pelvis in case of lateral compression injury. Outlet View Taken with X-ray beam directed from foot to symphysis at forty five levels angle. Comparing the ischial tuberosity, one can choose the shortening due to pelvis shift. Oblique Views Oblique views thorough sacroiliac joints also present impaction of sacrum if any. If one suspects related acetabulum fracture then Judet views are of nice assist. The anterior lesion is both separation of symphysis or vertical fracture through the 1458 TexTbook of orThopedics and Trauma His idea of partial stability is when the pelvic ring is rotationally unstable however stable vertically and posteriorly. This is because the posterior ligament complex or pelvic flooring is unbroken, giving vertical stability to pelvis. In open e-book kind of damage, the pelvic ground could additionally be broken, however posterior sacroiliac ligaments being intact, the pelvis is vertically steady. When the pelvis is totally unstable, both rotationally as vertically, all of the restraining ligaments are compromised. The sacrospinous, sacrotuberous, anterior and posterior sacroiliac ligaments are minimally stretched. The pelvic floor muscular tissues and ligaments are torn, so are the anterior and posterior sacroiliac ligaments, making the pelvis unstable. Due to loss of temponade from harm to sacrospinous, sacrotuberous and sacroiliac ligaments, the bleeding spreads to retroperitoneal space quickly. Signs of Instability Clinical � Severe displacement � Marked posterior disruption characterised by bruising, inside degloving � Instability on manual palpation � Associated visceral, neural or vascular injury � Open fractures. The anterior element is either separation of symphysis or vertical fractures by way of pubic rami, the posterior component is usually via sacroiliac joint, however can be sacral fracture or iliac wing fracture. Here again pelvic floor ligaments, anterior and posterior sacroiliac ligaments are ruptured. Radiological � � � � � Displacement of sacroiliac joint >1 cm Presence of hole rather than impaction posteriorly Avulsion of sacral or spinous part of sacroiliac ligament Avulsion of L5 transverse course of Vertical fracture through pubic or ischial rami. Combined Mechanical Injury Many accidents have mixture of injury vector acting hence there could probably be combined displacement of fracture fragments. Tile Classification Mervin Tile categorised these accidents by pressure vector as suggested by Pennal and incorporated of their classification by Young and Burgess, and likewise added stability component. Management Pelvic injuries being high velocity accidents, the patient with pelvic damage, except proved otherwise, is a polytraumatized affected person. If one follows this philosophy, then one should ask himself, "Am I capable to handle this affected person He, relying on patient stability standing would resolve the priority in surgical management. As mentioned earlier, one needs to triage the patients in accordance with hemodynamic and skeletal stability as follows: 1. Stable patient, steady pelvis: In this example one has to decide, whether or not the steady pelvis has acceptable discount or not. But if the pelvis inlet has turn out to be slim, especially in a lady in childbearing age, then it would be crucial to scale back the deformity and align the pelvis and fix it. Stable patient, unstable pelvis: In this situation, you will want to make the pelvis stable either by exterior or inside fixation, till it heals. Unstable affected person, stable pelvis: Here one needs to consider the cause of hemodynamic instability and deal with the same. Once the affected person is hemodynamically steady then the pelvic damage has to be treated on its merits. Surgical Procedures According to Location of the Lesion Pelvic accidents are grouped into anterior lesions and posterior lesions. The anterior lesions include separation of symphysis or fractures by way of the rami. The posterior lesions encompass fracture by way of the sacrum, fracture dislocation or dislocation by way of sacroiliac joint or fracture through iliac wing. In instances of sacroiliac fracture dislocations and fractures, it will require some discount to obtain the stability. In previous, the usage of external fixation using pin purchase within the iliac wing was thought of panacea for stabilizing any sort of pelvic injury. But varied biomechanical studies have proved that external fixator at the most could make grossly unstable fracture into partially secure and will help in reaching temponade only in few injury patterns.
Buy avodart nowInitially carry out needle rupture adopted by steroid injection and digital therapeutic massage to disperse the cyst contents after first giving native anesthesia and arm tourniquet. Mucous Cyst Mucous cyst is a ganglion of the distal interphalangeal joint presenting dorsally simply proximal to the nail or to one aspect. Longitudinal grooving of the nail is a helpful early signal, produced because of pressure on the nail matrix. A curved incision that may allow rotation and advancement of the flap is to be most popular. It was a long-standing, painless, soft and pseudofluctuant mass lesions promptly recur, and improperly removed ones go away ugly hypertrophic scars. Sometimes they might have a slightly agency and multilobular consistency more in line with a fibrolipoma. Surgical clearance is straightforward but occasionally becomes tedious as a result of the "tumor" wraps around neurovascular bundle and tendons, and these must be protected throughout excision. Hemangiomas Hemangiomas are "tumors" of independently growing blood channels and possibly have their origin as embryonic rudiments of mesodermal tissue. Widespread hemangiomatosis with high-output cardiac failure or bleeding caused by sequestration of platelets (Kasabach-Merritt syndrome) have been described. He additionally famous that the glomus exists in large numbers beneath nails and finger pads and in substantial numbers elsewhere within the hand. The characteristic epithelioid cell of the glomus tumor is derived from the pericyte of Zimmermann. After eradicating the nail to one aspect, the mattress is incised and the tumor is eliminated completely. Meticulous repair of nail bed with 6-0 absorbable suture is adopted by substitute of the nail. Patients current with a well-defined, gradual growing tumor not often with nerve compression or tingling distally on percussion over the mass. Loupe dissection is required if the fascicles of the nerve are splayed to stop iatrogenic harm to the already compressed adjoining fascicles. Benign Bone Tumors Enchondroma Enchondroma is the commonest primary bone tumor within the hand seen within the proximal phalanx, middle phalanx and metacarpal shaft in that order of frequency (Alawneh et al. It continues to grow slowly and often presents as pain secondary to pathological fracture. If a fracture has occurred and alignment of the finger remains normal, the fracture is allowed to heal spontaneously. Otherwise open reduction, curettage followed by autogenous or allograft bone is carried out. Methylmethacrylate to fill defects has been described however appears completely unnecessary within the hand considering that only a small amount could also be required and bone graft will serve the aim higher. If any of the quiescent lesions on this condition turn into painful or enlarged all of a sudden, then the danger of degeneration into chondrosarcoma ought to be considered. Treatment in these instances is deferred till positive prognosis of histology is obtained after tissue is eliminated by incisional biopsy. They are often hereditary and the widespread nature of some produce important disfigurement. Angular deformities, inhibition of longitudinal development and mechanical blockage of joint motion could occur. They are benign hemorrhagic cystic bone lesions more generally seen in the second and third a long time. En bloc excision with osseous substitute by strut grafts or allograft bone will stop or minimize recurrence. Osteoid Osteoma Osteoid osteoma is an uncommon hand tumor with very attribute options. Presents within the second and third many years of life, occurring in phalanges, metacarpals on carpal bones and gives rise to aching pain worse at nights. Osteochondromas have a stalk comprising of bone at their base with a cartilage cap. A sclerotic ring with a nidus is the attribute function Giant Cell "Tumor" of Bone It is seen in young adults. These lesions additionally behave more aggressively within the hand than elsewhere with 12% of hand lesions turning into malignant based on Averill et al. Radiographs reveal an eccentric, expansile, radiolucent lesion on the epiphyseal portion of a tubular bone. It is beneficial to remember that this well-defined lytic tumor usually entails the subchondral area. Malignant Tumors within the Hand It is essential for the reader to know that the majority hand tumors happen in areas and never in compartments. Enneking proposed a staging system in 1980 for musculoskeletal sarcomas, and there are apparent difficulties in its sensible utility for the hand. Tendon compartments lengthen into the forearm and are subsequently a very impractical consideration. The tumor grade is predicated on degree of cellularity, pleomorphism, mitotic activity and necrosis. Tumors corresponding to rhabdomyosarcoma, synovial sarcoma and angiosarcoma are considered high grade regardless of their cellular differentiation (Russell et al. Radiotherapy, chemotherapy and regional node dissection all have a role apart from surgical procedure (Rosenburg et al. She sought medical consideration only 9 months after the onset area regularly involve adjoining carpals and metacarpals as nicely, so radial or ulnar hemiamputation may be required. Soft tissue cover should all the time be regional and never from more proximal sites or else malignant implantation at proximal sites will threaten each life and limb. They current in young adults as small, mounted lesions enlarging slowly and are painful in only a few situations. Radiographs reveal erosions of articular cartilage and flecks or calcification inside the tumor mass. Their microscopic options exhibit a biphasic composition General Surgical Plan Tumors that contain the distal phalanx are finest treated by amputation of the finger. Tumors that involve the middle and proximal phalanges are managed by ray amputation and with digital transposition as required. Lesions affecting the metacarpal 1856 TexTbook of orThopedics and Trauma Fibrosarcoma Fibrosarcoma is a malignancy on the most extreme finish of the spectrum of a fibromatous diagnosis. Prognosis is claimed to be higher in younger females with tumors of less than 5 cm diameter. Wide native excision, chemotherapy and regional node dissection is really helpful by Cadman et al.
Cera Flava (Beeswax). Avodart. - High cholesterol, ulcers, diarrhea, hiccups, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Beeswax.
- How does Beeswax work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Beeswax?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96326
Order avodart lineClassifications are helpful in helping determination making process and in documentation for tutorial purposes. The classification proposed by Letournel and Judet is based on fracture morphology and is extensively used. Letournel and Judet Classification four All fractures are divided into elementary fracture kind or associated fracture kind. In elementary fractures all or a part of a single column of the acetabulum is fractured. The associated fracture sorts are either a mixture of elementary fracture patterns or an elementary pattern with an additional fracture component. The solutions to the following questions about the radiographic observations are used to determine the acetabular fracture pattern: 1. Disruption of the ilioischial line happens in fractures involving the posterior column or fracture in the transverse group. Disruption of the iliopectineal line indicates anterior column involvement or one of the transverse fractures. A fracture of the obturator ring signifies either a T-shaped or column fracture (with the exception of the hemitransverse fracture). Posterior wall fracture can happen in isolation or in combination with posterior column or transverse fractures. Management the protocol of acetabular fracture management is summarized within the Flow chart 2. The following steps should be followed sequentially in order that acetabulum fracture can be treated effectively: 1. Treatment of related life-threatening head, chest, stomach, or other accidents. Urgent discount of dislocations: Gentle closed reduction of posterior dislocations on an emergent basis. If difficulty is encountered, shut reduction under common anesthesia is important. For central fracture-dislocations, heavy longitudinal skeletal traction by an upper tibial or lower femoral Steinmann pin and, if required, lateral skin traction at the higher thigh. Steinman pin on the proximal femur for lateral traction must be averted as it could predispose for an infection on subsequent surgical procedure. Flow chart 2 Management algorithm for acetabular fractures Fracture Patterns the nature and mechanism of harm assist predict the fracture sample and the associated injuries. In the presence of pre-existent arthrosis, a complete hip substitute may be a better choice than open reduction of the acetabular fracture. Principles of Operative Management Goal of Treatment Fracture displacement results in articular incongruity of the hip joint and trigger abnormal pressure distribution on the articular cartilage floor. This can lead to fast breakdown of the cartilage surface, resulting in disabling arthritis of the hip joint. Anatomic reduction and secure fixation of the fracture, such that the femoral head is concentrically lowered under an sufficient portion of the weight-bearing dome of the acetabulum, is the treatment objective in these tough fractures. The first thing in preoperative analysis is to assess whether patient is medically fit for surgery or not. It is greatest to wait 2�3 days after the harm, so that the initial bleeding from the intrapelvic vessels subsides. If the surgical procedure is carried out beyond three weeks, the probabilities of obtaining an excellent result decrease significantly. Blood group identification and cross-matching ought to be carried out in order that blood can be organized in the perioperative interval easily and instantly. Anticipated Intraoperative Problems There could also be increased blood loss because of disruption of the forming soft callus. The fracture traces are difficult to recognize because of muscular protection, impaction of the fracture fragments, and hematoma. Among these approaches, generally ilioinguinal is used for anterior column or T-shaped or bicolumnar fractures with mild comminution in the posterior column, and the Kocher-Langenbeck publicity for posterior column accidents. The incision begins at the posterior superior iliac spine, proceeds to the higher trochanter, and then continues distally alongside the femur approximately 10 cm. The fascia lata and the gluteus maximus fascia are divided in line with the incision. The maximus is break up along its fibers, with care taken to protect the inferior gluteal nerve. The insertion of the gluteus maximus on the femur could additionally be divided partially or completely to improve exposure. The gluteus medius and minimus are raised subperiosteally from the ilium and retracted with a Steinmann pin. The superior gluteal vessels and nerve, which emerge from the internal pelvis on this area, should be protected. The fracture fragments usually are found connected to the capsule, which forms the only soft-tissue attachment to the fragments and, hence, their only source of blood provide. To increase the exposure of the roof of the acetabulum, a trochanteric osteotomy may be carried out. Another alternative is to do a "trochanteric flip" by which the abductor and the vastus lateralis, in continuity, with a small medallion of the trochanter (which is osteotomized in a sagittal plane), are retracted anteriorly to expose the dome of the acetabulum. The benefit of this over a routine trochanteric osteotomy is that the abductors and the vastus lateralis stay in continuity by way of the trochanter, so easy restoration of anatomy is possible. The ilioinguinal method offers exposure of the whole inner desk of the innominate bone from the symphysis pubis to the anterior side of the sacroiliac joint, including the quadrilateral surface and the pubic rami. Because the abductors muscle tissue stay undisturbed, postoperative rehabilitation turns into sooner. The buildings vulnerable to damage with this strategy are the iliac vessels, lymphatic system, femoral nerve, and lateral cutaneous femoral nerve. If a combined strategy (anterior and posterior) is deliberate, the floppy lateral position is then most popular. The origin of the stomach muscular tissues from the iliac crest is erased sharply and retracted medially. The iliacus origin is then erased subperiosteally, and the dissection is carried out posteriorly and inferiorly to expose the anterior sacroiliac joint and pelvic brim. Through the medial part of the incision, the external inguinal ring is recognized and the spermatic cord (round ligament in females) is protected with a rubber catheter. The distal flap of the external indirect aponeurosis is raised to attain the mirrored part of the inguinal ligament. This ligament is incised along its length so as to depart 1 mm of the ligament hooked up to the interior indirect and transversus abdominis origins and the transversalis fascia.
Syndromes - Avoid kissing children under the age of 6 on the mouth or cheek.
- Hoarseness or changing voice
- Has the baby been ill, especially with vomiting, diarrhea, or excessive sweating?
- Heavy bleeding
- Hand tremor
- Digestive tract: abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting
- Breathing support
Generic avodart 0.5mg without prescriptionIf the partial damage exceeds 50% thickness, deal with it like a whole tear with a core sew and a operating stitch. The intact part of the tendon will permit early rehabilitation as compared to an entire rupture. Both stress on the necessity for mobilization of the tendons inserting minimum stress throughout the suture line. Young and Harmon9 (1960) described a technique (commonly misquoted because the Kleinert10 (1977) technique), which has been followed popularly. A plaster of Paris dorsal slab is utilized with the wrist in impartial or 5�10� of flexion. The rubber band is hooked onto a pin on the volar side of dressing on the forearm. A more modern addition, to appropriate the vector of pull is the protection pin, which acts as a pulley at the midpalmar stage, under which the rubber band is handed earlier than being anchored to the forearm pin. Once prolonged the finger is allowed to resume the flexed place passively by the pull of the rubber band. Thus, no pull occurs on the suture line however gliding of the restore and the tendon occurs because the tendon ends heal. As little as 3�5 mm of intrasynovial repair site excursion is necessary to stop adhesions. Duran and Houser devised one other method of controlled mobilization to get this 3�5 mm of excursion through the therapeutic part. Active mobilization of this vary is completed over the subsequent 2� weeks and vary of motion workouts are performed out of plaster following this. This technique is credited with better movements and lesser contractures than the previous technique. This method relies closely on the understanding of the affected person and the surgeon or therapists familiarity with its use. Place and hold, immediate active protocols, and lightweight lively mobilization are a few of them. These have had restricted successes and some studies quote high rupture flexor Tendon injury charges. More finetuning and longterm research are required before they can be really helpful for basic use. After 6 weeks, blocking workouts enable directing all flexor power to particular person joints. It can be a trigger for a poor consequence, when the affected person has began sturdy lively flexion, earlier than the restore site is robust enough to resist gapping. Assessment of the formation of adhesions early within the postoperative interval is tough. Weeks and Wray have shown that the most energetic function after a grafting takes about 22 weeks after surgery. Early try at tenolysis deprive the healing tendon of its nutrition and predisposes it to a rupture. It is prudent to keep up the efforts of rehabilitation for six months earlier than deciding to do a tenolysis. The early management of adhesions contains mild stretching followed by serial casting with a every day change in the plaster. Cylindrical corrective casts may be utilized to the involved finger and altered day by day with an hour or two of supervised mobilization. The Capener sort spring loaded splints and dorsal gutter rubber splints with adjustable straps are splints that are helpful for stretching out contractures. Localizing the world of adhesions is essential to limit the surgical publicity and to maximize the end result. When the passive vary of motion at a joint is significantly more than the active vary with full effort, adhesion formation must be thought-about. The actual web site of adhesions can additional be localized by the presence of a fixed lengthlike phenomenon on passive examination. The use of excessive frequency dynamic ultrasonography in identifying adhesions and tendon excursion is invaluable but needs an skilled sinologist and a linear array transducer. The flexor profundus and sublimis can also adhere to one another and must be separated. Tenolysis is greatest done underneath distal anesthetic blocks with the affected person conscious. The patient could thus actively flex and show the benefit and adequacy of the procedure. Ruptures Struggling and shivering during reversal after a general anesthetic or when being shifted out of a very cold operating room to a warm ward could cause irregular forces on the restore causing it to rupture. At 3 weeks, when the protective plaster support is discarded, the patient should be warned to be careful to progressively increase the loading on the finger. Attempts to use sprays utilizing the injured finger to press the nozzle and other such innocuous however powerful activity can lead to disruption of the nascent therapeutic of the tendon. Power grip and strong pinch is to be prevented for an extra 3 weeks until the tendon has gained sufficient strength for such actions. As the tendons transfer away and the moment arm increases, the efficiency of the tendon to carry out its perform efficiently decreases. During these reconstructions, a silicone rubber tem porary prosthesis (Hunter) is useful to maintain the lumen of the tendon sheath, while the grafted pulleys are therapeutic. Important donors of the graft are palmaris longus, sublimis, extensor of a toe and plantaris. Ask the affected person to oppose the tips of the thumb and ring finger while flexing the wrist whereas revisiting wrist flexion. The use of blunt malleable probes or bougies to attempt to trace the original passage, which is bound to have collapsed should be carried out with plentiful caution. The distal attachment of the tendon to the terminal phalanx may be done by any certainly one of many profitable strategies. The classical Bunnell tendon to bone insertion is troublesome and the delicate terminal phalanx must be dealt with fastidiously. Pulling out the terminal portion of the graft from the fingertip, having drawn it across the pulp, is a good method. In addition, the graft could also be passed via the stump of the profundus and stitched to it. Anchoring the tendon to the bone utilizing micromini anchors is beneficial in newer papers. Following adjusting the tension and doing the proximal repair, the finger will lie in flexion. The proximal junction is related to the profundus tendon, distal to the origin of the lumbricals.

Order avodart discountAcknowledgment the authors like to thank Dr Jeyapalan (Consultant Radiologist) for providing some of the images which might be getting used in this book chapter. An international survey of hospital apply within the imaging of acute scaphoid trauma. The suspected scaphoid harm: resource implications within the absence of magnetic resonance imaging. Diagnostic accuracy of imaging modalities for suspected scaphoid fractures: meta-analysis Fractures of Other Carpal Bones Kim et al. Undisplaced capitate fractures are treated by closed discount and solid and displaced capitate fractures require operative reduction and inner fixation. Pisiform fractures are generally as a outcome of direct trauma or due to avulsion of Flexor carpi ulnaris tendon. Most fractures are handled nonoperatively and pisiform may be excised if still symptomatic. Prediction of consequence of non-operative therapy of acute scaphoid waist fracture. Management of displaced fractures of the waist of the scaphoid: meta-analyses of comparative research. Union charges after proximal scaphoid fractures: meta-analyses and evaluate of obtainable evidence. Definition of union after acute fracture and surgical procedure for fracture nonunion of the scaphoid. Use of computed tomography to predict union and time to union in acute scaphoid fractures treated nonoperatively. A comparison of the charges of union after cancellous iliac crest bone graft and Kirschner-wire fixation in 1903 12. Interobserver reliability of computed tomography to diagnose scaphoid waist fracture union. Analysis of carpal malalignment attributable to scaphoid nonunion and evaluation of corrective bone graft on carpal alignment. The collaborating bones of the wrist, specifically, the scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate and the hamate are intricately linked to one another. The identical wrist can also be able to transmitting immense masses across its constituents and onto the distal radius and ulna with consummate ease. Instability of the carpal bones has long been an space of interest for hand and upper limb surgeons. The complexities concerned have only succeeded in complicated and confounding the situation. Newer modalities of visualization and investigations have, within the recent previous, shed immense mild on the kinematics of the wrist joint. The lunate finds its way through this weak spot to dislocate out from its position in perilunate dislocations. Apart from the thumb ray, all the ulnar 4 rays are practically fastened to the bases of the metacarpals. The distal radius has a separate scaphoid fossa and a lunate fossa to home these two bones. The distal radial anatomy is answerable for the style by which the carpal bones move during wrist movements. The ligaments of the wrist are complicated in nature and a fundamental understanding of the identical is essential. They could additionally be divided into extrinsic and intrinsic ligaments for the purpose of debate. The palmar and dorsal elements of each of those are strikingly totally different and must be considered in detail. The dorsal intercarpalligament and the dorsal radiocarpal ligament are vertically oriented. This is likely considered one of the strongest ligaments and remains as the last intact ligament in a perilunate dislocation. On the ulnar aspect, the ulnocarpal ligaments include the oblique ulnocapitate ligament and deeper to this ligament are the ulnolunate and the ulnotriquetral ligaments that are vertical. The other ligament on the dorsum fans out from the triquetrum to the radial aspect and inserts on the scaphoid, the trapezium and trapezoid. The palmar and dorsal elements of the scapholunate ligament are sometimes ligamentous. The proximal portion of the scapholunate ligament is a fibrocartilaginous membrane. The lunotriquetral articulation is in many ways similar to the scapholunate articulation. The dorsal intercarpal ligament stretches between the triquetrum on the ulnar side and fans out to insert on the scaphoid, the trapezium and the trapezoid dorsally. On the volar aspect brief fan formed ligaments and appear to radiate from the capitate to the trapezoid, the scaphoid, the triquetrum and the hamate. The short intrinsic ligaments join each bone to its adjacent mate and are often aligned perpendicular to the bone margins. Trying to perceive the complex movement patterns and cargo transmission throughout the wrist, each has contributed in some measure to demystify this. Dividing the carpal bones into three vertical rows and attributing a perform to each was the simplistic manner during which Navarro interpreted carpal kinematics. The central column of lunate, capitate and hamate were attributed the perform of flexion-extension whereas the scaphoid, trapezium and trapezoid contributed to the lateral column that was supposedly the load bearing column. The ulnar column was related to rotation and included the triquetrum and the pisiform. Taleisnik3 included the trapezium and trapezoid within the central column and excluded the pisiform. The distal carpal row is extra or less mounted to the metacarpal bases with little or negligible motion occurring at these articulations. The cell proximal row is linked within the method of a ring to the capitate and hamate. The actions of this row is additional depending on the shapes of the confines of the radiocarpal joint and the degree of flexibility of the ligaments connecting the bones of the proximal row. The full range of dorsiflexion (75 degrees) and palmar flexion (80 degrees) happens as a composite of actions on the radiocarpal and the midcarpal joints. Almost 60% of the palmar flexion and 30% of the dorsiflexion occurs at the midcarpal joint. There is clearly extra ulnar deviation (40 degrees) as in comparability with radial deviation (20 degrees) on the wrist. The actions of the midcarpal joint have been the focus of attention of many employees within the latest previous.
Order cheap avodart onlineWith continual tears, thickening of the tendon on the rupture web site is seen together with disruption of the conventional echo sample. Magnetic Resonance Imaging the normal patellar tendon demonstrates homogeneous low sign depth throughout a lot of its course on proton density images. Hemorrhage and edema may also be seen to extend posteriorly to the infrapatellar fat pad. The role of mechanical loading in tendon development, maintenance, injury, and restore. Mersilene strip suture in restore of disruptions of the quadriceps and patellar tendons. Ipsilateral hamstring tendon graft reconstruction for continual patellar tendon ruptures: average-5. Reconstruction of patellar tendon disruption after total knee arthroplasty: results of a brand new technique using artificial mesh. Separate vertical wiring for the fixation of comminuted fractures of the inferior pole of the patella. Fixation of patella fractures with braided polyester suture: a biomechanical study. Clinical experience of patellar fracture fixation utilizing steel wire or non-absorbable polyester-a study of 37 circumstances. Outcomes after operative fixation of complete articular patellar fractures: assessment of practical impairment. Complications following tension-band fixation of patellar fractures with cannulated screws compared with Kirschner wires. Uber die kneischeibenbriiche und ihre behandlung mit besonderer berocksichtigung der dauerresultate im licht der nachuntersuchungen. Influence of evident components on the tendency to redislocation and the therapeutic outcome. Inferior patellar pole avulsion fractures: osteosynthesis compared with pole resection. In the Schatzker system, fracture sorts are categorised in what was presumed to be an increasing order of severity. In clinical apply, the coronal posteromedial fragment is difficult to stabilize through a regular medial approach with a medial buttress plate. In addition, these posteromedial fractures are often difficult by posterolateral tibial plateau impaction, which is tough to scale back and repair. The fracture sample dictates the remedy plan, the chance for complications, and, to some extent, the affected person end result. Because different fracture patterns require completely different affected person positioning, surgical approaches, and treatment methods, it may be very important distinguish significantly different accidents from each other. In this fashion, therapy could be matched to the fracture sample, which may optimize outcomes and enhance communication between physicians. A thorough understanding of fracture morphology might help surgeons better understand the mechanism of damage and permit them to plan and select the appropriate surgical procedures. However, presently, no consensus has been made regarding the classification of medial tibial plateau fracture patterns. Bilateral dual plating is often recommended because the particular fixation for this type of fracture. Traditionally, the treatment for tibial plateau fractures is predicated on two-dimensional classification methods. Most of the present classification systems for tibial plateau fractures use two-dimensional images, which often direct surgeons to pay consideration to medial and lateral fixation without considering of posterior fixation. This fixation idea for tibial plateau fractures has been poorly reported in the English literature. Multiplanar advanced tibial plateau fractures, particularly these involving the posterior column, are quite difficult to handle clinically. With this method, posterior column fixation is careworn when the fractures contain the posterior side of the plateau. Some of those fractures are simple to misunderstand, particularly fractures involving the posterior facet of the tibial plateau. As a outcome, 43% (18 of 42) of the fractures had been underneath evaluated by plain radiographs. On the other hand, such fractures may be difficult to fit into the classification systems at present used, which makes diagnosis and preoperative planning troublesome. For example, when the fracture entails the posterior�lateral facet of the plateau, the fracture could be visible by way of an anterior method, however the reduction and fixation are quite difficult, especially for these without an intact posterior cortex (disruption of the posterior column). Direct discount via posterior approaches and posterior buttress plating has been recommended by a number of authors. A bilateral twin plating method using a posterior-medial strategy combined with an anterior-lateral approach has been suggested by several authors. Posterior-lateral depressed fracture fragments are impossible to deal throughout the supine place and can solely be lowered and buttressed posteriorly within the inclined position. Unilateral locking plates have additionally been used to deal with complicated tibial plateau fractures. The different shapes and morphologic features of these fragments implicated supplementary fixation when managing such a fracture. The posterolateral strategy creates problems around the publicity of the widespread peroneal nerve and management of posterior tibial recurrent artery (a department from the proximal part of the anterior tibial artery). The lateral column fracture is normally manipulated with minimal invasive strategies; the small proximal incision is used to cut back the articular floor and the metaphyseal area is plated percutaneously. Coronal computed tomography scan indicating each medial and lateral columns are concerned. If operative therapy is chosen, fixation must be stable enough to enable early mobilization with none wound issues. This subclassification system could improve the understanding of fracture anatomy, preoperative remedy planning, the discount and fixation technique and patient practical outcome. This tends to happen in older people, and, if the despair is more than 5�8 mm or instability is present, most should be treated by open reduction, elevation of the depressed plateau "en mass," bone grafting of the metaphysis, fixation of the fracture with cancellous screws and buttress plating of the lateral cortex. After elevation, the created void should be supported by bone grafting and stabilized by cancellous and buttress plate. However, use of buttress plate is advisable to protect the lateral condyle from late collapse and valgus deformity. Routinely an anterolateral submeniscal strategy is taken to expose the depressed fragment. A separate incision is taken medially on the metaphyseodiaphyseal region where a small window is made. The operative technique entails inser tion of impactor by way of this window nicely beneath the depressed articular fragments, and by sluggish and meticulous pressure, elevation of the articular fragments and compressed cancellous bone as one massive mass. The impactor is passed to elevate the depressed fragment beneath fluoroscopic management and direct visualization of articular fragment via submeniscal view. Once the elevation of the fragment is satisfactorily achieved temporary stabilization by two K-wires is completed.
References - Zuckerman JM, McCammon KA, Tisdale BE, et al: Outcome of penile revascularization for arteriogenic erectile dysfunction after pelvic fracture urethral injuries, Urology 80:1369n1373, 2012.
- McKenzie CH: Dystocia due to solitary pelvic ectopic kidney, J Lancet 70:215n217, 1950.
- Kelami A: Implantation of small-carrion prosthesis in the treatment of erectile impotence after priapism: difficulties and effects, Urol Int 40(6):343n346, 1985.
- Ahn JJ, Shnorhavorian M, Oelschlager A-MEA, et al: Use of 3D reconstruction cloacagrams and 3D printing in cloacal malformations, J Pediatr Urol 13(4):395.e1-395.e6, 2017.
- Acimi S: Vaginoplasty using the inner surface or mucosa of the prepuce in children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia, J Pediatr Urol 9(6 Pt B):1038n1042, 2013.
|
|