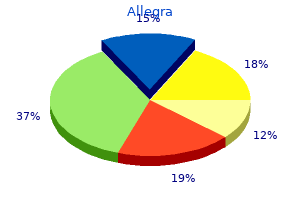
"Order allegra 180mg without a prescription, allergy testing groupon."By: Danielle Marie Brander, MD - Assistant Professor of Medicine
- Member of the Duke Cancer Institute
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/danielle-marie-brander-md
Buy cheap allegra 180 mg onlineAs they enter the vertebral canal, the spinal arteries divide into postcentral, prelaminar and radicular branches. The postcentral branches, which are the main nutrient arteries to the vertebral our bodies and to the periphery of the intervertebral discs, anastomose beneath the posterior longitudinal ligament with their fellows above and under, in addition to throughout the midline. The majority of the vertebral arch, the posterior epidural tissues and dura and the ligamentum flavum are provided by the prelaminar branches and their anastomotic plexus on the posterior wall of the vertebral canal. Veins of the vertebral column kind intricate plexuses alongside the whole column, exterior and internal to the vertebral canal. Both groups are devoid of valves, anastomose freely with each other and join the intervertebral veins. Interconnections are broadly established between these plexuses and longitudinal veins early in fetal life. When development is complete, the plexuses drain into the caval and azygos ascending lumbar techniques via named veins that accompany the arteries described earlier. The veins also communicate with cranial dural venous sinuses and with the deep veins of the neck and pelvis. The venous complexes related to the vertebral column can dilate significantly and can kind alternative routes of venous return in patients with major venous obstruction within the neck, chest or abdomen. The absence of valves allows pathways for the wide and sometimes paradoxical spread of malignant illness and sepsis. Those on the temporal lobe anastomose with basal veins and center cerebral veins and drain to the cavernous, superior petrosal and transverse sinuses. Several days later he notes increasing pain in and across the left eye, along with double vision, lid ptosis and protrusion of the affected eye. On examination, he demonstrates unilateral exophthalmos, ptosis, ophthalmoparesis, orbital oedema and papilloedema with retinal haemorrhages. Discussion: this man has developed a carotid cavernous fistula secondary to head trauma, with laceration of the carotid artery within the cavernous sinus. In a small proportion of instances the lesion is spontaneous, secondary to rupture of a previously unrecognized carotid aneurysm. Several buildings within the cavernous sinus are variously affected, together with the pulsatile exophthalmos, orbital congestion and oedema secondary to involvement of the carotid artery within the sinus itself. The differential analysis includes, most importantly, cavernous sinus thrombosis secondary to unfold of sepsis from an infection in the sinuses or the upper face. Under these circumstances, the patient is generally febrile and acutely ill; physical findings are otherwise a lot the identical as in a traumatic carotid cavernous fistula, as observed on this affected person. A Postlaminar department Prelaminar branch Radicular (neural) branch Spinal artery Dorsal department Postcentral department Spinal artery Lumbar artery Precentral branches B Posterior central department Anastomosis. B, Arterial anastomoses between postcentral branches of spinal arteries throughout the vertebral canal. External Vertebral Venous Plexuses - the external vertebral venous plexuses are anterior and posterior. Anterior exterior plexuses are anterior to the vertebral our bodies, communicate with basivertebral and intervertebral veins and obtain tributaries from vertebral bodies. Posterior external plexuses lie posterior to the vertebral laminae and around spinous, transverse and articular processes. They anastomose with the internal plexuses and be a part of the vertebral, posterior intercostal and lumbar veins. Internal Vertebral Venous Plexuses - the interior vertebral venous plexuses happen between the dura mater and vertebrae and obtain tributaries from the bones, red bone marrow and spinal wire. They type a denser network than the exterior plexuses and are arranged vertically as 4 interconnecting longitudinal vessels, two anterior and two posterior. The anterior internal plexuses are large plexiform veins on the posterior surfaces of the vertebral our bodies and intervertebral discs. The posterior internal plexuses, on each side in entrance of the vertebral arches and ligamenta flava, anastomose with the posterior external plexuses by way of veins that move via and between the ligaments. Around the foramen magnum they kind a dense community connecting with vertebral veins, occipital and sigmoid sinuses, the basilar plexus, the venous plexus of the hypoglossal canal and the condylar emissary veins. Basivertebral Veins - the basivertebral veins emerge from the posterior foramina of the vertebral bodies. They are giant and tortuous channels in 104 Chapter 6 / Vascular Supply of the Brain and Spinal Cord A Anterior inside vertebral (epidural) venous plexus Posterior internal vertebral (epidural) venous plexus Anterior exterior vertebral venous plexus Basivertebral vein Posterior external vertebral venous plexus Intervertebral vein B Posterior exterior plexus Anterior inner plexus Posterior inner plexus Intervertebral vein Segmental vein Basivertebral vein Anterior exterior plexus. The basivertebral veins also drain into the anterior external vertebral plexuses via small openings within the vertebral our bodies. Posteriorly, they type one or two brief trunks that open into the transverse branches and unite the anterior inside vertebral plexuses. Intervertebral Veins - the intervertebral veins accompany the spinal nerves by way of intervertebral foramina, draining the spinal wire and inside and exterior vertebral plexuses and ending within the vertebral, posterior intercostal, lumbar and lateral sacral veins. Upper posterior intercostal veins may drain into the caval system by way of brachiocephalic veins, whereas the lower intercostals drain into the azygos system. Lumbar veins are joined longitudinally in front of the transverse processes by the ascending lumbar veins, during which they might terminate. Alternatively, they could proceed across the vertebral bodies to drain into the inferior vena cava. Whether the basivertebral or intervertebral veins contain efficient valves is uncertain, but experimental proof strongly suggests that their bloodflow could be reversed (Batson 1957). Three major longitudinal vessels-a single anterior and two posterior spinal arteries (each of which is typically doubled to pass on either facet of the dorsal rootlets)-originate intracranially from the vertebral artery and terminate in a plexus across the conus medullaris. The anterior spinal artery types from the fused anterior spinal branches of the vertebral artery and descends within the anterior median fissure of the twine. Each posterior spinal artery originates either directly from the ipsilateral vertebral artery or from its posterior inferior cerebellar branch and descends in a posterolateral sulcus of the twine. The segmental arteries are derived in craniocaudal sequence from spinal branches of the vertebral, deep cervical, intercostal and lumbar arteries. These vessels enter the vertebral canal via the intervertebral foramina and anastomose with branches of the longitudinal vessels to kind a pial plexus on the floor of the twine. The segmental spinal arteries send anterior and posterior radicular branches to the spinal cord alongside the ventral and dorsal roots. Most anterior radicular arteries are small and finish in the ventral nerve roots or in the pial plexus of the twine. The small posterior radicular arteries also provide the dorsal root ganglia; branches enter at both ganglionic poles to be distributed round ganglion cells and nerve fibres. Segmental Medullary Feeder Arteries - Some radicular arteries, primarily situated within the decrease cervical, lower thoracic and higher lumbar regions, are massive enough to attain the anterior median sulcus, the place they divide into slender ascending and huge descending branches. They anastomose with the anterior spinal arteries to kind a single or partly double longitudinal vessel of uneven calibre alongside the anterior median sulcus. The largest anterior medullary feeder, the good anterior segmental medullary artery of Adamkiewicz, varies in stage, arising from a spinal branch of one of the lower posterior intercostal arteries (T9�11) or subcostal artery (T12) or, less regularly, a spinal branch of the higher lumbar arteries (L1 and L2). Reaching the spinal wire, it sends a branch to the anterior spinal artery below and another to anastomose with the ramus of the posterior spinal artery, which lies anterior to the dorsal roots. Central branches of the anterior spinal artery enter the anterior median fissure and then flip right or left to supply the ventral gray column, the base of the dorsal grey column, including the dorsal nucleus, and the adjoining white matter. Each posterior spinal artery contributes to a pair of longitudinal anastomotic channels, anterior and posterior to the dorsal spinal roots.
Order allegra with amexThe first commissures to develop are these related to the palaeocortex and archicortex. Fibres of the olfactory tracts cross in the ventral or decrease part of the lamina terminalis and, together with fibres from the piriform and prepiriform areas and the amygdaloid our bodies, type the anterior part of the anterior commissure. In addition, the 2 hippocampi turn out to be interconnected by transverse fibres that cross from fornix to fornix within the higher a part of the lamina terminalis as the commissure of the fornix. The commissures of the neocortex develop later and observe the pathways already established by the commissures of the limbic system. Fibres from the tentorial floor of the hemisphere be part of the anterior commissure and constitute its bigger posterior half. All the opposite commissural fibres of the neocortex affiliate themselves intently with the commissure of the fornix and lie on its dorsal floor. These fibres increase enormously in number, and the bundle rapidly outgrows its neighbours to form the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum originates as a thick mass connecting the two cerebral hemispheres around and above the anterior commissure. The rostrum of the corpus callosum develops later and separates a half of the rostral end of the limbic space from the remainder of the cerebral hemisphere. Further backward growth of the trunk of the corpus callosum then results in the entrapped part of the limbic space changing into stretched out to kind the bilateral septum pellucidum. As the corpus callosum grows backward, it extends above the choroidal fissure, carrying the commissure of the fornix on its undersurface. In this way a brand new ground is formed for the longitudinal fissure, and extra constructions come to lie above the epithelial roof of the third ventricle. In its backward growth, the corpus callosum invades the world hitherto occupied by the upper a part of the archaeocortical hippocampal formation, and the corresponding elements of the dentate gyrus and hippocampus are lowered to vestiges, the indusium griseum and the longitudinal striae. However, the posteroinferior (temporal) archaeocortical areas of both the dentate gyrus and the hippocampus persist and enlarge. First, the neuroblasts turn into apposed to the radial glial cells and establish an axis of polarity away from the ventricular floor. They then continue to differentiate according to their ultimate place, and later-born neuroblasts migrate past them toward the pial floor. Cortical neurones or cerebellar granule cells appear equally capable of migrating on hippocampal or cerebellar Bergmann glia, indicating conservation of migration mechanisms in different mind areas. Various lines of proof help the proposal that the laminar destiny of neurones is set previous to migration. In the mutant reeler mouse, laminar formation is inverted so that layers type in an outside-in quite than insideout array, but axonal connections and neuronal properties appear regular, suggesting that the cells differentiate according to their time of origin quite than their location. Likewise, the prevention of neuronal migration by irradiation results in the manufacturing of cells that remain apposed to the ventricular surface however develop an applicable phenotype and efferent projections. Transplantation of labelled cells suggests that dedication to a particular cortical lamina happens shortly after S part. Neurones of preexisting laminae which have begun axonogenesis might present suggestions on the forming cortical layers, offering a type of developmental clock for histogenesis. These include major areas such as the motor cortex, unimodal association areas involved with the mixing of data from one of the main areas and multimodal affiliation areas that integrate info from multiple modality. There are also areas involved with features which might be even much less nicely understood, such as the frontal lobes, concerned with goal-orientation duty and long-term planning. Moreover, some neurones might migrate tangentially on the radial glial cells, on account of glial cell branching in the cortical plate. Two models have been proposed to clarify the development of this complicated cortical group. The radial glial cells translate this map from the ventricular zone to the cortical plate, where the pattern is refined by innervating axons. Any or all of these will be the parts of short-range signalling centres along the perimeters of the cortex. Manipulations of the creating cortex by deafferentation or manipulation of inputs give some indication of the state of commitment of cortical areas. The columnar cells elongate, and their non-nucleated peripheral processes now constitute a marginal zone, while their nucleated, paraluminal and mitosing areas represent the ventricular zone. Some of their progeny leave the ventricular zone and migrate to occupy an intermediate zone. Ultimately, teams of progenitor cells kind: at first, generations of definitive neurones, and later, glial cells that migrate to and mature in their last positions. Subsequently, proliferation wanes in the ventricular zone but persists for appreciable periods in the immediately subjacent subventricular zone. From the pial floor inward, the following zones may be defined: marginal, cortical plate, subplate, intermediate, subventricular and ventricular. The marginal zone provides rise to the outermost layer of the cerebral cortex, and the neuroblasts of the cortical plate and subplate form the neurones of the remaining cortical laminae (the complexity varies in different locations and with further additions of neurones from the deeper zones). The intermediate zone steadily transforms into the white matter of the hemisphere. Meanwhile, different deep progenitor cells produce generations of glioblasts that additionally migrate into the more superficial layers. As proliferation wanes and at last ceases in the ventricular and subventricular zones, their remaining cells differentiate into basic or specialised ependymal cells, tanycytes or subependymal glial cells. The first teams of cells to migrate are destined for the deep cortical laminae, and later teams cross through them to extra superficial regions. The cumulative impact of this radial and tangential progress is clear in a marked improve in cortical thickness and surface area. In the pallial walls of the mammalian cerebral hemisphere, the phylogenetically oldest areas, that are the primary to differentiate throughout ontogeny, are people who border the interventricular foramen and its extension the choroidal fissure, the lamina terminalis and the piriform lobe. Note radial glial cells (black) extending from the internal to external limiting membrane; these provide contact steering paths for neuroblasts. When the lateral geniculate nucleus and the visual cortex had been ablated and space was created within the medial geniculate by ablating the inferior colliculus, cells in the somatosensory or auditory cortex were visually driven, and receptive field and response properties resembled these seen within the visual cortex. These outcomes counsel that the modality of a sensory thalamic nucleus or cortical area may be specified by inputs during growth. The improvement of cortical projections has been investigated by way of both laminar and area-specific connectivity. Recently, attention has centered on the concept that connections might be influenced by the existence of a transient inhabitants of subplate neurones that later dies. The cortex develops inside a preplate, consisting of corticopetal nerve fibres and the earliest generated neurones. This zone is then cut up into two zones-the subplate underneath the cortical plate, and the marginal zone at the pial surface-by the arrival of cortical neurones. Subplate neurones extend axons by way of the internal capsule to the thalamus and superior colliculus earlier than different cortical neurones have been born. Layer 5 neurones in various cortical areas prolong axons to totally different repertoires of targets. For instance, layer 5 neurones of the visible cortex project to the tectum, pons and mesencephalic nuclei, whereas these within the motor cortex project to mesencephalic and pontine targets, the inferior olive and dorsal column nuclei and the spinal cord. An interesting feature of those cortical projections is that they come up by collateral formation quite than by projection of the primary axon or by growth cone bifurcation.
Order allegra 180mg without a prescriptionPlasma albumin binds nonionized calcium (in low-albumin states, less nonionized calcium is protein sure making more out there to return to storage websites, such as bone and teeth). Nonionized plasma calcium ranges must be interpreted with data of the plasma albumin concentration. Calcium is important for neuromuscular transmission, skeletal muscle contraction, cardiac muscle contractility, blood coagulation, and intracellular signaling in its operate as a second messenger. Hypocalcemia may result from decreased plasma focus of albumin, hypoparathyroidism, acute pancreatitis, vitamin D deficiency, persistent renal failure related to hyperphosphatemia, and citrate binding of calcium (in the case of transfused blood, particularly in hepatic failure and reduced citrate metabolism). Hyperparathyroidism is crucial reason for hypercalcemia and may be main from parathyroid adenoma (85%), parathyroid hyperplasia (10%) which can be associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes, or, hardly ever (1%), parathyroid carcinoma. Secondary hyperparathyroidism outcomes from irregular suggestions loops current in failure and tertiary hyperparathyroidism from overactive responses to regular unfavorable feedback mechanisms. Potassium is the second most typical cation within the body and the principal intracellular cation. Disturbances of potassium homeostasis contribute to cardiac dysrhythmias, skeletal muscle weak point, and acid�base disturbances. The kidney is the principal organ involved in physique potassium homeostasis, primarily via control of energetic potassium secretion in the urine. Diuretics that induce renal potassium loss are probably the most typical explanation for hypokalemia. Catecholamines shift potassium intracellularly and agonists could additionally be useful in the remedy of hyperkalemia. Drugs that improve serum potassium concentrations do so by redistribution, Chapter 17 � Intravenous Fluids and Electrolytes 349 suppression of aldosterone secretion, inhibition of potassium secretion in the distal amassing duct, or by direct cell destruction. Extracellular movement of potassium can lead to plasma hyperkalemia without an increase in whole body potassium (succinylcholine causes a release of potassium from skeletal muscle cells, leading to a rise of the serum potassium focus by as a lot as 0. Skeletal muscle weak spot and a predisposition to cardiac dysrhythmias are essentially the most outstanding signs of clinically vital hypokalemia. At the cellular degree, hypokalemia causes hyperpolarity, will increase resting potential, hastens depolarization, and increases automaticity and excitability of cardiac cells, predisposing to tachydysrhythmias. It is important to determine the trigger of hypokalemia before aggressive potassium replacement is initiated (if serum potassium concentrations are acutely decreased because of intracellular redistribution and potassium therapy is initiated, potentially critical hyperkalemia may occur). The choice to deal with hyperkalemia, in contrast to hypokalemia, relies on the degree of improve within the serum potassium focus and the signs and signs which might be current (if the serum potassium focus is 6. Glucose-insulin infusion (50 mL of 50% glucose plus 10 models of regular insulin) produces a sustained switch of extracellular potassium into cells, resulting in a 1. Potassium elimination from the body also could also be achieved by loop diuretics or, most rapidly and effectively, with hemodialysis. Phosphate is the major intracellular anion and the conventional plasma focus of phosphate is three. Phosphorus regulation is a result of the interplay of phosphate and calcium ranges, vitamin D, and parathyroid hormone on gastrointestinal absorption, renal reabsorption, and bone storage. Causes of hypophosphatemia include alcohol abuse, extended parenteral diet, hemodialysis, salicylate poisoning, and gram-negative bacteremia. Iron deficiency is estimated to be current in 20% to 40% of menstruating females however only about 5% of grownup males and postmenopausal females. Causes of iron-deficiency anemia include inadequate dietary intake of iron, increased iron necessities due to being pregnant or blood loss, or interference with absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. Partial gastrectomy, malabsorptive bariatric surgery, and sprue are causes of insufficient iron absorption. Iron deficiency initially leads to a decrease in iron shops and a parallel lower within the erythrocyte content material of iron. Plasma ferritin concentrations of lower than 12 g/dL are diagnostic of iron deficiency. Prophylactic use of iron preparations ought to be reserved for individuals at high risk for growing iron deficiency (pregnant and lactating females, lowbirth-weight infants, females with heavy menses). In iron-deficiency anemia, administration of medicinal iron will increase the rate of erythrocyte production leading to a rise in hemoglobin focus within seventy two hours. Ferrous sulfate administered orally is the most frequent selection for the therapy of irondeficiency anemia and is on the market as syrup, drugs, or tablets. Copper is present is a constituent of enzymes and is an integral part of several proteins. Zinc is an enzymatic cofactor important for cell progress and the synthesis of nucleic acid, carbohydrates, and proteins. Epinephrine is a circulating hormone synthesized, saved, and launched from the adrenal medulla. Its natural functions upon release into the circulation embrace regulation of myocardial contractility, coronary heart rate, vascular and bronchial smooth muscle tone, glandular secretions, and metabolic processes similar to glycogenolysis and lipolysis. It is a potent activator of -adrenergic receptors and likewise activates 1 and a pair of receptors. Epinephrine is poorly lipid soluble, stopping its prepared entrance into the central nervous system and accounting for the shortage of cerebral effects. Clinical makes use of of epinephrine embrace treatment of life-threatening allergic reactions/anaphylaxis, therapy of severe asthma and bronchospasm, administration during cardiopulmonary resuscitation as a significant therapeutic drug, administration during periods of hemodynamic instability to promote myocardial contractility and enhance vascular resistance, and continuous infusion for continuous help of myocardial contractility and vascular resistance. Epinephrine is added to local anesthetic solutions to lower systemic absorption prolonging the length of action of the anesthetic for regional and local anesthesia. The cardiovascular effects of epinephrine result from stimulation of - and adrenergic receptors (see Table 18-1). Smooth muscle tissue of the bronchi are relaxed by epinephrine-induced activation of 2 receptors. Epinephrine has the most important impact on metabolism of all the catecholamines. Release of endogenous epinephrine and the ensuing glycogenolysis and inhibition of insulin secretion is the more than likely clarification for perioperative hyperglycemia. Selective 2-adrenergic agonist results of epinephrine are imagined to reflect activation of the sodiumpotassium pump in skeletal muscles, leading to a transfer of potassium ions into cells. The statement that serum potassium measurements in blood samples obtained immediately before induction of anesthesia are decrease than measurements 1 to three days preoperatively is presumed to reflect stress-induced release of epinephrine. In making therapeutic selections primarily based on a preinduction serum potassium measurement, especially in sufferers with no cause to expertise hypokalemia, one ought to consider the possible role of preoperative nervousness and the discharge of epinephrine. Epinephrine causes contraction of the radial muscle tissue of the iris, producing mydriasis. Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and isoproterenol produce rest of gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Activation of -adrenergic receptors relaxes the detrusor muscle of the bladder, whereas activation of -adrenergic receptors contracts the trigone and sphincter muscular tissues. Hepatosplanchnic vasoconstriction occurs in addition to impaired renal blood flow as cardiac output is diverted to the dilated skeletal muscle vasculature.
Buy allegra 120mg without prescriptionThe most typical side effects of the fibrates are gastrointestinal (abdominal ache, nausea) and headache. Gemfibrozil increases the ldl cholesterol content material of bile (lithogenicity) and may improve the formation of gallstones. The major impact of this fatty acid is to lower plasma concentrations of triglycerides. During surgical procedure, an utilized respiratory physiologist and an understanding of the physiology and pharmacology pertaining to the respiratory system is prime to anesthetic management. The air passages extending from the nares and lips by way of the nasopharynx and oropharynx, by way of the larynx to the cricoid cartilage make up the functional upper airway. The upper airway serves a host of capabilities: warming and humidifying passing air, filtering particulate matter, and preventing aspiration. The higher airway mucosa is extremely vascular and well innervated (must be appreciated when performing nasopharyngeal intubation with endotracheal tubes, nasogastric sumps or feeding tubes, or fiberoptic bronchoscopes). The pharynx is 12- to 15-cm lengthy and is divided into the nasopharynx, the oropharynx, and the laryngopharynx (lying posterior to the larynx). The supine position, sleep, and basic anesthesia may promote obstruction of the oropharynx by the tongue, soft palate, and pharyngeal musculature as their tone decreases. The larynx is a complex construction that lies anterior to the 4th to the 6th cervical vertebrae and consists of several muscles, their ligaments, and associated cartilaginous buildings. The larynx serves as the organ of phonation, plays an essential position in coughing, and in airway protection from aspiration. Note the relationship of the superior laryngeal, inferior laryngeal, and recurrent laryngeal nerves and the posterior side of the larynx, thyroid, and trachea. Essential anatomy and physiology of the respiratory system and pulmonary circulation. The paired vocal cords connect posteriorly to the vocal course of of every arytenoid and anteriorly meet at the junction of the thyroepiglottic ligament of the anterior portion of the thyroid cartilage. The triangular opening formed by the vocal ligaments is the glottis with its apex anteriorly. Note the triangular-shaped glottic introitus with its narrowest facet at the anterior commissure. The airways proceed to divide into smaller diameter conduits till one arrives on the bronchioles with diameters lower than 0. The average distance from the tracheal carina to the take-off of the best higher bronchus is 2. Blood move via the pulmonary circulation is generally equal to the blood circulate through the systemic circulation (a major exception being intracardiac shunting when it exceeds systemic circulation). Only one-third of the bronchial circulation returns to the systemic venous system; the rest drains into the pulmonary veins and this constitutes the largest portion of the normal extrapulmonary venoarterial shunt. This bronchial shunt is lower than 1% of the cardiac output in wholesome individuals however may increase to 10% in bronchiectasis, emphysema, and some congenital cardiac circumstances. The bony thorax is composed of the 12 ribs, the sternum anteriorly, and the thoracic vertebral column posteriorly. Expansion of the chest cavity occurs when three respiratory muscle teams (diaphragm, intercostal, and accessory) work in live performance. The diaphragm is exclusive in that its muscle fibers radiate from a central tendinous structure to insert peripherally on the ventrolateral facet of the primary three lumbar vertebrae, the aponeurotic arcuate ligaments, the xiphoid process, and the higher margins of the decrease six ribs. Contraction of the diaphragm causes a big caudal displacement of the central tendon resulting in a longitudinal enlargement of the chest cavity. The supine and Trendelenburg positions or surgical retractors can significantly interfere with this stomach movement particularly within the morbidly obese, necessitating managed air flow underneath anesthesia. Expiration is a passive course of in quiet respiration and is essentially the response to rest of the inspiratory muscles and the balance of forces generated by the elastic recoil of the lungs and chest wall. Innervation of the stomach musculature is from thoracic nerves 7 via 12 and the first lumbar nerve. The basics of mechanical function of the respiratory system are the interaction of two opposing springs: the chest wall, which at relaxation is making an attempt to increase, and the lungs, which at rest try to contract. The lungs and chest wall transfer collectively as a unit (made attainable by the enclosed, air-tight thoracic cavity the place the outer surface of the lungs and its visceral pleura are in shut proximity to the parietal pleura, covering the internal surface of the chest wall and the mediastinal structures). Pathologic circumstances such because the introduction of air or blood into the intrapleural house (pneumothorax, empyema, pleural effusion, bronchopleural fistula) can quickly disrupt this lung�chest wall interplay, resulting in a compromise in respiratory perform but in addition intervene with cardiovascular operate. By conference, the static and dynamic subdivisions of fuel contained throughout the lung are given a typical nomenclature of volumes and capacities (Table 24-1). Complete pulmonary function testing in the laboratory will commonly report measurements of quantity ratios, flows, lung resistance, and lung diffusion capacity for carbon monoxide (Dlco). These values are in comparability with normal information for age, sex, and top and given a proportion of predicted worth. This leads to the increase of venoarterial admixture ("shunt") and reduce in arterial oxygen tension (Pao2) seen in the aged and through basic anesthesia. Resistance in the respiratory system is necessary as a outcome of, within the perioperative interval, issues similar to bronchospasm or secretions in an endotracheal tube or partial circuit obstruction will present primarily as increased resistance. Work of respiratory is commonly used to denote the ongoing power expenditure required by the respiratory system. The oxygen requirement for the work of respiratory is lower than 2% of the normal basal oxygen consumption (3 to 4 mL/kg/minute). The diaphragm could be rested for a brief interval by mechanical air flow however histologic evidence of muscle fiber atrophy can be seen after as little as 18 hours of mechanical ventilation and scientific proof of weakness is seen within days. Pulmonary circulation consists of the pulmonary circulation from the principle pulmonary artery and the smaller bronchial circulation arising from the aorta. The bronchial circulation serves to present dietary support to the airways and their related pulmonary blood vessels. Despite receiving all of the cardiac output from the proper ventricle, the pulmonary vasculature maintains a comparatively low pulmonary blood stress. This matching is closer throughout spontaneous air flow than throughout positive strain ventilation. With constructive stress ventilation, the consequences of alveolar stress are elevated and pulmonary blood circulate distribution becomes much less homogeneous (concept of perfusion zones of the lung). Dead house could be subdivided into physiologic lifeless space and equipment useless house (breathing circuit). Airway useless space is comparatively fixed however does differ immediately with lung volume and bronchodilation will increase airway useless space. A healthy particular person, respiratory spontaneously, may have practically no alveolar useless area. In the upright position, each ventilation and blood circulate are larger on the base of the lung than at the apex. Alveolar useless house, nonetheless, turns into clinically essential during positive strain air flow and in any situation of altered hemodynamics. Decreased cardiac output, pulmonary embolism, and modifications in posture will all have clinically important results on alveolar useless house. Shunt or venous admixture is the portion of the venous blood returned to the guts that passes to the arterial circulation with out being uncovered to usually ventilated lung models. This classic description primarily based on the work of West divides pulmonary blood circulate into four zones.
Discount allegra 180 mg visaPatients with myasthenia gravis are uniquely prone to skeletal muscle weak spot if treated with an aminoglycoside. Macrolides are stable within the presence of acidic gastric fluid, and as a result, these antimicrobials are properly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Erythromycin has a spectrum of exercise that includes most gram-positive bacteria. Oral erythromycin prolongs cardiac repolarization and is associated with reports of torsades de pointes. Azithromycin resembles erythromycin in its antimicrobial spectrum, however an extraordinarily prolonged elimination half-time (68 hours) permits once-a-day dosing for five days. Large doses of clindamycin can induce profound and long-lasting neuromuscular blockade within the absence of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants and after full recovery from the results of succinylcholine has occurred. Vancomycin is a bactericidal glycopeptide antimicrobial that impairs cell wall synthesis of gram-positive micro organism. The oral route of administration is used only for the remedy of staphylococcal enterocolitis and antimicrobial-associated pseudomembranous enterocolitis (poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract). Concomitant administration of an aminoglycoside is commonly necessary when vancomycin is used within the treatment of enterococcal endocarditis. Vancomycin is the drug of selection within the therapy of infections brought on by methicillin-resistant S. Infusion over 60 minutes produces sustained plasma concentrations for up to 12 hours. Rapid infusion (30 minutes) of vancomycin has been associated with profound hypotension and even cardiac arrest. Hypotension is usually accompanied by signs of histamine release characterised by intense facial and truncal erythema ("red man syndrome"). Arterial hypoxemia manifesting as an sudden lower in the Spo2 could happen in association with vancomycin administration, perhaps reflecting druginduced vasodilation in the lungs resulting in a rise in air flow to perfusion mismatching. Oral H1 (diphenhydramine 1 mg/kg) and H2 (cimetidine 4 mg/kg) receptor antagonists administered 1 hour before induction of anesthesia lower histamine-related side effects of rapid vancomycin infusion (1 g over 10 minutes). Ototoxicity is likely when persistent high plasma concentrations (30 g/mL) are current. The administration of vancomycin to a patient recovering from succinylcholine-induced neuromuscular blockade has resulted in a return of neuromuscular blockade. Bacitracins are a group of polypeptide antibiotics efficient against quite so much of gram-positive bacteria. Use of these antimicrobials is restricted to topical software in ophthalmologic and dermatologic ointments. Metronidazole is bactericidal against most anaerobic gram-negative bacilli and Clostridium species. Concurrent ingestion of alcohol might cause a reaction much like that produced when alcohol is ingested by patients taking disulfiram. Fluoroquinolones are broad-spectrum antimicrobials which are bactericidal against most enteric gram-negative bacilli. The dose of the fluoroquinolones ought to be decreased in the presence of renal dysfunction. Fluoroquinolones have been helpful clinically within the therapy of genitourinary and gastrointestinal infections. Fluoroquinolones are associated with an elevated risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture. Ciprofloxacin is highly efficient within the therapy of urinary and genital tract infections, together with prostatitis, and gastrointestinal infections. Moxifloxacin is lengthy acting for the treatment of acute bacterial sinusitis, acute bacterial exacerbation of persistent bronchitis, community-acquired pneumonia, skin infections, and sophisticated intraabdominal infections. Decontamination of the pores and skin with antiseptic preparations reduces the burden of pores and skin flora (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention tips suggest showering or bathing with an antiseptic resolution before surgery). Alcohols are applied topically to lower native cutaneous bacterial flora (quick drying and antisepsis) earlier than penetration of the skin with needles. On the skin, 70% ethyl alcohol kills practically 90% of the cutaneous bacteria within 2 minutes. Alcohol-based surgical options can create a fireplace hazard (flash fire) especially if the answer is allowed to pool. Chlorhexidine disrupts cell membranes of the bacterial cells and is effective in opposition to each gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. As a hand wash or surgical scrub, 2% chlorhexidine causes a greater initial decrease in the number of regular cutaneous bacteria than does povidone-iodine or hexachlorophene. Iodine is a rapid-acting antiseptic that, within the absence of organic material, kills micro organism, viruses, and spores (1% tincture of iodine will kill 90% of the bacteria in ninety seconds, whereas a 5% resolution achieves this response in 60 seconds). Iodophors are a free complex of elemental iodine with an organic provider that not solely will increase the solubility of iodine but additionally provides a reservoir for sustained launch (most broadly used iodophor is povidone-iodine). The iodophors have a broad antimicrobial spectrum and are widely used as hand washes, including surgical scrubs; preparation of the skin earlier than surgical procedure or needle puncture; and treatment of minor cuts, abrasions, and burns. A normal surgical scrub with 10% povidone-iodine options (Betadine) will lower the same old cutaneous bacterial inhabitants by greater than 90%, with a return to normal in about 6 to eight hours. A disinfectant which incorporates an iodophor in isopropyl alcohol (DuraPrep) is more effective than povidone-iodine in decreasing the number of optimistic pores and skin cultures. Chemical burns to the cornea could follow publicity (accidental splashes) to a variety of disinfectant options (chlorhexidine, hexachlorophene, iodine, alcohol, detergents containing iodine-based solutions). Povidone-iodine answer without detergent appears to be least poisonous to the cornea. Quaternary ammonium compounds are bactericidal in vitro to all kinds of gram-positive and gram-negative micro organism. Alcohol enhances the germicidal exercise of quaternary ammonium compounds in order that tinctures are simpler than aqueous solutions. Chapter forty one � Antimicrobials, Antiseptics, Disinfectants 681 these compounds could additionally be used preoperatively to lower the variety of microorganisms on intact skin. Quaternary ammonium compounds have been broadly used for the sterilization of instruments (endoscopes and different instruments made of polyethylene or polypropylene absorb quaternary ammonium compounds, which can lower the concentration of the energetic ingredient to beneath a bactericidal concentration). Hexachlorophene (pHisoHex) is a polychlorinated bisphenol that displays bacteriostatic activity in opposition to gram-positive however not gram-negative organisms. Immediately after a hand scrub with hexachlorophene, the cutaneous bacterial population could additionally be decreased by solely 30% to 50% in contrast with greater than 90% following use of an iodophor. After 60 minutes, the bacterial inhabitants surviving a hexachlorophene scrub will decrease to about 4%, whereas with the iodophor scrub, the bacterial inhabitants could have recovered to about 16% of normal. Hexachlorophene may be absorbed by way of intact skin in adequate amounts to produce neurotoxic results, including cerebral irritability. Formaldehyde is a risky, wide-spectrum disinfectant that kills micro organism, fungi, and viruses by precipitating proteins (used to disinfect surgical instruments). Glutaraldehyde is much less risky than formaldehyde and hence causes minimal odor and irritant fumes.
Buy allegra with amexPreterm labor may be managed with acceptable tocolytic medicine (postoperative ache medications may make it troublesome for the affected person to observe early contractions). Venous thrombosis prophylaxis must be instituted until surgically contraindicated. The maternal blood concentration of a drug is often the first determinant of how a lot drug will ultimately reach the fetus. Placental switch of unstable brokers, benzodiazepines, local anesthetics, and opioids is facilitated by the comparatively low molecular weights, neutral charge, and relative lipophilicity of these medication. Fetal blood is more acidic than maternal and the lower pH creates an setting where weakly fundamental medication corresponding to native anesthetics can cross the placenta as a nonionized molecule and turn out to be ionized within the fetal circulation (ion trapping). During fetal distress (lower pH within the fetal circulation), greater concentrations of weakly fundamental medication such as local anesthetics can be trapped. The anatomy of the fetal circulation helps to decrease fetal exposure to doubtlessly high concentrations of medication in umbilical venous blood. Drugs coming into the fetal inferior vena cava via the ductus venosus are initially diluted by drug-free blood returning from the fetal decrease extremities and pelvic viscera of the fetus (these anatomic characteristics of the fetal circulation markedly lower fetal plasma drug concentrations in comparability with maternal concentrations). In common, the second trimester is most popular for surgical intervention as it is a interval after much organogenesis has taken place and yet minimizes the chance of preterm labor associated with the third trimester. Monitoring for contractions is beneficial and, in some situations, suppression with magnesium is really helpful after surgery. As the long-term impact of basic anesthesia on the fetus is unknown, regional anesthesia is favored when attainable for the surgical procedure. Spinal reflex responses to noxious stimuli occur early in fetal growth earlier than cortical connections are practical. Later in fetal growth, a noxious stimulus will activate a peripheral sensory neuron that project to neurons that kind the spinothalamic tract. Heart failure is probably the most frequent explanation for hospitalization in sufferers older than sixty five years of age. It is necessary to separate the cardiovascular results of growing older from these of widespread diseases with increased prevalence within the aged (atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes mellitus). The coronary heart increases in measurement during growing older because of concentric ventricular hypertrophy that happens in response to the increase in left ventricular afterload. The coronary heart fee response to extreme train is diminished (increases in cardiac output in response to extreme exertion are attenuated by approximately 20% to 30%). Cardiac dysfunction in growing older is largely related to impaired diastolic left ventricle function with increased prevalence of diastolic heart failure exacerbated by several coexisting diseases (Table 46-1). Both the heart and vasculature undergo quite a few alterations during growing older on account of deregulation of molecular longevity pathways, resulting in compromised function. Dyspnea in the elderly might point out congestive cardiac failure and/or pulmonary illness. Structural modifications in the large vessels (elongated, tortuous, dilated, intima thickened) are an necessary component of the getting older process and contribute significantly to the age-related changes in the coronary heart. In the aged, the pulse wave is reflected again from the peripheral circulation and augments systolic stress. Diastolic pressure tends to be lower in the elderly than in youthful individuals (pulse stress are elevated and left ventricular afterload is elevated). Age-related endothelial dysfunction could be characterised as a lower in the capability of the endothelium to dilate or contract blood vessels in response to physiologic and pharmacologic stimuli. There are a number of necessary agerelated structural and useful modifications in the cardiac conduction system (sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, and conduction bundles additionally turn into infiltrated with fibrous and fatty tissue). Aging is associated with elevated norepinephrine entry into the circulation and poor catecholamine reuptake at nerve endings (elevated circulating concentrations of norepinephrine are traditional, generating chronically increased adrenergic receptor occupancy). The cardiovascular response to elevated adrenergic stimulation is attenuated by downregulation of postreceptor signaling and lowered contractile response of the myocardium. Receptor downregulation is answerable for the agerelated decline in maximum coronary heart rate throughout exercise. Orthostatic hypotension is widespread in the elderly and is associated with syncope, falls, and cognitive decline. Chapter forty six � Physiology and Pharmacology of the Elderly 753 anesthetics (anesthetic preconditioning) or several transient periods of ischemia (ischemic preconditioning) might enhance tolerance to subsequent ischemia, improve cardiac operate, and cut back infarction size. Anesthetic and ischemic preconditioning may be markedly attenuated in the aged, potentially explaining the problem of translating promising preclinical results to remedy. Decreased respiratory reserve may be unmasked by sickness, surgery, anesthesia, and other perioperative occasions. Common respiratory diseases and the consequences of smoking and environmental pollution frequently exacerbate the decline in respiratory operate with aging (anticipation and amelioration of their effects is critically important to anesthetic management in the aged as postoperative respiratory issues result in 40% of perioperative deaths in patient older than 65 years). The chest wall becomes less compliant with aging, presumably associated to modifications within the thoracic skeleton and a decline in costovertebral joint mobility (produce a restrictive practical impairment). The diaphragm and belly muscular tissues assume a higher function in tidal respiratory (diaphragmatic function declines with age, predisposing the elderly to respiratory fatigue when required to considerably improve minute ventilation). The residual quantity is the amount remaining within the lungs after a maximal expiration. Aging is associated with a progressive increase in residual volume of up to 10% per decade. Airway closure may occur in small airways (1 mm) whose caliber is decided by their transmural pressure. Gas trade impairment as a end result of shunting in areas of airway closure is typical within the aged throughout regular tidal respiration. The supine place makes airway closure throughout regular tidal respiration more likely. Gas trade effectivity declines with growing older on account of increasing intrapulmonary shunting and decreasing lung diffusing capacity (result is a linear decline in resting supine Pao2 between early adulthood and 65 years of age). Cough effectiveness is lowered in the aged due to diminished reflex sensitivity and impaired muscle perform. The will increase in coronary heart rate and minute air flow in response to elevations in Paco2 or decreases in Pao2 are markedly attenuated in the aged. The change in alveolar/arterial oxygen tension with age (shunt fraction or % shunt). Influence of aging on lung function-clinical significance of adjustments from age twenty. The aged are at particular threat from life-threatening respiratory despair within the perioperative period. The incidence of sleep disordered breathing will increase with age, particularly in males (estimated that 20% of elderly individuals have clinically significant obstructive sleep apnea). Obstructive sleep apnea doubles the risk for postoperative delirium in the aged. Hyperthermia and hypothermia in the elderly are poorly tolerated and extreme chilly and heat stress are associated with increased mortality in comparability with youthful individuals (not clear whether the greater susceptibility to thermal stress is expounded to getting older per se or to underlying socioeconomic conditions, basic fitness, activity levels, and the results of coexisting disease within the elderly). The inability to effectively conserve warmth Chapter forty six � Physiology and Pharmacology of the Elderly 757 Table 46-4 Factors Associated with Reduced Resting Core Temperatures within the Elderly Neurologic illness Diabetes Low body weight Lack of self-sufficiency Consumption of lower than two meals per day Smoking Alcohol consumption in the elderly is exacerbated by the age-related decrease in skeletal muscle mass. Aging is related to a decrease in liver mass and hepatic blood flow but hepatocellular metabolic operate seems to be comparatively well preserved all through life. Because first-pass metabolism is reduced, the oral bioavailability of propranolol and labetalol are increased in the aged.
Buy cheap allegra 120 mg onlineThe regular HbA oxygen saturation curve shifts to the left or right secondary to a wide range of physiologic modifications (pH, temperature, 2,3-diphosphoglycerate). The excess hydrogen (H) ions generated in the red blood cell are transferred to the plasma in trade for chloride ion (Cl). Ventilation will improve in a linear trend as Paco2 rises till a maximal stimulation someplace over a Paco2 of 100 mm Hg is reached. Peripheral chemoreceptors are positioned primarily in the carotid our bodies on the bifurcation of the carotid arteries and likewise in aortic our bodies above and under the aortic arch. The hypoxic drive because of the peripheral chemoreceptors is decreased by risky anesthetics (even in very low concentrations such as 0. Several recognized irregular patterns contain dysfunction of the central chemoreceptors. Cheyne-Stokes is probably the most severe type of periodic respiration, which is seen to some degree in neonates and the aged and during sleep in any respect ages. The geometry of the chest and diaphragm is altered under basic anesthesia with leisure of the chest wall and a marked cephalad displacement of probably the most dorsal portion of the diaphragm at end-expiration. Absorption atelectasis can happen when the speed of fuel uptake into the blood exceeds the rate of ventilation of the alveolus (rate of gasoline absorption from unventilated areas is dependent on the initial Fio2). In the spontaneously respiration patient, awake or throughout anesthesia, the majority of fuel trade is due to caudal displacement of the diaphragm, which occurs primarily within the dorsal portions of the thoraces. The weight of the abdominal contents pushes cranially on the dorsal diaphragm and during inspiration, with optimistic stress air flow, gasoline preferentially distributes to the now more compliant ventral portions of the lungs. Matching of ventilation/perfusion is decreased with induction of anesthesia and further decreased with paralysis and optimistic strain ventilation. Approximately 20% of the population has issues of respiration during sleep, ranging from simple loud night time breathing to obstructive sleep apnea. The disturbance of normal sleep leads to daytime somnolence and the periods of hypoxia may contribute to cardiovascular morbidity. Most trendy business vaporizers ship reasonably correct dosages of risky anesthetics at modest elevations (6,000 ft). Pressure in the air-filled cuff of an endotracheal tube or laryngeal mask airway will increase and decrease significantly with modifications in ambient stress, which may be related to medical air transport. Indications include gas embolism, decompression illness, necrotizing soft tissue infections, and carbon monoxide poisoning. Prolonged exposure to a excessive Pao2 causes pulmonary oxygen toxicity and a restrictive lung disease. All airways are proportionately smaller in infants than adults and airway resistance is greater, leading to increased work of breathing at relaxation and particularly during higher or lower airway infections (croup). Hypoxia initially causes increased air flow, as within the grownup, but then leads to a decrease in ventilation. The increased oxygen necessities are met by both elevated minute air flow and elevated cardiac output. Fetal hemoglobin has a low P50 (18 to 19 mm Hg), which will increase oxygen loading within the placenta but decreases oxygen unloading within the tissues. Changes in the respiratory system with age embody decrease of muscle tone within the dilators of Chapter 24 � Gas Exchange 479 the pharynx, predisposing to upper airway obstruction during anesthesia. The imply Pao2 of healthy patients will decline to roughly eighty mm Hg at age 70 years, after which it stays secure. The responsiveness of each central and peripheral chemoreceptors to hypercarbia and hypoxemia decreases with age. Supplemental oxygen have to be administered postoperatively to stop the hypoxemia associated with the unavoidable fall in useful residual capability. The dysfunctional right ventricle is poorly tolerant to sudden increases in afterload such because the change from spontaneous to managed air flow. Chronic recurrent hypoxemia is the trigger of the proper ventricle dysfunction and the following development to cor pulmonale. Positive stress ventilation can be used safely in patients with bullae, offered the airway pressures are kept low. Due to the decrease solubility of nitrogen in plasma compared to nitrous oxide, when a affected person is converted from breathing air to respiratory a combination containing nitrous oxide during anesthesia, the nitrous oxide will diffuse into a bulla quicker than the nitrogen can be absorbed, and the bulla will increase in size with the attendant threat of rupture. Restrictive lung illnesses are often a part of a multisystemic disease process corresponding to connective tissue disorders. The airway stress gradient between the ventilated and nonventilated thoraces tends to encourage blood circulate to the nonventilated lung. Surgery and cardiac output can have variable effects both rising or reducing the proportional flow to the ventilated lung. The supply of medicines to the lungs can have systemic effects and/or direct effects on the airway (inhaled anesthetics have bronchodilatory effects, whereas -adrenergic agonists delivered through aerosol exert direct results on bronchial smooth muscle with few systemic effects). The parasympathetic nervous system regulates airway caliber, airway glandular activity, and airway microvasculature. Anticholinergics can present bronchodilation even within the resting state as a end result of the parasympathetic nervous system produces a basal degree of resting bronchomotor tone. Although the sympathetic nervous system performs no direct role in command of airway muscle tone, 2-adrenergic receptors are present on airway easy muscle cells and cause bronchodilation through stimulatory G mechanisms (allows for pharmacologic manipulation of airway tone). The mainstay of therapy for bronchospasm, wheezing, and airflow obstruction is -adrenergic agonists (typically delivered by way of inhalers or nebulizers). Short-acting 2 agonists similar to albuterol, levalbuterol, metaproterenol, and pirbuterol are prescribed for the rapid relief (rescue therapy) of wheezing, bronchospasm, and airflow obstruction. Long-acting 2 agonists are prescribed for management of signs when rescue therapies are used more than two times per week. Hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia can also happen with 2-agonist therapy but the severity of those unwanted effects tends to diminish with common use. Tolerance to 2 agonists can occur with common use over a interval of weeks and, while not affecting peak bronchodilation, could be evidenced by a lower in the duration of bronchodilation and the magnitude of unwanted effects. Terbutaline may be given orally, subcutaneously, or intravenously; albuterol (salbutamol) could be given intravenously; and epinephrine is often given subcutaneously or intravenously. The side effect profile of systemic adrenergic agonists is much like the aspect impact profile for inhalational adrenergic agonists (tremor, tachycardia). Inhaled anticholinergics are poorly absorbed and therefore severe unwanted aspect effects are unusual (dry mouth, urinary retention, pupillary dilation, blurred vision). The systemically administered anticholinergics atropine and glycopyrrolate act via the same mechanisms as inhaled anticholinergics, however their use is mostly restricted by unwanted effects. Atropine, because of its tertiary ammonium construction, has a tendency to trigger tachycardia, gastrointestinal upset, blurred vision, dry mouth, and central nervous system results secondary to its capability to cross the blood� brain barrier. Patients presenting to the working room with obstructive airway illnesses have a excessive chance of taking antiinflammatory therapies for management of their illness (Table 25-2). Chapter 25 � Respiratory Pharmacology 485 Table 25-2 Pharmacologic Influence on Inflammation Inhaled Corticosteroids Monotherapy Beclomethasone Budesonide Ciclesonide Flunisolide Fluticasone Mometasone Triamcinolone Combination Therapy Budesonide/ Formoterol Fluticasone/ Salmeterol Leukotriene Modifiers Antagonists Montelukast Zafirlukast Pranlukast (not in U. Volatile anesthetics scale back bronchomotor tone and all commonly used volatile anesthetics, except desflurane, produce a degree of bronchodilatation (may be helpful in sufferers with obstructive lung illness or in patients that have any diploma of bronchoconstriction).
References - Shim B, Kim KH, Yoon H, et al: Body image following radical cystectomy and ileal neobladder or conduit in Korean patients, Korean J Urol 55(3):161n166, 2014.
- Reinhart H, Obedeanu N, Hooton T, et al: Urinary excretion of Tamm-Horsfall protein in women with recurrent urinary tract infections, J Urol 144(5):1185n1187, 1990.
- Levine LA, Newell M, Taylor FL: Penile traction therapy for treatment of Peyronieis disease: a single-center pilot study, J Sex Med 5(6):1468n1473, 2008.
|
|