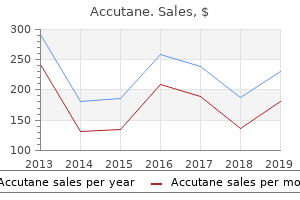
"Cheap 5 mg accutane amex, acne light therapy."By: Keira A Cohen, M.D. - Co-Director, The Johns Hopkins Center for Nontuberculous Mycobacteria and Bronchiectasis
- Assistant Professor of Medicine
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/10003818/keira-cohen
Purchase accutane 30mg overnight deliveryNo different imaging studies are indicated when the clinical presentation and radiographic findings are typical, although the usage of a bone scan has been reported. The medical findings may counsel infection, which is extraordinarily unlikely on this location with no penetrating injury. Kohler illness has been categorized by Siffert (369) as a secondary articular osteochondrosis as a end result of involvement of the articular and epiphyseal cartilage, if any, is a consequence of avascular necrosis of the subjacent bone. There is proof that the illness develops in navicular bones that are constitutionally and biologically inferior and, therefore, vulnerable to damage by mechanical forces that standard bone is able to stand up to (370). Karp (422) discovered that ossification of the navicular occurs earlier in women than in boys. Half of the women studied had a navicular that was ossified by the age of 2 years, and one-third of the boys had been more than 3� years of age by the time ossification occurred. In addition to the results of mechanical stress at the time of ossification, avascular necrosis appears to play a role within the growth of Kohler disease. The blood supply to the navicular bone is critical, with a network of perichondrial vessels. However, at the time of early ossification, arteries penetrate the cartilaginous navicular with out their mature anastomotic community, predisposing them to vascular harm. Vascular theories are supported by biopsy research exhibiting areas of necrosis within the navicular (417). Waugh (423) investigated the vascular anatomy of the navicular and located two patterns of blood provide. He felt that compressive forces may occlude the vessels and produce avascular necrosis of the bone. Histologic examination of the affected bone has disclosed areas of necrosis, resorption of lifeless bone, formation of latest bone, and interference with regular ossification. The navicular reconstitutes itself in 4 months to 4 years after onset and is regular at skeletal maturity (418ʹ20). Apparent avascular adjustments in the navicular of an adolescent or grownup symbolize a special condition with an unpredictable consequence. The length of signs was 7 to 15 months for these casted <8 weeks or those treated by other regimens. And besides for the period of symptoms, therapy had no impact on the final consequence of the illness (418ʹ20). Macrodactyly is the time period used to describe enlargement of the digits of the toes or palms. The term means giant digit, however the metatarsal or metacarpal can also be enlarged. Macrodactyly may happen as an isolated situation or as part of a syndrome, similar to neurofibromatosis, Klippel-Trenauny-Weber, lymphangioma, and Proteus (424). Surprisingly, in Klippel-Trenaunay-Webber, a syndrome of venous lymphatic malformation, ipsilateral macrodactyly is regularly current with a vascular part, and contralateral macrodactyly is current as a fibrofatty disorder. In Proteus syndrome, a cerebriform skin sample on the plantar surface of the foot in addition to asymmetries of development and nevi are current. The relative dimension of the complete extremity must also be assessed to rule out hemihypertrophy as the underlying disorder. Fifty p.c of patients with foot involvement in macrodactyly have a dorsally angled digit with weak toe flexors (427). Standing anteroposterior and lateral radiographs of the foot are useful for monitoring the relative growth charges of the digits and for surgical planning. An overabundance of fibrofatty tissue makes up the bulk of the soft-tissue enlargement. Macrodactyly may be static, by which the digit is enlarged at birth and development is proportional to the conventional digits. Alternatively, it may be progressive, by which case the concerned digit grows disproportionately sooner than the normal ones (429). Although the appearance is usually grotesque, the principle disability is with shoe becoming. A: Macrodactyly most commonly includes the second ray; in this case, the hallux and third toe are concerned to some extent. B: Radiographic look demonstrates enlargement of bone in addition to soft tissue. C: Clinical look after second ray resection and third toe interphalangeal joint disarticulation. Surgical options embrace soft-tissue debulking, ostectomy, epiphysiodesis, complete or partial toe amputation, and ray resection, either as isolated procedures or together (425, 426, 430ʹ33). A combination of soft-tissue debulking with epiphysiodesis of the proximal phalanx or metatarsal or both is really helpful for mild, static deformities. Large residual circumference of the foot, somewhat than length, is usually the greater problem for shoe becoming. Adduction of the metatarsals creates a concave medial border of the foot, a convex lateral border, and prominence on the base of the fifth metatarsal. Bleck (444, 445) revealed two classification systems: one based mostly on the severity and one on the pliability of the deformity. Berg (446) developed a classification system for metatarsus adductus and skewfoot based on radiographs of the feet of a small group of kids between the ages of 2 and 17 months. Radiographs are indicated for the older baby and adolescent with severe residual deformity, pain, or different incapacity when operative intervention is being considered. Ruth Wynn-Davies reported the incidence of metatarsus varus at 1 in 1000 stay births and 1 in 20 in siblings of sufferers with metatarsus varus (94). The actual incidence is unknown because of the shortage of a strict definition of the situation. An increased reported incidence through the previous century might be as a end result of an increased awareness of the situation by primary care physicians (5, 436ʹ38). Although earlier studies (439, 440) indicated an affiliation of metatarsus adductus with hip dysplasia, more recent studies (441, 442) have shown no vital association between the 2 circumstances. The severity of metatarsus adductus is determined by the relation between the toes and the distal finish of the line bisecting the heel. B: A versatile foot could be passively overcorrected into abduction with little effort. Whereas some authors have proposed the etiology to be joint malalignment deformity secondary to in utero positioning, others have proposed the etiology to be muscle imbalance resulting from contracture and anomalous insertion of the tibialis anterior (437, 448, 449) or tibialis posterior (450). Two studies on cadavers with metatarsus adductus have documented an abnormality in the shape of the medial cuneiform (451, 452). No patient required surgical correction and hallux valgus was not an recognized drawback. The percentage of toes with metatarsus adductus that bear spontaneous correction with out remedy may very well be even higher than reported in these studies, due to the likelihood of underreporting of gentle, flexible instances.
Purchase accutane 40 mg without a prescriptionA: Typical radiographic findings embrace a prominence of the tibial tubercle with irregularity of the bone on the insertion of the patellar tendon. Time, relaxation, and occasional immobilization normally end in marked enchancment of symptoms (295Ͳ99). Activity should be limited till the pain resolves and the athlete demonstrates a full painless range of knee motion. After the acute part, a maintenance program of stretching, particularly of the quadriceps, and strengthening of the quadriceps and hamstrings may help the athlete. If the affected person is skeletally mature and nonetheless symptomatic, excision of the free ossicle resolves the signs in most cases (300, 301). The lateral radiograph greatest demonstrates the irregularity on the inferior pole of the patella. However, their use seems justified, given the inflammatory nature of these circumstances. Synovial plica are regular synovial folds within the knee joint that can cause knee ache. With trauma or repetitive movement, the plicae may hypertrophy, inflicting ache and indicators of intra-articular pathology (305ͳ09). The most typical plica to cause signs is the medial patellar plica, which anatomically runs from the superior medial pole of the patella or midpatella to the medial patellar fats pad (305). Most plicae are asymptomatic, however sometimes this situation is a real symptomatic entity. The affected person complains of anterior or anteromedial knee pain, typically after repetitive activities similar to running, leaping, or squatting. The athlete could complain of a popping or snapping sensation with their knee in midflexion. Physical examination often reveals tenderness instantly over the plica because it comes over the medial femoral condyle to the infrapatellar fats pad, and probably a palpable snapping sensation because the knee is flexed from 30 to 60 levels of flexion whereas the patient is weight bearing or standing. In some cases, synovial plicae are related to indicators of lateral patellar instability. This syndrome is a medical prognosis of exclusion after different causes of knee ache and popping have been dominated out. Symptomatic plicae show hypertrophy and irritation which lead to thickening and eventual fibrosis. With important fibrosis, changes in the articular surface and even subchondral bone may happen (310). Arthroscopic resection of the plica is indicated in these rare cases, with wonderful outcomes anticipated in 90% of instances (307, 312ͳ20). At the time of surgical resection, the joint is totally examined for different causes of inside derangement corresponding to meniscal tear or patellar maltracking. Originally described by Hoffa (321) in 1904, very little is understood about this condition in youngsters or adolescents. Anatomic research of the fat pad have revealed a densely innervated tissue, and due to its anatomic location, its function as a potential reason for anterior knee ache is debated (322ͳ26). In the latter condition, maximal tenderness is at the inferior pole of the patella. In Hoffa syndrome, the maximal space of tenderness is at the anterior joint line on either facet and deep to the patellar tendon. A diagnostic intra-articular local anesthetic injection directly into the fat pad could also be of help in these sufferers whose symptoms fail to resolve. There is little information as to the efficacy of surgical administration for this situation (327). However, anterior knee pain in children and adolescents can exist in the absence of constructive bodily findings for any of the pathologic situations causing knee pain. The ache is made worse with physical exercise similar to working, jumping, squatting, going up and down stairs, or after extended sitting with the knee in flexed place. Physical examination could reveal so-called miserable malalignment together with excessive internal femoral torsion, exterior tibial torsion, delicate genu valgum with medial deviation of the patella, and an inclination to pes planus or foot pronation. The suprapatellar (superior) plica, the midial plica, which is certainly one of the most commonly symptomatic, and the inferior plica (ligamentum mucosum), which overlies the anterior cruciate ligament. The patella may be hypermobile and have some evidence of maltracking, however without indicators of patellar subluxation or dislocation. There could also be atrophy of the quadriceps and patellar crepitus with flexion and extension of the knee or a patellar compression check. Examination of patellar monitoring should embrace evaluation of the Q angle, lateral tilt, and lateral tracking. Historically, the time period "chondromalacia patellae" has been used to describe this entity (330). In kids and adolescents with idiopathic anterior knee pain, however, the articular surface is usually normal. Therefore, one ought to avoid the use of the time period "chondromalacia patellae" in the case of patients with idiopathic anterior knee ache. In what ought to be a basic article, Sandow and Goodfellow reported on the natural historical past of untreated anterior knee ache in adolescent girls followed up for 2 to eight years (331). The symptoms of most of those sufferers resolved over time or were considerably improved. Treatment must be nearly exclusively nonsurgical and encompass exercise modification, flexibility workout routines of the quadriceps and hamstrings, strengthening workouts of the same muscle teams, and the usage of other modalities such as ice, warmth, ultrasound, and transcutaneous electrical muscle stimulation (331ͳ38). Some patients will profit from foot orthotics, particularly if pes planus is a component of the problem. Knee orthotics such as a patellar stabilization brace or patellar sleeve or strap may be helpful. In summary, idiopathic anterior knee ache in adolescents is usually referred to as a "headache of the knee" (331). The orthopaedist should assume the role of the "knee psychiatrist" when treating these patients, with a careful and complete scientific historical past and physical examination, and nearly evangelical enthusiasm for nonoperative remedy. There is often no associated intra-articular pathology in kids with this symptom (339). Transillumination of the cyst or ultrasound can doc the cystic nature of the lesion and rule out stable soft-tissue lesions similar to rhabdomyosarcoma. Anatomically, the cyst arises from the posterior side of the knee joint itself, between the medial head of the gastrocnemius and the semimembranosus. Although it could be firmly hooked up to the fascia of the medial gastrocnemius, it nearly all the time communicates with the knee joint. Spontaneous resolution of popliteal cysts tends to occur, however this usually takes up to 12 to 24 months (339).
Cheap 5 mg accutane amexAfter the medial cortex is divided to a point a minimum of four cm below the iliopectineal line, the proximal lateral cortex can be carefully divided with a chisel, as a bone spreader distracts the iliac osteotomy, stressing the remaining bone bridges. The remaining deep medial bone bridge is often no extra than about 2 cm in size. Using a T-handle chuck and lamina spreaders via the anterior portion of the iliac osteotomy, the remaining bone bridge will fracture. It is essential to be certain that the chisel is no less than four cm beneath the pelvic brim in order to avoid an intraarticular osteotomy. The ordinary correction maneuver includes anterior rotation of the acetabulum within the axis of the ilium, which improves each anterior and lateral protection. Occasionally, lateral rotation is required as well, as is medial rotation to keep away from retroversion. After the specified quantity of correction is achieved, two or three provisional k-wires are placed via the iliac crest into the acetabular fragment. A plain anteroposterior radiograph is then taken to confirm correct fragment positioning. It is essential to assess not only that the weight-bearing zone is horizontal or near-horizontal but in addition the congruity of the hip joint, the model of the acetabulum, the extent of medialization or lateralization, and Shenton line. The capsulotomy is closed at this point, if it has not already been closed, and the fragment is secured with a minimal of three screws. The straight head of the rectus is secured through the outlet left by the Schanz screw, giving a powerful transosseous restore. The periosteum and abdominal wall musculature is secured through drill holes to the iliac crest. This 15-year-old female determine skater introduced with a 1-year history of progressive anterolateral left hip pain. A΃: Anteroposterior, fake profil, and von Rosen views present left hip dysplasia with decreased anterior and lateral center-edge angles and an upsloping sourcil. The rim fracture has healed, anterior and lateral center-edge angles have improved, the sourcil is horizontal, and her symptoms have resolved. There has been significant confusion in the literature as to what particularly is a Dega osteotomy. Whereas the Pemberton osteotomy ends within the ilioischial limb of the triradiate cartilage and fully divides the iliac bone from anterior to this level, the Dega osteotomy ends just above the horizontal portion of the triradiate cartilage (the ilioischial and iliopubic portions) and leaves a posterior portion of each the inner and outer iliac cortex simply anterior to the sciatic notch intact, forming its hinge. After the iliac apophysis is break up, the inside and outer tables of the ilium are uncovered subperiosteally, which is enough to expose the sciatic notch on either side. If more anterior protection is desired (A), the plane of the osteotomy is more transverse. If lateral protection is desired (B), the airplane of the osteotomy is inclined more laterally. After that is determined (C), a small, osteotome can be utilized to outline the osteotomy by slicing the cortex of the inner and outer desk. The osteotomy is begun about 1 cm above the anteroinferior iliac spine and proceeds posteriorly, preserving about 1 to 1. Care in exposing the sciatic notch as far inferiorly as potential makes this error simpler to keep away from by seeing the portion of the ilium that lies between the sciatic notch posteriorly and the capsule of the hip joint anteriorly. It is neither attainable, necessary, nor advisable, nevertheless, to expose this right down to the triradiate cartilage. The similar downside exists when cutting the cortex of the inner desk, however to not the identical extent. By twisting it, the tissue is retracted, giving good publicity to the posterior area distal to the sciatic notch the place visualization is most difficult. After the inner and outer cortices of the ilium are divided as far as may be seen, a wider curved osteotome is used to connect these two cuts. At this level, an osteotome with a right-angled curve is inserted into the osteotomy. This can be made simpler by prying down on the acetabular roof with an osteotome and inserting a small lamina spreader to hold the osteotomy apart. When the osteotomy is full, the acetabular roof may be levered down into the desired place and held there with a lamina spreader. Grooves are ready within the cancellous surface on both sides of the osteotomy to provide safe fixation of the bone graft. When femoral shortening accompanies the process, the resected femur may be used because the supply of the bone graft. When in place, the bone graft ought to be safe and steady, and this can be verified by making an attempt to dislodge the graft. A radiograph instantly after surgical procedure (A) demonstrates the osteotomy extending into the triradiate cartilage and never breaking into the sciatic notch. Radiographs at 6 weeks (B) and 6 months (C) demonstrate the fast therapeutic and the wonderful protection of the femoral head. The positioning and publicity for the Dega osteotomy are the same as for the opposite pelvic osteotomies. The sciatic notch should be clearly visualized posteriorly (A), the false acetabulum recognized, if present, and the true acetabular edge identified. Because this takes only a minute and provides little to the morbidity of the case, the additional publicity may be advisable until expertise is gained. The osteotomy (B) begins on the lateral cortex alongside a curvilinear line, which starts just above the anteroinferior iliac spine, continues to arch posteriorly, staying above the acetabulum, and ends posteriorly 1 to 1. Because of the difficulty in viewing such a complex three-dimensional structure as the acetabulum in two dimensions on a radiographic display screen, three pins should be used. One pin is positioned anteriorly, one on the highest level above the acetabulum, and one posteriorly. After the outer cortex is minimize, a straight osteotome is directed medially and caudally. The steeper the acetabular slope, the upper the start line is above the acetabulum, in order that the medial minimize at all times emerges above the horizontal portion of the triradiate cartilage. The osteotome should exit medially, just above the horizontal limb of the triradiate cartilage, which is composed of the ilioischial and iliopubic parts. The path of the rotation is decided by the extent of division of the inner cortex on the internal wall of the ilium. If extra anterior protection is needed, the inner wall is divided, except for the 1-cm posterior hinge just anterior to the sciatic notch. If more lateral protection is needed, nevertheless, about one-third of the internal cortex is left intact. This (B) now strikes the hinge to the medial wall of the ilium and determines that the rotation is anterior and lateral. The rotation turns into more anterior as more of the internal wall is divided, and the rotation becomes extra lateral as extra of the internal wall is left intact.

Accutane 10mg discountIn such cases the incision could come down instantly over the posterior tibial nerve, as illustrated right here. This construction is the primary landmark to identify in the posterior compartment and is definitely acknowledged as the only tendon passing behind the medial malleolus by which the muscle stomach extends this low. This dissection is continued across the medial facet of the ankle so far as the posterior facet of the medial malleolus. The dissection is facilitated by opening the sheath of the flexor hallucis longus tendon longitudinally until the sustentaculum tali is encountered. This is the purpose at which the tendon can no longer be seen and is the landmark that identifies the subtalar joint, as that joint is instantly adjacent to the sustentaculum tali. This early and definitive identification of the subtalar joint helps ensure subsequent proper identification of the ankle joint which is usually troublesome, especially in severe deformities. A Senn or Langenbeck retractor can be utilized to retract all these structures, giving a clear view of the posterior capsules from the midline to the medial malleolus (B). This is most simply completed by incising the fascia over the peroneal muscle bellies. These muscles are enveloped in fats and fascia lateral to the flexor hallucis longus, whose muscle stomach is proven exposed along the neurovascular bundle. After the muscle tissue is recognized, a scissors is used to open this fascial envelope around the peroneal muscle tissue and tendons (A). This incision ought to be carried to the purpose the place the peroneal tendons curve under the lateral malleolus in order that these tendons can be retracted sufficiently to allow a whole division of the calcaneofibular ligament, which lies beneath the peroneal tendon sheath (B). This completes the exposure of the posterior facet of the tibiotalar and subtalar joints. In a extreme clubfoot, the posterior fringe of the calcaneus could additionally be in direct contact with the posterior border of the tibia, obscuring the talus. To facilitate this publicity, the fibrofatty tissue over the posterior side of the joints is sharply excised with a knife. The subtalar joint, which has already been identified following launch of the flexor hallucis longus tendon sheath right down to the sustentaculum tali, can be released from medial to lateral with a scalpel or scissors. The peroneal tendons are retracted and the incision within the capsule is sustained across the lateral aspect, including launch of the calcaneofibular ligament. The tibiotalar joint can be recognized proximal to the subtalar joint by palpation and inspection whereas the foot is plantar and dorsiflexed. The fibrofatty tissue is first excised with a knife, after which the scissors is inserted with one blade within the joint and the opposite outside the joint. Occasionally, the posterior talofibular ligament and the calcaneofibular ligament stand out, the latter showing like a tendon. The geographic cuts within the posterior capsule of the tibiotalar and subtalar joints divide the ligaments as proven: the posterior tibiotalar ligament (A), the posterior talofibular ligament (B), the tibiofibular ligament (C), the calcaneofibular ligament (D), and the deltoid ligament (E). Division of this a half of the deltoid ligament is prevented by limiting the capsulotomy of the tibiotalar joint as a lot as the posterior side of the medial malleolus. A: the plantar-medial release is carried out via the antero-medial extension of a Cincinnati incision. A vessel loop surrounds the posterior tibial neurovascular bundle (blue arrow) posterior to the medial malleolus. C: the bottom (1) of the 3 origins of the abductor hallucis muscle is launched from the calcaneus superficial to the lateral plantar neurovascular bundle. D: the plantar fascia and quick toe flexors are subsequent launched superficial (plantar) to the lateral plantar neurovascular bundle. H: the deep plantar-medial release begins with z-lengthening of the tibialis posterior. The talonavicular joint capsule is launch medially, extending to various degrees dorsal and plantar, as required, to allow eversion of the subtalar joint. However, in a clubfoot it must be remembered that the navicular is displaced medially, inflicting it to lie on the medial facet of the neck of the talus and nearer than regular to the medial malleolus. In addition, the area between the tuberosity of the navicular and the medial malleolus is full of dense, fibrous tissue. This joint is discovered by directing the scissors distally towards the first metatarsal between the neck of the talus and the navicular (A). The error is to reduce transversely across the foot as if the anatomic relationship between the navicular and the talus had been regular. At the identical time, the surgeon should be careful to avoid opening the naviculocuneiform joint. This will additional devascularize the navicular and have a tendency to destabilize it permitting it to rotate out of position. The talonavicular joint capsule should be released totally on the medial and plantar elements, as those are probably the most contracted parts. The dorsomedial capsule ought to be released solely to the extent that it limits eversion of the subtalar joint. Excessive release of the talonavicular joint capsule might lead to hypermobility and dorsal subluxation of the navicular, a difficult situation from which to get well. To free it, the plantar calcaneonavicular (spring) ligament and the anterior portion of the deltoid ligament inserting into the navicular (tibionavicular ligament) have to be divided. Because these ligaments are condensations of the capsules, they are going to be divided when the capsules between the talus and the navicular dorsomedially and the calcaneus and the cuboid on the plantar aspect are opened. This may be accomplished with a scissors or a knife when the surgeon is definite that she or he has recognized the joint. Plantar and lateral to the talonavicular joint, and almost according to it, is the medial aspect of the calcaneocuboid joint (B). Because the peroneus longus tendon crosses the most plantar and lateral facet of this joint, it ought to be retracted. The medial capsule of the calcaneocuboid joint, like all the opposite capsules, may be opened safely with a scissors, although some experienced surgeons choose to use a knife. This must be accomplished after the completion of the complete launch and after the foot is reduced. The tendon could also be repaired finish to end with a Kessler sort of sew or side to facet. The restore should be under modest tension to avoid unnecessary weakening of the gastrocnemius muscle. In the older youngster, one or more osteotomies could additionally be essential to correct residual deformities that are identified after the joints are aligned by soft-tissue releases. Residual midfoot adduction and supination are often a problem after clubfoot correction. In the previous, painful midfoot adduction was typically handled by metatarsal osteotomies (459, 460) or tarsometatarsal capsulotomies (Hyman-Herndon procedure) (456). More recently, nonetheless, these operations have been used much less incessantly as a outcome of they either fail to provide the specified correction or they lead to painful stiff joints (457, 458, 461, 462).
Generic 40mg accutane with mastercardA current report demonstrated the benefits of early fitting with articulated knees in youngsters as younger as 17 months. All kids learned to walk with an articulated knee, regardless of their age differences (157). Most elements carry specific weight pointers, and many kids attain these ranges nicely earlier than maturity. For instance, an adult hydraulic polycentric knee is routinely used on 8-year-old boys whose weight has surpassed a hundred lb. It is generally thought of when amputees require most late-stance stability due to weak knee extensors, knee-flexion contractures, or poor midto late-stance steadiness (227). By changing the hardness of the bumper, the prosthetist is ready to successfully change the properties of the foot. This foot is greatest fitted to the transfemoral amputee, in whom full-foot contact with the ground is important to improve stability. The multiaxis foot permits passive dorsi- and plantar flexion, inversion, and eversion. The multiaxis foot was once thought best suited for the amputee who because of uneven terrain or a lifestyle that includes golf or various sports requires flexibility and some rotational control: It has now discovered its means into the pediatric inhabitants. This class of foot has gained broad acceptance within the pediatric arena, partly because of its ability to absorb forces at the ankle and scale back transmission of those forces to the socket. The dynamic-response foot has found its way into competitive-level sports activities as well as day-to-day activities. It is essential to use components that may maximize performance and on the same time be applicable for the patient (228). B: the Little Feet kind design incorporates distinctive energy dynamics with flexible toes all in sizes beginning at 10-cm length. The length of the keel controls the toe lever arm and thus the hyperextension moment at the knee, and the compression of the elastomer heel absorbs and deflects the forces at heel strike. C: the dynamic multiaxial TruPer foot permits rotation, inversion and eversion, flexion, and extension actions. It is used for the older, stronger, and physically energetic youngster who has the physical ability to use such a foot. The involvement in aggressive sports activities is normally an excellent benchmark to provoke becoming adolescents with the highestperformance dynamic-response feet. The similar is true of the transtibial amputee, who lacks the muscle power to control the foot, often leading to premature muscle fatigue. In the selection of a quantity of components, the prosthetist should marry the characteristics of all elements, so that most benefit may be available to the amputee. The most necessary consideration in the becoming of the partial-foot amputee is to make sure that enough load-bearing is designed into the prosthesis of alternative. As a common rule, the more proximal the level of amputation, the higher the prosthesis should fit over the ankle complex and the extra proximally it must match on the tibia and fibula. Tissue situation, perform of the remaining foot advanced, and activity of the kid all play a job in figuring out the prescription and design of the prosthesis. Complete or partial absence of the toes normally requires little greater than a shoe filler. A carbon fiber insert to higher management forces from heel to toe-off may be integrated within the shoe filler. In the case of the very younger child, no intervention may be required until a need has been demonstrated, for instance, the shortcoming to maintain the shoe on, particularly when the child becomes extra active in sports. This incorporates a beauty foot shell, silicone-laminated socket with modified foot sole, and a posterior zipper for ease of donning and doffing. The socket trim line is proximal to the malleoli and is fitted intimately to ensure enough control. The design of a partialfoot prosthesis may include a removable insert, to accommodate the necessity for corrective alignment of the residual foot. Overall, this type of prosthesis is perfectly suited for the child amputee and resists premature wear and tear. If wanted, a partial-foot prosthesis must be prescribed as quickly as the child is pulling to furniture, in order that foot management will begin at an early age. It ought to be noted that a low-profile insert (distal to the malleoli), used at the side of a hightop boot, will provide adequate function and cosmesis till a decrease cut shoe is requested by the mother or father. The prosthesis must encompass the ankle joint, and it usually rises proximally to the patellar tendon in an effort to scale back forces on the tibial crestγocket interface. Selection of prosthetic ft is compromised due to the lack of house distally, and commercially out there carbon foot plates require everlasting attachment with vulcanizing rubber cement. This negates any adjustments caused by growth, and realignment to compensate for gait modifications is nearly impossible. The selections left open to the prosthetist are quite a few and, at times, controversial. Where some clinics maintain rigid protocols for terminal device choice, other clinics rely more on affected person and parent input, combined with historic success charges for gadget varieties. Clinics that preserve very high caseloads for myoelectric devices, for instance, will most probably have way more expertise in fitting externally powered prostheses, in comparison with a clinic that will solely see a handful of potential myoelectric candidates. In simple phrases, the terminal devices may be divided into arms and hooks, and they are often physique powered (cable and harness) or externally powered (electric). Patton lists the practical and prescription standards for the various terminal units (203). The initial fitting of a child with upper extremity limb deficiency begins at 4 months of age in a passive prosthesis with a stylized passive hand. This allows for equal arm lengths for the event of propping up on the amputated facet and larger acceptance by the parents. Following initial sitting steadiness, the clenched-fist terminal system is exchanged for a small infant passive hand. When the toddler begins to attain out (at 15 to 18 months of age), the clinic group begins to assess the need for both body-powered or externally powered prostheses. A: the Lange silicone partial-foot prosthesis is a custom-made prosthesis that may incorporate a keel to aid in foot stability and push-off in gait. B: It is useful for youngsters with partial amputations of the foot or congenital longitudinal deficiencies of the foot, shown right here. The hand incorporates a flexible thumb that permits objects to be placed for simple grasp and launch features. It appears a bit extra like a hand, which often makes this selection popular with dad and mom. D: the Variety Village hand is one of the mostly used myoelectric palms in the pediatric age group. The canted design of the 12P hook permits for higher visual suggestions to the wearer. In the Otto Bock 2000 hand, the identical precept is applied, besides that from the open to closed place, the thumb sweeps from a lateral position to meet the two opposing fingers upon close.
Syndromes - Throat, tooth, or mouth infections
- Abnormal breath sounds
- AIDS
- Sleep problems
- Diarrhea
- Viral or bacteria infections
- Pain with ejaculation

20mg accutaneThe varus angle usually decreases with development (197, 369, 370); nonetheless, if there was physeal plate harm secondary to the illness, this remodeling potential may be lost, and the patient might have permanent shortening and short-term or permanent weak point of the hip abductors (153, 370ͳ74). The proponents of varus osteotomy, with or with out derotation, report 70% to 90% passable anatomic outcomes utilizing this methodology (127, 153, 231, 358, 359, 362, 371, 373, 375ͳ85). This procedure could increase the forces on the femoral head by lateralizing the acetabulum and rising the lever arm of the abductors (359), although this supposition has so far not been substantiated. Innominate osteotomy can also cause a persistent acetabular configuration change the place there was a beforehand normal acetabulum, resulting in lack of motion, notably flexion (392). Satisfactory anatomic outcomes from this procedure vary from 69% to 94% (348, 373, 387ͳ89, 393ͳ97). There is significant biomechanical proof to present that neither method of surgical containment, innominate or femoral osteotomy, might successfully defend an extensively necrotic phase of the femoral head from stress (339, 340, 398, 399). Wenger (22) reported a excessive incidence of complications in surgically treated patients, even when the accepted strategies had been used and conditions have been met. Several short-term results of mixed varus osteotomy plus innominate osteotomy have been reported in patients with severely concerned Catterall group 3 or 4 illness. This mixed procedure has the theoretical advantage of maximizing femoral head containment while avoiding the complications of both process alone. The femoral osteotomy directs the femoral head into the acetabulum, while theoretically lowering any rising strain or stiffness of the joint that might outcome from the pelvic osteotomy. The coverage provided by the innominate osteotomy reduces the diploma of correction needed from the femoral osteotomy, thereby minimizing the complications of excessive neck-shaft varus, associated abductor weak spot, and limb shortening. Advocates of this procedure also believe that permanent correction of the deformity, early weight bearing, and shortened therapy time are obtained. The disadvantages of the process embody these mentioned for varus osteotomy and innominate osteotomy alone. Surgical time is increased, potential blood loss is magnified, and the mixed procedures are technically tougher. Satisfactory anatomic outcomes from this mixed process are reported in up to 78% of sufferers. As would be anticipated in short-term followup, the medical outcomes are wonderful (400ʹ04). Innominate osteotomy offers for containment by redirection of the acetabulum, providing higher protection for the anterolateral portion of the femoral head. The femoral head is positioned in relative flexion, abduction, and inner rotation with respect to the acetabulum within the weight-bearing position. Any shortening caused by the disease may be corrected (124, 348, 368, 373, 386ͳ91). Prerequisites for innominate osteotomy include restoration of a full vary of movement, a spherical or almost round femoral head, and congruency of the joint, demonstrated arthrographically. Treatment have to be carried out early in the course of the illness, and the pinnacle must be nicely seated in flexion, abduction, and inner rotation. The tendinous portion of the iliopsoas muscle is all the time launched at the musculotendinous junction, and any residual contractures of the adductor muscles are launched by subcutaneous adductor tenotomy (124, 348). Partial weight bearing may be resumed in a cooperative youngster several days after surgical procedure; however, in an uncooperative patient, immobilization in a spica solid for 6 weeks is required. The disadvantages of innominate osteotomy are the related risks and cost factors of the surgical process and the procedure for pin elimination. Only one intermediate-term follow-up study exists, but proponents of this technique of remedy believe that containment of the femoral head by shelf arthroplasty, earlier than important deformity can develop, improves transforming of the femoral head (316, 406, 407). The shelf procedure may cowl the anterolateral portion of the top, stopping subluxation and lateral overgrowth of the epiphysis. Risk factors for poor results with this technique are age older than 11 years, female gender, and Catterall group 4 disease. These procedures must be seen as salvage procedures, with each having particular limited aims, which can include pain reduction, correction of limb-length inequality, rising femoral head coverage, enchancment in motion of the joint, and strengthening of a weak abductor (412). Reports of the usage of triple innominate osteotomy to treat Perthes disease have begun to floor within the literature (408, 409). This procedure, initially introduced for the remedy of developmental hip dysplasia, is theoretically higher able to cover the deforming femoral head. Only longer follow-ups will let physicians know if it will supply higher long-term outcomes in contrast with extra generally utilized osteotomies. Recently, stories have been printed advocating using hip distraction (arthrodiastasis) for durations of four to 5 months, with or without soft-tissue launch, in older children with Perthes disease (410, 411). The author has considerations concerning the impact of pin tract contamination on the future outcome of complete hip alternative in patients treated by this system. A judgment about the usefulness of these procedures must await additional follow-up. Regardless of the tactic of containment chosen, any episode indicative of lack of containment, such as recurrent pain or loss of vary of movement, should be treated aggressively with rest, traction, and reassessment of containment clinically and probably radiographically. Treatment Options within the Noncontainable Hip and the Late-Presenting Patient with Deformity. Patients presenting with deformity within the later stages (reossification) of the illness, these with noncontainable deformities, and those who have lost containment after undergoing both surgical or nonsurgical containment procedures current a management challenge. These patients often show hinge abduction on arthrography and have an extremely poor prognosis without further therapy (193, 208, 209, 246, 348, 412). They usually current with persistent pain, shortening of the involved extremity, and a fixed deformity, usually 10 to 15 levels of mounted flexion and 15 to 20 degrees of fixed adduction (246, 412). In patients within the energetic stage of the illness no matter their age with a noncontainable hip or patients with a painful hip after therapeutic who demonstrate hinge abduction, abduction osteotomy must be thought-about. In addition to altering the relation of the femoral head to the acetabulum, valgus osteotomy of the hip lengthens the leg and lowers and lateralizes the greater trochanter. Many hips appropriate for valgus osteotomy also have a short femoral neck, and the lateralization of the shaft tends to lengthen the neck. This situation usually requires the modification of present gadgets by bending, to avoid medialization of the femoral shaft or by shortening of the blade, of the blade plate units used for adults. The wound is usually pretty dry after the osteotomy is secured, and in our expertise little drainage is collected in the suction canister. How dependable are the mother and father and children within the following directions about activity? Adolescents are usually large enough to permit wonderful fixation and seldom want a cast. On the opposite hand, youthful kids are sometimes greatest immobilized for six weeks in a single-leg spica forged. Depending on circumstances, the forged may end above the knee and crutch walking may be permitted. The preliminary outcomes with this modality of treatment indicate enchancment in limb length, lower in limp, and improvement in perform and range of movement (412).
Purchase 5mg accutaneThe distal osteotomy is made instantly proximal to , and parallel with, the airplane created by the two distal information pins. It passes via the mid-body of every of the three cuneiform bones and the distal finish of the cuboid. To avoid excessive shortening of the foot, the osteotomies should be fashioned in order that no hole of bone is current on the plantar apex of the wedge. It is possible to rotate the distal segment, if needed, to right pronation deformity. This could be corrected by supinating the forefoot; however, care should be taken to not produce an unintended malrotation. The dorsal floor of the cuneiform bones is often larger than the navicular, and this will likely make staple fixation more difficult. It should begin in the first metatarsal at an indirect angle directed dorsally and laterally. This pin ought to engage the first metatarsal, the primary cuneiform bone, the navicular, and the talus. The lateral pin is started distal to the flare at the base of the fifth metatarsal and is aimed medially and slightly dorsally, crossing the cuboid bone and coming into the calcaneus. The patient is then ambulated with a three-point, nonηeight-bearing crutch gait for 6 weeks. A short-leg strolling forged is utilized, and the patient is permitted partial weight bearing for an additional four to 6 weeks, at which period healing ought to be complete. B Removal of a dorsally based mostly wedge from the tarsal bones to correct a set cavus deformity with its apex within the midfoot has been described by Cole (63). This disadvantage is offset by preservation of the metatarsalδarsal joints distally and the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints proximally. Because this operation corrects solely the cavus deformity, the absence of fixed-heel varus is a prerequisite. Jhass (66) has described an analogous osteotomy that removes the wedge distally, excising the metatarsalδarsal joints. The talocalcaneal, talonavicular, and calcaneocuboid joints are resected, separating the foot into three movable segments: the forefoot, the calcaneus, and the talus and ankle mortise. If the proper wedges of bone are resected, the place of the foot might be correct when the bony surfaces are apposed. More importantly, it has been shown in many long-term follow-up research that triple arthrodesis causes stress shifting and untimely degenerative arthrosis (19Ͳ1, 26, 27, 55) or Charcot arthropathy (82) in adjacent unfused joints, such because the ankle joint. Furthermore, Schwend and Drennan (72) have proven that, even after solid triple arthrodesis, there can be progressive deterioration and recurrence of deformity over time secondary to muscle imbalance. Before starting the triple arthrodesis operation, the surgeon ought to give some thought and planning relating to the wedges of bone to be eliminated and, specifically, the quantity of bone to be removed. Simplify the cuts to parallel and perpendicular in relationship to apparent giant bony landmarks. Visualizing the foot at surgery and making the osteotomy cuts to create the wedges, as described in the subsequent discussion, seems rather more practical and accurate. The commonest deformity for which triple arthrodesis is performed is mounted cavovarus deformity. To correct this deformity, a laterally based wedge of bone is faraway from each of the joints to be resected. The wedge that can allow correction of the forefoot will excise the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints. To achieve correction to a impartial position, the distal reduce is perpendicular to the lengthy axis of the forefoot and the proximal cut is perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the calcaneus (A). To right the varus of the hindfoot, a laterally primarily based wedge have to be faraway from the subtalar joint. To right the heel to a impartial position, the proximal cut from the undersurface of the talus must be perpendicular to the long axis of the tibia (or parallel with the ankle mortise), whereas the distal minimize from the superior surface of the calcaneus should be parallel to the bottom of the heel (B). This is as a outcome of the medially primarily based wedges which might be created using the espoused ideas must be removed from the lateral side (C). This task is simplified if all of the joints are widely released by extensive capsulotomies and the interosseous ligament of the subtalar joint is sectioned. In this circumstance a posteriorly based wedge is removed from the subtalar joint, which permits correction of the calcaneus deformity. A dorsal wedge is removed from the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints to allow the forefoot to be dorsiflexed (D). The triple arthrodesis operation is illustrated for the most typical deformity: cavovarus. The affected person is placed on the operating table with a sandbag underneath the hip on the side to be operated, thus bringing the lateral aspect of the foot into higher position. A small, sterile sandbag or other help is placed beneath the medial aspect of the foot. The incision is a straight lateral incision that crosses the lateral facet of the talonavicular joint and the distal finish of the calcaneus. It should prolong from simply medial to essentially the most lateral extensor tendons dorsally to simply past the peroneal tendons volarly. After the fascia over the extensor brevis muscle is incised, the proximal insertion of this muscle is identified and the muscle is elevated to expose the lateral capsules of the calcaneocuboid and talonavicular joints. The fibrofatty tissue is faraway from the sinus tarsi, exposing the lateral aspect of the subtalar joint. The talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joint capsules are incised circumferentially, exposing the joint surfaces. It will assist removing of the bone wedges from the subtalar joint if the capsule of the subtalar joint is also practically circumferentially launched. At this level, almost the entire capsule of the subtalar joint can be visualized and incised, the interosseous ligament could be divided, and a large bone skid can be used to pry the joint open. This will give the surgeon a wonderful view of the two bony surfaces of the subtalar joint which are to be excised. The chisel, with its flat floor as opposed to the double-beveled floor of an osteotome, is much less complicated to carry on a straight course (A). The cut in the bottom of the talus should be parallel with the ankle mortise from lateral to medial (B). The reduce into the dorsal floor of the calcaneus ought to be parallel to the bottom of the heel (C). It is greatest to take benefit of proximal and distal aspects of those cuts first and the center portion in between them final. This is because the center half will be the most troublesome to remove with remaining capsule hooked up to the outstanding sustentaculum tali and probably the most worrisome to reduce through with the neurovascular bundle in shut proximity.
Order 30 mg accutane mastercardThe restore is began proximally by bringing the minimize edge of the vastus medialis and vastus lateralis collectively over the remaining portion of the quadriceps tendon, which is pushed deep to the repair. As the restore reaches the proximal pole of the patella, the patella begins to rotate medially, elevating the lateral portion of the patella. Rather, when the patella is rotated and displaced medially to a adequate diploma, the medial flap is sutured to the periosteum on the lateral two-thirds of the patella with out additional effort to pull the patella medially. The affected person is placed supine on the working desk, and the whole leg is draped free. Although a medial parapatellar incision makes it slightly simpler to reach the semitendinosus tendon, a protracted midline incision, as described for proximal realignment, is better cosmetically. The semitendinosus is probably the most posterior, behind the knee, and is the deepest or most posterior tendon inserting into the tibia. The infrapatellar department of the saphenous nerve can normally be noticed emerging from the Sartorius. Although a couple of of its sensory twigs could also be divided, care must be taken with this nerve to keep away from a large area of anesthesia (B). With the knee flexed, the skin flap is retracted with an extended blade retractor and blunt dissection is sustained posteriorly and proximally (A). Next, the tendon ought to be adopted to its insertion posterior to the Sartorius and gracilis tendons, releasing all extraneous attachments with care to avoid cutting the saphenous nerve (B). A full lateral launch must be performed, on the minimal, together with each the capsule and the synovium. At this level, the surgeon can resolve whether to carry out a extra intensive realignment of the patella with advancement of the vastus medialis muscle or a whole proximal realignment. If nothing more is to be done (as illustrated here for simplicity), a small incision ought to be made within the medial capsule at the distal finish of the patella. This will allow palpation of the inferior surface of the patella for extra correct placement of the drill gap. With the patella held within the desired place and the tendon pulled across the surface of the patella, the right course for the drill gap can be determined (A). Starting on the inferior medial fringe of the patella, a gap of adequate size to enable passage of the tendon is drilled, rising on the superior lateral corner of the patella (B). In directing the drill, the surgeon should be careful to keep away from penetrating the articular floor. Sufficient pressure ought to be placed on the tendon to maintain the patella consistent with the intercondylar notch. This can be examined by flexing the knee whereas an assistant holds tension on the tendon. Note the infrapatellar department of the saphenous nerve that penetrates the Sartorius muscle and branches over the medial capsule of the knee. The primary branch of the saphenous nerve emerges from between the Sartorius and gracilis tendons to proceed down the leg. Care should be taken throughout each the dissection and the routing of the tendon to be certain that these nerve are neither blocked nor kinked. The operation is completed by suturing the semitendinosus tendon to the periosteum of the patella and, if enough size is on the market, to itself. To restore rigidity to the patellar tendon and impact some redirection in its line of pull, a Goldthwait process could be added. This entails splitting the patellar tendon in half, detaching the lateral half, directing this half beneath the medial half of the tendon, and attaching it to the periosteum of the tibia beneath reasonable pressure. At the completion of this step, any muscle advancements or other steps to increase the realignment are completed, and the wound is closed over a suction drain. Semitendinosus Tenodesis of Patella for Recurrent Dislocation: the Galeazzi Procedure. The Galeazzi process transfers the semitendinosus to the inferior pole of the patella. From there, it courses via a drill hole positioned obliquely by way of the patella, exiting the superior lateral aspect. This offers a medial tether and effectively alters the web vector of the patellar tendon towards the medial side. Typically, the vastus medialis is superior roughly one-third the width of the patella. C: the Fulkerson modification entails an oblique minimize that leads to anterior translation because the tubercle is moved medially. This reduces the patellofemoral contact forces while shifting the pull of the patella medially. This is now my preferred technique of surgical administration of the adolescent with recurrent patellar dislocation. If the Q angle is extreme, distal realignment is carried out; the Roux-Goldthwait procedure is used for the skeletally immature sufferers as much as 14 years of age and the Elmslie-Trillat process for sufferers older than 14 years. The greater therapeutic potential of the pediatric meniscus and the results of meniscectomy in a younger lively patient (increased contact forces and early osteoarthritic changes) underscore the importance of correct analysis and treatment of pediatric meniscal injuries. New surgical strategies have facilitated arthroscopic meniscal repair which has become the standard of take care of repairable tears. The lateral half is transferred beneath the medial aspect and sutured to the periosteum alongside the metaphysis. Acceptable results can be expected in as much as 90% of cases employing the Roux-Goldthwait process. An choice is to sharply dissect the entire patellar tendon from its insertion using a scalpel and to resuture it extra medially to restore a traditional Q angle (62). Care must be taken to not transfer the insertion too distally, which may lead to patella baja and important pain. It is crucial to transfer the knee early, and immobilization in a removable knee immobilizer for three to four weeks is sufficient for healing. Active range of motion and strengthening are essential parts of the rehabilitation program, and a resumption of sports exercise can be anticipated in four to 6 months. These forestall the medial meniscus from translating more than 2 to 5 mm with knee movement. The round lateral meniscus covers 70% of the lateral tibial plateau and lacks attachments to the fibular collateral ligament and on the popliteus hiatus. This results in increased mobility of the lateral meniscus, which usually interprets 9 to eleven mm during knee motion. Meniscal blood provide arises from the geniculate arteries which type a peripheral perimeniscal synovial plexus. The developing meniscus is fully vascularized at birth, and its vascularity gradually diminishes to the peripheral 10% to 30% of the meniscus (red-red zone) by age 10 at which period it resembles the adult meniscus (64, 65). Synovial diffusion is responsible for diet of the central portion of the meniscus. The menisci are load sharing and cut back contact stresses throughout the knee joint, transmitting 50% to 70% of the load in extension and 85% of the load in 90 levels of flexion (66). Nondiscoid meniscal tears often happen in older youngsters following a twisting knee injury (65, 67Ͷ9). Meniscal accidents in youngsters typically present with joint line pain and swelling.
Order accutane visaFor correction of proximal tibial varus, the plate is positioned simply anterior to the fibula. They are of enough length to interact the bone without extending past the mid-axis of the bone. The largest staples could additionally be used when the physis is abnormally wide as could also be seen in hypophosphatemic rickets. For varus in the proximal tibia, typically two 3/8 inch staples are positioned parallel to the physis, the primary staple positioned simply anterior to the fibula, the second placed 5-mm anterior to the primary. For correction of angular deformity in the distal femur, two or three 5/8 inch staples are used and are centered about the longitudinal axis of the femur. The preconstructed round fixator is positioned over the leg and applied with a combination of transfixing wires and halfpins. Ring technique and placement of transfixing wires range depending on the presence of open development plates, the necessity for fibular transport to right ligamentous laxity, and the need for distal tibial valgus-correcting osteotomy (112, 124). The proximal tibial osteotomy is carried out by way of a restricted incision, using drill bits and osteotomes. The affected person is encouraged to undertake full weight bearing as early as possible, and physical remedy is instituted to keep mobility and joint range of movement. Adjustments in the circular body are made as essential to right all planes of the deformity. The fixator is left in place and progressively dynamized until consolidation and cortication of the osteotomy site is complete. Correction of the second extremity is usually deliberate within 6 months of completion of the primary side. There have been very few surgical issues in these sufferers despite their extraordinarily massive size (112, 114, 121). All osteotomies, including those who included lengthening, have healed directly. The knee and ankle joints have been realigned and the conventional mechanical axis of the leg restored. The severity of the deformity can easily be assessed and documented by standing photographs. Radiographic analysis is indicated in these youngsters with clinically excessive femoral tibial angles, those who current exterior of typical age vary for physiologic valgus, these with uneven deformity, or those who fall beneath the tenth percentile of top. Most youngsters youthful than 6 years of age who present with a concern of knock-knees are normal (46). The differential prognosis contains metabolic bone illness such as rickets, posttraumatic valgus, or skeletal dysplasia (127ͱ30) (Table 27. If the onset of rickets (osteomalacia) happens when physiologic valgus is present, a knock-knee deformity is extra likely to develop. Valgus could result from overgrowth of the proximal medial tibia following a proximal tibia fracture (Cozen fracture) or from an damage to the distal lateral femoral physis (130ͱ32). Benign neoplastic processes similar to a quantity of hereditary exostoses and focal fibrocartilaginous dysplasia may produce a valgus deformity (133). Parental considerations concerning knock-knees are far less common than these concerning bowed legs (5, a hundred twenty five, 126). Parents usually notice the flat look of the foot before the valgus knee place is noted. This range includes measurements of � eight to 10 levels, which means that regular femoralδibial angles might vary from 2 levels of varus to 20 levels of valgus at three to 4 years of age and impartial to 12 degrees of valgus after 7 years of age (46, a hundred twenty five, 126). B: these lengthy cassette movies of a 12-year-old woman verify the presence of valgus. C: Stapling of the medial physis of each distal femurs in a growing adolescent leads to rapid correction. Physiologic knock-knee predictably remodels to regular alignment (slight valgus) by 7 years of age (2, 5, 46, a hundred twenty five, 126). Minimal, if any, change in femoralδibial angle should happen through adolescent growth. Walking might become awkward due to the knees rubbing or hitting collectively because the baby tries to narrow the bottom of support. This genu valgum is a pathologic state and infrequently requires surgical remedy (134, 135). The decrease extremities should be placed in order that the patellae are going through immediately ahead. A regular mechanical axis passes via the central third of the knee, roughly outlined by the tibial spines, or by way of zones +1 to -1 the place positive values represent valgus and unfavorable values varus (41, 89, one hundred thirty five, 136). Genu valgum that ends in mechanical axis deviation past the lateral margin of the tibia is pathologic and warrants correction. In addition to improving the appearance of lower limb alignment, correction can restore a standard mechanical axis (132, 135, 136). Gait analysis has demonstrated abnormal moments concerning the hip and knee in proportion to the deviation from normal (134). A line is constructed from the middle of the femoral head to the center of the ankle. For consistent serial measurements, the knees are positioned with the patellae going through ahead. To decide the mechanical axis of the tibia, the proximal tibia is longitudinally divided into 4 elements. Zone 1 is centered over the tibial spines, zone 2 is throughout the tibial condyle, and zone three is beyond the cortex. Whether that is performed within the distal femur, proximal tibia, or both will depend upon the location of the deformity and the amount of development remaining (131, 137, 140). Most often, genu valgum deformity happens secondary to asymmetrical growth of the distal femur and sometimes also of the proximal tibia. The technique of inserting an eight-plate or staple(s) implant though easy requires consideration to a few essential particulars to maximize its effectiveness and decrease the potential for growth-plate harm (88, 89, 131, 135). On the lateral view, the implant ought to be positioned centrally (equidistant from the anterior and posterior edges of the physis) to keep away from inadvertent creation of a sagittal aircraft deformity. Timely follow-up is essential for all sufferers chosen for growth modulation, significantly those with greater than 2 years of growth remaining. Some improvement within the decrease extremity mechanical axis must be apparent three to 6 months after the insertion of the implant. Following implant removal, rebound medial overgrowth can happen leading to some loss of correction. It is unclear how lengthy both an extraperiosteal eight-plate or staples can safely span a progress plate with out affecting future development. It has been our apply to take away the implant inside 18 to 24 months if resumption of growth is desired. Stevens has reported resumption of growth following elimination of an implant that was across the physis for greater than 2 years in patients with quite a lot of deformities. As the process is often bilateral and performed near skeletal maturity, absolutely the quantity of shortening is normally not vital. Alternatively, permanent hemiepiphysiodesis can successfully be used to correct valgus angulatory deformities of the older baby and/or young adolescent (137).
Cheap accutane master cardThe controversy over these designs has been increasingly dispelled, with additional medical experience. There are various suspension mechanisms which may be utilized for the safe attachment of the socket to the residual limb. These devices may provide auxiliary suspension which is hooked up to the socket to droop or improve suspension. The Silesian belt attaches to the anterior/medial facet and the lateral aspect of the transfemoral socket and lies across the pelvis on the waist. The accommodation for variations in tissue compressibility, pressure tolerance, underlying bony constructions, and vascular integrity are factors taken under consideration prior to socket design. Dynamic forces exerted via floor reaction forces and resulting moments, including torque and shear forces, enhance the vulnerability of the skinγocket interface. Amputees on the hip disarticulation level require in depth prosthetic intervention. The socket encompasses the amputated pelvic remnant and encloses the contralateral side for suspension. The conventional socket design rises proximally to the waist and fits similarly to a Boston spinal orthosis. The diagonal socket is a modified model of the usual design, and it affords a extra comfy match and elevated flexibility. Prosthetic hips arc on a single axis and are mounted on the outside anterior distal side of the affected facet. Hip and knee flexion are easy to activate via pelvic tilt, if the prosthesis is perfectly aligned. A: the quadrilateral socket is helpful for the younger child, particularly if finish bearing is feasible. This design can show impossible in small infants, due to the fatty thigh and buttocks in addition to the diapers. The nonconventional or extension prosthesis allows the child to "stand" on the prosthesis, extending his limb to the ground and accommodating the deformity. A,B: the nonconventional or extension prosthesis with no knee joint, which is common. Once the valve is in place, the amputee expels air every time the prosthesis is in touch with the bottom. During swing part, the unfavorable pressure inside the socket holds the prosthesis in place. Air that leaks into the socket is quickly expelled via the one-way valve, and a relentless unfavorable pressure is maintained. Total contact suction sockets are usually used for the transfemoral amputee with a mature residual limb and at the completion of skeletal growth. Short limbs, volumetric adjustments, and extreme scarring are contraindications for the suction-suspended socket. Although most amputations in children are disarticulations, progress adjustments within the fibular deficiency typically lead to a transtibial-level residual limb that is a distal-end weight-bearing limb. Total contact design allows for increased pressure bearing over the patellar tendon, medial flare of the tibia, medial shaft of the tibia, and lateral shaft of the fibula, and the anterior and posterior compartments. A: the Silesian belt is sort of universally used within the young pediatric patient to suspend a transfemoral prosthesis or occasionally a knee disarticulation or transtibial prosthesis. B: the suction socket is a tight-fitting socket design with a one-way valve that allows air to be expelled with weight bearing to maintain a suction match on the residual limb. The socket design consists of an outer shell, inside gentle liner, and a beauty cover. The medial, lateral, and anterior walls prolong proximally, to absolutely enclose the patella and femoral condyles. E: the neoprene sleeve suspension supplies very safe suspension for the very lively amputee. The cuff is fabricated from leather and encompasses the femoral condyles and patella. Recent advances in silicone and urethane expertise have increased consolation, flexibility, and cosmesis of the sleeve suspension techniques. Once the liner is donned, the amputee locations the limb in the socket, and the pin and shuttle engage and lock into place. Pressing of a button hidden on the medial distal facet of the prosthesis releases the pin, and the residual limb can be removed from the socket. Because of the physical traits of the liner, the greater the distracting forces positioned on the prosthesis, the tighter the liner grips the residual limb. Where area is at a premium, a cushioned silicone liner used at the facet of a socket expulsion valve and a silicone sleeve allows the amputee to obtain a exceptional stage of suspension using a modified suction method. The detachable or segmented liner socket incorporates a full foam liner that has been constructed up to the same circumference as the distal bulbous end. An atrophied residual limb with a small heel pad is greatest fitted to this design, and the degree of beauty restoration will be very good. The soft silicone liner has a serrated pin incorporated into the bottom of the liner. The patient rolls the liner on the residual limb (A), then inserts the limb into the prosthesis (B). A: Obturator design is usually needed if the distal finish of the residual limb is massive and bulbous or the medial malleolus is distinguished. B: the detachable or segmented liner consists of a complete separate foam liner, which has a cut up in the aspect to allow the distal finish of the limb to pass. Once the affected person applies the liner, she or he slides the limb coated by the liner into the prosthesis. The patient will have to have the guide dexterity and strength to use this suspension, which is able to remove some patients with hand anomalies from using it. C: the bladder design has a built-up silicone sleeve, which the patient slides the limb past. All of the above designs maintain total contact, and the proximal brim is on the degree of the patellar tendon. This ensures that the biomechanical forces are adequately spread up to a load-bearing landmark to improve consolation and performance. It has been estimated that greater than 100 prosthetic knees are commercially available, and the number is rising annually (223). Although most are for adults, just lately there are a variety of new knees out there for kids. The prosthetic knee is composed of the knee mechanism or body and may comprise a management unit. The management unit consists of a pneumatic, hydraulic, or mechanical system, or some mixture of those three. The control unit responds to adjustments in cadence and dampens sudden, abrupt changes.
References - Sui W, Onyeji IC, James MB, et al: Risk factors for priapism readmission, J Sex Med 13(10):1555n1561, 2016.
- Morrison, R. S., et al. (2000) iWe donit carry thati o Failure of pharmacies in predominantly nonwhite neighborhoods to stock opioid analgesics. New England Journal of Medicine, 342, 1023n1026.
- Pfau A, Sacks T: The bacterial flora of the vaginal vestibule, urethra and vagina in the normal premenopausal woman, J Urol 118:292n295, 1977.
|
|