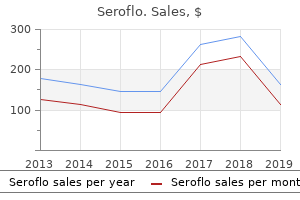
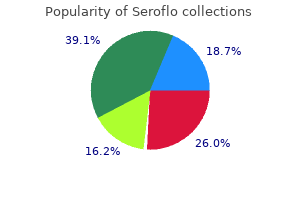
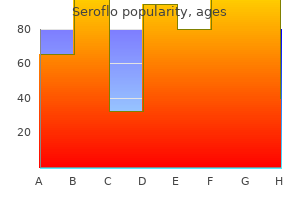
"Purchase seroflo in united states online, allergy shots for hives."By: Keira A Cohen, M.D. - Co-Director, The Johns Hopkins Center for Nontuberculous Mycobacteria and Bronchiectasis
- Assistant Professor of Medicine
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/10003818/keira-cohen
Purchase seroflo without prescriptionThe ache takes 4�5 days to resolve and the lesion slowly fibroses, usually leaving a palpable, persistent nodule. Anal Fistula Anal fistulas represent a communication between the anal canal and the perianal skin. The overwhelming majority of anal fistulas seen in surgical practice are because of persisting infection of the anal glands in the intersphincteric house � the cryptoglandular speculation. They may be considered to be the continual sequel of the father or mother situation, acute anorectal sepsis, although many years might elapse between the two clinical situations. Anal fistulas are also seen in association with other particular situations corresponding to inflammatory bowel disease, tuberculosis, malignancy, actinomycosis, lymphogranuloma venereum, trauma and international bodies. Patients with anal fistulas complain of intermittent anal pain and discharge, both purulent or combined with blood; the two signs are sometimes inversely associated, with the ache growing till it eases off when the pus drains out by way of the exterior opening. There is commonly a history of acute anal sepsis, both handled surgically or that has settled after a spontaneous discharge of pus or insidiously, leaving a gap on the perianal skin. The surgical management of anal fistulas depends upon an correct knowledge of each the anatomy of the anorectal sphincter and the course of the fistula by way of it. An understanding of the aetiology and anatomy is fundamental to the right management. Patients with acute anal sepsis current with a narrative of accelerating pain in the area, often a lump, and sometimes a purulent or bloody discharge and fever. The situation of a excessive intermuscular abscess is uncommon however have to be thought of within the differential prognosis of a affected person with fever, vague deep anorectal pain, perhaps issue in passing urine and possibly no visible abscess, however in whom digital examination of the anorectum is extraordinarily painful. The key to their distinction from boils associated with anal problems can typically be discovered in the microbiology and the smell of the pus. The incidence of anorectal sepsis due to pores and skin organisms � and nothing to do with fistulas � is equally divided between the sexes, whereas sepsis due to intestine organisms is more frequent in males, reflecting the same (unexplained) male predominance of the chronic condition, the anal fistula. A historical past of previous sepsis on the similar web site can be indicative, however not diagnostic, of a communication with the anorectal lumen. Such fistulas may be uncomplicated, consisting only of the first track opening onto the skin of the buttock, or can have a high blind secondary track that ends either below or above the levator ani muscle tissue. Some are iatrogenic in origin, arising from overzealous probing of the ischiorectal fossa in a patient who presents with an ischiorectal abscess. It is necessary to understand the fundamental primary tracks of the 4 recognized forms of anal fistula. Superimposed on these major tracks are extensions or secondary tracks that might be blind or may open onto the perineal skin or again into the anorectal lumen (usually due to injudicious probing). Besides vertical and horizontal unfold, sepsis may also spread circumferentially in any of the three tissue planes: intersphincteric (or intermuscular, which means no restriction to below the anorectal ring), ischiorectal or pararectal. The relative positions of the inner and exterior openings point out the doubtless course of the first track, and the presence of any palpable indurations, especially supralevator, alerts the surgeon to a high secondary track. The distance between the external opening and the anal verge could assist the differentiation between an intersphincteric and a trans-sphincteric fistula; and the higher the space, the extra the probability of a complicated upward extension. The position of the external opening also offers a clue to the probably web site of the interior opening. The inner opening may be felt digitally as an indurated nodule or pit, or could also be seen at proctoscopy, aided if needed by light downward retraction of the dentate line, which may expose openings concealed by distinguished anal valves. Sigmoidoscopy and/or colonoscopy could additionally be required to exclude inflammatory bowel illness. Patients discover themselves in a vicious circle by which they anticipate that the subsequent bout of defecation might be painful; hence they avoid passing a stool and turn out to be progressively more constipated. Pruritus ani is an insatiable itch around the perianal region; it could lengthen to the introitus in girls and women. The pores and skin is usually moist from an anal or vaginal discharge of infected material, mucus or faeces. Thrush is frequent, and urinary leakage may be due to a cystocele or an ectopic ureter. This is normally as a result of extended contact with urine or faeces but could additionally be as a result of a fungal an infection or a response to an emollient. A prolapse may be brought on by straining excessively at stool, particularly if the pelvic ground muscles are weak. Although the young and the aged are most incessantly seen with the condition, any age group may be affected. If present for a long time, the prolapse might ulcerate and the affected person could then current with bleeding and mucus discharge. Occasionally, a prolapse can become ischaemic and present as a surgical emergency. The highest charges are seen in homosexual males, though heterosexual individuals are certainly not immune, the condition being nearly invariably sexually transmitted. Patients with perianal warts usually complain of itching, bleeding and perianal lumps; there may also be symptoms from warts elsewhere on the genitalia. It normally affects the axillae but could involve the again of the neck, the areola of the breast, the groins and the perineum. Its aetiology is unknown, although weight problems, pimples, poor hygiene and extreme sweating have been instructed as predisposing elements. It may be seen in a big selection of endocrine issues, suggesting that a relative androgen extra or elevated target organ androgen sensitivity may be implicated. Occlusion of the apocrine gland ducts leads to bacterial proliferation within the glands, with rupture and the unfold of an infection to adjacent glands. Secondary an infection causes additional native extension, skin damage and fibrosis, ultimately leading to multiple speaking subcutaneous fistulas. In the primary stages, it presents with a number of, tender, raised, red lesions across the perianal region, but in its continual kind a quantity of sinuses are seen, with secondary infection leading to gross fibrosis and scarring. The location is characteristically over the bony sacrum, usually in the midline. It is presumably congenital, but a traumatic aetiology is suggested by the truth that the opening is within the natal cleft between the ischial tuberosities at a site of maximum shearing stresses when an individual seated. Such pits are commonly seen as incidental findings on examination and may by no means be associated with pilonidal illness, which is characteristically seen in hairy truck drivers. Abscess formation throughout the sinus results in the development of secondary lateral tracks since discharge via the midline is prevented by the fibrous septa connecting the skin to the fascia over the sacrum. Such lateral tracks may move caudally and create an appearance that may resemble hidradenitis suppurativa or fistula-in-ano, both of which can coexist with pilonidal illness. The acute abscess usually lies to one side of the midline, although a midline pit is all the time current. Rarer variations of the situation are seen on the hands, at the umbilicus and in the axillae.
Cheap 250mcg seroflo visaA single renal lobe consists of a calyx, collecting ducts, and its overlying renal cortex. Coronal reconstructed computed tomography picture present delicate indentations along the margin of the left kidney, typical of persistent fetal lobation. Note also the fat that extends from the higher renal sinus on the best to the perirenal fats (arrow); this is associated to the junctional parenchymal defect, an anomaly as a outcome of partial fusion of embryonic parenchymal plenty often known as renunculi. In utero, renal lobar anatomy is evident as early because the fourth month of gestation. During maturation, mobile multiplication within the renal cortex continues and leads to lack of definition of gross lobar anatomy in most people. Hypertrophy leads to not an increased variety of glomeruli, but rather to enlargement and increased capability of the prevailing glomeruli. This enlargement may find yourself in world or focal enlargement of the kidney, as is often seen in sufferers after lack of substantial volumes of functioning renal tissue. The remaining kidney enlarges and increases its excretory capacity to compensate for the misplaced renal parenchyma. In older people, however, the capacity for renal hypertrophy is less than in youngsters. When focal, this can lead to masslike areas of distinguished, however regular renal parenchyma, generally known as a pseudotumor. At birth, the kidneys lie within the upper lumbar area as a result of the differential migration of fetal tissues during gestation. This obvious ascent of the kidney is definitely because of the fast longitudinal progress of the embryo in the lumbar and sacral regions caudal to the creating kidney. This cephalic migration to the adult place happens from the fourth to the eighth week of gestation. A and B, Axial unenhanced computed tomography images by way of the higher and lower elements of the kidney and (C) a coronally reconstructed image present bulging areas of parenchyma in the left upper pole and the best lower pole. The patient had an extended historical past of urinary tract infections starting as a young lady. During ascent from the true pelvis, vascular supply to the kidneys comes from progressively greater branches off the aorta, and the inferior branches regress. The renal artery then arises laterally from the aorta at roughly the level of the second lumbar vertebra. Although progressive ascent normally results in regression of the inferior blood vessels, anomalous vessels are commonly seen supplying the kidney. In addition, failure of full ascent resulting in anomalous renal position, as seen with pelvic and horseshoe kidneys, is nearly at all times related to coexistent anomalous blood supply to the affected kidney, which displays persistence of those inferior branches. Obviously, kidney improvement includes a posh sequence of developmental processes throughout gestation. It is interesting to note that successive growth and maturation of the primitive excretory organs- the pronephros, mesonephros, and metanephros- recapitulate the complex evolution of excretory organs in species of varying ranges of sophistication. A, An unenhanced computed tomography image obtained for left flank ache reveals a stone in the left kidney, and the kidney is enlarged (compensatory hypertrophy). B, Axial picture via the pelvis shows absence of the right seminal vesicle (arrow). Abnormalities of Number Renal Agenesis Renal agenesis outcomes from failure of the ureteric bud to attain the metanephric blastema because the ureteric bud fails to form or degenerates prematurely. These embrace absence of the ipsilateral ureter and its related hemitrigone, or presence of a blind-ending ureteral stump, a remnant of the incompletely developed ureteral bud. Axial computed tomography reveals the normal wishbone shape of the proper adrenal gland, and the flattened, single limb of the left adrenal gland (arrow) in the absence of the left kidney from the renal fossa. A, An enhanced computed tomography image via the higher stomach reveals proper renal agenesis and left renal compensatory hypertrophy. B, An image via the anatomic pelvis reveals two apparent uterine horns on this patient with a bicornuate uterus. These complex m�llerian duct anomalies are considered a part of the Mayer-Rokitansky-K�ster-Hauser syndrome. Absence of the ipsilateral adrenal gland is associated with renal agenesis in 10% of patients. With absence of one kidney, bowel (duodenum or colon on the right and colon on the left) may fall into the empty renal fossa. With absence of the left kidney, the descending colon could course medially with respect to the distal transverse colon resulting in a looped configuration of the splenic flexure (Box 2-4). Bilateral involvement is uncommon, occurring approximately once in every 3000 live births. With bilateral renal agenesis, intrauterine progress does happen as a outcome of the placenta serves because the excretory organ for the fetus. Potter syndrome features a typical facial pattern with low-set ears, a broad flat nose, and outstanding pores and skin folds under the lower eyelids, coupled with pulmonary hypoplasia and development of pneumothoraces at start. Unilateral renal agenesis could stay asymptomatic as long as the contralateral kidney functions normally. With unilateral renal agenesis, congenital malformations within the remaining solitary kidney are common. If these abnormalities impair renal function, then symptomatic renal insufficiency can develop. Supernumerary Kidney Very not often, more than two discrete kidneys are current, most likely due to the formation of two ureteral buds on one aspect. Usually, the supernumerary kidney occurs on TheKidneyandRetroperitoneum 45 the left side caudal to the conventional kidney and is hypoplastic. In the primary sort, a bifid ureter also drains the second kidney on the ipsilateral side. Rotational anomalies occur when the kidney fails to rotate usually about its longitudinal axis during ascent. Some of the calyces shall be situated medial to the renal pelvis, a trademark of rotational anomalies. Renal Ectopia Renal ectopia describes arrest or exaggeration of the conventional caudal-to-cranial ascent of the kidney. Anomalous blood provide to the kidneys is just about all the time related to renal ectopia. Renal ectopia can also be related to anomalies of fusion or lateral crossed anomalies. Depending on the diploma of ascent, low kidneys could lie in the true pelvis, in the iliac fossa opposite to the iliac crest, or in the lumbar region, above the iliac crest however under the L2 vertebral physique. Ectopic kidneys are often associated with contralateral renal anomalies, including renal agenesis or ectopia of the contralateral kidney. If the medial segments of the kidney fuse, the mixed kidney mass types a ringlike renal construction within the pelvis. Either a single ureter or two separate ureters may be current to drain this mass of renal parenchyma. Pelvic kidneys are often asymptomatic, though they do seem to be much less well protected from trauma than kidneys positioned normally within the retroperitoneal higher lumbar region.
Purchase seroflo in united states onlineThe relative evacuation of contrast-laden urine from a diverticulum after bladder emptying is important as a end result of it might affect the choice to deal with sufferers surgically, especially those with recurrent urinary tract infections. Cystocele Cystocele is irregular descent of the bladder with prolapse into the vagina. Concomitant prolapse of the bladder and urethra (cystourethrocele) is incessantly current with stress urinary incontinence. In addition, cystocele may be associated with bladder-outlet obstruction or hydronephrosis, particularly when the degree of prolapse is extreme. B, Axial computed tomography picture confirms the presence of a fluid-filled reservoir (arrow) for an inflatable penile prosthesis. Cystoceles are graded from delicate to extreme according to the degree of descent of the bladder under the superior pubic margin. Prolapse of up to 2 cm beneath the superior pubic margin defines a light cystocele, whereas a cystocele that descends under the level of the rami is severe. In adults, the vast majority of bladder herniations result from agerelated weakening of the supportive structures of the abdominal wall. Such herniations usually have a tendency to happen in the presence of bladder-outlet obstruction that requires straining throughout voiding and results in bladder distention. These bladder ears are a normal variant in infants and are of little scientific significance. In most sufferers bladder herniation is asymptomatic and is discovered by the way throughout herniorrhaphy. Other sufferers present with a basic history of twostage voiding: the affected person empties the bladder proper first however then must compress manually the herniated bladder. The wall of the hernia is smooth, until the hernia is difficult by lithiasis or irritation. On fluoroscopic analysis, continuity the most typical reason for the radiographic finding of air within the lumen of the bladder is latest catheterization or instrumentation (Box 6-12). The two essential pathologic circumstances that should be thought-about are fistula between the bladder and the bowel or vagina, and infectious cystitis attributable to a gas-forming an infection. Enterovesical and Colovesical Fistulas In addition to pneumaturia, a fistula from both the small bowel or colon may trigger persistent infectious cystitis or fecaluria (Box 6-13). These signs often dominate the medical presentation of enterovesical and colovesical fistulas. Carcinoma of the rectosigmoid is difficult by colovesical fistula more typically than is carcinoma of the cecum. Enterovesical fistula has been reported in as many as 5% of adults and 10% of youngsters with Crohn illness. Rectosigmoid illnesses that lead to fistula formation usually involve the left and posterior bladder partitions. Conversely, infectious or inflammatory processes originating from the cecum, appendix, or distal small bowel are inclined to have an effect on the best facet of the bladder, both anteriorly or laterally. A, Oblique picture in the course of the cystographic section of intravenous urogram reveals marked focal prolapse of the bladder base (arrows = distal proper ureter). B, Computed tomography demonstrates the ureters (arrows) getting into the trigone, which has prolapsed to the extent of the ischial tuberosities. Fistulas from bladder to bowel may be tough to demonstrate by cystoscopic or radiologic methods. Fistulous connections are diagnosed with standard cystography and barium enema in only 30% to 60% of sufferers; the accuracy of cystoscopy is analogous. The contrast is infused into the bladder by gravity via a urethral or suprapubic catheter. Also seen are vaginal apical descent/uterine prolapse (short black arrow) and a rectocele (asterisk) in this affected person with global pelvic flooring laxity. A, Image from cystography with the patient at relaxation exhibits the bladder above the level of the superior pubic margin. Anteroposterior view through the cystographic part of an intravenous urogram demonstrates bilateral focal outpouchings of the inferolateral bladder wall according to small bladder herniations. In creating nations, obstetric injury is a typical cause of vesicovaginal fistula. Other much less common etiologies embody overseas body (Foley catheter) and tuberculous or bilharzial cystitis. The medical hallmark of vesicovaginal fistulas is continuous urinary incontinence. Vaginoscopy or speculum examination after cystoscopic instillation of indigo carmine or milk within the urinary bladder can be used for direct visualization of a fistula. Emphysematous Cystitis Emphysematous cystitis is a uncommon type of cystitis that tends to occur in women with poorly controlled diabetes. Management with appropriate antibiotics and control of diabetes are normally efficient, although surgical management may be essential in difficult instances. The pattern of air inside the bladder wall could additionally be linear, streaky, or multicystic. A and B, Axial pictures via the pelvis at two ranges show herniation of the left anterior facet of the bladder into a left inguinal hernia (arrows). Calcification in the Bladder Wall or Lumen Common and uncommon causes of mural or luminal bladder calcification are shown in Box 6-14. Bladder Stones As with nephrolithiasis, bladder stones have a tendency to form when urinary stasis and an infection are current. A, Abdominal plain film demonstrates two massive pockets of air (arrows) in the pelvis. C, Percutaneous cystogram demonstrates two filling defects, specifically, one resulting from purulent particles (arrow) and the opposite ensuing from invasive recurrent rectal most cancers (open arrow). Therefore small uric acid stones are sometimes undetectable on plain films, especially compared with larger uric acid and struvite stones. If the affected person is within the supine position, bladder stones are most likely to rest within the midline; laterally positioned stones, especially if there are a number of faceted stones in shut proximity, suggest location within a diverticulum. A large, nonopaque calculus with rim calcification can simulate bladder wall calcification on plain stomach radiographs. Differentiation of stone from mural-based mass could be achieved if mobility is shown on plain film or sonograms. A small quantity of gas is also present within the urinary bladder secondary to the fistula (white arrow). A, the bladder wall is thickened and intraluminal gasoline is present (arrow) in a patient with Crohn disease. Tethering of extra loops of small bowel and colon is famous on this affected person with fistulizing Crohn disease (short arrows).
250 mcg seroflo saleOther circumstances that have to be differentiated from a distended bladder embrace an ovarian cyst, fibroid uterus and pregnant uterus. Ninety-five per cent of testicular cancers are germ cell tumours, and four per cent are lymphomas, the latter occurring predominantly in males aged over 50 years. Rarely, testicular most cancers presents with manifestations of metastatic disease, together with weight reduction, chest symptoms and again ache. Testicular tumours occasionally trigger severe scrotal ache secondary to intratumoural haemorrhage. Examination of the involved testis usually reveals a tough painless mass throughout the testis, which can prolong into the epididymis and spermatic twine (Table 39. If the tumour has penetrated the tunica albuginea, a secondary hydrocele could also be present. General examination can reveal cachexia, enlarged lymph nodes, chest signs, hepatomegaly and gynaecomastia. Although prostate most cancers is the second most typical reason for most cancers dying in males, extra men die with prostate cancer than due to the illness. In this case, males typically falsely imagine that their symptoms are a result of the diagnosed prostate cancer. Men with locally superior or systemic disease might current with bone pain from skeletal metastases, indicators of renal impairment from unilateral or bilateral ureteric obstruction or bowel symptoms from impingement on the rectal canal (despite the shut proximity of the gland to the bowel, prostate most cancers hardly ever instantly invades the rectal wall). Spinal metastases can invade or compress the spinal wire, resulting in decrease limb neurological signs and/or autonomic dysfunction, together with urinary retention or less frequently bowel or bladder incontinence. Prostate examination is due to this fact an important examination in all men presenting with unexplained decrease limb neurological symptoms as therapy must be initiated earlier than irreversible damage occurs. The prognosis of males presenting with prostate most cancers is influenced by a quantity of elements, especially the stage of the illness (Table 39. The scientific staging of prostate cancer by palpation may be difficult and requires expertise. The primary treatment is inguinal orchidectomy except the patient presents with advanced metastatic illness, during which case urgent referral for primary chemotherapy should be thought of. Delayed analysis also occurs as some patients are misdiagnosed and inappropriately managed by their primary care physician. There are many premalignant penile lesions that, if treated appropriately, can be prevented from progressing to invasive carcinoma. Bowenoid papulosis predominantly impacts young sexually active men and is highly contagious. The lesions are normally a number of, pink and velvety, and affect the penile shaft, glans and prepuce. Condylomata acuminata are exophytic, warty lesions that can have an effect on any a part of the anogenital region, especially the coronal sulcus. It usually presents as pale, atrophic plaques on the glans, prepuce and less generally the meatus and anterior urethra. A cutaneous penile horn is a uncommon keratotic lesion that arises secondary to chronic inflammation. Leukoplakia is characterised by white plaques that happen on the glans and prepuce. As most patients are uncircumcised, the lesion may not be discovered till it erodes via the prepuce, turns into contaminated or bleeds. In superior circumstances, the patient might present with a fungating mass involving the metastatic inguinal lymph nodes. Urinary incontinence is a multifactorial disease course of that impacts 1 in four girls and 1 in 9 males during their lives (Table 39. A large variety of varied pathologies and conditions can intervene with these mechanisms, leading to urinary incontinence. Stress urinary incontinence normally happens as a end result of urethral sphincter muscle weak spot and/or an anatomical defect within the urethral help, leading to inadequate closure pressure within the urethral throughout bodily activity. The urethral sphincter could additionally be weakened after pelvic surgical procedure, neurological harm or pelvic irradiation. Damage to the nerves, muscle and connective tissues of the pelvic floor during childbirth is probably the commonest reason for stress incontinence. Urge incontinence could result from detrusor myopathy, neuropathy or a mix of each. Mixed and urgency incontinence predominate in older ladies, while stress incontinence is more common in younger and middle-aged girls. During the bodily examination of patients with urinary incontinence, you will need to examine for conditions which will contribute to or exacerbate urinary incontinence or affect management decisions. The stomach should be examined for masses that may contribute to stress incontinence or may trigger bladder outflow obstruction with related overflow incontinence. The exterior genitalia and perineum may be erythematous and inflamed secondary to urinary leakage. In girls, the tissues of the genitalia could additionally be pale and skinny, suggesting oestrogen deficiency (although the position of oestrogen in the continence mechanism remains unclear). The suburethral area and anterior vaginal wall ought to be inspected for signs of a diverticulum (associated with post-micturition dribbling) or the opening of a fistula tract. This kind of incontinence is commonly as a outcome of a urinary tract fistula or ectopic ureter Urge urinary incontinence approximately 33 per cent after the age of 60 years. Renal Angiomyolipoma A renal angiomyolipoma is a benign renal tumour that consists of adipose cells, clean muscle and blood vessels. Approximately 20 per cent of circumstances are associated with tuberous sclerosis syndrome, which is characterised by mental retardation, epilepsy and adenoma sebaceum. Tumours larger than four cm in diameter usually have a tendency to cause symptoms, together with large retroperitoneal haemorrhage, which may require selective embolization or complete nephrectomy. Mixed urinary incontinence Continuous urinary incontinence With assistance from a speculum, a detailed pelvic ground assessment should be performed to search for indicators of pelvic organ prolapse, including a cystocele, rectocele, uterine or vaginal prolapse. The affected person ought to be asked to cough and strain to reveal stress urinary incontinence by the involuntary leakage of urine from the urethra. A focused neurological examination, concentrating on the sacral segments, should be a half of the evaluation to exclude a neurological cause for the incontinence. Ureter Pelviureteric Junction Obstruction Obstruction of the flow of urine from the renal pelvis to the proximal ureter can result in hydronephrosis and progressive renal impairment. Pelviureteric junction obstruction is normally congenital, and multiple aetiologies have been proposed. Clinical examination is often unremarkable unless the kidney is considerably hydronephrotic, when it might be palpable. The diagnosis of pelviureteric junction obstruction requires functional assessment, and the investigation of alternative is diuresis renography. Urinary Tract Fistulas Urinary tract fistulas are irregular communications between the urinary tract and the outside, or with another viscus such because the bowel, uterus or vagina. Vesicovaginal and ureterovaginal fistulas commonly happen as a complication of gynaecological surgical procedure, pelvic radiation or extended and obstructed labour in creating nations. Patients often present with steady urinary incontinence that may be exacerbated by bodily activity, resulting in confusion with stress incontinence. Patients who develop a ureterovaginal fistula following pelvic surgical procedure usually expertise fever, flank pain and gastrointestinal signs post-operatively secondary to urinary extravasation.
Discount 250 mcg seroflo mastercardThe ordinary path of slippage of the epiphysis is posteriorly and medial to the femoral neck. The different hip is concerned in 40 per cent of cases, however only 50 per cent of these will produce symptoms. The situation is extra prevalent with elevated weight and excessive joint stress actions. Stiffness, significantly after an extended interval of rest, leads to issue in placing on sneakers, socks and stockings. As the condition deteriorates, the strolling distance is reduced and walking is associated with a limp. There could additionally be a historical past of acute damage, but the majority may have had symptoms for weeks or months. The swelling is situated in the femoral triangle however is too lateral to be a femoral hernia. There is ache with flexion and abduction of the hip because the psoas tendon rubs in opposition to the infected bursa. Tenderness over the anterior hip is a characteristic, and stretching workout routines are the beneficial remedy. Any apparent shortening is eliminated by inserting both legs in the identical orientation with respect to the pelvis. The majority of instances of osteoarthrosis of the hip constitute a main condition. Premature osteoarthrosis of the hip may result as a secondary process in youthful individuals from developmental dysplasia of the hip, Legg�Calv�Perthes disease, a slipped higher femoral epiphysis or osteonecrosis of the top of the femur. The situation often outcomes from the iliotibial tract passing over the larger trochanter. The snapping hip could be reproduced with passive flexion from an adducted place. This situation ought to be differentiated from intra-articular snapping, which stems from the iliopsoas tendon impinging on the hip capsule. Chronic Low-grade Infection the affected person complains of a steady ache in the groin or thigh, usually starting some weeks or months after hip alternative. Plain radiographs may show some indicators of loosening, and a bone scan shows an elevated uptake consistent with an infection. There is death of the trabecular bone and bone marrow, followed by collapse of the bony structure. Later on, after the femoral head bone has collapsed, the indicators are similar to those of an arthritic hip. The prognosis is confirmed in later circumstances by plain radiographs as these present the collapse of the femoral head and narrowing of the joint area. Aseptic Loosening of the Hip Some patients have a satisfactory consequence of their hip replacement for a quantity of years before progressively rising pain develops in the groin or thigh. There is an related stiffness, an incapability to bear weight and a progressive limitation of the vary of movement. Examination involves flexing the hip and the knee to 90� and applying axial compression or traction to the femur. This often produces ache because the femoral part of the prosthesis pistons or subsides within the femur. A plain radiograph will show a defined sclerotic line around the loose stem and, in advanced circumstances, migration of the prosthetic components. Meralgia Paraesthetica this is a compressive neuropathy of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve of the thigh when it turns into entrapped underneath the inguinal ligament or often by way of the fascia lata. This nerve is purely sensory, leading to an area of hyperaesthesia and tingling over the lateral side of the thigh. This is worse on standing and walking but is relieved by sitting as flexion of the hip shortens the course of the nerve. This affords explicit advantages in allowing a good range of motion and reducing the frictional torque inside the hip. The path of the dislocation is governed by the alignment of the acetabular and femoral parts, in addition to the surgical approach used. With the generally used lateral surgical method, the danger of dislocation is best when the hip is flexed and adducted. The affected person complains of sudden severe ache within the hip and feels the hip coming out of the socket. Trochanteric Bursitis this is inflammation of the trochanteric bursa that happens primarily after increased physical exercise. Palpation over the greater trochanter causes pain, as might getting the affected person to abduct their leg towards resistance. The analysis of a fracture is confirmed by anteroposterior and lateral radiographs. Isolated Trochanteric Fractures A direct fall onto a hip may cause an isolated fracture of the larger trochanter. There is usually bruising and swelling across the trochanter, with native tenderness. The hip actions are often reasonably nicely preserved, though painful, and the analysis is confirmed radiologically. Avulsion of the lesser trochanter in isolation tends to happen in schoolchildren who hurdle and is due to violent contraction of the psoas. If this fracture is seen in an elderly particular person, the clinician ought to think of a pathological fracture. Fracture of the Neck of the Femur Two forms of fracture occur here, but the medical picture is similar. The capsule of the hip joint extends down the neck of the femur so far as the top of the trochanters, and fractures might occur inside or outside this capsule. At this point, the blood provide to the head of the femur is commonly interrupted, resulting in a lack of blood provide to the pinnacle. Reduction and inner fixation of the fracture could not at all times lead to passable union of the bone, and a prosthetic alternative is often the remedy of selection in the aged. The majority of fractures occur by way of osteoporotic bone and are seen within the elderly. There is pain in the hip, and there could also be bruising within the region of the higher trochanter. If the leg is severely externally rotated (90�) and short, the fracture is probably extracapsular. Lesser levels of exterior rotation and shortening are seen in intracapsular fractures because of the constraints of the hip capsule. Some intracapsular fractures are undisplaced, or the bone ends are impacted, giving rise to little or Fractures of the Shaft of the Femur these result from a extreme mechanism of damage, corresponding to a high-velocity motorcar accident, and range from easy transverse or spiral undisplaced fractures to extreme, shattered, comminuted lesions, which may be open and likewise accompanied by vascular compromise. There can be a considerable blood loss in these type of harm, and immediate resuscitation could additionally be required. Traumatic Dislocations of the Hip these are comparatively uncommon and usually require a extreme mechanism of injury. The leg lies internally rotated, is shortened and is usually barely flexed at the hip.
Syndromes - Remaining unconsciousness (coma)
- Is it present continuously, or only from time to time?
- Tumor (including cancer)
- Enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia)
- Treat the person for shock if he or she appears faint, pale, or if there is shallow, rapid breathing.
- Septic shock

Generic seroflo 250 mcg mastercardAgranulocytosis Agranulocytosis is an acute condition involving severe and harmful neutropenia. The ulcers are necrotic, with a whitish or greyish floor, typically with out indicators of irritation. Lingual Torus A mandibular torus is a compact bony lesion that occurs along the lingual side of the mandible, often on either side of the midline. Wasting and Deviation of the Tongue Unilateral losing of tongue is associated with long-standing hypoglossal nerve palsy, with the tongue deviating to the affected web site. This can outcome in an obstruction of the circulate of saliva from the gland, leading to recurrent swellings of the submandibular gland. It has a gentle, doughy consistency, is well encapsulated and has no associated cervical lymphadenopathy. It might symbolize the one functioning thyroid tissue, and its elimination may render the affected person hypothyroid. Carcinoma of the Tongue Carcinoma of the tongue often happens on the lateral border of the anterior two-thirds of the tongue however can often contain the posterior one-third. Deviation of the tongue to the facet of the lesion and ankyloglossia are signs of deep tumour infiltration. They end result from a failure of the mesenchyme to penetrate the junctions between the primary processes (the frontonasal and maxillary process) that fuse to kind the nose, lips and palate. A cleft lip is primarily a cosmetic problem, but a cleft palate may trigger problems with feeding and speech, in addition to an increased risk of respiratory and ear infections. A submucosal cleft is a rare type of cleft palate by which the mucosal covering is undamaged however there could also be abnormal muscle positioning or an underlying bony cleft. There is extreme nasality of speech, a blue line could additionally be seen within the midline of the palate, and the situation is sometimes related to a bifid uvula. A cleft palate could happen in affiliation with micrognathia and glossoptosis in a condition often known as Pierre Robin syndrome. In these babies, the tongue may fall backwards, leading to respiratory obstruction or sleep apnoea. Carcinoma Carcinoma within the palatal region is commonly seen to arise from either the minor salivary glands within the palate or the maxillary sinus. Paralysis Paralysis of the taste bud could additionally be unilateral from a lesion of the vagus nerve or bilateral in bulbar poliomyelitis. The analysis of oral lesions depends on the age of presentation, the attribute morphological look and the medical options. Lesions of the dentition comprise an important a part of the lesions of the mouth and a data of these conditions is essential. An examination reveals several lesions on the lips and buccal mucosae; some are tiny and vesicular, while some have damaged right down to kind shallow ulcers. The lesions are in the type of small vesicles that break down to kind shallow ulcers. Herpes zoster lesions are usually unilateral, and lie alongside the distribution of a particular department of the trigeminal nerve; they could be fairly painful. Oral malignancy presents with non-healing ulcers or frank growths that bleed to the touch, are sometimes indurated and may be accompanied by enlarged neck nodes. Leukoplakia seems as a whitish plaque-like lesions in the absence of any apparent trigger, and carries a small but definite malignant potential. Submucous fibrosis, or progressive stiffening of the oral mucosa, with trismus might remodel into malignancies. This assertion is untrue as ameloblastomas are often benign tumours which might be domestically aggressive. All of the following are premalignant lesions of the oral cavity besides which one For each of the following descriptions, select the most probably analysis from the list of lesions and tumours of the oral cavity beneath: 1 Dental cyst 2 Leukoplakia 3 Oral squamous cell cancer four Pemphigus 5 Ranula 6 Submucous fibrosis 7 Erythroplakia eight Epulis a A 5-year-old girl presents with a swelling in her oral cavity. On examination, a fluctuant swelling may be seen on the ventral facet of the tongue, extending to the ground of the mouth. The floor of the oral swelling exhibits distended veins, and clear fluid may be aspirated from the swelling. A ranula is a cystic swelling that arises from the sublingual salivary gland, and its ordinary position is in the anterior flooring of mouth. The discovering of a hard neck node within the submandibular region (which is the standard draining area of oral cavity) further substantiates the analysis. Atresia of the posterior nares, which can be bony or membranous, may end result from persistence of the primitive bucconasal membrane. Unilateral atresia might go unnoticed, but bilateral atresia presents quickly after start with intermittent asphyxia or asphyxia during feeding. The youngster may present cyanosis at relaxation but an improvement on crying (paradoxical cyanosis). An absence of condensation after inserting a chilly spatula beneath the nostrils and an incapability to cross a gentle plastic tube by way of the nose are seen in atresia. Rhinitis Acute and Chronic Rhinitis Acute rhinitis presents with rhinorrhoea, nasal obstruction and constitutional disturbances. Chronic rhinitis could present as relapsing assaults of acute rhinitis (lasting more than 12 weeks) or secondary to sinusitis. On posterior rhinoscopy, a mulberry-like enlargement of the posterior end of the inferior turbinate is seen. Secondary atrophic rhinitis can follow granulomatous an infection, intensive nasal surgical procedure and trauma. Vasomotor Rhinitis Vasomotor rhinitis presents with sneezing, watery rhinorrhoea and nasal obstruction of unknown aetiology. Hereditary components, psychological factors, atmospheric circumstances and dusty environments might set off paroxysmal symptoms. Syphilis Congenital syphilis causes a purulent rhinitis, vestibule excoriation and different stigmata in infants up to about 3 months of age. In the acquired type, it may cause a chancre as a tough, painless, ulcerated papule with non-tender rubbery nodes at about 3�6 weeks of age. A secondary type could cause persistent rhinorrhoea, with crusting and fissuring of the vestibule at about 6�9 weeks. The gumma happens within the tertiary stage after 1�5 years and impacts the periosteum of the septum, resulting in perforation of the bony septum and ensuing within the attribute saddle deformity. Mucocoeles Frontoethmoidal mucocoeles are frequent because of the complexity of the drainage. They present as headache, orbital displacement and visible disturbances in the late levels.
Discount seroflo 250mcg overnight deliveryThe degree of flexion of the hip when the lumbar lordosis is flattened constitutes the quantity of the mounted flexion deformity. If ache is elicited within the contralateral lower extremity this suggests the presence of inflammation around the sacroiliac joint, which should be differentiated from true intra-articular pathology of the hip. The toddler lies supine on a flat floor, and the examiner flexes the knees and hips to 90�. The examiner then pushes the larger trochanters anteriorly with their fingers, while abducting the hips. The patella can be utilized as a reference point to evaluate the rotation of the decrease extremities. A limitation of internal rotation is indicative of intra-articular pathology of the hip. Adduction and Abduction the examiner grasps the contralateral anterior superior iliac spine firmly with one hand so as to repair the pelvis towards the examination desk. Grasping the lower tibia or ankle with the opposite hand, the examiner then moves the leg away from the midline to check for abduction, and in the path of the midline to check for adduction. The situation may be associated with extreme anteversion of the femoral head with increased inner rotation of the hip on the affected side. Beware, nevertheless, that bilateral dislocation with symmetrical bodily signs may make diagnosis difficult. Bilateral involvement could also be advised by widening of the perineum and an elevated lumbar lordosis. There is often an associated household historical past of developmental dysplasia of the hip, and an increased incidence is seen in breech presentations and with oligohydramnios. It covers a spectrum of diseases starting from dysplasia to subluxation and instability to full dislocation. It is advisable that two experts study every baby on two occasions to improve the yield from screening. Toddler (18 Months to three Years) these youngsters current with a delay in walking, a limp, leg length discrepancy, elevated shoulder sway and hyperlordosis of the backbone. Adult Life Symptoms usually begin within the early 30s with pain, weak spot and a limp. Compensatory scoliosis and hyperlordosis in the lumbar backbone may predispose to degenerative modifications and even instability. In the hip, limited abduction and inner rotation is characteristic because of intra-articular degeneration and underlying elevated femoral anteversion. Neonate (0�6 Months) Most cases are recognized by routine screening on this age group. Septic Arthritis of the Hip this condition develops normally because of trauma, adjacent osteomyelitis or direct haematogenous spread. It is a surgical emergency as a end result of the infective process ends in destruction of the articular cartilage. Tuberculous Arthritis Tuberculosis of the hip joint is now not often seen in developed countries. Radiographs of the hip present a widened joint space early on before joint destruction ensues. The severity of the situation is dependent on the extent of femoral head involvement. Boys are affected more commonly than girls, with a ratio of 4:1, and in 10 per cent the problems are bilateral. An elevated incidence is seen in affiliation with a positive family historical past, a low delivery weight and an abnormal delivery presentation. There is a decreased range of movement on the hip joint, notably abduction and inner rotation. The signs are ache within the hip and a decreased active and passive range of movement in all directions, with accompanying protective muscle spasm. The generalized indicators of sepsis may be current, and infants may current with high-grade fevers with an unclear focus. A thorough statement of the child often reveals that the leg is immobile � pseudoparalysis � as a outcome of ache. This position maximizes the intracapsular area and reduces the ache that results from excessive fluid strain inside the joint capsule. The presence of hip pain, an lack of ability to ambulate, an elevated white cell depend and inflammatory markers is diagnostic of this condition. Transient Synovitis of the Hip this could be a common condition of the hip in childhood and must be a prognosis of exclusion. There may be a history of trauma (<5 per cent), an antecedent viral illness (30 per cent) and even an allergic reaction. All hip movements but particularly extension and internal rotation cause ache, and the vary of motion is proscribed, although not as severely as in septic arthritis. The pathological process is a traumatic or immunologically mediated aseptic inflammation of the synovium, resulting in an effusion inside the hip joint. Infection should be excluded by in search of the signs and signs of sepsis and by haematological investigations. Raised interferon ranges have been discovered, but the erythrocyte sedimentation rate is normally under 20 mm per hour. Radiographs and ultrasound scans of the hip can reveal the presence of synovitis and effusion. Adult Hip Conditions 245 the diagnosis can be confirmed at the time of presentation by plain radiographs. The differential prognosis can embrace juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, proximal femoral osteomyelitis, irritable hip and hypothyroidism. Radiographic findings vary with the stage however embrace cessation of development of the ossific nucleus, medial joint space widening and the crescent signal, which represents a subchondral fracture. Revascularization and remodelling of the head of the femur happen over a interval of some years. A good consequence outcomes from restoration of the sphericity of the top throughout healing. In a central dislocation of the hip, the top of the femur is pushed via the floor of the acetabulum, which is fractured, creating a protrusio acetabuli kind of damage. There may be indicators of a direct blow to the facet of the hip and the leg tends to be abducted. Anterior dislocation could be very uncommon and normally happens after a fall from a height onto the toes. There is normally no shortening as a end result of upward migration of the hip is prevented by the iliofemoral ligament. The pelvis and acetabulum kind a solid unit that often fails in important traumatic stress. As with all different joints, examination of the hip begins with inspection, palpation and assessment of the vary of movement. Paediatric hip pathologies vary according to the age of presentation and frequency of the situation. They could also be divided into hereditary or developmental pathologies, such as developmental dysplasia of the hip, Legg�Calv�Perthes illness and inflammatory or infectious circumstances, such as poisonous synovitis and septic arthritis.

Order cheap seroflo onlinePatients who receive haemodialysis for polycystic kidney illness are notably susceptible to perinephric abscess formation. Typically, a perinephric abscess presents with symptoms just like those of acute pyelonephritis, including fever, flank and belly ache, weight reduction, malaise and gastrointestinal symptoms. In contrast to most sufferers with an uncomplicated pyelonephritis, those that present with a perinephric abscess have often been symptomatic for at least a week. Physical findings embrace abdominal tenderness and a flank mass, particularly if the abscess is large and situated in the region of the inferior pole of the kidney. During movement, the affected person may experience ache on flexion of the contralateral thigh and lateral flexion of the backbone. The situation requires immediate prognosis and administration as any delay can lead to sepsis, irreversible renal impairment and dying. Patients may present with asymptomatic bacteruria or, extra generally, infective urinary signs, loin pain and a fullness or mass within the flank. Treatment is with a mix of intravenous antibiotics and decompression of the renal pelvis by inserting a percutaneous nephrostomy tube or less incessantly an endoscopically inserted ureteric stent. Through the centre of the prostate passes the first part of the urethra (prostatic urethra), into which the prostatic glands drain and the ejaculatory ducts move to open adjacent to the verumontanum. The examination is commonly carried out with the patient within the left lateral position, with the knees and hips flexed so that the buttocks are close to the sting of the examining couch or bedside. Using a generous quantity of lubricant gel, the gloved index finger is inserted into the rectum after which turned to face the anterior surface, where the lobes of the prostate can be palpated via the rectal mucosa. The seminal vesicles and vasa, neither of which is palpable in the regular individual, lie cranial to the prostate. It is important to assess the size of the prostate, doc the utmost transverse distance between the lobes, in addition to the consistency, and check for the presence of tenderness, nodules and asymmetry. If the prostate feels boggy, this means the presence of a prostatic abscess, and radiological imaging should be requested. If the patient is systemically unwell, prostatic massage for bacteriology is contraindicated and solely the midstream urine is collected for urine culture. Urinary retention must be managed utilizing a suprapubic catheter to keep away from instrumentation of the prostatic urethra. Severe cases of acute bacterial prostatitis require antimicrobial agents first intravenously and then adopted by a 3�4 week oral course. About 5 per cent of instances of acute bacterial prostatitis progress to continual bacterial prostatitis, which is characterized by recurrent genitourinary and back pain with related urinary frequency, urgency and dysuria. In distinction to acute bacterial prostatitis, the bodily findings in chronic bacterial prostatitis are sometimes regular. The diagnosis is often made by the culture of urine samples taken before and after prostatic massage. The prostatic massage ought to be performed in the course of the rectal examination and often requires agency palpation to get hold of prostatic secretions from the urethral meatus. Bacilli can unfold into the lower urinary tract from renal granulomas that erode into the calyceal system. Involvement of the bladder usually initially manifests within the region of the ureteric orifices with fibrosis and obstruction or ureteric reflux. In severe circumstances of infection of the scrotal contents, a discharging sinus may form. Schistosomiasis It is estimated that over 200 million people worldwide are contaminated with organisms of the genus Schistosoma, with 97 per cent of instances of centred round North and West Africa and the Middle East. Urinary tract schistosomiasis is caused by infestation with a trematode fluke, the most common species being Schistosoma haematobium, S. Travel to endemic areas and swimming, bathing and wading in contaminated water can result in infection. Schistosomiasis is the results of direct penetration of the skin by free-swimming cercariae launched from freshwater snails. The cercariae enter the venous system, traverse the pulmonary circulation and migrate to the perivesical veins. On their way, they induce a granulomatous response resulting in ulceration of the mucosa on the discharge of the eggs into the lumen. However, most infected patients exhibit haematuria and, on cystoscopic examination, have typical perioval granulomas seen on the mucosal surface. Lower ureteric involvement is a feature of heavy or extended infection and results in obstruction and hydronephrosis. Epididymitis and Orchitis Epididymitis and orchitis are inflammation, normally secondary to an infection, of the epididymis and testicle, respectively. Infection of the epididymis that progresses to the adjoining testicle is referred to as epididymo-orchitis. Both pathologies sometimes current with scrotal ache and swelling, which develop over a couple of days, in contrast to torsion of the spermatic twine, which presents within hours. Associated symptoms embody dysuria, urinary frequency, urgency and sometimes fever and urethral discharge. A frequent explanation for isolated orchitis is mumps, during which testicular pain is normally preceded by fever, malaise and parotiditis. On examination, orchitis and epididymitis are characterised by swelling and tenderness of the respective tissue with erythematous and oedematous overlying scrotal skin. In superior cases, a reactive hydrocele may occur, making scrotal examination tougher. The most common presenting features are urinary frequency, nocturia, dysuria, fever, suprapubic pain, flank ache, haematuria and pyuria. Delayed diagnosis and intervention typically results in important morbidity and infrequently death. The supply of the an infection is normally the big bowel, urinary tract or skin of the genitalia. Patients often have multiple comorbidities that compromise the immune system, which precipitates and augments the an infection. Sexually Transmitted Infections Gonorrhoea Gonorrhoea is a standard infectious situation attributable to the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Approximately 10 per cent of infected men and 50 per cent of contaminated women are asymptomatic. The latter is normally caused by an infection with Chlamydia trachomatis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, Mycoplasma hominis or Trichomonas vaginalis. In major genital herpes, the patient typically begins to experience constitutional symptoms (fever, headache, malaise) and native symptoms (pain, dysuria, itch, urethral and vaginal discharge) after an incubation interval between 1 day and three weeks. Recurrent genital herpes is common, occurring in as a lot as ninety per cent of sufferers throughout the first 12 months. Infection has been associated with modifications in the cervical epithelium that may progress to cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and later to invasive carcinoma. The main route of an infection is thru sexual contact, but it could even be transmitted from mother to fetus in utero or at birth (congenital syphilis). During the latent phase, which can last many years, affected individuals are often asymptomatic. The manifestations of tertiary syphilis embody symptoms of neurosyphilis and cardiovascular syphilis.
Seroflo 250mcg overnight deliverySevere periportal fibrosis and the resulting hepatic insufficiency and portal hypertension are predominant. Patients with this form generally current during teenage with acute higher gastrointestinal bleeding from varices or with other indicators of liver failure. Unless treated, this type causes demise, often during the second or third decade of life because of hepatic insufficiency and complications of portal hypertension. The increased echogenicity is as a result of of the multitude of acoustic interfaces created by cyst growth in the tubules, and a hypoechoic rim at the periphery of the kidney representing compressed cortical tissue could also be seen. After the administration of intravenous contrast materials, a striated nephrogram is normally demonstrated. The striations end result from usually functioning, contrast-filled tubules adjoining to the cystically dilated, urine-filled nonfunctional tubules. The rarity of this dysfunction helps to distinguish it from other polycystic kidney illnesses. This film from an upper gastrointestinal series demonstrates serpiginous filling defects in the esophagus (arrows). Note the peripheral hypoechoic regions (arrows) in both kidneys as a result of compression of the cortical tissue. In some sufferers a single renal pyramid could additionally be involved, but in different sufferers all renal pyramids could present the modifications. Stasis can result in precipitation of minerals from the usually supersaturated urine. The nephrocalcinosis outcomes from punctate calcifications within the ectatic tubules of the affected medullary pyramid. It is in all probability going that a few of these calcifications are handed into the calyces and function a nidus for nephrolithiasis. This includes unilateral renal enlargement, which is usually associated with scoliosis and leg-length discrepancies. Focal cylindrical or saccular collections of distinction material are famous within the renal medulla adjoining to a calyx. After distinction material administration, the excreted iodinated distinction materials opacifies the dilated tubules and obscures the calcifications. At imaging, the stones could seem to enlarge and that is referred to because the growing calculus signal. Renal papillary blush, commonly seen in normal individuals undergoing imaging with low-osmolar contrast brokers, refers to hyperconcentration of iodinated contrast material in the distal portion of the amassing tubules. Papillary necrosis can even lead to punctate pools of contrast material in the renal medulla. Other causes of medullary nephrocalcinosis and their medical traits are discussed in Chapter 4. Multilocular cystic renal tumor is the name applied to two histologically distinct lesions that are indistinguishable on medical or imaging findings. Approximately two thirds of the instances occur in youngsters between 3 months and a pair of years of age with a 2: 1 male predominance. The remaining tumors occur in sufferers over the age of 30 with an 8: 1 feminine predominance. Mural or septal calcifications are occasionally seen however internal hemorrhage is rare. Definitive analysis is most likely not possible preoperatively however surgical removal is curative. Also often identified as a pyelogenic cyst, the calyceal diverticulum is an intraparenchymal cavity lined by transitional epithelium, which communicates with the renal accumulating system. Numerous calyceal diverticula are generally seen in sufferers with the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Calyceal diverticula are thought to end result from failure of an ampullary branch of the ureteric bud to induce nephron improvement within the overlying renal parenchyma. Type I, by far the commonest, is a diverticulum instantly linked to a calyx, typically on the fornix. C and D, Excretory-phase photographs at the same ranges reveal that the stones are contained inside dilated tubules throughout the papillary tips, now opacified with distinction materials. This computed tomography urogram reveals a quantity of websites of calyceal distortion, and filling of small and large papillary cavities from papillary necrosis. The smaller cavities, peripheral to the calyces (arrows), give a ball-on-tee appearance. All kinds of calyceal diverticula are smoothwalled outpouchings, which fill with excreted contrast material somewhat later in an imaging sequence than do the traditional calyces. Calyceal diverticula are inclined to have slender necks speaking with the normal collecting system. This leads to urinary stasis, which in turn leads to issues of stone formation and infection, the commonest reasons for symptomatic presentation. The commonest sort of diverticula, those arising instantly from a calyx, is positioned peripherally close to the corticomedullary junction. Diverticula must be differentiated from a hydrocalyx that develops proximal to a narrowing within the amassing system, resulting in focal dilatation. Mesoblastic Nephroma Mesoblastic nephroma is the most typical renal neoplasm of infancy with the majority occurring in the first 6 months of life; its incidence continues to be fairly uncommon. Originally described as a leiomyoma-like tumor, the tumor is now thought to characterize a spectrum, ranging from a basic benign lesion to a more aggressive cellular variant. The typical lesion is strong and the minimize floor has the appearance of a uterine leiomyoma. Cellular variants might present heterogeneous inner structure and they typically tend to invade the perinephric fats while sparing the renal pelvis and vascular pedicle. The etiology of those tumors is unknown, but one hypothesis means that they develop from a line of metanephric cells which have lost their potential for divergent differentiation. Unenhanced (A), enhanced (B), and delayed-phase (C) imaging exhibits a multiloculated proper renal mass with enhancing septations. Primitive metanephric blastema tissue can normally be current until 36 weeks of gestation. After this era, the presence of these embryonal cells, also known as nephrogenic rests, is abnormal. Severe forms of nephroblastomatosis result in marked renal enlargement, with multifocal areas of persistent nephrogenic tissue. The collections of primitive renal tissue can even cause mass effect with calyceal distortion. Unenhanced (A), nephrographic (B), and delayed-phase (C) images reveal dependent stones in a fluid-containing construction situated centrally in the right kidney (arrow in A). The structure remains unopacified on nephrographic section imaging, and is just partially stuffed on the delayed-phase picture. The temporal delay in distinction opacification of the diverticulum occurs because it must fill from the collecting system. This contrast-infused computed tomography demonstrates multifocal subcapsu- lar areas of low attenuation on this child. This radiographic sample in a younger youngster is very suggestive of nephroblastomatosis.

Cheap seroflo lineThis is consistent with metastatic disease from muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Resection is the therapy method of selection as a outcome of as many as 10% of papillomas might develop ultimately into invasive carcinoma if left unmanaged. This tumor presents as an isolated, well-defined intramural mass that could be as a lot as a number of centimeters in dimension. Intravesical growth pattern is commonest, adopted by extravesical and submucosal patterns of growth. A, Axial high-resolution T2weighted image reveals extension of a large bladder mass into the perivesical fats (white arrow). Muscle invasion is indicated by disruption of the T2 hypointense muscularis propria (between the black arrows). B, Delayed postcontrast T1-weighted image with fats saturation exhibits an infiltrative bladder mass extending to the pelvic side-wall and ventral belly wall (arrows). Diffuse Thickening of the Bladder Wall the most typical causes of diffuse bladder wall thickening are bladder nondistention, pancystitis, and trabeculation (Box 6-6). There is diffuse thickening of the bladder wall (asterisk) on this axial T2-weighted image. A massive mass (open arrow) invades the perivesical fats extensively (arrow) and has grown to the sidewall of the left hemipelvis. Coned-down view of the bladder demonstrates a focal filling defect with a lobulated margin (open arrow) close to the left ureterovesical junction. The bladder mucosa and submucosa present a similar diploma of enhancement to the bladder tumor (short white arrows); nevertheless, the muscularis propria (arrowhead) is hypoenhancing relative to the tumor, mucosa, and submucosa. Trabeculation Trabeculation of the bladder wall is noticed mostly in sufferers with chronic bladder-outlet obstruction or neurogenic bladder. Radiographically, trabeculation is a generalized irregularity of the internal or luminal contour of the bladder when the bladder is filled with urine. Bladder wall thickening resulting from detrusor contraction or incomplete rest is normal in an underfilled bladder. Cystometry has proven a powerful affiliation between radiologic trabeculation of the bladder and detrusor instability, outlined as a stress rise of more than 15 cm H2O during bladder filling. In the absence of detrusor instability, outflow obstruction with excessive intravesical stress produces the identical impact on the detrusor muscle, and therefore trabeculation. Trabeculation was as soon as thought to outcome from hypertrophy of the detrusor muscle in response to an increase in bladder outflow resistance. This opinion was based on the frequent correlation of trabeculation with bladder-outlet obstruction, particularly when it resulted from benign prostatic hyperplasia. However, histologic studies of trabeculated bladders have discovered infiltration of detrusor clean muscle by connective tissue elements and not muscle hypertrophy. A, Computed tomography demonstrates a soft-tissue mass (arrow) anterior to the apex of the prostate gland. These indicators embody prostatic impression on the base of the bladder, hooking or J configuration of the juxtavesical ureters caused by elevation of the trigone, and huge postvoid residual. A, Coned-down view of the bladder from an intravenous urogram demonstrates diffuse thickening of the bladder wall (small arrows), which has a finely lobulated contour. A focal, rounded filling defect (open arrow) is seen next to a big prostatic impression along the base of the bladder. B, Sonography of the bladder within the transverse airplane demonstrates focal enlargement of the median lobe of the prostate as the purpose for the rounded filling defect. An aged patient with benign prostatic hyperplasia offered with severe pelvic pain. Sonography confirmed a number of hypoechoic areas (arrows) within the wall of the trabeculated bladder. Cystitis Cystitis is inflammation of the urinary bladder wall and could additionally be focal or diffuse. For simplicity of discussion here, cystitis is assessed in accordance with etiology (Box 6-7). The term cystitis is commonly mixed with a medical descriptor, particularly if the etiology is multifactorial or unknown (Box 6-8). For occasion, viral, radiation, or cyclophosphamide cystitis might manifest as a hemorrhagic cystitis. Polypoid cystitis is a reactive urothelial hyperplasia that protrudes into the lumen of the bladder as a polyplike progress (polypoid pseudotumor). The phrases cystitis cystica and cystitis glandularis refer to specific histopathologic variants of chronic cystitis, which may be higher characterised as types of urothelial metaplasia. Cystitis glandularis (intestinal type) has been associated with an elevated risk of adenocarcinoma of the urinary bladder and these sufferers should be monitored carefully. Acute cystitis refers to bladder inflammation of recent symptomatic onset and somewhat quick period. Bladder compliance usually is decreased in patients with persistent cystitis, and elevated intravesical pressures may trigger ureteral dilatation and vesicoureteral reflux. Although the inflammatory course of often affects the whole bladder wall (pancystitis), occasionally cystitis is extra marked or at least extra radiographically apparent focally. A common instance is bullous edema, which regularly accompanies pancystitis of various causes. Mechanical cystitis, often ensuing from 206 GenitourinaryRadiology:TheRequisites irritation by a foreign body similar to a catheter, is also a focal course of in lots of patients. Bacterial cystitis is the most frequent kind of infectious cystitis encountered in developed countries. In ladies, routine radiographic evaluation is normally not indicated unless cystitis is recurrent or troublesome to eradicate. In males, cystitis is most often associated with bladder-outlet obstruction, sometimes secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urinary tract calculi, urethral strictures, and urethral catheterization can also predispose to cystitis. Evaluation of the bladder and urethra is indicated with the primary episode of bacterial cystitis in males to exclude decrease urinary tract anomalies or obstruction. Emphysematous cystitis, an uncommon manifestation of bacterial cystitis, is mentioned later within the chapter. An unusual manifestation of recurrent bacterial an infection is malacoplakia, a granulomatous inflammatory process that affects the urinary bladder and the distal ureter. This disease is more frequent in immunocompromised patients and in patients with diabetes mellitus and is associated with E. The proffered pathogenesis of malacoplakia is deficient operate of lysosomes in macrophages, inflicting a continual and ineffective response to urinary tract an infection. At histology, basophilic inclusions are seen inside macrophages (Michaelis-Gutmann bodies). On radiologic imaging studies, malacoplakia normally appears as multiple raised but sessile filling defects, 5 to 10 mm in diameter.
References - Schlatter M, Rescorla F, Giller R, et al; Childrenis Cancer Group, Pediatric Oncology Group: Excellent outcome in patients with stage I germ cell tumors of the testes: a study of the Childrenis Cancer Group/Pediatric Oncology Group, J Pediatr Surg 38(3):319n324, discussion 319n324, 2003.
- Tourchi A, Di Carlo HN, Inouye BM, et al: Ureteral reimplantation before bladder neck reconstruction in modern staged repair of exstrophy patients: indications and outcomes, Urology 85(4):905n908, 2015.
- Madjar S, Halachmi S, Wald M, et al: Long-term follow up of the inFlowTM intraurethral insert for the treatment of women with voiding dysfunction, Eur Urol 38:161n166, 2000.
|
|

