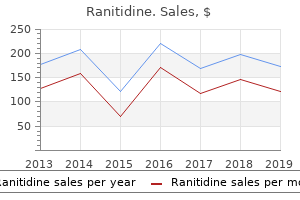
"Buy ranitidine 150 mg low cost, chronic gastritis weight loss."By: Dawn Sowards Brezina, MD - Assistant Professor of Medicine
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/dawn-sowards-brezina-md
Buy ranitidine lineYou look at the affected person in your clinic and discover that his hand seems warm and properly perfused. The patient says that the symptoms started 3 weeks earlier and that they happen solely throughout dialysis. A 47-year-old smoker develops extreme ache and coldness in his left forearm and hand throughout dialysis utilizing a left brachiocephalic fistula. You look at him in your clinic and find that his hand seems heat and properly perfused. A 39-year-old male presents to the workplace from dialysis for evaluation of his right prosthetic brachial-axillary upper arm graft, which is presently being used for dialysis. On bodily examination of his right arm, you observe a thrill and bruit overlying his graft. There are two separate 5-cm soft pulsatile plenty alongside the size of the graft with mild skin ulcerations overlying the masses however no erythema or edema and palpable radial, ulnar, and brachial artery pulses. A 65-year-old feminine presents with growing edema of her left higher extremity approximately 18 months after the creation of a proper brachiocephalic upper arm fistula. On bodily examination of her right arm, you observe a bounding pulse overlying the fistula, average edema, and palpable radial, ulnar, and brachial artery pulses. Venography of the proper higher extremity exhibits an 80% subclavian vein stenosis and patent inner jugular and innominate veins with no stenosis. Right subclavian vein�to�internal jugular vein bypass with autogenous saphenous vein graft Questions 7 and 8 check with the identical clinical situation. A 42-year-old male presents with a thrombosed right prosthetic forearm loop arteriovenous graft that was being used for dialysis access till 3 days earlier. A 42-year-old-male presents with a thrombosed right prosthetic forearm loop arteriovenous graft; it was being used for dialysis access until three days earlier. Start the affected person on an oral Factor Xa inhibitor, comply with up in clinic in 1 week d. Admit the patient to hospital, place dialysis catheter Bibliography Berardinelli L. Vascular steal syndrome and ischaemic monomelic neuropathy: two variants of upper limb ischaemia after haemodialysis vascular access surgical procedure. The Society for Vascular Surgery: clinical practice pointers for the surgical placement and maintenance of arteriovenous hemodialysis access. Selecting optimal hemodialysis catheters: material, design, advanced options, and preferences. End-stage renal illness in the United States: an update from the United States Renal Data System. Chronic hemodialysis utilizing venipuncture and a surgically created arteriovenous fistula. Multidisciplinary predialysis care and morbidity and mortality of sufferers on dialysis. Noninvasive evaluation of hand circulation before radial artery harvest for coronary artery bypass grafting. The worth of noninvasive testing earlier than and after hemodialysis access within the prevention and administration of issues. The Addition of Ultrasound Arterial Examination to Upper Extremity Vein Mapping before Hemodialysis Access. Tunneled hemodialysis catheters: use of a silver-coated catheter for prevention of infection-a randomized examine. Surface-Treated versus Untreated LargeBore Catheters as Vascular Access in Hemodialysis and Apheresis Treatments. Surface heparinization of central venous catheters reduces microbial colonization in vitro and in vivo: results from a prospective, randomized trial. Randomized comparability of split tip versus step tip high-flow hemodialysis catheters. A randomized, prospective analysis of the Tesio, Ash split, and Opti-flow hemodialysis catheters. A randomized study of left versus right inner jugular vein cannulation in adults. Ultrasound guidance for placement of central venous catheters: a meta-analysis of the literature. Use of real-time ultrasound steerage for the location of hemodialysis catheters: a systematic evaluate and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Vascular Access for Placement of Tunneled Dialysis Catheters for Hemodialysis: A Systematic Approach and Clinical Practice Algorithm. Unconventional central entry: catheter insertion in collateral or in recanalized veins. Traditional and non-traditional methods to optimize catheter function: go with more flow. Natural history of tunneled dialysis catheters positioned for hemodialysis initiation. Catheter patency and performance after catheter sheath disruption: a pilot study Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. Prospective validation of an algorithm to maximize native arteriovenous fistulae for persistent hemodialysis entry. Clinical Analysis of Radiocephalic Fistula Using Side-to-side Anastomosis with Distal Cephalic Vein Ligation. Comparison of efficacy of facet to facet versus end to side arteriovenous fistulae formation in persistent renal failure as a permanent hemodialysis entry. Comparison of Side-to-side Brachiocephalic Arteriovenous fistula with Ligation of the Perforating Vein with End-to-side Brachiocephalic Arteriovenous fistula. Pre-operative regional block anesthesia enhances operative strategy for arteriovenous fistula creation. Dialysis Access Surgery: Does Anesthesia Type Affect Maturation and Complication Rates Does regional compared to native anaesthesia affect end result after arteriovenous fistula creation A systematic evaluation and meta-analysis of systemic intraoperative anticoagulation throughout arteriovenous entry formation for dialysis. Experience with arterial substitutes in the construction of vascular access for hemodialysis. Suggestion of Better Outcomes With TwoStage Brachiobasilic Vein Transposition: A Meta-Analysis. Importance of medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve anatomical variations in higher arm surgery J Neurosci Rural Pract. The superficial femoral-popliteal vein transposition fistula: description of a new vascular entry procedure. Saphenous vein loop to femoral artery arteriovenous fistula: a sensible alternative. The effect of two completely different hand workout routines on grip energy, forearm circumference, and vascular maturation in patients who underwent arteriovenous fistula surgery Ann Rehabil Med. Surveillance of arteriovenous hemodialysis access: a scientific evaluate and meta-analysis.
Purchase genuine ranitidine onlineT1 and T2 tumors are localized to the kidney and are outlined by their best dimensions. T2 tumors are more than 7 cm and are subclassified as T2a (>7 cm but 10 cm) or T2b (>10 cm). Lymph nodes submitted and uninvolved by tumor outline N0; node involvement is staged N1. In this occasion, the tumor cells are spindled and pleomorphic, and harking back to undifferentiated sarcoma. Nucleoli are distinctly seen at four hundred � magnification, however inconspicuous or invisible at one hundred � magnification. Tumor reveals the presence of tumor big cells and/or excessive nuclear pleomorphism and/or sarcomatoid differentiation and/or rhabdoid differentiation. Tumor cells resemble rhabdomyoblasts Tumor cells are barely discohesive, with central eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions and huge eccentric and irregular nuclei, some of which have outstanding nucleoli. After the initiating event involving the 3p gene, further genetic alterations occur in clonal tumor cell populations as tumor development occurs and metastatic functionality will increase. Consequently, these extra genetic abnormalities, when detectable, are sometimes related to higher histologic grade, greater pathologic stage, and an antagonistic prognosis. It is an autosomal dominant illness related to the event of retinal angioma, cerebellar and spinal angioma and hemangioblastoma, bilateral multifocal pheochromocytoma, papillary cystadenoma of the epididymis, pancreatic cyst and malignant neuroendocrine tumor, inner ear endolymphatic sac tumor, and renal cyst. The cut floor is at least partly a attribute brilliant golden yellow color, owing to the abundance of ldl cholesterol, phospholipids, and impartial lipids within the tumor cells. The minimize surface is typically variegated with areas of gray-white fibrosis and recent or old hemorrhage. Areas of cystic change and calcification are commonly discovered, notably within areas of necrosis. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma involves the adrenal in a radical nephrectomy specimen, not by direct extension. Bosselated, well-circumscribed, low-grade clear cell renal cell carcinoma, shiny golden yellow with in depth hemorrhage and fibrosis. Infrequently, small papillary buildings lined by clear cells may be current focally but account for an insignificant proportion of the general structure. High-grade clear cell renal cell carcinoma, not sharply circumscribed, extensively involving renal sinus and perirenal fat, as nicely as Gerota fascia. Although most sufferers are asymptomatic, and their tumors are discovered by the way, a minority have both a palpable mass, gross hematuria, abdominal or again discomfort, or hardly ever, systemic symptoms. Imaging studies normally reveal a fancy cystic mass that will have focal calcification. More than 20% of tumors show calcifications within the septa, and metaplastic bone formation is typically observed. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma composed of nests of cells with clear cytoplasm, surrounded by abundant thin-walled blood vessels. Grade and tumor necrosis have been mentioned in the earlier part Grading Renal Cell Carcinoma. Progressively greater tumor grades are associated with progressively worsening prognosis. Tumor necrosis accounting for more than 10% of the whole tumor quantity is associated with a less favorable end result. Patients whose tumors exhibit sarcomatoid change have a 5-year survival fee of 15% to 22%; for these whose tumors exhibit rhabdoid differentiation, the median survival is 8 to 31 months. Grossly this tumor had the appearance of a thick-walled cyst crammed with liquefied bloody material; a sarcomatoid papillary renal carcinoma within the wall had already metastasized to type a big hilar mass. The small cortical nodule (arrow) was a papillary renal cell carcinoma that had metastasized to type a big hilar mass. In this kind 1 tumor the papillae are delicate and are lined by cells with small, darkish nuclei and scant cytoplasm. Macrophages, somewhat than populating the papillae, usually have a tendency to be discovered close to areas of necrosis. The histologic distinctions noted earlier have been augmented by molecular analysis. In this kind 2 tumor the papillae are thicker and are lined by cells with giant irregular nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Diffuse strongly positive cytokeratin 7 immunostaining is obvious in this stable variant of papillary renal carcinoma. Tumor cells have comparatively abundant cytoplasm and spherical nonoverlapping nuclei which are arranged linearly towards the cell apices and bear inconspicuous nucleoli (A to C). Male affected person, aged 48 years, with a historical past of metastatic renal cell carcinoma, was seen in a dermatology clinic concerning multiple redbrown firm dermal nodules. However, most of the large nuclei exhibit very distinguished inclusion-like orangiophilic or eosinophilic nucleoli, surrounded by a clear halo (B). Consequently, recognition of the characteristic options of this tumor are essential not solely in managing the affected affected person however in counseling and follow-up of members of the family. Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma Chromophobe cells have been first described in chemically induced renal tumors in rats. Patients range in age from childhood to extreme old age, with a slight male preponderance. A minority show hemorrhage or necrosis, and these options, when present, are restricted in extent. Numerous chromophobe cells have ample flocculent cytoplasm and sharply outlined plantlike cell membranes. This eosinophilic kind of chromophobe carcinoma is mahogany and properly circumscribed. Perinuclear halos are incessantly present within the more eosinophilic cells, and this function may be of appreciable diagnostic importance. The tumor cells are smaller, with extra densely granular eosinophilic cytoplasm, raisinoid nuclei, and perinuclear halos. This eosinophilic variant closely mimicked oncocytoma, however mitotic figures have been readily evident in parts of the tumor. This eosinophilic variant intently mimicked oncocytoma, but it confirmed sturdy and diffusely positive immunostaining for cytokeratin 7. Typically chromophobe carcinoma shows strongly and diffusely optimistic immunostaining for cytokeratin 7. Section from a renal neoplasm in a affected person with Birt-Hogg-Dub syndrome exhibits an admixture of e eosinophilic cells with spherical nuclei resembling oncocytes and cells with clear or flippantly eosinophilic cytoplasm and outstanding nuclear membranes, reminiscent of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. Female, aged 29 years, who had eight oncocytic tumors removed from her left kidney at age 26 years, underwent excision of five extra oncocytic tumors from her proper kidney, shown right here.
Buy ranitidine 150 mg low costVariable acinar dimension is of value, notably when there are small, irregular, abortive acini with primitive lumens. The association of the acini is diagnostically helpful; malignant acini typically have an irregular haphazard association, typically splitting or distorting muscle fibers within the stroma, with variable spacing between acini. The stroma incessantly accommodates younger collagen that seems flippantly eosinophilic, and desmoplasia could also be distinguished, though this is an uncommon and unreliable feature when assessed in isolation. An understanding of the Gleason grading system is of value for interpretation of small foci due to its reliance on architectural patterns (see later). Enlarged nuclei are sometimes current in most malignant cells, and enlarged nucleoli are present in many. Every cell has a nucleolus, so one searches for "outstanding" nucleoli, that are a minimal of 1. Compressed stromal fibroblasts might mimic basal cells however are normally solely seen focally on the periphery of acini. An intact basal cell layer is present surrounding benign acini, whereas carcinoma entirely lacks a basal cell layer. Sometimes, small foci of adenocarcinoma cluster around bigger acini that have intact basal cell layers, compounding the problem. Triple immunostain (not shown) revealed racemase staining, as nicely as absence of p63 and keratin 34E12 staining. Irregular loose cluster of small to intermediate acini, including a couple of with foamy cytoplasm (bottom) that stand in distinction with the adjoining benign acini (B and C). This was recognized as "foamy gland prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia" at another medical heart without acquiring immunostains. This immunoprofile effectively excludes prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia from consideration and, together with the architectural abnormalities, is diagnostic of adenocarcinoma (Gleason 3 + three � 6) with focal foamy gland sample. Proteinaceous secretions are often present in affiliation with crystalloids and corpora amylacea. The focus of adenocarcinoma (left) displays marked nuclear and nucleolar enlargement compared with adjoining benign epithelium (right). Collagenous micronodules are fashioned by subepithelial accumulations of fragmented collagen fibers, presumably related to the digestion by collagenase produced by prostatic adenocarcinoma cells. The term mucinous fibroplasia has been erroneously applied by some to collagenous micronodules, however these micronodules are sometimes not associated with mucin, so this term ought to be deserted. Complete circumferential growth, intraneural invasion, and ganglionic invasion are almost at all times restricted to most cancers. However, benign acini can hardly ever mimic cancer with perineural indentation, monitoring, wrapping, or even intraneural unfold, so warning is warranted in relying on this characteristic to the exclusion of all others. Only a couple of research have tried to distinguish between lymphatic and vascular channels due to the difficulties in differentiation by light microscopic examination. Mean blood vessel count is larger in tumors with metastases than in these without metastases, and most, however not all, studies reveal a correlation with pathologic stage. In equivocal instances, diagnosis may be aided by staining with basal cell�specific antibodies to high-molecular-weight keratin 34E12. Adenocarcinoma arising in the transition zone characteristically accommodates clear cells and is well or reasonably differentiated. In distinction, Gleason grade 3 and four carcinomas often include cells with clear cytoplasm, beforehand referred to because the hypernephroid sample. In addition, remedy similar to androgen deprivation induces abundant clear cell change in benign and carcinomatous acini, and the prognosis of adenocarcinoma in such cases could additionally be tough (see dialogue later in this chapter). The clear cell pattern of carcinoma could also be confused with histiocytes, vacuolated stromal clean muscle cells, and metaplastic cells. This is usually caused by the small measurement of the main focus, distorted acini with architectural options of malignancy that lack convincing cytologic features, and acinar atrophy or outstanding irritation during which the adjoining benign acini present distortion and reactive atypia with nuclear and nucleolar enlargement. In such instances, it might be applicable to describe the case as "small acinar proliferation suspicious for but not diagnostic of malignancy" and to recommend rebiopsy. A broad variety of lesions could mimic adenocarcinoma, significantly in small specimens (Table 9. When this concern arises, it is recommended that each one remaining tissue be submitted for histologic evaluation to minimize the priority for incomplete sampling. Genotypic analysis to confirm affected person identity in instances of "vanishing" most cancers appears prudent to reassure sufferers. In one report, biopsies were overdiagnosed as most cancers in two of four cases with no residual cancer after prostatectomy. Another report discovered that 11% of patients skilled recurrence and one had systemic development, but that retrospective report consisted chiefly of partially and incompletely sampled prostate. However, grading techniques are much less successful in subdividing most moderately differentiated adenocarcinomas that have intermediate clinical and biologic potential. Since 1999, Gleason grading is the recognized international commonplace for prostate cancer grading and, in our expertise, is now routinely utilized by most pathologists all over the world. In biopsies, these issues are compounded by small pattern measurement, tumor heterogeneity, and undergrading of biopsy samples. Gleason Grading System the Gleason grading system resulted from the Veterans Administration Cooperative Urological Research Group examine of greater than 4000 patients between 1960 and 1975. Tumor heterogeneity is accounted for by assigning a major sample for the dominant grade and a secondary pattern for the nondominant grade; the histologic score is derived by adding these two patterns collectively. The success of the Gleason grading system is because of 4 elements: (1) histologic patterns are identified by the degree of acinar differentiation without relying on morphogenetic or histogenetic models; (2) a simplified and standardized drawing is available; (3) the Veterans Administration research supplied plentiful potential info that allowed objective computer-generated development of this self-defining grading system; and (4) unlike some other grading system within the physique, the Gleason system provided for tumor heterogeneity by identifying main and secondary patterns. Nonetheless, important correlation with nearly each end result measure attests to the predictive strength and utility of grading in the palms of most investigators, together with the classic Gleason grading system. Intraobserver settlement is actual in as much as 78% of circumstances and � 1 rating unit in up to 87%. Coard and Freeman demonstrated 60% total concordance in consensus Gleason scores. The prudent diagnosis within the absence of enough features for most cancers is atypical small acinar proliferation. Look for microvacuolated cytoplasm, nuclear enlargement, and macronucleoli to diagnose most cancers. These sievelike spaces lose their round, inflexible, punched-out contours and elongate; the acini collapse into solid areas. Interobserver reproducibility of p.c grades four and 5 is a minimum of nearly as good as that of Gleason rating. This decline in the reported incidence of lowgrade prostate most cancers appeared to be the outcomes of Gleason score reclassification because the late Nineties, reflecting a statistical artifact generally recognized as the "Will Rogers phenomenon. Reproducibility of the 2005 modified Gleason rating (primary grade + highest grade) (see later) was as excessive as that of Gleason rating, however there was clustering in odd scores (scores 5 and 7), and disagreement was extra generally noticed than with classic Gleason score. Of discordant cases, similar numbers of biopsies were upgraded and downgraded with the 2 techniques, with minor differences in the score distributions. There was also related concordance for cancers that acquired a rating of seven (either three + four or 4 + 3).
Quality 300 mg ranitidineEctopic seminiferous tubules within the tunica albuginea of regular and dysgenetic testes. The spectrum of persistence of testicular blastema and ectopic testicular parenchyma: a potential results of focal delay in gonadal improvement. A clinicopathological presentation and physiological issues in 4 sufferers with Leydig cell tumours of the testis or secondary Leydig cell hyperplasia. A novel mutation of the luteinizing hormone receptor gene inflicting male gonadotropinindependent precocious puberty. Histological versus stereological methods applied at spermatogonia throughout regular human improvement. Quantitative histology of germ cells in the undescended testes of human fetuses, neonates and infants. Testicular histology in fetuses with the prune stomach syndrome and posterior urethral valves. Solid tumors and germ cell tumors induce nonneoplastic germ cell proliferations in testes of infants and younger children. Cell proliferation and hormonal modifications throughout postnatal growth of the testis within the pig. Hyperplasia and the immature appearance of Sertoli cells in main testicular disorders. Observations on the testis in anencephaly with particular reference to the Leydig cells. The androgen insensitivity syndrome (testicular feminization): a clinicopathologic examine of forty three circumstances. Objective measurement of testicular volume by ultrasonography: analysis of the approach and comparability with orchidometer estimates. Postnatal development and differentiation of contractile cells inside the rabbit testis. A quantitative structural model of the testis of fertile males with regular sperm counts. Testicular involution in elderly males: comparability of histologic quantitative studies with hormone patterns. Tubular fluid secretion in the seminiferous epithelium: ion transporters and aquaporins in Sertoli cells. Ultrastructural observations on nucleoli and related buildings throughout human spermatogenesis. Regulation of junction dynamics in the testis� transcriptional and post-translational regulations of cell junction proteins. Biology and regulation of ectoplasmic specialization, an atypical adherens junction type, in the testis. Major involvement of connexin forty three in seminiferous epithelial junction dynamics and male fertility. A seamless trespass: germ cell migration across the seminiferous epithelium during spermatogenesis. Zona occludens-2 is important for blood-testis barrier integrity and male fertility. The nice construction of the monkey (Macaca) Sertoli cell and its role in sustaining the blood-testis barrier. Continual maintenance of the blood-testis barrier during spermatogenesis: the intermediate compartment principle revisited. Retinoblastoma protein plays a number of essential roles within the terminal differentiation of Sertoli cells. Expression and localization of N- and E-cadherin within the human testis and epididymis. Changes in the lipid inclusion/Sertoli cell cytoplasm space ratio during the cycle of the human seminiferous epithelium. The phagocytic operate of Sertoli cells: a morphological, biochemical, and endocrinological examine of lysosomes and acid phosphatase localization within the rat testis. Evidence that vinculin is co-distributed with actin bundles in ectoplasmic ("junctional") specializations of mammalian Sertoli cells. Cell junction dynamics within the testis: Sertoligerm cell interactions and male contraceptive development. Immunocytochemical demonstration of cytoskeletal proteins in seminiferous tubules of grownup rams and bulls. Sertoli-Sertoli and Sertoli-germ cell interactions and their significance in germ cell motion in the seminiferous epithelium throughout spermatogenesis. Sertoli cells keep Leydig cell quantity and peritubular myoid cell exercise within the adult mouse testis. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of testicular transferrin by germinal cells of the rat testis. Regulation of activin and inhibin within the grownup testis and the evidence for practical roles in spermatogenesis and immunoregulation. Human testis cytosol and ovarian follicular fluid comprise excessive amounts of interleukin-1-like factor(s). The roles and regulation of Sertoli cells in fate determinations of spermatogonial stem cells and spermatogenesis. Immunohistochemical localization of proliferating cell nuclear antigen as a device to research cell proliferation in rodent and primate testes. Decrease in the variety of human Ap and Ad spermatogonia and within the Ap/ Ad ratio with advancing age. Regulation of spermatogonial stem cell selfrenewal and spermatocyte meiosis by Sertoli cell signaling. Kinetics of spermatogenesis in mammals: seminiferous epithelium cycle and spermatogonial renewal. The fine construction and growth of the neck region of the mammalian spermatozoon. Regulation of spermatogenesis in the microenvironment of the seminiferous epithelium: new insights and advances. Further observations on the numbers of spermatogonia, spermatocytes, and spermatids connected by intercellular bridges in the mammalian testis. Computer-aided three-dimensional reconstructions of the arrangement of major spermatocytes in human seminiferous tubules. A secure isotope-mass spectrometric method for measuring human spermatogenesis kinetics in vivo. Morphometrical evaluation of Sertoli cell ultrastructure in the course of the seminiferous epithelial cycle in rats. Stagespecific alerts in germ line differentiation: management of Sertoli cell phagocytic activity by spermatogenic cells. Apoptosis in testis germ cells: developmental modifications in gonadotropin dependence and localization to selective tubule stages.
Quality ranitidine 300mgTumor consists of small cystic areas separated by delicate septa, with a "spider internet" or "lace doily" look. Depressed immunity, extreme free radical manufacturing associated to inflammation, impaired antioxidant defenses, and deposition of oxalate crystals have been postulated. Tumors are recognized primarily through routine screening protocols, though some present with microscopic hematuria or flank pain. Foci of hemorrhage and necrosis are widespread, and a few have focally calcified capsules. Histologically the tumor architecture demonstrates numerous mixtures of strong sheetlike, papillary, acinar, and cribriform and tubulocystic patterns. The tumor cells are sometimes massive with abundant granular eosinophilic cytoplasm and huge round to oval, mildly irregular nuclei with outstanding nucleoli. This carcinoma exhibits tubulocystic structure and plentiful calcium oxalate crystals. A stable and cystic neoplasm is present in a background of intensive cystic change on this affected person with a long-standing historical past of dialysis for renal failure. Abundant oxalate crystals are demonstrable under polarized mild, a singular property of this neoplasm. A large multinodular and partially necrotic tumor is current in a background of acquired cystic kidney illness. The tumor is sharply circumscribed and extensively cystic, but nodules of strong tumor are readily seen. Most cells lining the papillary and tubular buildings exhibit clear cytoplasm and a low nucleolar grade. A small subset of tumors (previously designated renal angiomyoadenomatous tumors) present comparable cytologic findings however with "collapsed" acini, variable tubular/acinar structure, and prominent elements of fibrous or clean muscle stroma. A typical discovering is the presence of areas of a densely and compactly arranged tubular buildings, lined by cells with clear cytoplasm, whose nuclei are of low nuclear grade and are organized on the apical finish of the cells, similar to early secretory phase endometrium. Tumor exhibits papillary architecture, but the papillae are comparatively small and blunt, with limited branching. Tumor cells have sharply defined cell membranes and ample eosinophilic granular cytoplasm, giving them an "oncocytoid" appearance. Tumor cell nuclei are medium sized and irregular, and a lot of bear distinguished nucleoli. There are insufficient data regarding molecular options and outcome for these tumors. Eosinophilic Solid and Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma More than 50 cases of this rare tumor have been well studied and reported. All tumors harbor variably sized macrocysts and microcysts; cells lining the cysts often exhibit a outstanding hobnail look. Tumors are composed of cells with voluminous eosinophilic cytoplasm and round to oval nuclei, with focally prominent nucleoli. A distinctive and striking function is the presence of cytoplasmic "stippling" by eosinophilic or basophilic amorphous granular buildings of variable size and prominence. A recurring set of genomic alterations has been identified: copy number gains in 16p, 7p, 13q, and 19p; copy quantity losses in Xp11. With increasing consciousness of this tumor, currently two patients are identified to have developed metastases (an incidence price of about 3% in known cases). In all instances, no evidence of thyroid cancer was discovered, concurrently or subsequently. About 70% are discovered by the way; the remainder expertise hematuria or flank or belly ache. Gross or microscopic extension into perinephric tissues is noted in 13% of instances, however extension into renal pelvis or renal vein has not been famous. This unusual renal neoplasm is remarkably paying homage to a thyroid follicular neoplasm, set in a diffusely hyalinized fibrotic background. Morphologic similarities in grownup cases embrace heterogeneous strong architecture, eosinophilic cells, mucinous cytoplasmic elements, rhabdoid cells, and intracytoplasmic lumina. Stroma reveals a clean muscle�like look and separates the neoplastic epithelial glandular buildings, many of that are rimmed by a prominent layer of endothelial cells that mimic a myoepithelial cell layer. Microscopically, the stroma incorporates areas with a easy muscle�like appearance, interspersed with stromal hyalinization and edema. Slitlike vascular areas dispersed in the smooth muscle stroma are at all times seen (similar to the solid sample of angioleiomyoma) and in some tumors the stroma also incorporates vascular channels with thicker, muscular partitions, just like the venous sample of angioleiomyoma. The cytoplasm of the epithelial cells is ample and varies from clear to pale, flocculent or eosinophilic. The measurement cutoff was increased in 2015, primarily based on analyses of the malignant potential of small renal masses. Evidence signifies that for each 1-cm enhance in tumor size, the incidence of synchronous metastases increases 22%. Combined experience in nephrectomies carried out at Mayo Clinic and Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center demonstrated that of 519 renal tumors less than 2 cm in diameter, none had synchronous metastases and none developed asynchronous metastases after surgical excision of the primary tumor. This small, utterly circumscribed papillary adenoma displays the options typical of the oncocytic variant of papillary renal cell carcinoma. In some patients the analysis is prompted by the invention of a palpable mass; in others the lesion is recognized throughout investigation of hypertension, hematuria, or flank or belly ache. Radiologic findings are too nonspecific to discriminate between oncocytoma and renal carcinoma, with the outcome that oncocytoma usually is managed by surgical excision. An area of central scarring is usually present (in up to 33%, notably in bigger tumors); different gross findings may embody recent hemorrhage (up to 20%) and, hardly ever, foci of cystic degeneration. Lesional cells are small, with scant cytoplasm and small, dark nuclei that lack nucleoli. Tumor is circumscribed, mahogany brown, and barely hemorrhagic, with a central stellate scar. Low-power view of an area of scarring demonstrates organoid structure and the disposition of cell nests in a hyalinized hypocellular stroma. Typical oncocytic cells with ample, densely granular eosinophilic cytoplasm and uniform, round nuclei with inconspicuous nucleoli. In the classic pattern, tumor cells kind nests, islands, organoid clusters, cords, trabeculae, or confluent stable sheets of cells lacking stroma. Findings noticed in some tumors embrace focal papillary structures projecting into dilated luminal structures, stromal calcifications, and osseous and myeloid metaplasia. Compact nests of cells, some of which show pronounced nuclear pleomorphism and hyperchromasia. This tumor was outstanding by the diploma of cystic change that was present; in any other case it was completely compatible with oncocytoma. Invasion of medium and large renal vessels, together with grossly seen tumor in the renal vein, is identified in about 1. A giant number of immunohistochemical stains has been evaluated areas of clear cell or spindle cell carcinoma, distinguished papillary structure, macroscopic or conspicuous microscopic necrosis, and atypical mitotic determine. Certain morphologic findings, when noted in tumors in any other case suitable with oncocytoma, raise concern for malignancy.

Tocopherol Acetate (Vitamin E). Ranitidine. - Breast cancer.
- Sores in the mouths of people who smoke.
- Colorectal cancer.
- Chest pain (angina).
- Lung infections in elderly persons.
- Head and neck cancer.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96917
Buy generic ranitidine 300 mg onlineIn childhood, hyperplasia is noticed in most cases of macroorchidism, as a outcome of a lot of the quantity of the testis at this time depends on the variety of Sertoli cells. Sertoli cell hyperplasia seen initially of puberty is attribute of cryptorchid testicles and reflects the inability of the growth in length and tortuosity of the seminiferous tubules, and, to a lesser extent, an absolute increase in number of Sertoli cells. The most frequent measures are Leydig cell number per tubular section or per unit space, or whole Leydig cell number per testis. Intertubular Connective Tissue the seminiferous tubules are normally closely packed, separated only by a small quantity of loose connective tissue that maintains cohesion among the tubules and incorporates scant Leydig cells, macrophages, mast cells, blood vessels, and nerves. This intertubular connective tissue may be altered, including elevated quantity, elevated cellularity, abnormal growth of lymphatic vessels, and the presence of cell varieties that are uncommon in this location. Some testes have thick fusiform cell bundles that separate teams of intently packed seminiferous tubules. These cells are paying homage to the cells that type ovarian stroma and are the most attribute histologic finding in Botella-Nogales-Morris syndrome (a intercourse differentiation dysfunction secondary to androgen insensitivity). Increase in Leydig cell quantity Congenital hyperplasia of Leydig cells (maternal diabetes mellitus). Testicular quantity correlates with peak, weight, physique mass index, and physique floor space, and it decreases in adulthood. Sertoli Cells Supporting Structures the tunica albuginea and interlobular septa make up the connective tissue framework of the testis. The tunica albuginea consists of three connective tissue layers: an outer layer of mesothelium apposed to the basal lamina (tunica vaginalis), a middle layer of dense fibrous tissue, and an inner layer of loose connective tissue (tunica vascularis) with nerve fibers and plentiful blood and lymphatic vessels. From the outer to the inside layers, the quantity of collagen fibers decreases, whereas the variety of cells increases. The fibers and cells in the two outermost layers form planes parallel to the testicular floor; cell sorts embody fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, mast cells, and nervous fibers. The thickness of the tunica albuginea will increase with age from four hundred to 445 m in young males to greater than 900 m in older men. The presence of many contractile cells showing excessive concentrations of guanosine monophosphate suggests that the tunica albuginea undergoes cycles of contraction and rest. The cells may regulate testicular measurement and favor the transport of spermatozoa into the epididymis. The interlobular septa divide the testis into approximately 250 pyramidal lobules, with the bases at the tunica albuginea and vertices on the mediastinum testis. The complete mixed size of the seminiferous tubules is approximately 540 m (range, 299 to 981 m). Nuclei are positioned near the basal lamina and seem triangular with an indented outline. They are euchromatic, as expected of cells that specific an excellent proportion of the genome to synthesize a large variety of substances required for its multiple features. It is externally lined by tunica albuginea, which is a thick layer shaped by collagenized fibrous tissue. The parietal layer has ample smooth muscle fibers, whereas the innermost layer of albuginea incorporates massive vessels (tunica vasculosa). Each germ cell sort types a unique layer within the seminiferous tubules and could also be identified by its nuclei. Spermatogonia are basal cells with pale cytoplasm, spherical nuclei, and eccentric nucleoli. Above these cells, the Sertoli cell nuclei could additionally be recognized by their large central nucleoli. The internal layers include primary spermatocytes displaying the chromatin pattern attribute of meiosis (semithin section). Testicular fluid is isosmotic, with a high content of potassium that exposes numerous membrane and water transporters. Ultrastructurally, Sertoli cells have attribute nucleoli, plasma membranes, and cytoplasmic elements. Nucleoli have a tripartite construction with spherical fibrillar centers, compact granular parts, and three-dimensional nets composed of intermingled fibrillar and granular portions. Sertoli-Sertoli junction specializations encompass adherens, tight junctions, and gap junctions which are dynamically reworked to allow the motion of germ cells throughout the seminiferous epithelium and the timely launch of spermatids into the tubular lumens. The blood-testis barrier is all the time secured by the existence of tight junctions both apically and basally to the cells. Terminal differentiation of Sertoli cells is regulated to an excellent extent by retinoblastoma protein. Actin filaments seem in both interSertoli cell junctions and ectoplasmic specializations that encompass germ cells. It is more ample subsequent to the heads of elongate spermatids (ectoplasmic specializations) and in the Sertoli cell cytoplasm that surrounds spermatids. Sertoli cells synthesize a number of products to make certain the nutrition, proliferation, and maturation of germ cells; they also stimulate other cells similar to Leydig cells and peritubular cells, and contribute to hormonal regulation (inhibin secretion) (Table 12. Sertoli cells are also concerned in migration of differentiating germ cells towards the tubular lumens. Nuclei are spherical, include a number of peripheral nucleoli, and have four completely different patterns according to their form, measurement, and nuclear staining features: Ad (dark), Ap (pale), Al (long), and Ac (cloudy). These are several micrometers long and are composed of quite a few 8- to 15-nm parallel filaments intermingled with ribosome-like granules. They later divide to make one other Ad (maintaining the stem cell reservoir) and an Ap spermatogonia. During replication, Ap spermatogonia become Ac after which divide by mitosis to kind two type B spermatogonia. Nuclei often are more distant from the basal lamina than are those of kind A spermatogonia and contain one or two large central nucleoli. The cytoplasm accommodates more ribosomes than sort A spermatogonia, and intermitochondrial bars are often not observed. Although all type A spermatogonia are located on the basal membrane, their distribution varies in the seminiferous tubules from one space to one other. In addition, Sertoli cells possess receptors for a quantity of components such as the nerve development issue produced by spermatocytes and younger spermatids, underscoring the complexity of the Sertoli cell�germ cell relationship. Seminiferous tubules present quite a few sort A spermatogonia within the center and sort B spermatogonia within the peripheral areas. Primary spermatocytes at interphase of the cell cycle lose contact with the basal lamina and inhabit cavities shaped by the Sertoli cell cytoplasm. Their cytoplasm incorporates more rough endoplasmic reticulum than that of spermatogonia, and the Golgi complexes are more developed. The leptotene spermatocyte, with filamentous chromatin, leaves the basal compartment and migrates first to an intermediate compartment after which to the adluminal compartment.
Syndromes - Too much of this protein leaking is often a sign of kidney damage.
- Nausea or vomiting
- When and how often does it occur?
- Organ meats
- Norepinephrine becomes normetanephrine and vanillylmandelic acid (VMA)
- Women: above 50 mg/dL
Order generic ranitidine from indiaThe reported incidence of melaninlike, lipofuscin-like prostatic pigment within the regular prostate varies from 4% to 70%. These findings recommend that this pigment is totally different from typical cutaneous melanin; the lipofuscin-like material ("wear and tear" or "old age" pigment) is probably an endogenous mobile by-product of prostate epithelium, quite than of melanocytic origin. It is important that the clinician provide the pertinent historical past of androgen deprivation or radiation therapy to assist the pathologist in rendering the right analysis. This dialogue summarizes therapy-related pathologic findings in the prostate, together with those from several ablation strategies. Androgen Deprivation Therapy One of the preferred forms of remedy for prostate cancer- androgen deprivation therapy-has been in use because the Sixties. Contemporary therapies have varying mechanisms of action, including mixed androgen blockage (gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists [e. These agents are used for preoperative tumor shrinkage, symptomatic relief of metastases, most cancers prophylaxis, and treatment of hyperplasia. There are a number of strategies to obtain androgen deprivation, and this form of therapy is commonly mixed with radiation therapy for enhanced impact. The altered epithelium shows involution and acinar atrophy, cytoplasmic clearing, nuclear and nucleolar shrinkage, and chromatin condensation, although modifications with 5-reductase inhibitors appear to be much less pronounced and variable than with different brokers (discussed later). After androgen deprivation remedy, benign and hyperplastic prostatic acini are atrophic and collapsed, typically with prominent basal cell hyperplasia and epithelial vacuolization. Luminal secretions are inspissated, resembling corpora amylacea, but normally lack discrete laminations or angulations; multinucleated cells are sometimes present at the periphery. Note the granular pigment within the epithelium, harking back to that seen in the seminal vesicles. Finasteride inhibits only the sort 2 isoenzyme of 5-reductase, thereby partly blocking conversion of testosterone. Shrinkage of the benign prostate by 5-reductase inhibitors has been documented in a number of preclinical and clinical studies. There is a 55% decline in epithelial content material after 6 months of treatment that correlates with volume lower. Conversely, one potential research of needle biopsy specimens from patients who have been handled for as much as 4 years and matched untreated controls found no important variations in benign epithelium. The greater sensitivity of the peripheral zone to dutasteride may be attributed to its greater density of androgen receptors in contrast with the transition zone, as shown by saturation binding assays with a competitive inhibitor. Finasteride treatment in rats and canines induces atrophy and involution, just like people, though the atrophy is usually patchy and incomplete, a discovering suggesting differential sensitivity throughout the gland. Compare with (D), during which the acinar basal cells are distinguished and surmounted by a cuboidal to low columnar secretory cell layer. The degree of histologic change attributable to radiation in benign, hyperplastic, and neoplastic tissues varies with the dose and duration of irradiation and the interval from remedy onset (Tables eight. Nuclear adjustments include nuclear enlargement (86% of cases) and outstanding nucleoli (50%). No variations are present in expression of neuroendocrine differentiation markers corresponding to chromogranin, neuron-specific enolase, -human chorionic gonadotropin, and serotonin. Multiple cryoprobe needles filled with circulating liquid nitrogen transform the prostate into an ice ball, resulting in substantial tissue destruction and demise of benign and malignant cells. The circulate of liquid nitrogen through the probes is adjusted to create the desired freezing sample and extent of tissue destruction in the prostate; no liquid nitrogen is available in contact with the tissue. Focal granulomatous irritation is associated with epithelial disruption resulting from corpora amylacea. Dystrophic calcification is infrequent and normally appears in areas with the greatest reparative response. In some circumstances the benign prostate appears unchanged, with no particular proof of tissue or immune response, a finding indicating lack of inclusion of that space within the ablation killing zone. As the postoperative interval will increase, biopsy is more more probably to include unaltered benign prostatic tissue. Cryotherapy is certainly one of multiple ablation methods that fluctuate by mechanism of tissue destruction (chemical, thermal, electrical), rapidity of cell demise (apoptosis: sluggish, 1 to 3 days; necrosis: immediate), effect on native proteins (intact or denatured), differential sparing of adjoining structures such as blood vessels and nerves (intact or ablated), and certain impression on the immune system and abscopal impact (nonstimulatory or stimulatory) (Table eight. Pathologists must be aware of these modifications that diminish the identical old reliance on nuclear and nucleolar size to identify most cancers. The pattern and extent of harm are determined by the tactic of thermocoagulation used, the duration of remedy, tissue perfusion factors, and the ratio of epithelium to stroma in the tissue being handled. Confluent coagulative necrosis occurs when multiple laser lesions are created in a single transverse aircraft. Marked nuclear abnormalities embrace variation in size and form and hyperchromasia. After 4 weeks, handled benign tissue is sharply demarcated, fully ablated, and consists only of necrotic and fibrotic tissue with out viable cells. Mild chronic irritation, hemosiderin, and coagulative necrosis are additionally observed. Electrical Membrane Breakdown Electrical membrane breakdown is a novel type of nonthermal tissue ablation that induces quick electrical pulse dose�related coagulative necrosis and nuclear pyknosis (Table 8. Expected results are classified as mild, moderate, or marked according to comparative literature evaluate and theoretical variables, specializing in the potential ability to vigorously and reproducibly stimulate the immune system to probably induce an abscopal effect. Prostatic morphogenesis, stromal-epithelial interactions, zonal anatomy, and quantitative morphometry. Prostate organogenesis: tissue induction, hormonal regulation and cell sort specification. Instructive induction of prostate progress and differentiation by a defined urogenital sinus mesenchyme. Growth and growth during early manhood as determinants of prostate measurement in later life. Relationship between the prostatic tissue elements and pure history of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Laparoscopic excision of seminal vesicle cyst revealed by obstruction urinary symptoms. Cysts of the ejaculatory system-a treatable cause of recurrent epididymoorchitis in children. Endoscopic management of seminal-vesical cyst with proper renal agenesis inflicting acute urinary retention: case report. Hyperplasia of prostatic mesonephric remnants: a possible pitfall in the analysis of prostate gland biopsy. Mesonephric remnants involving renal pelvis and prostatic urethra: a diagnostic problem in the course of adenocarcinoma. Florid hyperplasia of mesonephric remnants involving prostate and periprostatic tissue. Prostatic epithelial and luminal area within the transition zone acini: morphometric evaluation in regular and hyperplastic human prostate. Stereological analysis of fibronectin within the periurethral area of the transitional zone from regular human prostates in contrast with benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Purchase genuine ranitidine lineInflammatory pseudotumor of the urinary bladder with aberrant expression of cytokeratin. Clinical utility of immunohistochemistry in the diagnoses of urinary bladder neoplasia. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors of the genitourinary tract-single entity or continuum Ureteral endometriosis: clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 7 cases. Endometriosis of the urinary tract: a evaluate of the literature and a report of 4 instances of vesical endometriosis. Malignant transformation in endometriosis of the urinary bladder: case report of clear cell adenocarcinoma. Immunohistochemical phenotype of the urinary bladder endocervicosis: comparability with normal endocervix and well-differentiated mucinous adenocarcinoma of uterine cervix. An attempt towards a systematic account of the appearances related with that malconformation of the urinary organs during which the ureters, as a substitute of terminating in an ideal bladder, open externally on the floor of the abdomen. Adenocarcinoma arising in exstrophy of the bladder: report of two circumstances and review of the literature. The obstetric and gynaecological complications of bladder exstrophy and epispadias. The significance of a profitable initial bladder closure in the surgical administration of classical bladder exstrophy: analysis of 144 patients treated on the Johns Hopkins Hospital between 1975 and 1985. Double bladder and related anomalies: scientific and embryological elements and a case report. Incomplete reduplication of the bladder with congenital solitary kidney; report of a case. Congenital deficiency of the stomach musculature and associated genitourinary anomalies: a report of 22 instances. Embryology, anatomy, and ailments of the umbilicus together with illnesses of the urachus. Diverticulum of the bladder- presentation and evaluation of remedy of 115 cases. The spectrum of histopathologic findings in vesical diverticulum: implications for pathogenesis and staging. Congenital bladder diverticulum presenting as bladder outlet obstruction in infants and kids. Limited smoothelin expression inside the muscularis mucosae: validation in bladder diverticula. Primary carcinoma in a diverticulum of the bladder, a report of four circumstances and evaluate of the literature. Primary osteosarcoma of bladder diverticulum mimicking intradiverticular calculus: a case report. The superficial cells are sometimes distinguished and will have vacuolization of the cytoplasm, eosinophilic syncytial or apocrine-like morphology, or may demonstrate mucinous metaplasia. Secondary budding of small fronds from larger simple major papillary fronds is commonly observed. Inverted Papilloma Inverted papilloma is often present in males in the sixth or seventh decade of life. Although the term inverted papilloma was initially launched in 1963 by Potts and Hirst to describe this architecturally distinctive urothelial neoplasm, the Viennese urologist Paschkis had beforehand reported 4 morphologically similar urothelial tumors in 1927 underneath the name of adenomatoid polyp. These invaginating constructions reveal mature urothelium centrally, with darker and palisading basal cells peripherally, usually surrounded by fibrotic stroma without marked inflammation. The glandular variant is composed of nests of urothelium with either pseudoglandular spaces lined by mature urothelium and even true glandular parts, containing mucicarminophilic secretions and mucous-secreting cells. Within the spectrum of findings in inverted papilloma, vacuolization and foamy xanthomatous cytoplasmic modifications could also be seen. These "clear cells" may be concentrated inside distinct regions of the tumor, however more frequently are diffusely intermingled with usual inverted papilloma cells. Foci of nonkeratinizing squamous metaplasia and neuroendocrine differentiation have been reported. Such distinction may be troublesome, particularly in limited biopsy specimens or when interpretation is confounded by crush artifact. In distinction, urothelial carcinoma with an inverted development sample usually has thick and irregular tumor columns with transition to more stable nests. In addition, the presence of an exophytic papillary component and unequivocal tumor invasion in the lamina propria or muscularis propria justifies a prognosis of inverted urothelial carcinoma. Several investigators have voiced concern concerning the malignant potential of inverted papilloma based on the subsequent development of urothelial carcinoma, but most sufferers with this complication have a history of a prior or concurrent urothelial carcinoma. It has been nicely documented by the discovering of nonrandom inactivation of X chromosomes that inverted papilloma is a clonal neoplasm that arises from a single progenitor cell. Two cases had exon 10 and 15 mutations, together with A366D, H412H, E627D, D641N, and H643D; five circumstances had N653H. These tumors are diploid with undetectable or very restricted nuclear p53 accumulation. There may be elevated vascularity in the stroma at the base of the papillary folds. Recent data suggest that papillary hyperplasia could also be a precursor to low-grade papillary neoplasms. Swierczynski and Epstein reported 15 cases of papillary urothelial hyperplasia with varying levels of atypia starting from dysplasia to flat carcinoma in situ (atypical papillary urothelial hyperplasia). These cases may be considered as urothelial carcinoma in situ or dysplasia with early papillary formation. Squamous Papilloma Squamous papilloma is a rare benign neoplasm; it might characterize the squamous counterpart of urothelial papilloma. The number of cell layers (usually lower than seven) may differ due to tangential sectioning. Urothelial compression artifact or tangential sectioning of mucosa with pseudopapillary development (lacking a real vascular core) may resemble flat urothelial hyperplasia. Great advances have been made within the molecular genetic and biomarker characterization of bladder most cancers in current times. Urothelial Reactive Atypia Urothelial abnormalities whose architectural and cytologic modifications are of lesser degree than those of dysplasia have typically been termed atypia. The intraobserver and interobserver variations in recognition and interpretation of urothelial atypia are substantial. Two similar categories of atypia have been just lately acknowledged, specifically reactive atypia and atypia of unknown significance. Reactive Atypia Reactive atypia is characterized by mild nuclear abnormalities occurring in acutely or chronically inflamed urothelium. Nuclei are uniformly enlarged, vesicular, and should have prominent, normally centrally situated nucleoli. Mitotic figures may be frequent but at all times occur within the decrease epithelial layers (Table 6.
Buy ranitidine on line amexSurgical margin size and placement affect recurrence rates after robotic prostatectomy. Pathologic and clinical findings to predict tumor extent of nonpalpable (stage T1c) prostate most cancers. Association of anterior and lateral extraprostatic extensions with base-positive resection margins in prostate most cancers. Pathological and three Tesla volumetric magnetic resonance imaging predictors of biochemical recurrence after robotic assisted radical prostatectomy: correlation with whole mount histopathology. Impact of surgical margin standing on long-term most cancers management after radical prostatectomy. High Gleason grade carcinoma at a positive surgical margin predicts biochemical failure after radical prostatectomy and will guide adjuvant radiotherapy. Impact of Gleason rating on biochemical recurrence in sufferers with pT3aN0/Nx prostate cancer with positive surgical margins: a multicenter research from the Prostate Cancer Research Committee. Importance of reporting the Gleason rating at the constructive surgical margin site: evaluation of four,082 consecutive radical prostatectomy instances. The prostatic perineural area and its relation to tumor spread: an ultrastructural research. Perineural invasion on biopsy is related to upstaging at radical prostatectomy in Gleason rating 3 + four � 7 prostate cancer. Prognostic parameters apart from Gleason rating for the day by day analysis of prostate most cancers in needle biopsy. Perineural invasion is related to elevated relapse after external beam radiotherapy for males with low-risk prostate most cancers and may be a marker for occult, high-grade most cancers. Twelve-month prostatespecific antigen values and perineural invasion as sturdy unbiased prognostic variables of long-term biochemical end result after prostate seed brachytherapy. Predictive components related to biochemical recurrence following radical prostatectomy for pathological T2 prostate most cancers with negative surgical margins. Relationship between perineural invasion in prostate needle biopsy specimens and pathologic staging after radical prostatectomy. Digital rectal examination, imaging, and systematic-sextant biopsy in identifying operable 525. Detection of clinically vital prostate cancer by transrectal ultrasound-guided systematic biopsies. Relationship of tumor quantity to scientific significance for therapy of prostate cancer. Standardized in vitro mapping with a number of core biopsies of complete prostatectomy specimens: localization and prediction of tumour quantity and grade. Identification of insignificant prostate cancers: evaluation of preoperative parameters. Computer simulation of the likelihood of detecting low volume carcinoma of the prostate with six random systematic core biopsies. Relationship between serum prostate specific antigen, needle biopsy findings, and histopathologic options of prostatic carcinoma in radical prostatectomy tissues. Failure of focal prostate most cancers on biopsy to predict focal prostate cancer: the significance of prevalence. Distinguishing clinically necessary from unimportant prostate cancers earlier than remedy: worth of systematic biopsies. Is the share of most cancers in biopsy cores predictive of extracapsular illness in T1-T2 prostate carcinoma Optimal technique for measuring tumor extent in needle biopsy specimens to establish small-volume prostate most cancers. Percentage of positive prostate biopsies independently predicts biochemical consequence following radiation therapy for prostate cancer. Tumor volume and prostate particular antigen: implications for early detection and defining a window of curability. The best dimension of prostate carcinoa is an easy inexpensive predictor of prostate specific antigen failure in radical prostatectomy specimens. Maximum tumor diameter is an easy and priceless index associated with the native extent of illness in clinically localized prostate cancer. Percentage carcinoma as a measure of prostatic tumor size in radical prostatectomy tissues. Implementation of a map in radical prostatectomy specimen allows visual estimation of tumor quantity. The definition and preoperative prediction of clinically insignificant prostate most cancers. Tissue shrinkage after fixation with formalin injection of prostatectomy specimens. Gross tumor volume and clinical goal quantity in prostate most cancers: how do satellites relate to the index lesion. Lymphovascular invasion is an impartial prognostic factor in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Prognostic components for multifocal prostate most cancers in radical prostatectomy specimens: lack of significance of secondary cancers. Prostate whole tumor extent versus index tumor extent-which is predictive of biochemical recurrence following radical prostatectomy Clinical and pathological significance of the level and extent of capsular invasion in medical stage T1-2 prostate cancer. Tumor quantity improves the long-term prediction of biochemical recurrence-free survival after radical prostatectomy for localized prostate most cancers with optimistic surgical margins. Tumor quantity and clinical failure in high-risk prostate most cancers sufferers treated with radical prostatectomy. Total intraglandular and index tumor volumes predict biochemical recurrence in prostate cancer. Association between very small tumour measurement and elevated cancer-specific mortality after radical prostatectomy in lymph node-positive prostate cancer. Pathological options of localized prostate most cancers in China: a recent evaluation of radical prostatectomy specimens. Transition zone carcinoma of the prostate gland: a typical indolent tumour sort that occasionally manifests aggressive behaviour. Zonal location of prostate most cancers: significance for disease-free survival after radical prostatectomy Analysis of differences in clinicopathological options between prostate cancers positioned within the transition and peripheral zones. Differences in biopsy options between prostate cancers positioned in the transition and peripheral zone. Comparison localization outcomes based mostly on prostate biopsy specimens with outcomes primarily based on radical prostatectomy specimens in prostate most cancers. Transition zone and anterior stromal prostate cancers: Evaluation of discriminant location standards using multiparametric fusion-guided biopsy. Current standing of lymph node-positive prostate cancer: Incidence and predictors of consequence.
References - Fiard G, Rambeaud JJ, Descotes JL, et al: Long-term renal function assessment with dimercapto-succinic acid scintigraphy after conservative treatment of major renal trauma, J Urol 187(4):1306n1309, 2012.
- Marien T, Bjurlin MA, Wynia B, et al: Outcomes of robotic-assisted laparoscopic upper urinary tract reconstruction: 250 consecutive patients, BJU Int 116(4):604n611, 2015.
- Nordling J, Meyhoff H, Hald T: Sympatholytic effect on striated urethral sphincter, Scand J Urol Nephrol 15:173n178, 1981.
- Merguerian PA, Agarwal S, Greenberg M, et al: Outcome analysis of rhabdomyosarcoma of the lower urinary tract, J Urol 160(3 Pt 2):1191n1194, discussion 1216, 1998.
- Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI) clinical practice guideline for nutrition in children with CKD: 2008 update. Executive summary, Am J Kidney Dis 53(3 Suppl 2):S11-S104, 2009.
|
|