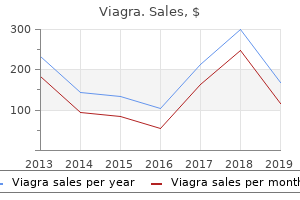
"Buy 50mg viagra with visa, impotence natural remedies."By: Dawn Sowards Brezina, MD - Assistant Professor of Medicine
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/dawn-sowards-brezina-md
Generic viagra 50mg without a prescriptionFurthermore, a pelvic mass or inflammatory process associated with actinomycosis could trigger exterior ureteral compression. In the retroperitoneum, enlarged lymph nodes or a tumor mass might compress the ureter. In patients with clotting abnormalities, blood clots or hematomas could hinder the urinary tract, as can sloughed papillae in patients with sickle cell disease or analgesic nephropathy (see earlier). Although leukemic infiltrates hardly ever cause obstruction in adults, in youngsters they cause obstruction in 5% of sufferers. The severity of the pain appears to correlate with the rate, somewhat than the diploma, of distension. The pain might current as typical renal colic (sharp ache that will radiate towards the urethral orifice), or, in sufferers with reflux, the pain could radiate to the flank only during micturition. Urinary tract obstruction is probably certainly one of the few situations that can lead to anuria, often because of bladder outlet obstruction or obstruction of a solitary kidney at any stage. Recurrent urinary tract infections will be the solely signal of obstruction, significantly in youngsters. As talked about earlier, prostatic disease with vital bladder outlet obstruction typically presents with issue initiating urination, decreased size or force of the urine stream, postvoiding dribbling, and incomplete emptying. The look of obstructive signs synchronous with the menstrual cycle can also be a sign of endometriosis. A palpable stomach mass, especially in neonates, may symbolize hydronephrosis, or, in all agegroups, a palpable suprapubic mass might symbolize a distended bladder. On laboratory examination, proteinuria, if present, is mostly lower than 2 g/day. Microscopic hematuria is a common finding, however gross hematuria could develop sometimes similar to in uncommon cases with appendiceal granuloma. Less widespread manifestations of urinary tract obstruction embody deterioration of renal operate with out obvious trigger, hypertension,110 polycythemia, and abnormal urine acidification and focus capacity. The findings of the history and physical examination ought to focus the analysis, in order that minimal period of time and expense are incurred in figuring out the reason for the obstruction. However, even patients with severe obstruction could additionally be asymptomatic, particularly in settings the place the obstruction develops steadily or in patients with spinal twine damage. The physical examination should focus first on very important signs, which can provide evidence of an infection (fever, tachycardia) or of frank volume overload (hypertension). The stomach examination could reveal a flank mass, which may symbolize hydronephrosis (especially in children), or a suprapubic mass, which may characterize a distended bladder. Features of chronic kidney illness, corresponding to pallor (anemia), drowsiness (uremia), neuromuscular irritability (metabolic abnormalities), or pericardial friction rub (uremic pericarditis), may also be noted. A thorough pelvic examination in women and a rectal examination for all patients are obligatory. A cautious historical past and a well-directed and full bodily examination usually reveal the precise cause of urinary obstruction. Polypeptides in the urine were identified and enabled diagnosis of the severity of obstruction. Pain, diploma of renal dysfunction, and the presence of an infection dictate the speed and nature of the analysis. Numerous imaging strategies are available; every has advantages and disadvantages, together with the power to determine the site and cause of the obstruction and to separate functional obstruction from mere dilation of the urinary tract. Patientspecific components, corresponding to the danger of radiocontrast within the setting of renal insufficiency or the danger of exposure to radiation in pregnant women, must also be weighed. Finally, ultrasonography could detect perinephric abscesses, which may complicate some forms of obstructive nephropathy. Unexplained kidney failure with benign urinary sediment should suggest urinary tract obstruction. Pyuria and bacteriuria may point out pyelonephritis; bacteriuria alone may recommend stasis. Crystals in a freshly voided specimen ought to result in consideration of nephrolithiasis or intrarenal crystal deposition. Hematologic analysis contains the hemoglobin level, hematocrit, and mean corpuscular volume (to establish anemia of continual kidney disease), and white blood cell rely (to establish potential hematopoietic system neoplasm or infection). These will assist establish issues of distal nephron function (impaired acid excretion or osmoregulation) and uremia. However, elastography can additionally be sensitive to mechanical and functional parameters such as hydronephrosis and exterior strain. Every experienced nephrologist has seen cases of obstruction with adverse ultrasonographic research results. Therefore the diagnosis of obstruction must still be thought of in patients with worsening renal operate, continual azotemia, or acute modifications in renal operate or urine output, even within the absence of hydronephrosis on ultrasonography. However, in some instances of acute urinary obstruction, ultrasonography might fail to detect pathologic processes. Renal ultrasound elastography provides measurement of kidney elasticity by the Shearwave technique. This finding is important within the prenatal counseling and treatment of boys with bilateral hydronephrosis and marked bladder dilation. Persistent postnatal renal abnormalities seem probably when the anteroposterior diameter of the fetal renal pelvis measures greater than 6 mm at lower than 20 weeks, more than 8 mm at 20 to 30 weeks, and greater than 10 mm at greater than 30 weeks of gestation. The long-term morbidity of gentle hydronephrosis (pelviectasis without calyceal dilation) is low. Cases of severe hydronephrosis (pelvicalyceal dilation with parenchymal thinning) may require surgical intervention for declining renal function, infection, or symptoms. Overall, because only roughly 5% to 25% of sufferers with antenatal hydronephrosis will in the end require surgical intervention,102,137 cautious long-term follow-up of those patients is required throughout childhood and into adulthood. However, within the absence of bilateral hydronephrosis, a solitary kidney, or suspected posterior urethral valve, practical imaging could be deferred until the primary four to 6 weeks of life. However, an infection within the setting of ureteral obstruction could cause significant morbidity, leading to an infant with sepsis, and renal injury is a potential comorbid situation. In urinary tract obstruction, pathophysiologic changes affecting the stress in the amassing system and kidney perfusion are properly imaged and form the basis for the proper interpretation of real-time ultrasonography and color duplex Doppler ultrasonography. A, Left hydronephrosis: dilated renal pelvis (arrows), with normal kidney on proper. Isotopic renography is often used to estimate the fractional contribution of every kidney to general renal perform. The noninvasive character of this examination with its excessive reproducibility makes it wonderful for monitoring sufferers, and it helps the urologist to decide whether to perform surgical intervention or watchful ready. Diuretic renography was introduced into clinical follow in 1978152 and could additionally be used to distinguish between hydronephrosis or pelvic dilation with obstruction and dilation with out obstruction.
Indian Balsam (Peru Balsam). Viagra. - How does Peru Balsam work?
- Cancer; intestinal worms; healing wounds, burns, leg ulcers, and bedsores; treating frostbite; and other conditions.
- What is Peru Balsam?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Peru Balsam.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96483
Buy viagra without prescriptionChen Y, Zhang J, Li J, et al: Expression of B7-H1 in inflammatory renal tubular epithelial cells. Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Pons H, Herrera-Acosta J, et al: Role of immunocompetent cells in nonimmune renal ailments. Fujiu K, Manabe I, Nagai R: Renal amassing duct epithelial cells regulate inflammation in tubulointerstitial injury in mice. Djudjaj S, Chatziantoniou C, Raffetseder U, et al: Notch-3 receptor activation drives inflammation and fibrosis following tubulointerstitial kidney harm. Schiffer L, Bethunaickan R, Ramanujam M, et al: Activated renal macrophages are markers of illness onset and illness remission in lupus nephritis. Wei X, Wang X, Xia Y, et al: Kindlin-2 regulates renal tubular cell plasticity by activation of Ras and its downstream signaling. Li Y, Wen X, Liu Y: Tubular cell dedifferentiation and peritubular irritation are coupled by the transcription regulator Id1 in renal fibrogenesis. Sugiura H, Yoshida T, Shiohira S, et al: Reduced Klotho expression level in kidney aggravates renal interstitial fibrosis. Spanou Z, Keller M, Britschgi M, et al: Involvement of drugspecific T cells in acute drug-induced interstitial nephritis. Lange-Sperandio B, Trautmann A, Eickelberg O, et al: Leukocytes induce epithelial to mesenchymal transition after unilateral ureteral obstruction in neonatal mice. Baylor P, Williams K: Interstitial nephritis, thrombocytopenia, hepatitis, and elevated serum amylase levels in a patient receiving clarithromycin remedy. Tintillier M, Kirch L, Almpanis C, et al: Telithromycin-induced acute interstitial nephritis: a primary case report. Whelton A: Nephrotoxicity of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicine: physiologic foundations and medical implications. Matsukura H, Itoh Y, Kanegane H, et al: Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis: potential association with cytomegalovirus an infection. Shibasaki T, Ishimoto F, Sakai O, et al: Clinical characterization of drug-induced allergic nephritis. Jahnukainen T, Saarela V, Arikoski P, et al: Prednisone within the remedy of tubulointerstitial nephritis in kids. Wu Y, Liu Z, Hu W, et al: Mast cell infiltration associated with tubulointerstitial fibrosis in persistent aristolochic acid nephropathy. Kabanda A, Jadoul M, Lauwerys R, et al: Low molecular weight proteinuria in Chinese herbs nephropathy. Depierreux M, Van Damme B, Vanden Houte K, et al: Pathologic elements of a newly described nephropathy associated to the extended use of Chinese herbs. Reginster F, Jadoul M, van Ypersele de Strihou C: Chinese herbs nephropathy presentation, natural history and destiny after transplantation. Stefanovic V, Cukuranovic R, Miljkovic S, et al: Fifty years of Balkan endemic nephropathy: challenges of examine utilizing epidemiological technique. Stefanovic V, Toncheva D, Atanasova S, et al: Etiology of Balkan endemic nephropathy and associated urothelial cancer. Blohme I, Johansson S: Renal pelvic neoplasms and atypical urothelium in sufferers with end-stage analgesic nephropathy. Effects of phenacetin and salicylate on mortality and cardiovascular morbidity (1968 to 1987). Ibanez L, Morlans M, Vidal X, et al: Case-control research of regular analgesic and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory use and end-stage renal illness. Pommer W, Bronder E, Greiser E, et al: Regular analgesic consumption and the chance of end-stage renal failure. Michielsen P, Heinemann L, Mihatsch M, et al: Non-phenacetin analgesics and analgesic nephropathy: scientific assessment of high users from a case-control study. Lepkifker E, Sverdlik A, Iancu I, et al: Renal insufficiency in longterm lithium remedy. Roncal C, Mu W, Reungjui S, et al: Lead, at low levels, accelerates arteriolopathy and tubulointerstitial harm in chronic kidney illness. Kido T, Nogawa K, Yamada Y, et al: Osteopenia in inhabitants with renal dysfunction induced by publicity to environmental cadmium. Trevisan A, Gardin C: Nephrolithiasis in a employee with cadmium exposure prior to now. Dahan K, Fuchshuber A, Adamis S, et al: Familial juvenile hyperuricemic nephropathy and autosomal dominant medullary cystic 1230. Preitner F, Bonny O, Laverriere A, et al: Glut9 is a serious regulator of urate homeostasis and its genetic inactivation induces hyperuricosuria and urate nephropathy. Darabi K, Torres G, Chewaproug D: Nephrolithiasis as main symptom in sarcoidosis. Thumfart J, Muller D, Rudolph B, et al: Isolated sarcoid granulomatous interstitial nephritis responding to infliximab remedy. Morino M, Inami K, Kobayashi T, et al: Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis in two siblings and concomitant uveitis in one. Other manifestations of genitourinary tract an infection are renal and perinephric abscesses, emphysematous cystitis and pyelonephritis, xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis, and pyocystitis. The term bacteriuria describes isolation of any bacteria within the urine, though in practice it often refers to isolation of organisms in concentrations that meet commonplace quantitative standards. Infection is asymptomatic when the urine culture outcome meets quantitative criteria for bacteriuria without signs or symptoms attributable to infection. Symptomatic urinary tract infection may manifest as bladder an infection (cystitis or decrease tract infection), kidney infection (pyelonephritis or higher tract infection), or prostate infection (acute or continual bacterial prostatitis). Acute uncomplicated urinary tract an infection happens in ladies with a normal genitourinary tract, normally manifesting as cystitis. A urinary tract an infection in a person must be thought of sophisticated until underlying abnormalities have been ruled out. Reinfection is infection that recurs after entry of an organism into the genitourinary tract, usually from the periurethral flora. However, when periurethral colonization with a potential uropathogen persists, the identical strain may be isolated from reinfection. Relapse occurs when an infecting organism persists within the urinary tract despite antimicrobial remedy; the identical organism is isolated from recurrent an infection after therapy. The normal flora of the distal urethra plays an important role in host defense by preventing colonization at this web site by potential uropathogens. The flora includes aerobic bacteria that are common skin commensals, such as coagulase-negative staphylococci, viridans group streptococci, and Corynebacterium species. The most essential host protection that maintains sterility of the urine is normal, unobstructed voiding. An array of urine and uroepithelial cell parts additionally contributes to upkeep of sterile urine in the regular genitourinary tract Table 37.
Buy 50mg viagra with visaDisease development has additionally been found to be similar for women and men with IgA nephropathy in most other research. A positive value signifies that male gender is associated with an adverserenaloutcome. A positive value signifies that male gender is associated with an antagonistic renal end result. However, this conclusion was largely the results of inclusion of a single Italian study that reported a highly statistically vital favorable association with male gender and illness development. Nonetheless, classifying race and ethnicity in biomedical research facilitates several essential actions, including the characterization of well being statistics, threat of adverse health outcomes, and examination of supply of health care providers across subpopulations. Also, these classifications can be utilized as a proxy for unmeasured biologic and social factors. However, the imperfect nature of the connection between race and these components highlights the significance of supplementing race and ethnicity knowledge, when attainable, with those on individual-level factors which might be often meant to be represented by race. To mirror components associated to social, cultural, and bodily environments and exposures most precisely, particular person race and ethnicity is commonly selfdesignated. Census Bureau in 1960, adopted by the chance to self-designate Hispanic ethnicity in 1970 and eventually, in 2000, the power to designate multiple race class. However, restricted data of ancestry, and the big and increasing frequency of migration, creates additional challenges for legitimate race classification. Finally, it has been instructed that ethnic teams that share a unique history, language, customs, ancestry, geography, religion, and/or particular genetic markers should replace conventional race classifications in biomedical analysis. Similar elevations in danger have been noted among black and different racial and ethnic minorities with hypertension. Finally, amongst sufferers with neither diabetes nor hypertension, black patients have been still three. For comparisons betweenracialandethnicgroups(withnon-Hispanic whites as the referent), P values are as follows (by age): for Mexican Americans, men, forty to 59 years, P<0. Both used admixture linkage dysequilibrium evaluation, which is based on the premise that when two genetically various populations combine, the admixed population receives chromosomal areas from either ancestry that can be identified by genotyping markers with totally different allelic frequencies between the ancestral populations. Racial variations in kidney disease threat are partially mediated by factors associated to socioeconomic status and social deprivation (see also Chapter 84). Socioeconomic status has been described as a distal threat factor for kidney illness that acts by way of several proximal elements, together with poverty and low revenue, lack of vitamin, low instructional ranges, exposure to heavy metals, substance abuse, and restricted entry to health care. As a outcome, several analyses have accounted for each individual- and area-level socioeconomic status. In addition, as in many disease processes that develop over protracted periods of time, past and current exposures are responsible for will increase in risk. Suboptimal health behaviors and poor control for glucose stage and blood pressure accounted for a considerable proportion of the remaining risk. Demographic, socioeconomic, lifestyle, medical components, and access to well being care accounted for 74% of this increased risk. Exposure to cadmium and lead, even at low levels, is associated with a considerably elevated prevalence of kidney disease. As famous, socioeconomic factors highly correlated with race and ethnicity account for a proportion of this excess threat. The affiliation with individual-level socioeconomic standing no longer remained significant after adjustment on this older population. Examination of the pattern of kidney illness throughout sexes has not yielded a constant relationship. Results are much less constant throughout sexes, however, concerning the development of IgA nephropathy and with development total in postmenopausal girls. More research are needed to elucidate any sex differences in the progression of lupus nephritis. Reported patterns of kidney illness throughout race and ethnic groups have been more constant than these reported across intercourse. There is some suggestion of interactions between socioeconomic status and race with kidney outcomes, however these want additional research. Additional research are wanted to clarify the influence of entry to well being care and early-life socioeconomic status on kidney well being. Ruggenenti P, Gaspari F, Perna A, et al: Cross-sectional longitudinal study of spot morning urine protein: creatinine ratio, 24-hour urine protein excretion fee, glomerular filtration rate, and endstage renal failure in persistent renal disease in sufferers without diabetes. Verzola D, Villaggio B, Procopio V, et al: Androgen-mediated apoptosis of kidney tubule cells: function of c-Jun amino terminal kinase. Kwan G, Neugarten J, Sherman M, et al: Effects of intercourse hormones on mesangial cell proliferation and collagen synthesis. Neugarten J, Ghossein C, Silbiger S: Estradiol inhibits mesangial cell-mediated oxidation of low-density lipoprotein. Arora P, Vasa P, Brenner D, et al: Prevalence estimates of continual kidney illness in Canada: outcomes of a nationally representative survey. Nitsch D, Grams M, Sang Y, et al: Associations of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with mortality and renal failure by intercourse: a meta-analysis. Moranne O, Watier L, Rossert J, et al: Primary glomerulonephritis: an replace on renal survival and determinants of development. Velo M, Lozano L, Egido J, et al: Natural history of IgA nephropathy in patients followed-up for more than ten years in Spain. Kobayashi Y, Fujii K, Hiki Y, et al: Steroid therapy in IgA nephropathy: a retrospective research in heavy proteinuric circumstances. Yoshikawa N, Ito H, Nakamura H: Prognostic indicators in childhood IgA nephropathy. Nieuwhof C, Kruytzer M, Frederiks P, et al: Chronicity index and mesangial IgG deposition are risk components for hypertension and renal failure in early IgA nephropathy. Koyama A, Igarashi M, Kobayashi M: Natural history and risk components for immunoglobulin A nephropathy in Japan. Mustonen J, Pasternack A, Helin H, et al: Clinicopathologic correlations in a collection of 143 sufferers with IgA glomerulonephritis. Hannedouche T, Chauveau P, Kalou F, et al: Factors affecting development in superior chronic renal failure. Jungers P, Hannedouche T, Itakura Y, et al: Progression price to end-stage renal failure in non-diabetic kidney illnesses: a multivariate analysis of determinant factors. Regression analyses of prognostic components affecting the course of renal perform and the mortality in 395 sufferers. Hannedouche T, Albouze G, Chauveau P, et al: Effects of blood stress and antihypertensive therapy on progression of superior persistent renal failure. Locatelli F, Marcelli D, Comelli M, et al: Proteinuria and blood pressure as causal components of development to end-stage renal failure. Hannedouche T, Chauveau P, Fehrat A, et al: Effect of moderate protein restriction on the speed of progression of chronic renal failure. Bogenschutz O, Bohle A, Batz C, et al: IgA nephritis: on the significance of morphological and clinical parameters in the longterm prognosis of 239 sufferers.
Cheap viagra 25mg without a prescriptionBladder dysfunction is incessantly related to other options of autonomic polyneuropathy, similar to postural hypotension, gastroparesis, constipation, and nocturnal diarrhea. Lewis E, Hunsicker L, Bain R, et al: the effect of angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. Yusuf S, Sleight P, Pogue J, et al: Effects of an angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular occasions in high-risk sufferers. Rossing P: the changing epidemiology of diabetic microangiopathy in sort 1 diabetes. Hovind P, Tarnow L, Rossing P, et al: Predictors for the event of microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria in patients with kind 1 diabetes: inception cohort research. Saito Y, Kida H, Takeda S, et al: Mesangiolysis in diabetic glomeruli: its role in the formation of nodular lesions. Toyoda M, Najafian B, Kim Y, et al: Podocyte detachment and decreased glomerular capillary endothelial fenestration in human sort 1 diabetic nephropathy. Benigni A, Gagliardini E, Tomasoni S, et al: Selective impairment of gene expression and assembly of nephrin in human diabetic nephropathy. Hirose K, Tsuchida H, �sterby R, et al: A sturdy correlation between glomerular filtration price and filtration floor in diabetic kidney hyperfunction. Bohle A, Wehrmann M, Bogenschutz O, et al: the pathogenesis of chronic renal failure in diabetic nephropathy. Predictors of 5-year urinary albumin excretion rate patterns in initially normoalbuminuric patients. Hovind P, Tarnow L, Rossing K, et al: Decreasing incidence of extreme diabetic microangiopathy in kind 1 diabetes. Klauser R, Prager R, Gaube S, et al: Metabolic effects of isradipine versus hydrochlorothiazide in diabetes mellitus. Rossing P, Rossing K, Gaede P, et al: Monitoring kidney operate in sort 2 diabetic patients with incipient and overt diabetic nephropathy. Perkovic V, Verdon C, Ninomiya T, et al: the relationship between proteinuria and coronary risk: a systematic evaluation and metaanalysis. Ninomiya T, Perkovic V, Verdon C, et al: Proteinuria and stroke: a meta-analysis of cohort research. Mazzucco G, Bertani T, Fortunato M, et al: Different patterns of renal damage in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a multicentric study on 393 biopsies. Shimizu M, Furuichi K, Kitajima S, et al: Long-term outcomes of Japanese kind 2 diabetic sufferers with biopsy-proven diabetic nephropathy. Hayashi H, Karasawa R, Inn H, et al: An electron microscopic examine of glomeruli in Japanese patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Moriya T, Moriya R, Yajima Y, et al: Urinary albumin as an indicator of diabetic nephropathy lesions in Japanese kind 2 diabetic patients. Nosadini R, Velussi M, Brocco E, et al: Course of renal function in sort 2 diabetic sufferers with abnormalities of albumin excretion rate. Gaede P, Vedel P, Larsen N, et al: Multifactorial intervention and heart problems in patients with sort 2 diabetes. Gaede P, Hildebrandt P, Hess G, et al: Plasma N-terminal probrain natriuretic peptide as a major risk marker for heart problems in patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Comas J, Arcos E, Castell C, et al: Evolution of the incidence of persistent kidney disease stage 5 requiring renal substitute therapy in the diabetic population of Catalonia. Borch-Johnsen K, Kreiner S: Proteinuria: worth as predictor of cardiovascular mortality in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Kapelrud H, Bangstad H-J, Dahl-J�rgensen K, et al: Serum Lp(a) lipoprotein concentrations in insulin-dependent diabetic sufferers with microalbuminuria. Earle K, Walker J, Hill C, et al: Familial clustering of heart problems in sufferers with insulin-dependent diabetes and nephropathy. Tarnow L, Hovind P, Teerlink T, et al: Elevated plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine as a marker of cardiovascular morbidity in early diabetic nephropathy in kind 1 diabetes. Jorsal A, Tarnow L, Flyvbjerg A, et al: Plasma osteoprotegerin levels predict cardiovascular and all-cause mortality and deterioration of kidney perform in type 1 diabetic sufferers with nephropathy. Hovind P, Rossing P, Tarnow L, et al: Serum uric acid as a predictor for improvement of diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes: an inception cohort study. Urinary albumin excretion, blood pressure and their relation to blood sugar levels. Deckert T, Kofoed-Enevoldsen A, Vidal P, et al: Size- and cost selectivity of glomerular filtration in sort 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic sufferers with and without albuminuria. Pietravalle P, Morano S, Christina G, et al: Charge selectivity of proteinuria in type 1 diabetes explored by Ig subclass clearance. Nakamura T, Ushiyama C, Suzuki S, et al: Urinary excretion of podocytes in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Jorsal A, Tarnow L, Frystyk J, et al: Serum adiponectin predicts all-cause mortality and end-stage renal illness in sufferers with sort I diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium, Matsushita K, van der Velde M, et al: Association of estimated glomerular filtration price and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: a collaborative meta-analysis. National Clinical Guideline Centre: Hypertension: the scientific administration of main hypertension in adults: replace of clinical tips 18 and 34 [Internet], London, 2011, Royal College of Physicians. Flyvbjerg A: the function of insulin-like progress factor I in initial renal hypertrophy in experimental diabetes. Rudberg S, Persson B, Dahlquist G: Increased glomerular filtration fee as a predictor of diabetic nephropathy-an 8-year prospective examine. Microalbuminuria Collaborative Study Group, United Kingdom: Risk components for growth of microalbuminuria in insulin dependent diabetic sufferers: a cohort research. Microalbuminuria Collaborative Study Group, United Kingdom: Predictors of the event of microalbuminuria in sufferers with kind 1 diabetes mellitus: a seven-year potential study. Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Diabetes Register Group: Near-normal urinary albumin concentrations predict development to diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes. Sk�tt P: Lithium clearance within the evaluation of segmental renal tubular reabsorption of sodium and water in diabetes mellitus. Andersen S, Blouch K, Bialek J, et al: Glomerular permselectivity in early stages of overt diabetic nephropathy. Rossing P: Promotion, prediction, and prevention of progression in diabetic nephropathy. Hayashi K, Epstein M, Loutzenhiser R, et al: Impaired myogenic responsiveness of the afferent arteriole in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: function of eicosanoid derangements. Verdecchia P, Angeli F, Borgioni C, et al: Changes in cardiovascular threat by discount of left ventricular mass in hypertension: a meta-analysis. Ritz E, Tomaschitz A: Aldosterone, a vasculotoxic agent-novel functions for an old hormone. Remuzzi G, Bertani T: Is glomerulosclerosis a consequence of altered glomerular permeability to macromolecules Torffvit O, Agardh C-D: Day and evening variation in ambulatory blood pressure in sort 1 diabetes mellitus with nephropathy and autonomic neuropathy.
Viagra 100 mg discountIn this case, placental ischemia, somewhat than causative, could mirror that the placenta is the earliest organ affected by this derangement of angiogenic steadiness. Animal models of preeclampsia based on induction of uteroplacental ischemia are characterised by elevated endogenous sFlt196,183 and sEng. Heme oxygenase 1 and its downstream metabolite, carbon monoxide, act as a vascular protecting issue by inhibiting the manufacturing of sFlt1. In addition to angiogenic alterations, ladies in whom preeclampsia develops even have proof of insulin resistance. For instance, lack of enough antenatal care is strongly associated with poor outcomes, together with eclampsia and fetal death. Higher blood pressure within the first or second trimester, even in the absence of overt hypertension, is associated with elevated threat for preeclampsia in wholesome nulliparous women. Presumably as a outcome of failed placental vascular reworking, preeclampsia is related to elevated placental vascular resistance and uterine artery waveform abnormalities in the second trimester, as measured by uterine artery Doppler ultrasonography. Test performance varies widely among research due to variations in populations studied, gestational age at the time of measurement, definition of an abnormal outcome, and severity and timing of preeclampsia detected: Sensitivities and specificities vary from 65% to 85%. Some data counsel that there could also be promise in combining uterine artery Doppler ultrasonography with measurement of serum biomarkers in screening for preeclampsia. Alterations in circulating ranges of the angiogenic factors sFlt1 and sEng happen weeks prior to the onset of preeclampsia and could additionally be helpful for screening and/or analysis. Prospective studies are ongoing to evaluate the clinical utility of those biomarkers for preeclampsia screening and threat evaluation. Later research have advised that circulating angiogenic elements in plasma or serum can be used to differentiate preeclampsia from different ailments that mimic preeclampsia, corresponding to continual hypertension, gestational hypertension, lupus nephritis, and chronic kidney illness. Aspirin and different antiplatelet agents have been evaluated in dozens of trials for the prevention of preeclampsia, both in high-risk teams and in healthy nulliparous women. Among women at high risk for preeclampsia, outcomes of a quantity of small, early trials advised that day by day aspirin had a significant protective effect. A subsequent comprehensive meta-analysis of antiplatelet brokers to forestall preeclampsia, which included greater than 32,000 ladies of varying threat status from 31 trials, discovered that antiplatelet brokers have a modest benefit, with a relative danger of preeclampsia of zero. Nevertheless, low-dose aspirin clearly appears to be secure: Early considerations about an increased threat of postpartum hemorrhage have clearly been assuaged. Given the small however vital protecting effect, aspirin prophylaxis should be thought of as primary prevention for preeclampsia solely in girls at excessive baseline danger, in whom the absolute threat reduction shall be biggest. Thus, calcium supplementation may be useful in ladies with low baseline calcium consumption. More work is needed to consider whether true deficiency of vitamin D is related to preeclampsia. Nutritional interventions have usually not been efficient in reducing preeclampsia danger. Obese girls with lower gestational weight gain (<15 kg) have a decreased incidence of preeclampsia. In preeclampsia manifesting between 24 and 34 weeks of gestation with out the extreme indicators and signs just described, postponing supply might enhance neonatal end result. The potential neonatal profit must be balanced against the potential of increased maternal morbidity as a end result of delaying delivery. Two small randomized managed trials demonstrated that in ladies presenting with severe preeclampsia between 28 and 32 weeks of gestation, expectant management (with delivery postponed 1 to 2 weeks after presentation) resulted in decreases in rate of neonatal complications charges and period of neonatal intensive care unit keep, with no significant increase in price of maternal issues. Retrospective research recommend that maternal and neonatal outcomes are comparable amongst ladies present process induction of labor and those undergoing cesarean section. Rather than looking for to reduce long-term cerebrovascular and cardiovascular complications, the aim of care is to maximize the likelihood of profitable supply of a wholesome toddler whereas minimizing the prospect of acute complications in the mom. Aggressive therapy of hypertension in pregnancy can compromise placental blood flow and fetal progress. For this purpose, antihypertensive therapy for preeclampsia is normally withheld except the blood stress rises above a hundred and fifty to one hundred sixty mm Hg systolic or a hundred to 110 mm Hg diastolic, above which the risk of cerebral hemorrhage becomes significant. Prior to the mid-1990s, proof for its use was largely derived from scientific experience and from small uncontrolled research. Over the last 20 years, magnesium has been proved to be superior to other brokers for the prevention and treatment of seizures in preeclampsia, though not for the prevention of preeclampsia per se. In women presenting prior to 24 weeks of gestation with severe preeclampsia, perinatal and neonatal mortality rates are extremely high (>80%) even with attempts to postpone supply, and maternal problems are common. For many years intravenous steroids have been instructed as an adjunct to ordinary administration, on the basis of retrospective and uncontrolled research. Data for the antepartum period are limited to a few cases sequence with mixed outcomes and no clear profit. Interfering with the manufacturing or signaling of sFlt1 may ameliorate the endothelial dysfunction of preeclampsia, permitting supply to be more safely postponed. In a pilot research restricted to three ladies with extreme early preeclampsia (24-32 weeks of gestation), Thadhani and colleagues lowered sFlt1 ranges using dextran sulfate apheresis and prolonged pregnancy by 2 to 4 weeks; importantly, this remedy promoted fetal development with no opposed results on the fetus or the mother. Pilot human trials to check the protection and efficacy of pravastatin in the course of the third trimester in sufferers with extreme preeclampsia are ongoing. In the therapeutic range (5 to 9 mg/dL), magnesium sulfate slows neuromuscular conduction and depresses central nervous system irritability. Women receiving continuous infusions of magnesium ought to be monitored fastidiously for signs of toxicity, including loss of deep tendon reflexes, flushing, somnolence, muscle weak spot, and decreased respiratory fee. Such monitoring is very important in girls with impaired renal operate, who also have impaired urinary magnesium excretion. Among ladies within the 24- to 34-week gestational window whose medical status seems 2. Gestational hypertension, in distinction, is often first noted after 20 weeks of gestation and, by definition, resolves after supply. In such cases, a lady with continual hypertension may be inappropriately labeled as having gestational hypertension when her blood strain rises in the third trimester. On the opposite hand, preeclampsia can sometimes manifest previous to 20 weeks of gestation; therefore, preeclampsia should all the time be suspected in ladies presenting with new hypertension and proteinuria close to midgestation. Chronic hypertension is present in 3% to 5% of pregnancies270 and is extra common with advanced maternal age, obesity, and black race. Women with delicate, uncomplicated persistent hypertension often have obstetric outcomes similar to those within the basic obstetric population. In the absence of underlying kidney illness, the new onset of proteinuria (>300 mg/ day), usually with worsening hypertension, is probably the most reliable signal of superimposed preeclampsia. Other signs and symptoms of preeclampsia, corresponding to headache, visual adjustments, epigastric pain, and pulmonary edema, and laboratory derangements, such as thrombocytopenia, new or worsening renal insufficiency, and elevated liver enzymes, also ought to immediate consideration of preeclampsia and, when current, are an indication of preeclampsia severity. Surgical intervention is typically postponed till after delivery every time possible. Hypertension and hypokalemia from primary hyperaldosteronism may be expected to improve throughout being pregnant, because progesterone antagonizes the impact of aldosterone on the renal tubule. Although the use of spironolactone has been reported during being pregnant, theoretical risks to the fetus are significant, and aldosterone antagonists must be avoided if possible.

Purchase 50mg viagraSpecific gravity is affected by protein, mannitol, dextrans, and radiographic contrast media. In these settings, specific gravity can be elevated disproportionately to the osmolality, falsely suggesting highly concentrated urine. Examples are maple syrup urine disease (maple syrup odor), phenylketonuria (mousy odor), isovaleric acidemia (sweaty toes odor), and hypermethioninemia (fishy odor). Most commonly, the double indicators methyl purple and bromthymol blue are used within the reagent strips to give a broad vary of colours at totally different pH values. Prolonged storage can lead to overgrowth of urea-splitting micro organism and the laboratory measurement of a excessive urine pH. Diuretic therapy, vomiting, gastric suction, and alkali therapy also can cause a excessive urine pH. Specific gravity is defined as the load of a solution relative to that of an equal volume of water. Ketones might seem within the urine, however not in serum, with extended fasting or starvation. False-negative outcomes are unusual however may be caused by ascorbic acid, a strong decreasing agent. False-positive outcomes could occur because of oxidizing contaminants, povidoneiodine, semen, or a excessive focus of bacteria with pseudoperoxidase activity (such as Enterobacteriaceae, staphylococci, and Streptococcus spp). When these substances are produced in massive quantities, as occurs in hemolysis or rhabdomyolysis, the capability for binding is overwhelmed they usually seem within the urine. A positive dipstick check result for hemoglobin within the absence of purple blood cells within the urine sediment due to this fact suggests either hemolysis or rhabdomyolysis. Factors which will enhance leukocyte lysis embrace permitting urine to stand for long durations, low pH, and low relative density. In these settings, there could also be a positive dipstick end result for leukocyte esterase with no leukocytes seen on microscopy. High ranges of glucose, albumin, ascorbic acid, tetracycline, cephalexin, or cephalothin or massive amounts of oxalic acid might inhibit the reaction and trigger false-negative results. In the reagent strip check, nitrite reacts with a p-arsanilic acid to kind a diazonium compound; additional reaction with 1,2,three,4-tetrahydrobenzo(h)quinolin3-ol ends in a pink shade end level. False-negative results are common and could additionally be because of extended pattern storage or low dietary intake. It could take up to 4 hours to convert nitrate to nitrite, so insufficient bladder retention time can also give false-negative outcomes. Hydrogen peroxide then reacts via a peroxidase with a lowered chromogen to type a coloured product. It restricts the passage of macromolecules, similar to albumin and globulin, and allows the excretion of an virtually protein-free ultrafiltrate containing water and small solvents. It consists of three main layers-endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane, and podocytes, which cover the basement membrane on the aspect of the urinary space. Podocytes are highly specialized epithelial cells with long, interdigitated foot processes that wrap around the glomerular capillaries, forming forty nm�wide gaps, known as filtration slits, between adjoining processes (see additionally Chapter 4). The podocyte plays a central role in integrating the components of the glomerular filtration barrier by interacting with the glomerular basement membrane and signaling on the slit diaphragm. Damage to any one of many three layers of the glomerular filtration barrier allows proteins through, leading to abnormal, "glomerular" proteinuria. Charge selectivity, by which the negatively charged proteoglycans and heparan sulfates in the glomerular basement membrane repel albumin molecules, is a principle seeking to explain the low glomerular sieving coefficient of albumin in relation to other molecules of its dimension. Because the plasma concentration of those proteins is far lower than that of albumin and globulins, nonetheless, the filtered load is small. Thus, proteins similar to 2-microglobulin, apoproteins, enzymes, and peptide hormones are usually excreted in solely very small quantities in the urine. Immunoglobulin A (IgA) and urokinase are additionally secreted by the renal tubule and seem in the urine in small quantities. Unlike the opposite sorts listed right here, glomerular proteinuria typically ends in urinary protein loss of more than 1 g per day. Overflow: Normal or abnormal plasma proteins produced in elevated quantities could additionally be filtered at the glomerulus and will overwhelm the resorptive capacity of the proximal tubule. This occurs notably with small or positively charged proteins and is of clinical importance principally in plasma cell dyscrasias. It may also happen with myoglobin in rhabdomyolysis and with hemoglobin in extreme intravascular hemolysis. Postrenal: Small amounts of protein, normally non-albumin IgG or IgA, may be excreted within the urinary tract in the setting of infection or stones. In normal physiologic circumstances, about half of the excreted protein is Tamm-Horsfall protein, and less than 30 mg of albumin is excreted per day. As protein loss increases, albumin becomes essentially the most vital single protein present. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 68:9-25, 2010; and Martin H: Laboratory measurement of urine albumin and urine complete protein in screening for proteinuria in continual kidney disease. A positive end result from a semiquantitative test, corresponding to a urinary dipstick check, should immediate further evaluation with a quantitative check. Both preanalytical factors and elements intrinsic to the evaluation itself may be sources of error in protein measurement. In the evaluation of the standard of a test, each accuracy and precision have to be taken into account. Although a take a look at might give reproducible outcomes, it could not accurately measure all clinically significant types of proteinuria. The heterogeneous forms of protein and the completely different molecular types of proteins (such as albumin) that may be present in urine make for a challenge to both accuracy and precision of measurement. Using a consistent form of measurement with a consistent assay to monitor proteinuria, and utilizing multiple measurements to verify findings, is therefore advisable. Many current guidelines suggest the measurement of urine albumin on the idea of a have to detect lower ranges of protein than were beforehand thought to be clinically significant. One difficulty with the implementation of albumin as a replacement for complete protein is the lack of a continuing numerical relationship between the two that would enable clinicians to translate the present evidence base from one to the other. Of sufferers who screened optimistic for albuminuria, 68% had negative results for proteinuria. Albuminuria performed properly as a screening test for proteinuria: Sensitivity was 91. However, among those with proteinuria, 8% excreted albumin inside the regular range. These methods are vulnerable to interference by inorganic ions and nonprotein substances in the urine. There is large sample-to-sample variation in the kind and composition of proteins present, making correct measurement troublesome. Turbidimetric strategies, which are generally used, are imprecise, with a coefficient of variation as high as 20%.
Syndromes - Aortic valve (the valve between the heart and the blood vessel to the rest of the body) is unable to open wide enough.
- Symptoms of chronic kidney disease
- Movement changes, such as involuntary or slowed movements
- Rickets
- Infections such as syphilis
- Frequent bleeding from the prostate
- Raw areas of the skin from scratching
- Oxygen
- EKG (electrocardiogram, or heart tracing)
Viagra 100mg without a prescriptionThe impact of being pregnant on the long-term course of renal perform in girls with diabetic nephropathy has not been clarified until somewhat lately. Finally, the rise in glomerular stress consequent to nephron adaption may be accentuated with concomitant diabetes, as suggested in animal studies. In cross-sectional research, the osteoprotegerin level was elevated in varieties 1 and a pair of diabetic sufferers with microvascular and macrovascular complications. Foot ulcers with sepsis leading to amputation happen frequently (>25% of cases), probably due to a combination of neural and arterial ailments. Autonomic neuropathy may be asymptomatic and manifest simply as abnormal cardiovascular reflexes, or it might end in debilitating signs. Almost all patients with nephropathy have grossly abnormal outcomes on autonomic function checks. Newer therapy options that are in growth or have been tested and failed just lately are subsequently discussed. Risk elements for progression from normoalbuminuria to microalbuminuria and macroalbuminuria have been recognized Table 39. Increased kidney dimension is associated with an exaggerated renal response to amino acid infusion, and research have instructed that each abnormalities could be corrected by three weeks of intensified insulin treatment. A worsening of diabetic retinopathy was noticed through the preliminary months of intensive remedy however, in the long run, the speed of decay was slower than in the sort 1 diabetic sufferers receiving typical treatment. The frequency of severe hypoglycemic episodes and diabetic ketoacidosis was discovered to be greater in a number of studies. This clearly paperwork the need for extra treatment modalities to scale back the burden of diabetic nephropathy. Thus, it has been found that rosiglitazone, which is a thiazolidinedione, reduces microalbuminuria independently of glycemia in a study by Bakris and coworkers. Therefore, further evaluation is needed to confirm whether or not these agents have a renoprotective impact above and past their impact on lowering blood glucose levels. However, it must be stressed that none of the trials was randomized, and the number of patients included was small. In contrast, most major potential observational research have indicated an important function for glycemic management within the development of diabetic nephropathy (see earlier). The effect of the calcium channel block verapamil alone was similar to that of placebo. Overall, there have been barely fewer cardiovascular occasions with olmesartan but more fatal occasions, although numbers were very small (15 vs. However, the research have used variable finish factors, intermittent or persistent microalbuminuria. Furthermore, the studies typically enrolled patients with very low ranges of urinary albumin excretion. A randomized study was conducted during which diabetic patients with microalbuminuria have been handled with perindopril or nifedipine for 12 months. Unfortunately, the research enrolled a heterogeneous group of hypertensive and normotensive sufferers with either sort 1 or type 2 diabetes. Ravid and associates carried out a double-blind randomized research of ninety four normotensive microalbuminuric sort 2 diabetic patients who obtained enalapril or placebo for 5 years. The baseline traits within the three subject teams had been comparable (placebo, irbesartan at one hundred fifty mg daily, and irbesartan at 300 mg daily). The average blood stress during the course of the research was 144/83 mm Hg within the placebo group, 143/83 mm Hg within the 150-mg group, and 141/83 mm Hg within the 300-mg group (P = zero. Serious antagonistic events had been less frequent among the sufferers handled with irbesartan (P = zero. The changes in interleukin-6 had been related to the changes in albumin excretion. This was comprised of behavior modification and polypharmacologic therapy aimed toward a quantity of modifiable danger components (hyperglycemia, hypertension, dyslipidemia, microalbuminuria), along with secondary prevention of heart problems with aspirin. This strategy was in contrast with a standard intervention addressing multiple risk factors. In conclusion, a target-driven, long-term, intensified intervention geared toward a quantity of risk elements in sufferers with sort 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria reduces the chance of cardiovascular and microvascular occasions by about 50%. In a poststudy follow-up, the results have been maintained after an additional 5 years. An audit of the implementation of this technique in scientific apply has demonstrated that the beneficial outcome found in the initial, short-term, randomized clinical trial results might be confirmed and maintained for 10 years. Because discount of proteinuria is a prerequisite for profitable long-term renoprotection, one study investigated whether individual affected person factors are determinants of antiproteinuric efficacy. In latest years, it has become clear that aldosterone should be thought of a hormone with widespread unfavorable results on the vasculature, coronary heart, and kidneys. The medication had similar effects on albuminuria and glomerular structural adjustments, but the quantity of interstitial fibrosis was attenuated to a larger extent with aliskiren. Systolic blood strain was significantly lowered after 7 days, with no additional discount after 28 days. Importantly, an extra antiproteinuric effect was seen when the brokers were combined. Side effects had been few; in particular, hyperkalemia was no more frequent within the intervention group. Hyperkalemia was considerably more frequent within the aliskiren group than in the placebo group (11. Whether this initial phenomenon is reversible (hemodynamic effect) or irreversible (structural damage) with extended antihypertensive treatment has been investigated in sort 1 diabetic sufferers with diabetic nephropathy. The number of sudden deaths was not considerably completely different in the numerous treatment teams. Taken collectively, the outcomes of these two landmark studies led to the next conclusion: "Losartan and irbesartan conferred significant renal advantages in sufferers with sort 2 diabetes and nephropathy. The cumulative demise fee was 18% at 10 years after the onset of diabetic nephropathy, and the median survival time was longer than 16 years. Less info on this essential issue is out there for kind 2 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy. Consequently, these patients ought to be treated with statins according to present guidelines for sufferers at excessive danger. There was no impact on development of urinary albumin excretion alone, but when data have been mixed for a barely improved regression from microalbuminuria to normoalbuminuria and a reduced progression of albuminuria, it was noticed that 2. A variety of new choices have been advised by experimental and medical studies Table 39. Vitamin D (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3) or activation of the vitamin D receptor with vitamin D analogues has lately been suggested to play a job in inhibiting the event of diabetic nephropathy.
Buy 50 mg viagra with mastercardHenry M, Amor M, Henry I, et al: Stents within the treatment of renal artery stenosis: long-term follow-up. Radermacher J, Weinkove R, Haller H: Techniques for predicting favourable response to renal angioplasty in sufferers with renovascular illness. Zeller T, Muller C, Frank U, et al: Stent angioplasty of severe atherosclerotic ostial renal artery stenosis in sufferers with diabetes mellitus and nephrosclerosis. Krumme B, Hollenbeck M: Doppler sonography in renal artery stenosis�does the Resistive Index predict the success of intervention Marckmann P, Skov L, Rossen K, et al: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: suspected causative function of gadodiamide used for contrastenhanced magnetic resonance imaging. La Batide-Alanore A, Azizi M, Froissart M, et al: Split renal perform end result after renal angioplasty in sufferers with unilateral renal artery stenosis. Mounier-Vehier C, Cocheteux B, Haulon S, et al: Changes in renal blood move reserve after angioplasty of renal artery stenosis in hypertensive patients. Jackson B, Franze L, Sumithran E, et al: Pharmacologic nephrectomy with persistent angiotensin changing enzyme inhibitor remedy in renovascular hypertension within the rat. Zhang X, Eirin A, Li Z, et al: Angiotensin blockade has protective effects on the poststenotic porcine kidney. Eklof H, Bergqvist D, Hagg A, et al: Outcome after endovascular revascularization of atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Blum U, Krumme B, Fluegel P, et al: Treatment of ostial renalartery stenoses with vascular endoprostheses after unsuccessful balloon angioplasty. Dorros G, Jaff M, Mathiak L, et al: Four-year follow-up of PalmazSchatz stent revascularization as therapy for atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Klahr S, Morrissey J: the role of vasoactive compounds, growth factors and cytokines within the progression of renal disease. Hypertension and/or renal disease occurring in the setting of pregnancy presents a novel set of medical challenges. The chapter critiques current information on epidemiology and management points relating to chronic hypertension, continual renal disease, and being pregnant in the setting of kidney transplantation as nicely. Early in pregnancy, systemic vascular resistance decreases and arterial compliance increases. Sympathetic activity is elevated, mirrored in a 15% to 20% improve in heart price. There is also cumulative retention of about 950 mmol of sodium distributed between the maternal extracellular compartments and the fetus. These changes are likely as a end result of mechanical compression of the ureters between the gravid uterus and the linea terminalis. Hydronephrosis of being pregnant is usually asymptomatic, however stomach ache, and barely obstruction, can occur (see "Obstructive Uropathy" section). Normal creatinine clearance in being pregnant rises to a hundred and fifty to 200 mL/min, and average serum creatinine falls from 0. The renin aldosterone angiotensin system is activated in pregnancy,4 resulting in renal salt and water retention. These circumstances are thought to be due to a combination of the elevated filtered load of glucose and amino acids and fewer efficient tubular reabsorption. The gene product mediating placental vasopressinase activity has been characterised as a novel placental leucine aminopeptidase. This syndrome of transient diabetes insipidus manifests in the course of the second trimester and disappears after supply. The late gestational rise in uric acid ranges is attributed to elevated renal tubular absorption of urate. The kidney achieves this steadiness flawlessly, and sodium steadiness is maintained usually: Pregnant women have normal excretion of an exogenous solute load and appropriately preserve sodium when intake is restricted. Animal research counsel that elevated aquaporin-2 expression in the amassing tubule could contribute to this impact. J Clin Invest 52:2682-2689, 1973, by copyright permission of the American Society for Clinical Investigation. Gestational renal hyperfiltration and vasodilation had been completely abolished in pregnant rats both administered relaxin-neutralizing antibodies or lacking a practical corpus luteum, suggesting a critical role for relaxin in mediating the renal circulatory changes during pregnancy. This transformation appears to be driven by invasion of the maternal spiral arteries by fetal-derived cytotrophoblasts, which rework from an epithelial to an endothelial phenotype as they substitute the endothelium of the maternal spiral arteries. Dysregulation of these angiogenic factors may contribute to problems of placental vasculogenesis, corresponding to preeclampsia (discussed more absolutely within the "Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia" section). Hence, preeclampsia is still a leading cause of preterm delivery and consequent neonatal morbidity and mortality within the developed world as properly as the most typical explanation for maternal dying within the United States. Most circumstances of preeclampsia happen in healthy nulliparous women, in whom the incidence of preeclampsia has been reported as high as 7. Several medical conditions are related to increased preeclampsia danger, together with continual hypertension, diabetes mellitus, renal disease, weight problems, and antiphospholipid antibody syndrome Table 49. Women who had preeclampsia in a previous pregnancy have a high danger of preeclampsia in subsequent pregnancies. Conditions associated with increased placental mass, corresponding to multifetal gestations and hydatidiform mole, are additionally related to increased preeclampsia danger. Teen being pregnant has been identified as a threat consider some research,forty one but this finding was not confirmed in a metaanalysis and systematic evaluate. Racial differences within the incidence and severity of preeclampsia have been troublesome to assess due to confounding socioeconomic and cultural factors. In Hispanic women, the incidence of preeclampsia seems to be increased, with a concomitant lower in danger for gestational hypertension. The analysis of preeclampsia in ladies with persistent hypertension and/or underlying proteinuric renal disease on medical criteria alone remains challenging. The severity of hypertension in preeclampsia can differ widely, from mild blood pressure elevations easily managed with antihypertensive medicine to extreme hypertension associated with headache and visible adjustments immune to multiple drugs. The latter state of affairs can typically herald seizures (eclampsia) and is a sign for urgent delivery. Medical administration of hypertension in preeclampsia is discussed within the next section. For a analysis of preeclampsia, proteinuria greater than 300 mg protein in a 24-hour urine collection or a urine protein-to-creatinine (P: C) ratio greater than zero. However, preeclampsia may be recognized even within the absence of proteinuria if a affected person presents with evidence of thrombocytopenia or elevated liver enzymes within the setting of hypertension (see Table 49. Routine obstetric care includes dipstick protein testing of a random voided urine pattern at every prenatal visit-a screening method that has been shown to have a high fee of false-positive and false-negative leads to comparison with 24-hour urine protein measurement. The urinary P: C ratio has turn into the preferred methodology for quantification of proteinuria within the nonpregnant inhabitants. A meta-analysis showed a pooled sensitivity of 84% and specificity of 76% utilizing a P: C ratio cutoff worth of larger than zero.
Generic 25mg viagra otcContreras G, et al: Outcomes in African Americans and Hispanics with lupus nephritis. Bhat P, Radhakrishnan J: B lymphocytes and lupus nephritis: new insights into pathogenesis and targeted therapies. In Jennette C, et al, editors: Pathology of the kidney, ed 5, Philadelphia, 1998, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, pp 541�624. Villanueva E, et al: Netting neutrophils induce endothelial injury, infiltrate tissues, and expose immunostimulatory molecules in systemic lupus erythematosus. Mannik M, et al: Multiple autoantibodies kind the glomerular immune deposits in sufferers with systemic lupus erythematosus. Reichlin M: Clinical and immunological significance of antibodies to Ro and La in systemic lupus erythematosus. Shakoor N, et al: Drug-induced systemic lupus erythematosus related to etanercept remedy. Ruiz-Irastorza G, et al: Increased fee of lupus flare throughout being pregnant and the puerperium: a potential examine of seventy eight pregnancies. Julkunen H, et al: Fetal end result in lupus being pregnant: a retrospective case-control study of 242 pregnancies in 112 sufferers. Petri M, Allbritton J: Fetal consequence of lupus being pregnant: a retrospective case-control study of the Hopkins Lupus Cohort. Chagnac A, et al: Outcome of the acute glomerular injury in proliferative lupus nephritis. Radhakrishnan J, et al: Renal transplantation in anticardiolipin antibody-positive lupus erythematosus sufferers. Moroni G, et al: "Nephritic flares" are predictors of unhealthy longterm renal outcome in lupus nephritis. Barete S, et al: Clinical options and contribution of virological findings to the administration of Kaposi sarcoma in organ-allograft recipients. Ciruelo E, et al: Cumulative fee of relapse of lupus nephritis after successful remedy with cyclophosphamide. Martins L, et al: Lupus nephritis: a retrospective evaluation of seventy eight circumstances from a single center. Grootscholten C, et al: Azathioprine/methylprednisolone versus cyclophosphamide in proliferative lupus nephritis. McKinley A, et al: Oral cyclophosphamide for lupus glomerulonephritis: an underused therapeutic possibility. Walsh M, et al: Mycophenolate mofetil or intravenous cyclophosphamide for lupus nephritis with poor kidney operate: a subgroup evaluation of the Aspreva Lupus Management Study. Tang Z, et al: Effects of mycophenolate mofetil for patients with crescentic lupus nephritis. Terrier B, et al: Safety and efficacy of rituximab in systemic lupus erythematosus: outcomes from 136 patients from the French AutoImmunity and Rituximab registry. Traczewski P, Rudnicka L: Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus with epratuzumab. Moroni G, et al: Antiphospholipid antibodies are related to an increased danger for chronic renal insufficiency in patients with lupus nephritis. Kaul M, et al: Assessment of the 2006 revised antiphospholipid syndrome classification criteria. Detkov, et al: Do antibodies to beta2-glycoprotein 1 contribute to the better characterization of the antiphospholipid syndrome Forastiero R, Martinuzzo M: Prothrombotic mechanisms primarily based on the impairment of fibrinolysis within the antiphospholipid syndrome. Raschi E, et al: Toll-like receptors: one other participant in the pathogenesis of the anti-phospholipid syndrome. Kaplanski G, et al: Increased soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 concentrations in sufferers with major or systemic lupus erythematosus-related antiphospholipid syndrome: correlations with the severity of thrombosis. Sacre K, et al: Asymptomatic myocardial ischemic illness in antiphospholipid syndrome: a controlled cardiac magnetic resonance imaging study. Pengo V, et al: Clinical course of high-risk patients diagnosed with antiphospholipid syndrome. Cervera R, et al: Antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Harada M, et al: High prevalence of anticardiolipin antibodies in hepatitis C virus infection: lack of results on thrombocytopenia and thrombotic complications. Cervera R: Update on the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of the catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome. Hanouna G, et al: Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome and pregnancy: an expertise of 13 instances. Nochy D, et al: the intrarenal vascular lesions associated with major antiphospholipid syndrome. Saracino A, et al: Kidney illness associated with main antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical signs and histopathological options in an case expertise of 5 cases. Fakhouri F, et al: the expanding spectrum of renal diseases associated with antiphospholipid syndrome. Riccialdelli L, et al: Hypertension because of renal artery occlusion in a patient with antiphospholipid syndrome. Daugas E, et al: Antiphospholipid syndrome nephropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Brunet P, et al: Antiphospholipids in hemodialysis sufferers: relationship between lupus anticoagulant and thrombosis. Ducloux D, et al: Prevalence and clinical significance of antiphospholipid antibodies in renal transplant recipients. Baid S, et al: Renal thrombotic microangiopathy related to anticardiolipin antibodies in hepatitis C-positive renal allograft recipients. Alarcon-Segovia D, et al: Prophylaxis of the antiphospholipid syndrome: a consensus report. Kobayashi S, et al: Immunoadsorbent plasmapheresis for a affected person with antiphospholipid syndrome throughout pregnancy. Jung H, et al: the protecting impact of antimalarial drugs on thrombovascular events in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ruiz-Irastorza G, et al: Clinical efficacy and unwanted facet effects of antimalarials in systemic lupus erythematosus: a scientific review. Shapira I, et al: Brief report: induction of sustained remission in recurrent catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome by way of inhibition of terminal complement with eculizumab. Gunnarsson R, et al: the prevalence and incidence of mixed connective tissue disease: a nationwide multicentre survey of Norwegian patients.
Order viagra online nowKidneys in neonates (<1 month of age) may be too immature to respond to furosemide, and neonates are thus not appropriate candidates for diuretic renal scintigraphy. A 17-year scientific experience at one institution proved that this protocol is beneficial for sufferers of all ages and for all indications. Nephrocalcinosis refers to diffuse or punctate renal parenchymal calcification occurring in both the medulla or cortex, normally bilaterally. Calcifications also happen in vascular structures, significantly in patients with diabetes and advanced atherosclerotic illness. Theleftkidneyhasnocontrast material in the pelvicalyceal system and accommodates solely nonopacifiedurine. Cortical calcification is most often associated with cortical necrosis from any cause. The stippled calcifications of hyperoxaluria could also be found in both the cortex and the medulla, as properly as in different organs, similar to the center. The distribution seems to be within the renal pyramid and may be either focal or diffuse and either unilateral or bilateral. Nephrocalcinosis happens in other illnesses during which hypercalcemia or hypercalciuria occur, corresponding to hyperthyroidism, sarcoidosis, hypervitaminosis D, immobilization, a quantity of myeloma, and metastatic neoplasms. These calcifications are nonspecific and punctate in appearance and are usually medullary in location. The calcifications tend to be uniform and distributed throughout the renal pyramids bilaterally. With medullary sponge kidney and renal tubular ectasia, small calculi kind in the distal amassing tubules, probably because of stasis. The look varies from involvement of only a single calyx to involvement of each kidneys all through. The calcifications are small, round, and inside the peak of the pyramid adjacent to the calyx. Medullary sponge kidney is also related to nephrolithiasis, as a end result of the small calculi in the distal amassing tubules may move into the collecting methods and ureters, resulting in renal colic. Medullary calcifications are also visible in patients with renal papillary necrosis. Retained tissue fragments might calcify and have the appearance of medullary nephrocalcinosis. The lifetime threat for developing renal calculi is 12%, with males being two to thrice more at risk than females. Most sufferers also have hematuria, although it may be absent if a ureter is completely obstructed by the stone. The ache that happens with a passing renal stone might be attributable to the distension of the tubular system and renal capsule of the kidney and by the peristalsis associated with ureteral contractions as the stone strikes distally. Unilateral hydronephrosis may be noticed, though the examination outcomes may be normal early in the passage of a renal stone. Distal ureteral stones close to the ureterovesical junction may be visualized through the urine-filled bladder transabdominally. The research are carried out with 3-mm collimation or much less, and the slices are reconstructed to be contiguous or slightly overlapping. The improvement of iterative reconstruction techniques has also lowered radiation doses. Calculi could additionally be visible in all components of the amassing system and the urinary tract. At the purpose of obstruction the stone may be seen inside the ureter, with gentle tissue thickening of the ureteral wall at that level. This thickening is probably caused by edema and irritation associated with the passage of the stone. Also, the dimensions may be precisely measured, which enables clinicians to make therapy decisions. Axial photographs of the kidneys present perinephric and peripelvic stranding and fluid on the best (A) attributable to forniceal rupture and leakage of urine on account of the distal obstructing stone at the right ureterovesicaljunction(B). Images reconstructed within the coronal airplane along the course of the ureters right down to the extent of the stone could also be useful. Coronal T2-weightedsequence(A)demonstrateshigh�signalintensityblood contained by left renal capsule (arrowheads). Axial T1-weighted picture (B) and gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted image (C) present mass effect on left kidney (arrowheads) attributable to a subcapsular hematoma. The signal intensity is consistent with the presence of intracellularmethemoglobin. This is as a result of of the presence of the adhesin P fimbriae and highly effective endotoxins that appear to inhibit ureteral peristalsis making a functional obstruction. Enzyme release results in destruction of tubular cells with subsequent bacterial invasion of the interstitium. As the an infection progresses, it spreads throughout the pyramid and to the adjacent parenchyma. Without sufficient remedy, necrosis of the concerned areas and microabscess formation occur. These microabscesses could coalesce into larger macroabscesses, which are likely to be surrounded by a rim of granulation tissue. Pyelonephritis may happen by hematogenous spread of bacteria to the cortex of the kidney and eventual involvement of the medulla. Blood-borne an infection is less widespread than ascending an infection and is normally observed in intravenous drug abusers, immunocompromised patients, or patients with a supply of infection outside the kidney, such as coronary heart valves or enamel. Imaging is used to assess problems of acute pyelonephritis, together with renal and perinephric abscess, emphysematous pyelonephritis, and xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis. Altered parenchymal echogenicity is the most frequent discovering with loss of the normal corticomedullary differentiation. Power Doppler imaging could enhance sensitivity in demonstrating focal hypoperfusion, however that is nonspecific. Wedge-shaped areas of decreased density extending from the renal pyramid to the cortex are most attribute. The changes in the nephrogram are related to decreased focus of distinction media in the tubules with focal ischemia. There is often a pointy demarcation between diseased tissue and the conventional parenchyma, which continues to enhance normally in the nephrographic phase. T2-weighted axial image (A), T1-weighted axial image (B),andpostcontrast T1-weightedaxial image(C) show an intrarenal hematoma(arrows) on the web site of incision aircraft. With hematogenous-related pyelonephritis, the early findings are inclined to be a quantity of, spherical cortical regions of hypodensity that turn into more confluent and involve the medulla with time. On noncontrast sequences, the affected area has increased T2 signal intensity and decreased T1 signal depth in relation to the conventional renal parenchyma. However, these methods have the drawbacks of extended imaging time (more than 24 hours) and higher radiation exposure. There may be diffuse generalized lower in renal uptake, which, in affiliation with a normal or slightly enlarged kidney, is suggestive of an acute infectious course of.
References - Wallen EM, Pruthi RS, Joyce GF, et al; Urologic Diseases in America P: Kidney cancer, J Urol 177(6):2006n2018, discussion 18n19, 2007.
- Novara G, Galfano A, Boscolo-Berto R, et al: Complication rates of tension-free midurethral slings in the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing tension-free midurethral tapes to other surgical procedures and different devices, Eur Urol 53:288n308, 2008.
- Achtari C, McKenzie BJ, Hiscock R, et al: Anatomical study of the obturator foramen and dorsal nerve of the clitoris and their relationship to minimally invasive slings, Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 17:330n334, 2006.
|
|