"Buy 4.5mg rivastigimine otc, medications that cause tinnitus."By: Danielle Marie Brander, MD - Assistant Professor of Medicine
- Member of the Duke Cancer Institute
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/danielle-marie-brander-md
Discount 3 mg rivastigimine amexThis profile is perpetually incomplete, since people incessantly modify the surroundings, thus increasing the danger of interaction with agents in opposition to which there could also be no protecting mechanisms. Of the assorted environmental hazardous compounds, cigarette smoke enjoys the very best causal relationship with most cancers risk in humans. Tobacco smoking performs a serious position within the etiology of lung, oral cavity, and esophageal cancers in addition to quite a lot of chronic degenerative ailments. The response generates G:C to A:T mutations, with the following activation of K-Ras proto-oncogene and the event of tumor initiation. Radiation additionally contributes to the causative physical factors that induce human cancers. Because of the genotoxicity potential, radiation at high doses evidently results in the looks of various tumors in people. Even at low doses, residential publicity to radioactive radon and its decay products, for example, could account for about 10�20% of all lung cancer deaths worldwide. In reality, epidemiological knowledge contributes to most of our understanding of the mechanisms of carcinogenic chemicals. Also, animal experimentation might assist the discussion by expanding on the reason of the elements that improve the danger for multistage carcinogenesis. Nevertheless, there are two complementary strategies for understanding how predilection for most cancers, and the brokers that predispose people to most cancers, could be prevented: 1. Animal experiments and human clinical trials assist this competition (see Review Articles). Antioxidants and section 2 enzyme inducers, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, omega-3 fatty acids, isothiocyanates, and dithiolethiones 4. Agents that selectively modulate cellular receptors and signal transduction, such as retinoids and vitamin D analogs 31. Mechanisms resulting in the inhibition of the multiple levels of carcinogenesis Chemopreventive agents may alter carcinogen toxicokinetics by either inhibiting the absorption of carcinogens or growing their cleansing. Alternatively, chemopreventive medication inhibit the three stages of carcinogenesis (initiation, promotion, and progression) by modulating a selection of cellular mechanisms and pathways, similar to 1. Several recent research have elucidated the molecular occasions resulting in the induction of antioxidative and part 2 enzymes by chemopreventive agents. The expression of the teratogenic response-that is, the embryotoxic effect of a compound on the expansion and development of the fetus- is usually manifested at delivery or within the immediate postnatal period. In addition, a chemical could intervene early within the reproductive cycle (first trimester) by impairing fertilization or interfering with implantation. These initial interactions between the prefertilized ovum and the xenobiotic may result in interference with ovum production, fertilization, implantation, or embryo improvement, or might provoke spontaneous termination of being pregnant. Clinical and nontherapeutic drug use in the course of the prenatal interval has elevated dramatically in current times. Excluding the generally prescribed prenatal nutritional vitamins, iron dietary supplements, and tocolytic* medicine, women under 35 years of age on common eat three prescriptions through the course of their pregnancies; for girls over 35, this number rises to 5. Some of the medicine used most extensively during pregnancy include antibiotics, analgesics, and narcotics, adopted by antiepileptics, antihypertensives, antinauseants, psychotherapeutic agents, and respiratory medications. For most of those medication, no well-controlled research have been carried out in pregnant people. Despite the present lack of information on the protection of drug products throughout pregnancy, there seems to be little reluctance to prescribe. Although initially alarming, lack of sufficient toxicological investigation is evidence for the complacency and dearth of information both within the public well being neighborhood and inside the medical occupation, and highlights the insidious risks of drug use during pregnancy. In addition, the well-intended practice of prescribing decrease doses of medicine throughout being pregnant to decrease publicity to the fetus is misguided. The complicating issue lies within the ubiquitous availability and distribution of therapeutic medicine, in addition to environmental chemicals and herbal merchandise, that essentially infiltrate the maternal/fetal setting. This leaves a mess of chemical substances used in the market without human embryotoxic knowledge. Developed as a sedative/hypnotic with no particular advantage over drugs of the same class, thalidomide was initially proven to lack teratogenic effects in all species tested besides rabbits. Soon after its introduction to the European market, the drug was linked to the event of a relatively rare start defect known as phocomelia. The epidemic proportions of the teratogenic impact of thalidomide prompted the passage of the Harris�Kefauver Amendment in 1962, considered one of many additions since to the Federal Pure Food and Drug Act. The Amendment requires extensive pharmacological and toxicological preclinical research earlier than a therapeutic compound could be marketed. This figure denotes how the primary 12 weeks roughly correspond to the primary trimester. This section is characterised as the time period for embryonic development, when the fertilized ovum differentiates into precursor stem cells, which progress to the launching of fetal membranes and the embryonic disc (weeks 1�3, embryo). The remainder of the pregnancy (13 to 38 weeks) is dedicated to fetal improvement, when the established blueprints of organs and tissues undergo further growth and maturity. Together, the two processes occurring during the weeks of embryonic and fetal growth are referred to as prenatal improvement. The package deal is printed inside and without with red warning labels alerting the prescriber, pharmacist, and patient to the precaution against its use in girls of childbearing potential. Cleavage (days 1�6): a sequence of cell divisions following fertilization of the ovum by the sperm cell and terminating at the blastocyst stage (day 6, weeks 1�3 in figure). Implantation (days 7�10, not shown): adhesion, attachment, and penetration of the uterine endometrial lining by the blastocyst; the trophoblast, amniotic cavity, and internal cell mass form and broaden during this stage; additional development of the yolk sac, chorion, allantois, amnion, and embryonic disc (from the inside cell mass) ensues during weeks 3 and four (beginning of organogenesis). Placentation (from weeks 2 to 10): starting as early as week 2, blood vessels type around the periphery of the blastocyst to establish the presence of the placenta; the placenta is characterised by the formation of chorionic villi and the looks of fetal vessels. Embryogenesis (also during weeks 4�12)-the strategy of differentiation and folding of the embryonic disc, producing a bodily and developmentally distinct and recognizable embryo. These structures are probably the most sensitive to medicine and chemical compounds (represented and labeled in red) and are liable for main congenital anomalies. However, publicity to xenobiotics in the course of the second trimester can additionally be responsible for minor congenital anomalies, that are manifested as useful defects within the newborn. The third trimester displays speedy growth and maturation of established organ techniques as the muse for impartial survival and function. For occasion, publicity to compounds 21 days after fertilization has the potential for best embryotoxicity, ensuing within the death of the fetus, whereas exposure to compounds between the third and eighth weeks is potentially teratogenic-that is, these agents could interfere with organogenesis. These effects are distinguished by the development of gross anatomic, metabolic, or useful defects and the precipitation of spontaneous abortions. Because the schematic for embryonic improvement is already established by the start of the second trimester, exposures to medicine or chemicals during the second or third trimester are much less more likely to be teratogenic. However, they nonetheless might intervene with the expansion and maturation of important organ techniques, resulting in underdevelopment or alterations of normal organ operate. Instead, maternal Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity 509 blood enters intervillous spaces (sinuses) of the placenta via ruptured maternal arteries and then drains into uterine veins for return to the maternal circulation. Fetal blood enters the placenta by a pair of umbilical arteries and returns to the fetal circulation by the umbilical vein. The umbilical arteries department into capillaries surrounded by the syncytial trophoblast, forming the network of chorionic villi.
Generic 1.5mg rivastigimine overnight deliveryThe targeted delivery of those cells with related osteoinductive substances is critical to profitable bone therapeutic. Current and novel therapeutic methods for fracture therapeutic should not only present efficacy (bone healing) however should additionally restrict unfavorable unwanted facet effects, thereby improving affected person outcomes. Diabetes causes the accelerated lack of cartilage during fracture repair which is reversed by insulin treatment. Inhibition of sclerostin by monoclonal antibody enhances bone therapeutic and improves bone density and strength of nonfractured bones. Cyclooxygenase-2 regulates mesenchymal cell differentiation into the osteoblast lineage and is critically involved in bone repair. Describe how periosteum, gentle tissue, bone marrow, and cortical bone reply differently to fracture. Briefly describe the 4 stages of fracture restore and the four biomechanical levels of fracture therapeutic. Describe why both anatomy and mechanics have to be taken under consideration when analyzing fracture healing. Mineral homeostasis may additionally be influenced by cytokines and different inflammatory mediators (see Chapter 4). As bone is negatively affected by continual insufficient dietary consumption of calcium or phosphate and by inherited or acquired defects in calcium or phosphate homeostasis, one may reasonably conclude that the first operate of calcium and phosphate homeostasis is to preserve bone integrity. However, processes within the bone, intestine, and kidney work in concert to obtain the primary goal of maintaining plasma calcium within a relatively slender vary. Appropriate variations happen in response to abnormalities in one system to combat calcium or phosphorus dysregulation. When bone resorption is elevated (during menopause or different illness states), plasma calcium increases with resulting suppression of each intestinal calcium absorption and renal calcium reabsorption. Conversely, when plasma phosphate concentrations improve, intestinal absorption is downregulated and renal phosphate reabsorption decreases to enable net phosphate excretion. Homeostatic mechanisms for calcium react rapidly within minutes to preserve plasma calcium within a slim vary. However, normal ranges of plasma phosphate are wider, and homeostatic responses are slower, gradually compensating for changes over hours to days. Consequently, plasma phosphate focus varies more throughout the day in a person than does plasma calcium. Abnormalities in these homeostatic mechanisms lead to important illness states with effects on muscle and bone. Distribution of Calcium and Phosphorus in the Body the grownup human body contains about a thousand g of calcium and seven-hundred g of phosphorus. Under normal homeostatic mechanisms, when plasma calcium or phosphate is high, intestinal absorption becomes downregulated, and the mineral stability is shifted towards bone deposition or kidney excretion of calcium or phosphate. When plasma calcium or phosphate is low, mechanisms are engaged that enhance intestinal absorption, skeletal resorption, and/or renal reabsorption. Dysregulation of these techniques ends in abnormal plasma levels of calcium or phosphate. Of the total circulating plasma/serum calcium, roughly one-third is nondiffusible, being certain to albumin (80%) or globulin (20%). The relaxation is diffusible, of which 80% is ionized (also known as free calcium), and the rest is complexed to anions corresponding to bicarbonate, citrate, and phosphate. Thus, solely a small percentage of the entire physique phosphorus is nonskeletal and extracellular. Only the remaining 30% is inorganic phosphate, which can be ionized, complexed with varied cations, or protein sure. Normal plasma phosphate concentrations range considerably with age, with the best concentrations current during infancy (Table 13. During a standard, full-term being pregnant, the human fetus accumulates 30 g of calcium. Approximately 80% of this accrual happens during the last 12 weeks (third trimester) of gestation. Fetal plasma whole and ionized calcium concentrations considerably exceed maternal plasma concentrations. The fetal calcium:phosphate accrual ratio is about 2:1, with the fetus acquiring about 16 g of phosphorus by the point of birth. Placental phosphate transport maintains fetal plasma phosphate concentrations larger than in maternal plasma facilitating fetal skeletal mineralization. The primary sources of dietary calcium are dairy merchandise (butter, cheeses, ice cream, milk, and yogurt), calcium-fortified juices, and canned fish (with bone), though calcium can be present in decrease quantities in numerous other meals. Intake during pregnancy and lactation are beneficial to be similar to the age-appropriate ranges. In common, however, after early childhood, most children, adolescents, and adults fail to consume enough dietary calcium. Once absorbed from the gut, calcium travels through the extracellular fluid, where it could be deposited in bone, taken up by cells, secreted again into the gut, or filtered out through the kidneys. Rates of calcium absorption and retention range markedly throughout childhood and adolescence, relying on the rate of skeletal growth. There is a peak in calcium absorption at about 6 months of age, when calcium absorption averages 60%. Phosphate transport is mediated by sodium-phosphate transporter type 2b (Npt2b), which is expressed on the maternal aspect. In contrast to calcium, phosphate is plentiful within the Western food plan, with almost all people reaching beneficial dietary intakes (Table 13. Many frequent meals have significantly high phosphate content material: high-protein foods (dairy merchandise, legumes, nuts, and whole grains), citrus fruits, and processed foods (which often include added phosphates as preservatives). Consequently, dietary phosphate deficiency is rare and, usually, happens within the context of general malnutrition or starvation, usually combined with poor intakes of calcium, vitamin D, and protein. Recommended intakes during being pregnant and lactation are similar to general age-appropriate ranges. Phosphate concentrations are highest in infants, most likely because of the larger want for phosphate to accommodate the rising skeleton, as properly as for general cellular development throughout childhood. During this time, calcium absorption from the intestines will increase significantly for incorporation into bone matrix. Peak bone mass is achieved through the early a part of the third decade of life (see Chapter 10). At this time, the human skeleton incorporates approximately 900 g of calcium in females and 1200 g in males, and complete physique calcium and phosphorus balance is roughly at steady state. In women, bone mass loss accelerates because of the elevated bone resorption seen with estrogen deficiency through the perimenopausal years.
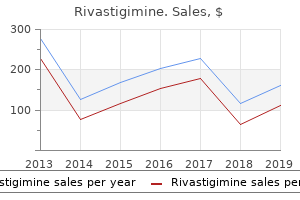
Buy 4.5mg rivastigimine otcThe same group confirmed that when purified G proteins were reconstituted into in any other case empty phospholipid vesicles, they were activated (by guanosine diphosphate [i. Efforts to perceive the signaling pathways concerned in mechanical sign propagation have uncovered a multitude of changes within the mechanically stimulated osteocyte/osteoblast, including gene expression adjustments, protein and lipid modifications. The challenge offered by these observations is to decide which amongst them are crucial for mechanotransduction to occur, and that are merely auxiliary occasions that have few functional consequences for the mechanotransduction process. More just lately, the Wnt signaling pathway has been identified as a major intermediate in bone cell mechanotransduction. Numerous target genes of -catenin are related to enhanced osteogenesis and decreased resorption. Using a reporter assemble, mechanical loading was shown to activate -catenin�mediated transcription both in vivo and in vitro. Remarkably, osteocytes appear to be the first cells to exhibit activated -catenin transcriptional activity after loading, suggesting that Wnt signaling in osteocytes could be a sensor cell response pathway. Recent work by the Novartis group identified Lrp4 as a key facilitator of sclerostin-mediated inhibition of Lrp5/6. Human sufferers with missense mutations of Lrp4 that disrupt sclerostin binding have excessive bone mass, just like patients with loss-of-function mutations in Sost. Whether Lrp4 plays a task in mediating the Wnt-centered mechanotransduction cascade in bone is yet unexplored. It is also important to contemplate that bone exists as an built-in tissue that very doubtless "talks" and "listens" to other tissues during mechanotransduction, via secreted factors. Other candidate mechanotransduction mediators between bone and muscle are more probably to exist, but this "cross-talk" space of investigation is in its infancy, and consequently, the sphere must await further discoveries to higher understand musculoskeletal mechanotransduction across tissues. Although bone is adaptive, not all forms of exercise are equally effective for eliciting an osteogenic response. This remark is supported by findings from animal studies, mentioned earlier, which have supplied important details about key loading traits essential to stimulate an adaptive skeletal response. From these research, human intervention trials have been carried out to consider the efficacy and effectiveness of varied exercise modalities and training doses on bone well being throughout the lifespan. This part summarizes what is understood about skeletal variations to train during growth and maturity, including train prescription tips for the optimal kind and dose of exercise (load magnitude, loading rate, variety of repetitions, frequency [sessions or days per week]) to maximize bone well being. Cortical bone thickness may be modulated by addition of bone to the periosteal surface or by adjustments in resorption and/or formation on the endocortical surface (periosteal resorption is rare but can occur in unidirectional cortical drift, and in addition in old age). In addition, tissue density can increase as a result of modifications to intracortical bone (via remodeling) and/or trabecular microarchitecture. Infancy Approximately 80% of neonatal bone mineral is accrued in the later phases of pregnancy, when development velocity is at its peak. Although a range of intrinsic and extrinsic elements are known to influence skeletal growth in utero, the importance of motion throughout this period is greatest demonstrated by the skeletal malformations in newborns with prenatal muscular and neurological pathologies that impair movement (mechanical stimulation). In preterm infants, introduction of assisted physical activity (range of motion and gentle compression, flexion and extension exercises) in the course of the first few weeks or months of life promotes larger bone development, mineral acquisition, and bone strength. Childhood and Adolescence Weight-bearing influence exercise in school-aged kids can improve bone mineral accrual, with the best benefits apparent through the prepubertal and early-pubertal years. Typically, these train interventions end in 1%�6% greater positive aspects in bone mass or density in comparison with controls, with the best benefits noticed on the proximal femur. These skeletal advantages are according to the outcomes from many animal research showing that temporary bouts of high-impact activities, where uncommon strain distributions are applied to bone, elicit the best osteogenic response. An essential consideration in maximizing peak bone mass is the age at which kids train. During the primary two decades of life, roughly 90%�95% of the grownup skeleton is shaped, with 25%�30% of adult bone mineral accrued in the course of the 2�3 years surrounding puberty (see Chapter 10). As that is equivalent to the quantity of bone lost during old age, optimizing peak bone strength represents an essential method for the prevention of osteoporosis later in life. A 10% enhance in peak bone mass can delay the event of osteoporosis by thirteen years and cut back the risk of fracture by as a lot as 50% (see Chapter 21). School-based train interventions reveal that the best exercise-induced skeletal advantages occur through the pre- and early-pubertal years; the results of train on bone postpuberty have been equivocal. Regular weight-bearing exercise during progress improves bone strength by inducing modifications in bone structural parameters, although the response appears to be maturity-dependent and sex-specific. The maturity-, sex-, and surface-specific responses of bone to loading are likely related to the position of the sex hormones. Androgens improve periosteal bone formation in males whereas estrogen inhibits periosteal growth and stimulates endocortical bone formation in females. These findings are essential for two reasons: (1) apposition of bone on the periosteal bone floor is more practical at increasing bone power than apposition of bone on the endocortical surface, and (2) bone loss throughout growing older happens totally on the endocortical surface, and thus the deposition of bone on this surface in females throughout development may be a compensatory mechanism to improve cortical thickness in preparation for loss later in life. During the prepubertal years, train enhances periosteal apposition in both girls and boys, but throughout or after puberty exercise seems to promote periosteal enlargement in boys and endocortical apposition (or lowered resorption) in girls. However, to date, no train trials in older adults or the aged have reported exerciseinduced periosteal bone expansion. Despite the advantages of weight-bearing impact exercise, for individuals with severe osteoporosis, a current history of fracture or different comorbidities such as pain from osteoarthritis, this mode of train may be contraindicated. This mode of coaching can place high loads on the skeleton through the direct action of muscle pulling on bone and/or by the elevated impact of gravity appearing on bone when the skeleton supports heavier weights. High-velocity resistance coaching (or power training), which includes rapid concentric muscle contractions that impart excessive pressure charges on bone, might have a constructive impact on bone, but the proof is presently limited. This is important because most nonvertebral fractures end result from a fall and are linked to impaired practical outcomes. Programs together with challenging stability training for a minimum of three h/week or reactive and volitional stepping coaching reduce the risk of falls by roughly 40%�50% in older people. There is a extensive range of various parameters utilized in these studies, including side-alternating versus oscillations platforms, different frequencies, intensities, cumulative doses, body positions. In abstract, exercise is the only identified technique obtainable that has the potential to improve all modifiable fracture danger parameters (fall threat, fall influence, bone strength), however the advantages are dependent on the proper type and dose prescribed. The following section summarizes the key training rules necessary to bone and the proof underpinning present exercise prescription tips for a healthy skeleton. The exact dose, as outlined by load magnitude, loading fee, number of repetitions, frequency (sessions or days per week) of loading, wanted to optimize bone power at completely different phases of the lifespan, remains uncertain. The American College of Sports Medicine has recommended that five key coaching principles be thought of when designing any train program to optimize bone well being. Principle of Specificity Skeletal variations to loading are highly site-specific and never systemic in nature. This is highlighted in studies of athletes taking part in unilateral dominant sports activities. A school-based weight-bearing impression train program also confirmed that there have been region-specific cortical bone adaptations within the anterior�posterior region of the tibia, which is the primary direction of bending in response to loading at this website. Clinically, these findings are necessary as localized femoral neck and trochanteric cortical thinning, with particular focal structural weaknesses within the superior femoral neck and lateral trochanteric regions, are related to an increased hip fracture risk.
4.5mg rivastigimineAntineoplastic Agents 323 compound causes cytolysis of cells entering mitosis, whereas at low concentrations, it prevents the cells from entering prophase. The enzyme L-asparaginase produces tumor cell death via the activation of apoptosis. This amino acid is crucial for protein synthesis as a end result of the enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of circulating asparagine to aspartic acid and ammonia. Consequently, L-asparaginase stops the progression of cells by way of the cell cycle. Its unique mechanism of action supports its inclusion with different antitumor drugs as a half of a chemotherapeutic program, particularly in the therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and other lymphoid malignancies. Hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions happen in 5 to 20% of patients, most notably when administered intermittently. Other toxicities associated to its mechanism of motion embrace hyperglycemia, coagulopathies, immunosuppression, and hemorrhage, all of which are probably fatal. This class of natural merchandise is derived from quite so much of eubacterial and actinomycete genera. For instance, hemolytic uremic syndrome, largely noticed with mitomycin C, is characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (anemia inside small blood vessels), thrombocytopenia (decrease in platelet count), and irreversible renal failure. Interestingly, although many of the antineoplastic antibiotics have antibacterial and antifungal properties, their toxicities preclude their routine use in the remedy of infectious ailments. The medication have the benefit of higher specificity for tissues responsive to * Compounds and their species of derivation embrace actinomycin D (dactinomycin, Cosmegen) from Streptomyces parvullus; pentostatin (Nipent) from S. The therapeutic advantage lies of their proclivity to inhibit uncontrolled cell proliferation with out important direct cytotoxic effects. Antineoplastic hormones are used initially or as adjunctive remedy within the palliative therapy of malignancies prone to the medicine, as famous in Table 21. The compounds are used within the preliminary and secondary therapy of ovarian carcinoma, testicular tumors, and superior bladder cancer. It is S section particular and interferes with the conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides by selectively blocking the enzyme ribonucleotide reductase. It is also used concomitantly with irradiation remedy in the administration of squamous cell carcinoma of the top and neck. They are diverse natural substances supplied in small quantities in the food plan and are present in quite a lot of chemical types and constructions. Vitamins have assorted essential biochemical roles in contributing to the maintenance of health and have distinctive therapeutic places in the therapy of associated issues. Originally, most nutritional vitamins had been used for the prevention of deficiency syndromes associated with insufficient nutritional intake. For instance, within the presence of a deficiency of a particular nutrient and the subsequent induction of the corresponding situation, adequate replacement of the deficient substance resulted in a treatment. And till lately, it was cheap to conclude that for a person following a balanced food plan, no further vitamin supplementation was essential. This assumption was legitimate for normal healthy youngsters, adolescents, and adults within the absence of deficiency (with the exception of being pregnant and lactation). This message has not been heeded in latest years, nevertheless, as evidenced by the rising consumption (megadoses) and infatuation with vitamin supplementation in the United States. This was inspired by the misinformation that if vitamins are necessary for the upkeep of well being, then larger ingestion must necessarily provide better health. This belief has been defended by the equivocal results of scientific and scientific research interpreted out of context. In particular, such research have concluded that medical advantages, corresponding to prevention of growing older, may be obtained from the helpful results of antioxidants towards elements that contribute to oxidative stress. The standards are based on periodic evaluate of the scientific proof for many wholesome individuals under normal day by day stresses. Almost all of these vitamins are supplied by a well-balanced dietary intake plan that features the 4 primary food teams. The values are primarily based on normal, wholesome, height- and weight-adjusted people and have modified dramatically over the past 5 years. In basic, vitamin supplementation is warranted in situations where a suspected vitamin deficiency contributes to the situation. In the United States, the relative danger for the development of vitamin deficiencies may be larger within the following people: 1. Ranges of day by day allowances are decided by age, peak, and weight (not shown) inside group; in general, requirements improve with age, except with some nutritional vitamins. Requirements are often greater through the first 6 months of lactation than in the course of the second 6 months. Vitamins 331 Vitamin toxicity as a result of overdose is documented in medical conditions however depends on experimental scientific proof for an sufficient description of such situations. Vitamins are classified in accordance with their biological inclination for distribution and elimination from the body. The water-soluble vitamins are readily eradicated within the urine and consequently, have a low incidence of poisonous results. In distinction, the fatsoluble vitamins are readily distributed throughout the body, with a propensity for storage in lipid-rich tissue. As a end result, they have an inclination to accumulate in physiologic compartments, risking potential cumulative toxicity. This article emphasizes the toxicity and deficiencies associated with vitamins and vitamin supplementation whose antagonistic reactions have been traditionally and therapeutically documented. Derivatives of vitamin A include retinol, retinal, retinoic acid, and -carotene (a precursor). These physiologically essential components assist proper functioning of the reproductive cycle, visual acuity, somatic development and differentiation, and visual adaptation to darkness, respectively. Oral or parenteral administration of vitamin A (Aquasol A injection, varied pill and capsule formulations) is indicated for the therapy of circumstances associated with, but not unique to , vitamin A deficiency states. Deficiency syndromes have been related to kwashiorkor,* xerophthalmia, keratomalacia, and malabsorption syndromes. It is characterized by anemia, edema, swollen abdomen, skin and hair depigmentation, and hypoalbuminemia. The cornea becomes softened and weak to ulceration and an infection, which may lead to blindness. Most symptoms resolve with immediate withdrawal of vitamin supplementation, although increased intracranial stress requires further palliative measures. As noted earlier, the retinoids are derivatives of retinoic acid that promote epithelial cell differentiation, keratinization, and local irritation. Therapeutically, the desired impact results in the discount of the severity and formation of the microcomedones characteristic of acne. The opposed effects of most of the topical merchandise are associated to transient or momentary native inflammatory responses (Table 22. Oral retinoids, such as isotretinoin, are reserved for severe recalcitrant nodular acne. The retinoids, however, are contraindicated in women of childbearing potential because of teratogenic danger. Major human fetal abnormalities have been reported with oral isotretinoin ingestion, together with skeletal, neurological, and cardiovascular anomalies.
Purchase rivastigimine discountAlthough the cure fee is 95% with correct remedy, it nonetheless accounts for 2300 deaths per yr, notably because of its ability to metastasize (about 3%) to the lymphatic vessels. Consequently, common dermal screening examinations, avoidance of daylight, and early treatment prevent complications and enhance prognosis. The malignant tumors come up from the deepest layer of the epidermis, and most are located on the face, arms, and different sun-exposed parts of fair-skinned persons. Early analysis and successful remedy are usually accompanied by a favorable prognosis. The look of the tumor varies from a red, irritated, patchy papule to a smooth, reddish-yellowish macule. It seems as a nest of nevus cells (altered melanocytes), often presenting as tan to brown macules or papules with well-defined rounded borders. The lesion usually adjustments in size, form, impression, or shade, with the appearance of bleeding. As the cells differentiate, the tumor advances to deeper layers of the skin (about four mm), reveals additional growth around the unique tumor cells (satellite tumor) or metastasizes to the lymphatics. Treatment entails elimination of the tumor by full surgical excision, adopted by grafting, chemotherapy, and radiation remedy. Photosensitive reactions contain the event of unusual responses to sunlight, typically exaggerated within the presence of quite so much of precipitating, seemingly unrelated circumstances. As with erythematous reactions, photo voltaic urticaria is a pruritic pores and skin eruption characterized by transient wheals of varying shapes and sizes. The development of urticaria is mediated by capillary dilation in the dermis in response to the release of vasoactive amines (histamine and kinins) on sun exposure. More severe photosensitivity reactions result in the development of bullae, thin-walled blisters on the pores and skin or mucous membranes * Involves scraping of the tumor tissue and destroying the thin surrounding layer with warmth. Radiation Toxicity 531 greater than 1 cm in diameter and containing clear, serous fluid. Dehydration, scaling, scarring, fibrosis, and necrosis develop as the exposed areas heal. Xeroderma pigmentosum,* lupus erythematosus, and porphyrias are among the pathologic situations which are accompanied by photosensitivity reactions. The ingestion or utility of antibacterial and antifungal antibiotics (sulfonamides, tetracyclines; griseofulvin, respectively) and thiazide diuretics is responsible for occasional photosensitive reactions. Contact with dermal products containing coal tar, salicylic acid, plant derivatives, and components of colognes, perfumes, cosmetics, and soaps are also sources of the problem. Preventive remedy and avoidance of daylight (use of protecting clothes, sunscreens, and shaded areas) are typically helpful in averting skin reactions. Accordingly, burns and thermal injury are the commonest penalties of publicity to direct low-energy rays. Deep penetration of dermal and subcutaneous tissue is observed when tissue intercepts the path of infrared or microwave rays. The latter are additionally able to disrupting the traditional perform of electronic medical gadgets similar to subcutaneously implanted cardiac pacemakers and screens. A systemic, inflammatory, multi-organ, autoimmune disease with attribute improvement of rashes and joint ache. The syndrome is a sporadic, autosomal dominant condition characterised by skin fragility on the dorsal palms and forearms, and facial hyperpigmentation. At the least, the induction of concern is a destabilizing force in a nation or state. The United States has solely just lately experienced critical terrorist threats with the occasions of September eleven, 2001. Terrorist methods comprise the use of radiological, chemical, and organic agents capable of widespread, mass casualties and destruction. The ease of availability, the low price of production, and the facility for wide dissemination of these technique of destruction make them very attractive weapons. Chemical and radiological toxicity have already been discussed all through several chapters on this guide (nerve gases, radiological toxicity). Therefore, solely the relevant lessons of chemical and radiological brokers are outlined beneath. Consequently, this chapter elaborates on the mechanisms of beforehand unclassified pathogenic brokers and their toxic biological products, some of which only recently have been identified as potential poisonous terrorist threats. Category A consists of high-priority agents and pathogens not often seen in the United States that pose a danger to nationwide security. They are highly infectious and straightforward to disseminate, and the clinical results from publicity lead to high mortality charges. By their nature, Category A brokers are able to inciting public panic and disruption. The brokers or ailments in Category A include anthrax, botulism, plague, smallpox, tularemia, and organisms that induce viral hemorrhagic fevers. The third category of highest-priority brokers, Category C, includes pathogens that could possibly be engineered for mass dissemination. Emerging threats, such as the Nipah virus and hantavirus, are available and simply produced and disseminated supplied there exists some technical data of microbiology. Human publicity Chemical and Biological Threats to Public Safety 537 to these agents could happen via inhalation, skin (cutaneous) publicity, or ingestion of contaminated food or water. Following exposure, physical signs could additionally be delayed and typically confused with naturally occurring diseases, thus contributing to the possible postponement in response. In addition, biological warfare agents may persist within the environment and cause problems long after their launch. The agents discussed here fall into three major classes of microorganisms: bacteria,* rickettsia, and viruses. In some circumstances, hazardous bacterial toxins are also produced as by-products of their pathogenic metabolism. To aid in understanding the pathogenic options of infectious agents, several tables are included. Incubation intervals, length of diseases, means of transmission, therapy, and prognosis are also famous for every of the organisms. Thus the organism may be present within the soil for many years, sometimes infecting grazing goats, sheep, and cattle. The growth of anthrax as a organic weapon by several international nations has been documented. Cutaneous an infection is the most common manifestation of anthrax in humans, accounting for 95% of cases. Inoculation via exposed pores and skin outcomes from contact with contaminated soil or animal products corresponding to hair, hides, and wool. A painless papule at the site of inoculation progresses rapidly to an ulcer surrounded by vesicles after which to a necrotic eschar. Systemic infection, complicated by massive edema and painful lymphadenopathy, is fatal in 20% of patients.
Zaffer (Safflower). Rivastigimine. - Dosing considerations for Safflower.
- How does Safflower work?
- Are there safety concerns?
- What other names is Safflower known by?
- What is Safflower?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Reducing LDL cholesterol.
- Fever, tumors, coughs, bronchial conditions, blood circulation disorders, pain, menstrual disorders, chest pain, traumatic injuries, constipation, inducing sweating, causing abortion, and other uses.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96138
Purchase rivastigimine 6 mg with visaWi/ days between label administration Average time between deposition of osteoid and initiation of mineralization = O. For a extra complete record of variables please see works by Parfitt, Recker, and Dempster in the advised readings. More particulars regarding these variables can be present in several of the instructed readings. Tissue Types Differentiating between woven and lamellar bone tissue could be useful for figuring out whether bone formation is going on in a standard style. Assessment of lamellar and woven bone is completed utilizing polarized light microscopy on unstained sections, although some stains allow collagen orientation to be visualized. As described in Chapter 1, lamellar bone is characterised by a series of parallel laminar sheets, whereas woven bone is quickly formed and extremely disorganized. Whether one examines the primary variables or the referent-adjusted variables can significantly have an effect on data interpretation (see textual content for explanation). Using stains for osteoid, the examination of mineralized versus nonmineralized bone can provide details about changes in the mineralization process. Analysis of osteoid includes measuring the extent of the bone floor coated by osteoid (and then normalizing it by the total bone surface examined) and either the width or quantity of osteoid. If osteoid width is regular, elevated osteoid floor is indicative of larger bone formation. Cell Number and Activity the extent of surfaces coated with osteoblasts and osteoclasts provides a main index of how bone formation and/or resorption are altered underneath numerous situations. Primary outcomes associated to osteoblasts embrace osteoblast surface and their number, both sometimes normalized to bone floor. Identification of lively osteoblasts could be challenging, and their assessment is typically restricted to areas with osteoid. In these situations, osteoid is first recognized and then partitioned into two categories: osteoid with osteoblasts (active formation surfaces) and osteoid with out osteoblasts (inactive formation surfaces). The extent of floor with osteoblasts and the variety of osteoblasts are then normalized either to complete surface or to osteoid floor. An various strategy to quantifying osteoblasts, although not generally utilized, is to carry out immunohistochemistry (such as with alkaline phosphatase) after which assess constructive cells adjacent to the bone surface. The most commonly used osteoclast outcomes are osteoclast surface and quantity, with both parameters normalized to whole bone floor inside the region of study. The variety of nuclei per osteoclast is less incessantly measured but can typically be useful in assessing osteoclast activity. In addition, properties of lamellae such as thickness and number could be quantified from these type of pictures. The majority of histologic assessments of woven and lamellar bone are qualitative, with papers reporting easy statements similar to "all bone was lamellar in nature" or "no woven bone was noticed. Erosion surfaces with osteoclasts on them are thought of energetic resorption websites, whereas erosion surfaces with out evident osteoclasts are thought of inactive. In cross part, lively resorption websites are seen as scalloped resorption holes (the cross section of a cutting cone) inside cortical bone or divots on trabecular or endocortical surfaces. Measures of abrasion depth are possible in medical biopsies and in bigger animals, but difficult in rodents. Various techniques primarily based in stereology exist for figuring out erosion depth (see works by Eriksen and Parfitt). A variable associated to erosion depth from earlier remodeling activity is average wall width (W. There is another assumption inherent on this measurement if one is trying to assess the results of an intervention; W. These can usually be difficult to discover experimentally, and so most investigators measure W. All bone surfaces within a area of curiosity are categorised as single, double, or no label. Dynamic Histomorphometry Although osteoblast operate could be inferred through measures of osteoid, probably the most generally used technique is the assessment of fluorochrome labels (dynamic histomorphometry), as a end result of it allows the calculation of rates of modeling and transforming. From these main measures, the mineralizing floor may be calculated as the entire double label plus half the only label, which is equivalent to the mean of the individually measured first label length and second label size. The distance between the 2 labels (interlabel distance) is measured and averaged throughout all double labels. Given the distinctive and essential data of every variable, it is recommended that each one three parameters are calculated and reported. Dynamic bone properties could be assessed on trabecular, periosteal, and endocortical surfaces utilizing the methods described above, by which surfaces are measured and normalized to complete surface. This is achieved by assessing labeled osteons, measuring the extent of single and double label, and then normalizing parameters to complete bone area. In circumstances of regular reworking, a region of bone is more likely to have a comparatively giant variety of reworking events, and thus the likelihood of catching a quantity of of these formation occasions in the course of the 2- to 3-week interval of labeling tends to be high. Morphologically, eroded surfaces are defined as scalloped surfaces which will or could not have osteoclasts within them. In human bone, eroded surfaces tend to be fairly simple to delineate because nearly all of surfaces are comparatively clean (A). An alternative means of assessing resorption surface makes use of fluorochrome labels in a slightly different trend than for assessing formation. In this technique, a fluorochrome label is given at time zero and a baseline group of animals is then euthanized and the extent of surface label is measured. A number of days later, perhaps after a treatment suspected to have an result on resorption, a second group of animals is euthanized and the extent of label is assessed. The difference between the label in the baseline animals and the experimental animals is assumed to happen by resorption. Although not routinely used, this strategy does afford a way of estimating resorption "exercise" in rodents. Osteocytes Histologic evaluation of osteocytes is primarily centered on cell quantity and standing. A number of stains for markers of apoptosis (such as caspase-3 or -8) can additionally be used to assess bone cell well being. The number of apoptotic osteocytes relative to total osteocytes is essentially the most commonly reported outcome. Marrow adipocyte quantity and area are generally reported and are expressed relative to complete marrow area. The biggest of these is the belief that bone turnover is in a steady state at the time of analysis. This means that for a given period (typically the time it takes for one complete transforming cycle) there was no alteration in the indicators that govern osteoblast or osteoclast improvement and performance. For instance, if a biopsy is taken too quickly after an intervention that stimulates bone turnover, there would probably be an increase in osteoclast floor with no concomitant increase in osteoblast surface or fluorochrome-labeled surface (as there was inadequate time for formation to increase). This would symbolize a transient deficit in bone quantity that may not mirror the underlying long-term bone balance.
Syndromes - Excessive bleeding
- Death
- Make an informed decision regarding options for prenatal diagnosis
- Leg pain or numbness that is very bad or is not going away, making it hard to do daily tasks
- Clonidine
- Stopping of menstrual cycle
- Heart failure
Purchase rivastigimine no prescriptionThe troponin I (TnI) isoform TnI-s is predominant in fetal life and changes to TnI-c by 9 months of age, allowing for elevated pressure of contraction. Mitochondria mixture in the heart of the immature myocyte and then turn into often distributed along the myofibrils with maturation. In immature hearts, lactate and carbohydrates are the first energy sources, with transition to long-chain fatty acid in mature hearts. Cardiac progress in fetal life is primarily due to cell division, with resultant improve in cell quantity. After birth, cardiac progress is primarily secondary to hypertrophy in present myocytes. Maternal Diseases With Fetal Cardiac Manifestations Diabetes mellitus: There is a five-fold improve of cardiac anomalies in infants of diabetic mothers. As the atrioventricular septum types through the fifth and sixth weeks, the center is transformed to align the creating left atrioventricular canal with the left atrium and ventricle, and the best atrioventricular canal with the proper atrium and ventricle. Red arrows indicate the path of realignment of the atrioventricular canal and outflow tract and formation of the muscular interventricular septum. The blue arrow in C indicates formation of an enlarging slit carved out of the muscular ventricular septum; that is responsible partially for repositioning of the tricuspid orifice to the right, as properly as for formation of the moderator band. The frequency of anomalies will increase with rising first-trimester maternal hemoglobin A1c. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can develop in response to maternal hyperglycemia within the third trimester. The cranial-lateral wall of the proper ventricle has been eliminated to present the inside of the proper ventricular chamber and the presumptive outflow tracts of each ventricles. These swellings are populated by endocardial and neural crest cell -derived cushion cells and develop in a spiraling configuration. They fuse with each other in a cranial-to-caudal direction, forming the conotruncal septum, which separates the aortic and pulmonary outflow tracts. The round buildings to the best of the growing outflow tract illustrate drawings of cross sections at three proximodistal ranges. Maternal B-mimetics corresponding to terbutaline can be used to deal with a fetus with a critically low coronary heart rate. Maternal infections throughout being pregnant: Parvovirus can cause fetal myocarditis, with poor ventricular contractility and/or high output cardiac failure because of extreme anemia. Congenital rubella is associated with patent ductus arteriosus and pulmonary artery stenosis. Model systems for the research of coronary heart improvement and disease: cardiac neural crest and conotruncal malformations. Molecular and morphogenetic cardiac embryology: implications for congenital heart illness. The most common cyanotic congenital coronary heart defect seen in infants of diabetic moms is which of the following Venous return to the fetal heart: Deoxygenated blood from the higher body returns to the guts via the superior vena cava and is directed by the foramen ovale and eustachian valve, throughout the tricuspid valve and into the best ventricle. Deoxygenated blood from the coronary sinus streams across the tricuspid valve to the proper ventricle because of its location adjoining to the tricuspid valve. Deoxygenated blood from the decrease physique returns through the inferior vena cava and streams across the tricuspid valve. Oxygenated blood from the placenta goes from the umbilical vein primarily into the ductus venosus, with a smaller amount directed to the left portal vein. Ventricular output of the fetal heart: the proper ventricle is dominant in fetal life, pumping 55% to 65% of the cardiac output. The right ventricle has higher mass and thus immediately affects the filling and ejection of the left ventricle within the fetus. Most of the best ventricular output is directed away from the lungs due to the very excessive pulmonary vascular resistance in fetal life. Blood is directed throughout the ductus arteriosus, with one-third delivered to the lower body and two-thirds delivered to the placenta via the umbilical artery for oxygen uptake. Left ventricular output supplies the oxygenated blood from the ascending aorta to the coronary arteries (7% of left ventricular output) and to the brain (55% of the left ventricular output). Prostacyclin is produced by lung distention and is a potent pulmonary vasodilator. Remodeling of the pulmonary vascular mattress decreases the muscularity of the proximal arterioles and leads to mature ranges of pulmonary vascular resistance by 2 months of age. The flap of the foramen ovale is functionally closed at birth, with the dramatic increase in pulmonary venous return inflicting left atrial stress to exceed proper atrial stress. Anatomic closure may not happen for months after start and stays open in 25% of people. Flow throughout the ductus arteriosus typically changes from proper to left to left to proper because of the decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance and enhance in systemic vascular resistance after delivery. Ductus arteriosus closure is initiated by increased oxygen content and decreased ranges of prostaglandins after delivery. Ventricular output dramatically will increase to meet new increased vitality calls for because of the work of respiratory and thermoregulation: Oxygen consumption triples at delivery. The left ventricle becomes the dominant ventricle within the transitional circulation because it pumps at greater pressure and ejects more blood due to the continued patency of the ductus arteriosus. In response to stress, fetal arterial output is redistributed, with elevated resistance in the placental and lower body vascular beds to preserve cerebral and cardiac oxygen delivery. When the arterial compensatory mechanisms are exceeded, and fetal coronary heart failure develops, abnormalities are seen within the venous system: the primary sign of decompensation is a bigger A wave within the inferior vena cava Doppler signal. Development of a reverse A wave in the ductus venosus Doppler trace develops as coronary heart failure progresses. Atrial pulsations in the umbilical venous Doppler hint happen in end-stage fetal heart failure. Hemodynamic Consequences of Perinatal Events Asphyxia impairs the transition of fetal to postnatal circulation: Hypoxia retains the ductus arteriosus open and promotes pulmonary vasoconstriction. Increased pulmonary vascular resistance promotes tricuspid insufficiency, which will increase right atrial stress and promotes continued right to left shunting on the patent foramen ovale. Cardiac output is maintained in early asphyxia as a outcome of systemic vasoconstriction shunting circulate away from less important organs, such because the intestine, muscle, and skin, and towards the heart and mind. This redistribution maintains oxygen supply to critical organs and leaves the less vital organs to depend on elevated oxygen extraction. Skin pallor is the scientific discovering that occurs secondary to this redistribution of flow. Bradycardia and hypertension end result from the reflexes that drive the flow redistribution. Central venous pressure rises in early asphyxia secondary to the vasoconstriction of capacitance vessels. As hypoxia and acidosis worsen, cardiac perform declines, inflicting hypotension, worsening bradycardia, and resulting in additional will increase within the central venous pressure. Correction of asphyxia sequelae in the early levels may be accomplished by establishing enough ventilation and oxygenation.
Discount rivastigimine master cardAsian indications are based on conventional Chinese and Indian compendia and will or will not be acknowledged as primary indications by Western medicine. Finally, there are numerous unproven makes use of for which a botanical has empirically been used but lacks enough data for proof of efficacy. The principal elements or elements of the botanical used within the preparation of the medicinal formulation are listed. The major active ingredients contained inside the herb are outlined, most of that are structurally categorized as aromatic or polycyclic glycosides. Because of toxicity and unreliable management of dose/effect, peyote is not beneficial to be used as an herbal preparation (see Effects, Table 23. Among the commonest antagonistic reactions noted with ingestion or application of natural products is the propensity for improvement of allergic reactions. In explicit, the lectin, glycosidic, or peptide components of the herbs behave as haptens. Haptens, by definition, are incapable of inducing inflammatory reactions alone but can stimulate an antigenic response by binding to circulating proteins. Toxicity of some herbs has also resulted from contamination of the product with metals and pharmaceutical brokers. Because of the lenient federal oversight for these products, some poisonings have resulted from misidentification, mislabeling, and inadequate purification of natural elements. In addition, the poisonous effects of natural compounds usually end result from ingestion of higher doses than beneficial or recommended doses for prolonged durations. As more info is gathered with the growing recognition of these brokers, notable drug interactions are surfacing, some of that are summarized in Table 23. In basic, several classes of medicine have the potential for undesirable interactions with botanical preparations. These embrace anticoagulants and other medications requiring therapeutic drug monitoring, medicine that require P450 biotransformation, medicine that sensitize the myocardium, and compounds that increase the risk of systemic allergic reactions. Code 2006, Title 21: Food and Drugs, Supplement 1, January 4, 2007 to January eight, 2008, U. Direct motion of those compounds entails interaction of the mother or father molecules with the substrates of biological pathways. Ethanol, methanol, and isopropanol are essential alcohols primarily due to their commercial availability, significance in quite so much of important chemical reactions, and involvement in intermediate chemical and biological pathways. Human exposure to this chemical has obtained appreciable attention as a end result of its human carcinogenic potential and developmental toxicity in laboratory animals. The presence of ethanol in wine, beer, and liquor and using it as a common solvent make it extensively available to adults. Ethanol is a socially accepted recreational drug due to its authorized approval and ubiquitous availability. Furthermore, research in pregnant girls demonstrate a few 10% incidence of alcohol consumption throughout being pregnant. It is thus able to readily distributing all through physiologic compartments; notably, it is prepared to penetrate the blood�brain barrier and placenta. The abdomen extracts about 20%, primarily by diffusion, with the majority of absorption occurring within the small intestine. Several components may delay absorption, including concomitant consumption with meals, medicine, and medical conditions that inhibit gastric emptying. After it enters the portal vein, ethanol first passes via the liver before it distributes systemically. More than 90% of ingested ethanol is oxidized to acetaldehyde by the liver and gastric mucosal cells; 5% to 10% is excreted unchanged by the kidneys and lungs and through dermal pores. The common fee of ethanol metabolism in adults is 100�124 mg/kg/hour in occasional drinkers and can be as a lot as a hundred seventy five mg/kg/hour in persistent drinkers. Thus, ethanol metabolism remains fixed above Vmax even because the focus increases. Based on these charges, the equilibrium fixed (or average enzyme fee constant, K m) is calculated as K m = 9. For a median 70 kg male, the general enzyme rate (Vmax) is Vmax = 18 mg dL hr which computes to an elimination fee (Kelim) for ethanol at K elim = a hundred mg kg hr Thus, the same 70 kg particular person metabolizing at 100 mg/kg/h will be succesful of get rid of 7 g hr (by weight) or 9 ml hr (by volume) of 100% (absolute) ethanol, assuming the particular gravity of ethanol = zero. Several cellular processes have been proposed to be crucially involved in ethanol-induced toxicity: 1. Ethanol instantly affects cell membrane fluidity and modifies membrane proteins, which can lead to alterations in the liquid-crystal state of membranes, membrane ion transport, transmembrane sign transduction. These molecules are able to oxidizing important biomolecules, including lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, leading to oxidative cell injury. These lipophilic molecules accumulate in cell membranes and mitochondria, resulting in impaired organelle function. The liver is crucial target organ of ethanol-induced toxicity, especially persistent ethanol intoxication. This inflammatory reaction triggers additional cytokine recruitment, aggravating hepatic harm. The era of reactive acetaldehyde, as a product of ethanol metabolism, results in the formation of protein adducts and enzyme inactivation. Moreover, acetaldehyde promotes glutathione depletion, free-radical-mediated toxicity, and lipid peroxidation. Acetaldehyde has also been proven to stimulate collagen synthesis by liver stellate cells, which may be concerned within the pathogenesis of ethanol-induced liver cirrhosis. Chronic ethanol intoxication induces cardiotoxicity by interfering with myocardial shops of catecholamines and by decreasing the synthesis of cardiac contractile proteins, leading to despair of myocardial contractility. For persistent drinkers who become tolerant to the effects of ethanol, the corresponding concentrations to elicit the identical diploma of toxicity could be much higher than those for casual drinkers. The medical manifestations of acute intoxication embrace sedation and reduction of hysteria, lowered rigidity and coordination, impaired concentration and reaction time, tachycardia, and extra severely, slurred speech, ataxia, and altered emotions (interestingly, respiratory despair is manifested solely at excessive concentrations). Clinical laboratory testing reveals hypoglycemia, ketosis, and electrolyte derangements in patients with severe ethanol intoxication. In addition, glucose is run for the prevention of hypoglycemia and ketosis. Electrolyte options are additionally administered to stop the dehydration that accompanies vomiting. Therefore, vitamins, such as thiamine, folate, and magnesium, accompany the course of therapy. Other strategies, including hemodialysis and gastric decontamination, have restricted efficacy in the administration of ethanol intoxication. The greater risk is principally as a end result of the higher incidence of alcoholic liver cirrhosis, infections, accidents, cancers, and cardiovascular illnesses. Administration of thiamine alleviates the ataxia, ocular issue, and confusion; however, a reminiscence deficit, generally recognized as Korsakoff psychosis, may linger. Moreover, ethanol may trigger bilateral and symmetrical visual impairment because of optic nerve degeneration. It is characterised by axonal degeneration of peripheral nerve fibers with earlier and extra frequent involvement of sensory fibers of the lower limbs.
Rivastigimine 1.5 mg onlineThis article offers a conceptual introduction to the microbiome in addition to a more detailed review of the present, albeit limited, understanding of how the microbiome might influence bone. The human microbiome increases in complexity and variety after the introduction of strong foods and weaning and achieves a steady state of over one thousand distinct microbial species by three years of age. The composition of the gut flora fluctuates over time due to variation in food regimen, host well being, and publicity to antibiotics. Additionally, there are variations within the constituents of the intestine microbiota amongst human populations in several regions of the world. In specific, there are large differences within the constituents of the intestine flora between city populations in western industrialized nations and rural agrarian societies. Geographic variations in the microbiome in human populations are dominated by variations in diet however can be influenced by host genetic background, host health, and the environment (soil, close by animals, and so forth. The effects of the microbiome on host physiology have been acknowledged because the initiation of widespread use of antibiotic remedies within the Thirties. Early studies confirmed that oral antibiotics elevated charges of growth in laboratory and cattle. In agriculture, low-dose oral antibiotics are used to modify the constituents of the intestine flora to improve calorie absorption and improve development charges (antibiotics used in this method are typically not absorbed within the intestine lining and due to this fact by no means immediately attain animal tissues or the meals chain). The human microbiome contains genetic components from micro organism, archea, singlecelled eukaryotes, and viruses. Phylogenomics-Sequencing used to determine the taxonomic classifications of organisms current in a microbiome sample. This features a germ-free state (the absence of a microbiota) as properly as mono- or multispecies colonization. Germ-free mice-Animals raised in a sterile incubator to make positive the absence of a microbiota. Such animals should be exposed to microbial products in sterilized food and water. Prebiotics-A nutrient used to promote the growth or survival of helpful organisms within a microbial neighborhood. There are quite lots of sequencing techniques useful for finding out the composition and function of the gut microbiome. Taxonomic sequencing can establish the prokaryotic organisms, most frequently in accordance with phylogenetic relationships (phylum, class, order, and so forth. The metagenome contains the bacterial genes current in the pattern and thereby represents the practical capability of the microbial group. The heatmap illustrates four teams of microbes (phylotypes) within the knowledge set (rows). Transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics are extra -omics tools which would possibly be increasingly used to perceive the exercise within the microbiome as nicely as host�microbe interactions. The most elementary interplay among microbiota is competitors for assets (nutrients) within the setting. In addition to competitors, symbiotic and parasitic interactions appear to be present among species. One important consequence of these interactions is that they complicate the identification of particular person species that affect host health. A second consequence of the interactions among species inside the microbiota is that a longtime community of microbial species is usually strong, making it difficult for a newly introduced species to compete for resources and thereby colonize the community. Although the constituents of the intestine flora fluctuate every day as a outcome of variations in food plan and host exercise, a small disruption of the gut flora (a dose of a probiotic, for example) sometimes has only a transient impact on the constituents of the gut flora. Resistance to colonization is advantageous to the host in that it reduces the flexibility of pathogens to colonize and trigger an infection. The rising area of "microbiome engineering" seeks to achieve further management over the contents of the microbiome and develop new microbiome-based remedies and interventions. Preclinical Manipulations of the Microbiome Animal models are the most effective out there method of figuring out the mechanisms behind an impact of the microbiome on host physiology. Mice have been the first experimental tool for studying the results of the microbiome on bone. The microbiome of experimental animals is influenced by small variations in food plan (possibly even together with the lot variety of animal chow), the kind of bedding within the cage (animals could ingest bedding), and the kind of housing facility (specific pathogen free or conventional). Additionally, there are well-described differences within the intestine flora among laboratory animal distributors; some amenities are populated by organisms which have a profound effect on the host immune system. Even inside the similar room inside the similar facility, cage-to-cage variation in the constituents of the microbiome is common and can contribute to variance in the experimental results. There are a quantity of other ways of modifying the gut microbiota in experimental animals. Experimental techniques embody the use of gnotobiotic mice (germ-free, monocolonized, altered Schaedler flora), switch of intestine flora, oral antibiotics, and genetic models. Germ-free mice are animals raised in a sterile environment and are by no means exposed to live microbes (microbial molecules may still be present in sterilized food and water). Germ-free mice are subsequently an excessive example of the effects of the whole absence of a stay microbial group on phenotype. A major limitation of germ-free mice is that the absence of microbial exposure prevents the development of a mature immune system, thereby influencing animal health and physiology. Mice colonized with particular organisms such as the altered Schaedler flora tackle this limitation to some degree. A major benefit of germ-free mice, nevertheless, is that the absence of an established gut flora enhances the power of the mouse to be colonized by transfer of gut flora from other mice or people. Demonstration that switch of gut flora additionally results in switch of a phenotype offers robust proof that the intestine flora is answerable for a phenotype. Oral antibiotics are a commonly used strategy for modifying the constituents of the intestine flora. There are numerous different oral antibiotic dosing regimens that provide various levels of control of the constituents of the intestine flora. Given the restricted information in people, much of our understanding comes from animal experiments. Each of these methodologies can be useful for understanding the affiliation between the gut microbiome and bone. The Effects of the Microbiome on Bone Mass, Remodeling, and Strength To date, solely a handful of animal studies have examined the effects of the microbiome on bone mass, bone reworking, or bone strength. The bone phenotypes of germ-free mice present clear evidence of an impact of the microbiome on the skeleton. Early research of the bone phenotype in germ-free mice offered conflicting outcomes that instructed that germ-free mice have increased or decreased bone mass. A doubtless clarification for the disagreements between studies was the use of animals with completely different age, sex, and genotype. The administration of antibiotics to modify the constituents of the gut microbiota results in adjustments in bone morphology, density, and material properties. Antibiotics are used as experimental manipulations in two methods: (1) to mimic scientific remedy and thereby determine the short- and long-term results of antibiotics on phenotypes influenced by the microbiome and (2) to trigger a drastic shift within the constituents of the microbiota by dosing with antibiotics which are poorly absorbed on the intestine lining, thereby focusing on the gut flora and having little direct impact on bone. Furthermore, the consequences of disruption of the gut flora with oral antibiotics could be partially reversed by way of oral supplementation with brief chain fatty acids. Short-term therapy with oral antibiotics (ampicillin and neomycin) can cause reductions in bone mass in male, however not female mice, and the effect is mediated to some extent by probiotics.
References - Black NA, Downs SH: The effectiveness of surgery for stress incontinence in women: a systematic review, Br J Urol 78(4):497n510, 1996.
- Maruschke M, Kreutzer HJ, Seiter H: [Bladder rupture caused by spontaneous perforation of an infected urachal cyst], Urol Ausg A 42:834n839, 2003.
- Kurien A, Symons S, Manohar T, et al: Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy in children: equivalent clearance rates to adults is achieved with fewer and lower energy shock waves, BJU Int 103:81, 2009.
|
|