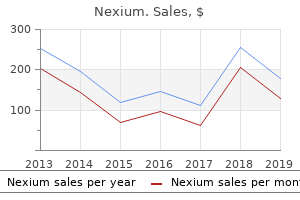
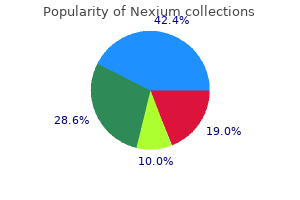
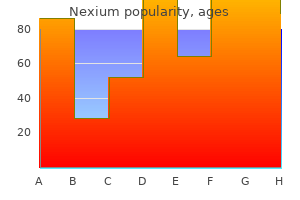
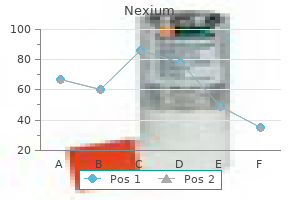
"Discount nexium 40 mg on line, gastritis diet on a budget."By: Keira A Cohen, M.D. - Co-Director, The Johns Hopkins Center for Nontuberculous Mycobacteria and Bronchiectasis
- Assistant Professor of Medicine
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/10003818/keira-cohen
Nexium 40 mg with amexThe following dialogue exhibits how these processes are concerned in amino acid metabolism. Depending on which amino acid is involved, the ensuing keto acid may be transformed to pyruvate, acetyl-CoA, or one of many acids of the citric acid cycle (fig. In gluconeogenesis, keto acids are used to synthesize glucose, primarily by way of a reversal of the glycolysis reactions. Protein Amino acids Keto acids Transamination, Ammonia, and Urea When an amino acid is deaminated, its amino group is transferred to a citric acid cycle intermediate, -ketoglutaric acid, converting it to glutamic acid. Such transamination reactions are the route by which a quantity of amino acids enter the citric acid cycle. In a pathway called the urea cycle, the liver shortly combines ammonia with carbon dioxide to produce a much less toxic waste, urea. The liver can make many of those amino acids from different amino acids or from citric acid cycle intermediates by transamination reactions. Liver Functions in Metabolism You may notice that the liver performs a wide variety of roles within the processes mentioned on this chapter-especially carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism. Except for phagocytosis, all of them are performed by the hepatocytes described in part 25. Such practical range is remarkable in mild of the uniform construction of these cells. Because of the numerous crucial functions performed by the liver, degenerative liver ailments such as hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver most cancers are particularly life-threatening (see Deeper Insight 26. When fat are converted to glucose, only the glycerol part is used on this means, not the fatty acid. This is a time during which nutrients are being absorbed and could additionally be saved or used immediately to meet vitality and other needs. The postabsorptive (fasting) state prevails within the late morning, late afternoon, and in a single day. Stores a 10-month supply of vitamin A and sufficient vitamin B12 to last from one to several years. Secretes hepcidin to regulate iron absorption; shops iron in ferritin and releases it as wanted. Digestion Synthesizes bile acids and lecithin, which emulsify fats and promote its digestion; produces micelles, which help in absorption of dietary lipids. Disposal of Drugs, Toxins, and Hormones Detoxifies alcohol, antibiotics, and many other medication. Deactivates thyroxine and steroid hormones and excretes them or converts them to a kind extra simply excreted by the kidneys. Stabilizes blood glucose focus by storing extra glucose as glycogen (glycogenesis), releasing glucose from glycogen when wanted (glycogenolysis), and synthesizing glucose from fats and amino acids (gluconeogenesis) when glucose demand exceeds glycogen reserves. Receives lactate generated by anaerobic fermentation in skeletal muscle and different tissues and converts it back to pyruvate or glucose 6-phosphate. Carries out most beta oxidation of fatty acids; produces ketone bodies from extra acetyl-CoA. Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism Carries out most deamination and transamination of amino acids. They differ in mode of transmission, severity of the ensuing sickness, affected age teams, and one of the best methods for prevention. It spreads quickly in such settings as day-care facilities and residential establishments for psychiatric sufferers, and it can be acquired by consuming raw seafood similar to oysters, as nicely as by sewage contamination of meals and water and by hand-to-mouth fecal transmission. Hepatitis A may cause up to 6 months of sickness, however most people get well after which have everlasting immunity to it. Hepatitis E, with an analogous mode of transmission, is unusual in the United States but a major cause of water-borne epidemics and mortality in less economically developed international locations. Initial indicators and signs of hepatitis include fatigue, malaise, nausea, vomiting, and weight reduction. Jaundice, or yellowing of the skin, tends to comply with as hepatocytes are destroyed, bile passages are blocked, and bile pigments accumulate within the blood. Hepatitis B and C typically result in chronic hepatitis, which can progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer. Most cases result from alcohol abuse, however hepatitis, gallstones, pancreatic irritation, and different circumstances can even bring it about. It develops slowly over a interval of years, however has a high mortality price and is doubtless considered one of the leading causes of dying in the United States. It is characterized by a disorganized liver histology during which areas of scar tissue alternate with nodules of regenerating cells, giving the liver a lumpy or knobby look and hardened texture. Protein synthesis declines because the liver deteriorates, resulting in ascites, impaired blood clotting, and other cardiovascular effects (see Deeper Insight 26. Obstruction of the hepatic circulation by scar tissue leads to angiogenesis, the expansion of recent blood vessels to bypass the liver. Deprived of blood, the condition of the liver worsens, with increasing necrosis and, typically, liver failure. It serves as the first fuel and spares the body from having to draw on stored fuels. The standing of main nutrient courses during this section is as follows: Carbohydrates. Most glucose passes via the liver and turns into obtainable to cells in all places within the body. Glucose in excess of quick want, however, is absorbed by the liver and may be converted to glycogen or fats. Most fats synthesized in the liver is released into the circulation; its further destiny is comparable to that of dietary fats, mentioned subsequent. As described earlier, lipoprotein lipase removes fats from the chylomicrons for uptake by the tissues, especially adipose and muscular tissue. Insulin regulates the speed of glucose uptake by nearly all cells besides neurons, kidney cells, and erythrocytes, which have independent charges of uptake. With those exceptions, insulin has the following results on its goal cells: Within minutes, it increases the mobile uptake of glucose by as a lot as 20-fold. It stimulates the energetic transport of amino acids into cells and promotes protein synthesis. Following a high-protein, low-carbohydrate meal, it might seem that the amino acids would stimulate insulin secretion; insulin would accelerate both amino acid and glucose uptake; and since there was relatively little glucose in the ingested food, this may create a threat of hypoglycemia. In actuality, that is prevented by the reality that a high amino acid degree stimulates the secretion of both insulin and glucagon. Regulation of the Absorptive State the absorptive state is regulated largely by insulin, which is secreted in response to elevated blood glucose and amino acid levels and to the intestinal hormones gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin, the Postabsorptive State the essence of the postabsorptive state is to homeostatically regulate plasma glucose focus inside about 90 to 100 mg/dL.
Buy discount nexium lineShell temperature is the temperature closer to the floor, particularly skin and oral temperature. Here, heat is misplaced from the body and temperatures are barely lower than rectal temperature. Shell temperature fluctuates because of processes that serve to preserve a stable core temperature. We depend on blood move to carry metabolic heat from the physique core to the shell, the place it could be dissipated into the surroundings. At relaxation, most warmth is generated by the mind, heart, liver, and endocrine glands; the skeletal muscle tissue contribute about 20% to 30% of the whole resting heat. Increased muscle tone or exercise greatly increases heat technology in the muscular tissues, nonetheless; in vigorous train, they produce 30 to forty occasions as much heat as all the remainder of the body. The physique loses heat in 4 methods: radiation, conduction, convection, and evaporation: 1. Conduction is the switch of kinetic power from molecule to molecule as they collide with one another. Heat generated in the body core is conducted to the surface through the tissues, then lost from the body by conduction from the skin to any cooler objects or medium involved with it. The heat of your body provides to the molecular motion of your clothes, the chair you sit in, the air around you, or water if you go swimming or sit in a cool bathtub. You can also achieve warmth by conduction, as on a extremely popular day when the air temperature is greater than your shell temperature, or whenever you use a heating pad for sore muscles, bask in a scorching tub, or lie on sizzling sand at the seaside. The enzymes that management our metabolism depend on an optimal, stable working temperature. In order to preserve this, the charges of metabolic warmth era and warmth loss from the physique must match. Conversely, an excessively high physique temperature, referred to as hyperthermia, could make some metabolic pathways race forward of others and disrupt their coordination to the point that this, too, can lead to death. Thermoregulation, the stability between warmth manufacturing and loss, is due to this fact a critically important facet of homeostasis. Most of the warmth generated by metabolism in the body core is carried by convection within the bloodstream to the physique floor. Warm air is much less dense than cool air, so it rises from the physique and is changed by cooler air from below. Such motion of a fluid caused completely by its change in temperature and density is called pure convection. This impact, called forced convection, is the explanation why, even at the identical temperature, we feel cooler on a windy day than on a day when the air remains to be. Forced convection will increase heat loss by each conduction and evaporation (discussed next), however has no effect on radiation. The cohesion of water molecules hampers their vibrations in response to warmth enter. If the temperature of water is raised sufficiently, nonetheless, its molecular movement turns into great enough for molecules to break free and evaporate. In extreme conditions, the body can lose 2 L or more of sweat and dissipate as a lot as 600 kcal of heat per hour by evaporative loss. The relative quantities of heat misplaced by completely different methods depend upon prevailing conditions. A nude physique at an air temperature of 21�C (70�F) loses about 60% of its warmth by radiation, 18% by conduction, and 22% by evaporation. If air temperature is larger than skin temperature, evaporation turns into the one means of warmth loss because radiation and conduction add more warmth to the body than they remove from it. Thermoregulation Thermoregulation is achieved by way of several adverse feedback loops that govern cutaneous blood move and different mechanisms for elevating or reducing body temperature. The preoptic space of the hypothalamus (anterior to the optic chiasm) features as a hypothalamic thermostat. It monitors blood temperature and receives indicators also from peripheral thermoreceptors located primarily within the pores and skin. In flip, it sends indicators either to the heat-loss (a) Heat transfers from the body to surrounding air molecules by conduction. The first and simplest of these is cutaneous vasodilation, which will increase blood flow to the body shell (skin and subcutaneous tissue) and thus promotes heat loss. In warm circumstances, the shell, or zone of relatively cool tissue, may be less than 1 cm thick (fig. If cutaneous vasodilation fails to restore normal temperature, the heat-loss center triggers sweating. This diverts heat blood from the shell and retains it deeper within the body so much less heat is lost via the pores and skin. In different mammals, the sympathetic nervous system additionally stimulates the piloerector muscle tissue, which make the hair stand on end. The human sympathetic nervous system makes an attempt to do this as nicely, however since our physique hair is so scanty, usually the only noticeable impact of that is goose bumps. If you allow a warm home on a really cold day, you may discover that your muscular tissues turn into tense, typically even painfully taut, and you begin to shiver. Shivering includes a spinal reflex that causes tiny alternating contractions in antagonistic muscle pairs. Nonshivering thermogenesis is a longer-term mechanism for producing warmth, occurring especially within the colder seasons of the yr. The sympathetic nervous system raises the metabolic rate as much as 30% after several weeks of cold weather. Just getting out of the sun greatly cuts down warmth achieve by radiation, for instance, and shedding heavy clothing or kicking off a blanket at night time helps to cool the physique. The high temperature elevates the metabolic rate and the physique generates warmth faster (a) In a sizzling surroundings, cutaneous vasodilation carries heat near the body floor and the shell is relatively thin. It is simple to see from this why frostbite so often impacts extremities similar to fingers and toes. Therefore, the elevated metabolic rate increases the fever and the fever increases the metabolic fee in a harmful optimistic suggestions loop. A core temperature of 44� to 45�C (111��113�F) can produce fatal metabolic dysfunction and neurological damage. Heat cramps are painful muscle spasms that outcome from electrolyte loss in the sweat. They happen especially when one begins to chill out after strenuous exertion and heavy sweating. Heat exhaustion results from more severe water and electrolyte loss and is characterized by hypotension, dizziness, vomiting, and sometimes fainting.
Discount nexium 40 mg on lineSuperficially, the muscle fiber appears to be giving its most response once the stimulus intensity is at threshold or larger. Twitches vary with the temperature of the muscle; a warmed-up muscle contracts extra strongly as a end result of enzymes such as the myosin heads work more quickly. Muscles should contract with variable power for different duties, corresponding to lifting a glass of champagne in contrast with lifting barbells at the gym. Let us study extra intently the contrasting effects of stimulus intensity versus stimulus frequency on contraction strength. Suppose we apply a stimulating electrode to a motor nerve that supplies a muscle, corresponding to a laboratory preparation of a frog sciatic nerve related to its gastrocnemius muscle. The reason for that is that higher voltages excite more and more nerve fibers within the motor nerve (middle row of the figure), and thus stimulate increasingly more motor items to contract. This is seen not simply in artificial stimulation, however is a half of the best way the nervous system behaves naturally to produce various muscle contractions. The neuromuscular system behaves based on the size principle-smaller, less powerful motor units with smaller, slower nerve fibers are activated first. This is enough for delicate tasks and refined actions, but if extra energy is needed, then bigger motor models with larger, sooner nerve fibers are subsequently activated. But even when stimulus intensity (voltage) remains constant, twitch energy can vary with stimulus frequency. High-frequency stimulation produces stronger twitches than low-frequency stimulation. At higher stimulus frequencies, say 20 to forty stimuli/s, every new stimulus arrives earlier than the previous twitch is over. Each new twitch "rides piggyback" on the earlier one and generates greater pressure (fig. This phenomenon goes by two names: temporal10 summation, as a outcome of it outcomes from two stimuli arriving shut collectively in time, or wave summation, as a outcome of it outcomes from one wave of contraction added to another. Wave upon wave, each twitch reaches a better stage of pressure than the one earlier than, and the muscle relaxes only partially between stimuli. This effect produces a state of sustained fluttering contraction called incomplete tetanus. In the laboratory, an isolated muscle may be stimulated at such excessive frequency that the twitches fuse right into a single, nonfluctuating contraction known as complete (fused) tetanus (fig. Complete tetanus is injurious to muscle and associated soft tissues, so spinal inhibition protects the muscular tissues by preventing complete tetanus. Despite the fluttering contraction seen in incomplete tetanus, we know that a muscle taken as a complete can contract very easily. The colored nerve fibers are the excited ones; observe that none are excited by the subthreshold stimuli above. When stimuli attain or exceed threshold (3�7), they excite increasingly nerve fibers and motor models; thus, they produce stronger and stronger contractions. Once all the nerve fibers are stimulated (7�9), further will increase in stimulus energy produce no further increase in muscle rigidity. Thus, physiologists communicate of various kinds of muscle contraction as isometric versus isotonic and concentric versus eccentric. At an unnaturally low stimulus frequency, as in laboratory preparations, the muscle relaxes completely between stimuli and exhibits twitches of uniform power. In this state, a muscle can attain three to 4 instances as much pressure, or pressure, as a single twitch produces. This happens firstly of any muscle contraction however is extended in actions corresponding to lifting heavy weights. This section is called isometric11 contraction- contraction with no change in length (fig. The isometric contraction of antagonistic muscle tissue at a single joint is essential in maintaining joint stability at rest, and the isometric contraction of postural muscles is what retains us from sinking in a heap to the floor. Isotonic12 contraction-contraction with a change in size but no change in tension-begins when inside tension builds to the purpose that it overcomes the resistance. The muscle now shortens, strikes the load, and maintains basically the same tension from then on (fig. Isometric and isotonic contraction are each phases of regular muscular motion (fig. In concentric contraction, a muscle shortens because it 11 12 maintains tension-for instance, when the biceps contracts and flexes the elbow. A weight lifter uses concentric contraction when lifting a dumbbell and eccentric contraction when reducing it. In abstract, throughout isometric contraction, a muscle develops pressure with out changing size, and in isotonic contraction, it modifications length while maintaining fixed tension. In concentric contraction, a muscle maintains pressure as it shortens, and in eccentric contraction, it maintains tension while it lengthens. State three or extra explanation why muscle twitch strength can vary even when stimulus depth stays fixed. Describe an everyday activity not involving the arms by which your muscles would switch from isometric to isotonic contraction. Describe an everyday activity not involving the arms that would involve concentric contraction and one that would contain eccentric contraction. When pressure overcomes the resistance of the load, the tension ranges off and the muscle begins to shorten and transfer the load (isotonic phase). The phosphagen system is particularly essential in actions requiring quick bursts of maximal effort, similar to soccer, baseball, and weight lifting. The level at which this happens is called the anaerobic threshold, or typically the lactate threshold as a result of one can begin to detect a rise in blood lactate ranges at this time. Playing basketball or operating utterly around a baseball diamond, for instance, depends closely on this energy-transfer system. Immediate Energy In a brief, intense exercise such as a 100 m dash, the myoglobin in a muscle fiber supplies oxygen for a restricted quantity of aerobic respiration on the outset, but this oxygen provide is rapidly depleted. Free phosphate (Pi) inhibits calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, calcium sensitivity of the contractile mechanism, and drive production by the myofibrils. Longdistance runners and cyclists name this "hitting the wall," and often endeavor to delay fatigue by the use of high-carbohydrate diets before the race, loading the muscle tissue with additional glycogen. The lack of electrolytes via sweating can alter the ion steadiness of the extracellular fluid sufficient to scale back muscle excitability. Exercising muscle generates ammonia, which is absorbed by the brain and inhibits motor neurons of the cerebrum. For this and other reasons not but properly understood, the central nervous system produces less sign output to the skeletal muscles. This is the place psychological factors come into play, corresponding to the need to full a marathon.
Order nexium 20 mg with mastercardMany have repetitious names, corresponding to the best and left muscular tissues of the same name and muscle collection between ribs and vertebrae. Muscle Connective Tissues, Fascicles, and Compartments A skeletal muscle consists of greater than muscular tissue. The connective tissue components, from the smallest to largest and from deep to superficial, are as follows (fig. This is a thin sleeve of free connective tissue that surrounds every muscle fiber. Muscle types are named throughout the highest and an instance of every sort throughout the underside. The endomysium additionally offers the extracellular chemical setting for the muscle fiber and its associated nerve ending. Excitation of a muscle fiber is predicated on the exchange of calcium, sodium, and potassium ions between the endomysial tissue fluid and the nerve and muscle fibers. Fascicles are visible to the naked eye as parallel strands-the grain in a cut of meat; should you pull apart "fork-tender" roast beef, it separates alongside these fascicles. The perimysium carries the bigger nerves and blood vessels in addition to stretch receptors known as muscle spindles. On its outer floor, the epimysium grades into the fascia, and its internal floor points projections between the fascicles to kind the perimysium. This is a sheet of connective tissue that separates neighboring muscles or muscle teams from one another and from the subcutaneous tissue. The biceps brachii of the arm and gastrocnemius of the calf are examples of this sort. Muscle energy is proportional to the diameter of a muscle at its thickest level, and fusiform muscular tissues are relatively robust. Some of those are elongated straps, such as the rectus abdominis of the stomach, sartorius of the thigh, and zygomaticus main of the face. Others are more squarish and are referred to as quadrilateral (four-sided) muscle tissue, such because the masseter of the jaw. Parallel muscle tissue can span lengthy distances, similar to from hip to knee, they usually shorten more than other muscle sorts. However, having fewer muscle fibers than a fusiform muscle of the identical mass, they produce much less pressure. Triangular (convergent) muscle tissue are fan-shaped-broad at one end and narrower on the other. Examples embrace the pectoralis main in the chest and the temporalis on the facet of the top. Despite their small localized insertions on a bone, these muscle tissue are comparatively sturdy as a result of they comprise numerous fibers within the wider a part of the muscle. Their fascicles insert obliquely on a tendon that runs the size of the muscle, like the shaft of a feather. These muscles generate extra drive than the preceding types as a end result of they fit more muscle fibers right into a given length of muscle. When they contract, they constrict the opening and have a tendency to forestall the passage of fabric via it. Examples embrace the orbicularis oculi of the eyelids and the exterior urethral and anal sphincters. Smooth muscle can even kind sphincters-for example, the pyloric valve at the passage from the abdomen to the small gut and a few sphincters of the urinary tract and anal canal. A compartment additionally incorporates the nerves and blood vessels that offer the muscle group. Such compartmentalization happens in the thoracic and abdominal partitions, pelvic flooring, and limbs. The tight binding of muscular tissues by these fasciae contributes to a scientific downside described in Deeper Insight 10. If a blood vessel in a compartment is damaged by overuse or contusion (a bruising injury), blood and tissue fluid accumulate within the compartment. The inelastic fascia prevents the compartment from expanding to relieve the strain. Mounting strain on the muscles, nerves, and blood vessels triggers a sequence of degenerative occasions known as compartment syndrome. If ischemia (poor blood flow) persists for more than 2 to 4 hours, nerves begin to die, and after 6 hours, so does muscle tissue. Nerves can regenerate after the strain is relieved, but muscle necrosis is irreversible. Myoglobinuria, the presence of myoglobin within the urine, gives the urine a dark color and is among the key signs of compartment syndrome and another degenerative muscle issues. Compartment syndrome is treated by immobilizing and resting the limb and, if necessary, making an incision (fasciotomy) to relieve the pressure. The Muscle Attachments Connective tissue parts of a muscle emerge from it as collagenous fibers that proceed into its tendon or different bone attachment, then into the periosteum and matrix of the bone, creating very strong structural continuity from muscle to bone. Some muscular tissues insert not on bones however on the fascia or tendon of one other muscle or on collagen fibers of the dermis. The distal tendon of the biceps brachii, for example, inserts partly on the fascia of the forearm. Many muscles of the face insert within the skin of the lips, eyelids, and different areas, enabling them to produce expressions corresponding to a smile. The triceps brachii is an antagonist of these two muscular tissues and is the prime mover in elbow extension. Which of these muscular tissues have direct attachments to the bones, and which have indirect attachments Direct and Indirect Attachments Muscles have two forms of attachment to bones-direct and oblique. In a direct (fleshy) attachment, such as within the brachialis and the lateral head of the triceps brachii in determine 10. At a microscopic level, however, the muscle fibers stop barely wanting the bone and the hole between muscle and bone is spanned by collagen fibers. In an indirect attachment, the muscle ends conspicuously in need of its bony destination, and the gap is bridged by a fibrous band or sheet referred to as a tendon. You can simply palpate tendons and really feel their texture simply above your heel (your calcaneal or Achilles tendon) and on the anterior facet of your wrist (tendons of the palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis muscles). Collagen fibers of the muscle (the endo-, peri-, and epimysium) proceed into the tendon and from there into the periosteum and matrix of the bone, creating very robust structural continuity from muscle to bone. This term initially referred to the tendon positioned beneath the scalp (hence the word root neuro-), but now it additionally refers to comparable tendons related to sure stomach, lumbar, hand, and foot muscle tissue. For instance, the palmaris longus tendon passes by way of the wrist and then expands into a fanlike palmar aponeurosis beneath the pores and skin of the palm (see fig. In some locations, groups of tendons from separate muscular tissues move under a band of connective tissue referred to as a retinaculum.
Buy 40mg nexium overnight deliveryAfter a meal, the hepatocytes take in glucose, amino acids, iron, nutritional vitamins, and other nutrients from it for metabolism or storage. At the same time, they secrete albumin, lipoproteins, clotting elements, angiotensinogen, and different merchandise into the blood. Between meals, they break down stored glycogen and launch glucose into the circulation. The sinusoids additionally include phagocytic cells known as hepatic macrophages, which take away micro organism and debris from the blood. The liver secretes bile into narrow channels, the bile canaliculi, between the back-to-back layers of hepatocytes within every plate. Bile passes from there into small bile ductules between the lobules, and these converge to ultimately type proper and left hepatic ducts. A brief distance farther on, this is joined by the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder (fig. Their union forms the bile duct, which descends via the lesser omentum toward the duodenum. Near the duodenum, the bile duct joins the duct of the pancreas and forms an expanded chamber known as the hepatopancreatic ampulla. The ampulla terminates at a fold of tissue, the most important duodenal papilla, on the duodenal wall. This papilla contains a muscular hepatopancreatic sphincter, which regulates the passage of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum. Between meals, this sphincter is closed and prevents the discharge of bile into the gut. In cross sections, the stroma is particularly visible within the triangular areas where three or extra lobules meet. The small gut receives not only chyme from the abdomen but in addition secretions from the liver and pancreas, which enter the digestive tract near the junction of the abdomen and small intestine. It has an amazing number of capabilities, but only one of them, the secretion of bile, contributes to digestion. Others are mentioned within the following chapter, which provides a more thorough physiological foundation for understanding nondigestive liver features. Gross Anatomy the liver has four lobes called the proper, left, quadrate, and caudate lobes. They are separated from one another by the falciform14 ligament, a sheet of mesentery that suspends the liver from the diaphragm and anterior belly wall. The spherical ligament (ligamentum teres), also seen anteriorly, is a fibrous remnant of the umbilical vein, which carries blood from the umbilical cord to the liver of a fetus. From the inferior view, we additionally see a squarish quadrate lobe subsequent to the gallbladder and a tail-like caudate15 lobe posterior to that. An irregular opening between these lobes, the porta hepatis,16 is a degree of entry for the hepatic portal vein and correct hepatic artery and some extent of exit for the bile passages, all of which journey within the lesser omentum. Circulation the liver receives blood from two sources: about 70% from the hepatic portal vein and 30% from the hepatic arteries. The hepatic portal vein receives blood from the abdomen, intestines, pancreas, and spleen, and carries it into the liver at the porta hepatis; see the hepatic portal system in table 20. All vitamins absorbed by the small gut attain the liver by this route apart from lipids (transported in the lymphatic system). Arterial blood certain for the liver exits the aorta on the celiac trunk and follows the route shown in determine 20. Both the hepatic portal vein and hepatic arteries travel to the liver by way of the lesser omentum. Within the liver, their finer branches meet one another within the areas between the liver lobules, and both drain into the liver sinusoids. After processing by the hepatocytes, the blood collects within the central vein at the core of the lobule. Blood from the central veins finally converges on a couple of hepatic veins that exit the superior floor of the liver and empty into the close by inferior vena cava. The Gallbladder and Bile the gallbladder is a pear-shaped sac on the underside of the liver that serves to retailer and concentrate bile. It is about 10 cm lengthy and internally lined by a extremely folded mucosa with a easy columnar epithelium. Its head (fundus) often initiatives barely beyond the inferior margin of the liver. Its neck (cervix) leads into the cystic duct, which leads in turn to the bile duct. Bile is a lightweight yellow-green colour when secreted by the liver, however becomes a deep, intense green when concentrated within the gallbladder. It is a watery solution of minerals, cholesterol, impartial fat, phospholipids, bile pigments, bile acids, and lipidtransport vesicles called micelles (explained in section 25. The principal bile pigment is bilirubin, derived from the decomposition of hemoglobin. The liver is omitted to present extra clearly the gallbladder, which adheres to its inferior floor, and the hepatic ducts, which emerge from the liver tissue. About half of this is reabsorbed within the small gut and excreted by the kidneys. Urobilinogen remaining within the gut is transformed to stercobilin, from which feces get their brown shade. In the absence of bile secretion, the feces are grayish white and marked with streaks of undigested fats (acholic feces). Bile acids, micelles, and lecithin, a phospholipid, help in fats digestion and absorption, as discussed later. When these waste merchandise turn into excessively concentrated, they may kind gallstones (see Deeper Insight 25. Bile will get into the gallbladder by first filling the bile duct, then overflowing into the gallbladder. Between meals, the gallbladder absorbs water and electrolytes from the bile and concentrates it by an element of 5 to 20 instances. About 80% of the bile acids are reabsorbed within the ileum, the last portion of the small gut, and returned to the liver, the place the hepatocytes absorb and resecrete them. This route of secretion, reabsorption, and resecretion, referred to as the enterohepatic circulation, reuses the bile acids two or extra times in the course of the digestion of a mean meal. The liver synthesizes new bile acids from cholesterol to replace the quantity misplaced in the feces. Cholelithiasis, the formation of gallstones, is most typical in overweight women over the age of forty and normally results from excess cholesterol.
Cheap nexiumThe definition of calorie and how this relates to dietary Calories (kilocalories) 9. Principal dietary sources of calories; the relative yield from fat as compared to carbohydrates and proteins; and the that means of empty calories 10. The distinction between macronutrients and micronutrients; the vitamins in every category 12. Forms and quantities of stored and cellular carbohydrates within the body; how the physique makes use of carbohydrates; how dietary carbohydrates affect the metabolism of fats 14. Hormones that regulate the balance between blood glucose and saved glycogen; the conventional vary of blood glucose concentration 15. The beneficial every day consumption of carbohydrates; the percentage of calories that come from carbohydrates in a typical U. What cells are primarily responsible for storing and releasing triglycerides; the essence of the lipogenesis and lipolysis carried out by these and other cells 2. The which means of ketogenesis; the metabolic use of ketone our bodies and the pathological effects of extreme ketone ranges; widespread circumstances by which excessive ketogenesis occurs four. A typical daily fee of protein turnover within the physique; where and why the fastest price of protein turnover happens; and the dietary and nondietary sources of the amino acids absorbed by the small gut 5. When the body is in its absorptive state; what issues happen in this state with respect to carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism 2. The primary hormone that regulates the absorptive state; its major metabolic results on this state; and what antagonist modulates its effects three. When the physique is in its postabsorptive state; what issues occur in this state with respect to carbohydrate, fat, and generally protein metabolism 4. Hormones that regulate the postabsorptive state, their results, and the position of the sympathetic nervous system in its regulation 5. The that means of thermoregulation; phrases for abnormally low and high body temperatures; and reasons why those two situations can be fatal 2. How most physique warmth is produced, and which organs are an important sources of body heat at relaxation and in exercise four. Four mechanisms by which body heat is misplaced, and the odds of total warmth loss attributable to each of them at relaxation and at a snug ambient temperature (21�C) 5. Two mechanisms for decreasing body temperature and two mechanisms of elevating it; areas of the hypothalamus concerned in every 7. The meanings of nonshivering thermogenesis and behavioral thermoregulation, and examples of the latter eight. Differences between warmth cramps, warmth exhaustion, and heatstroke; the position of positive feedback loops in hyperthermia; and how and at what temperature range heatstroke can lead to demise 9. The function of constructive feedback loops in hypothermia, and how and at what temperature vary hypothermia can lead to demise Testing Your Recall 1. Which of the next store(s) the best quantity of power for the smallest amount of area within the physique The brightly coloured, iron-containing, electron-transfer molecules of the internal mitochondrial membrane are referred to as 20. The circulate of H+ from the intermembrane house to the mitochondrial matrix creates an electrical present used by the enzyme to make. Extremely low-fat fad diets are inclined to produce potentially harmful excessive levels of blood ketones. Gluconeogenesis happens particularly in the absorptive state throughout and shortly after a meal. At an air temperature of 21�C (70�F), the physique loses more warmth as conduction to the surrounding air than by another means. Also clarify whether or not cyanide poisoning might be handled by giving a affected person supplemental oxygen, and justify your reply. Chapter 17 defines and describes some hormone actions that are synergistic and antagonistic. Identify some synergistic and antagonistic hormone interactions within the postabsorptive state of metabolism. Explain why a patient whose liver has been extensively broken by hepatitis could present elevated concentrations of thyroid hormone and bilirubin within the blood. Your understanding of male reproductive anatomy may benefit if you refresh your reminiscence of the pelvic girdle (see part 8. Sexual development and adult operate depend upon the gonadotropins and sex steroids launched in sections 17. The physique suffers numerous degenerative changes as we age, and ultimately our time is up and we must say good-bye. In this chapter, we study some general aspects of human reproductive biology after which concentrate on the function of the male in replica. The subsequent two chapters deal, respectively, with feminine reproductive perform and on the embryonic growth of people and modifications on the other finish of the life span-the modifications of old age. Two issues are essential for reproduction to be successful: gamete motility to permit them to achieve contact, and nutrients for the creating embryo. In any sexually reproducing species, by definition, a person that produces eggs is female and one which produces sperm is male. In mammals, the female can also be the mother or father that provides a sheltered inner surroundings for the development and diet of the embryo. For fertilization and growth to occur in the female, the male will need to have a copulatory organ, the penis, for introducing his gametes into the feminine reproductive tract, and the female will have to have a copulatory organ, the vagina, for receiving the sperm. This is the obvious distinction between the sexes, but appearances could be deceiving (see fig. Overview of the Reproductive System the reproductive system in the male serves to produce sperm and introduce them into the feminine physique. The feminine reproductive system produces eggs, receives the sperm, provides a spot for the union of those gametes, harbors the fetus, offers delivery, and nourishes the offspring. The main sex organs, or gonads,three are organs that produce the gametes-testes of the male and ovaries of the female. The secondary sex organs are organs aside from gonads which are needed for copy. In the male, they represent a system of ducts, glands, and the penis, involved with the storage, survival, and conveyance of sperm. In the feminine, they embody the uterine tubes, uterus, and vagina, concerned with uniting the sperm and egg and harboring the fetus. According to location, the reproductive organs are categorized as external and inside genitalia (table 27. Most of them are externally visible, aside from the accessory glands of the feminine perineum. The internal genitalia are situated primarily within the pelvic cavity, except for the male testes and a few related ducts contained in the scrotum. Secondary intercourse traits are features that additional distinguish the sexes and play a job in mate attraction.

Order nexium onlineIn compelled respiration, the accent muscle tissue raise intrapulmonary strain as excessive as +40 cm H2O. The impact of pulmonary elasticity is obvious in a pathological state of pneumothorax and atelectasis. If the thoracic wall is punctured between the ribs, for instance, inspiration sucks air via the wound into the pleural cavity and the visceral and parietal pleurae separate; what was a possible space between them becomes an air-filled cavity. Without the negative intrapleural pressure to hold the lungs inflated, the lungs recoil and collapse. Atelectasis can also result from airway obstruction-for instance, by a lung tumor, aneurysm, swollen lymph node, or aspirated object. Resistance to Airflow Pressure is one determinant of airflow; the other is resistance. Two factors are of particular importance: diameter of the bronchioles and pulmonary compliance. Like arterioles, the massive variety of bronchioles, their small diameter, and their ability to change diameter make them the first technique of controlling resistance. The trachea and bronchi can also change diameter to a degree, however are more constrained by the supporting cartilages in their walls. Epinephrine and the sympathetic nerves (norepinephrine) stimulate bronchodilation and increase airflow. All pressures given listed under are relative to atmospheric pressure exterior to the body, which is considered to be zero as a point of reference. Note that pressures governing respiratory airflow are measured in cm H2O (centimeters of water), not mm Hg. Like bucket handles, each rib is attached at both ends (to the spine and sternum) and swings up and down during inspiration and expiration. Many people have suffocated from the acute bronchoconstriction brought on by anaphylactic shock or bronchial asthma (see Deeper Insight 21. Pulmonary compliance means the ease with which the lungs broaden, or extra exactly, the change in lung volume relative to a given strain change. Inspiratory effort may produce the same intrapleural pressure in two individuals, however the lungs will expand much less in an individual with poorer compliance (stiffer lungs), or at least that individual should expend extra effort to inflate the lungs to the same diploma as the other. Compliance is lowered by degenerative lung illnesses such as tuberculosis and black lung illness, by which the lungs are stiffened by scar tissue. In such conditions, the thoracic cage expands normally however the lungs increase comparatively little. A main limitation on pulmonary compliance is the thin movie of water on the respiratory epithelium, especially from the respiratory bronchioles to the alveoli. This film is necessary for gasoline exchange, however creates a potential problem for pulmonary air flow. Water molecules are attracted to each other by hydrogen bonds, creating floor tension, as we noticed in part 2. You can respect the energy of this attraction should you mirror on the issue of separating two sheets of wet paper compared with two sheets of dry paper. If it went unchecked, components of the airway would collapse with every expiration and would strongly resist reinflation. This is particularly so in small airways such as the respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts leading to the alveoli. The resolution to this problem takes us again to the nice alveolar cells and their surfactant. A surfactant is an agent that disrupts the hydrogen bonds of water and reduces floor pressure; soaps and detergents are on an everyday basis examples. These molecules are partially hydrophobic, so that they spread out over the floor of the water movie, partially embedded in it like ice cubes floating in a bowl of water. As the small airways deflate, the surfactants are squeezed nearer together, like the ice cubes being pushed collectively into a smaller area. If the air spaces have been lined with a movie of water solely, they could continue collapsing, as a result of water molecules can pile up right into a thicker film of moisture. As they turn into crowded into a small area and resist layering, they retard after which halt the collapse of the airway. Patients just lately out of surgical procedure are inspired to breathe deeply, even though it may harm, to have the ability to promote this unfold of surfactant up the alveolar ducts and small bronchioles. Premature infants typically have a deficiency of pulmonary surfactant and experience great problem respiration (see "Premature Infants" in section 29. Alveolar Ventilation Air that really enters the alveoli becomes available for gasoline change, but not all inhaled air gets that far. The lifeless area is typically about 1 mL per pound of physique weight in a healthy particular person. Some alveoli could also be unable to trade gases as a outcome of they lack blood circulate or because the pulmonary membrane is thickened by edema or fibrosis. Physiological (total) lifeless area is the sum of anatomical dead house and any pathological alveolar lifeless space that may exist. In a state of relaxation, parasympathetic stimulation keeps the airway considerably constricted. This minimizes the dead space in order that more of the inhaled air ventilates the alveoli. In a state of arousal or exercise, in contrast, the sympathetic nervous system dilates the airway, which will increase airflow. If an individual inhales 500 mL of air and a hundred and fifty mL of it stays in the lifeless house, then 350 mL ventilates the alveoli. Beyond this point, the air passages are so slim and their resistance to move is so great that bulk circulate ceases. Oxygen completes its journey to the alveoli, and carbon dioxide leaves them, by easy diffusion. Pulsation of the pulmonary arteries generated by the heartbeat most likely accelerates this process, nonetheless. It takes about ninety seconds, or roughly 18 breaths at a mean price and depth of respiration, to fully exchange all pulmonary air. Four of those values are called respiratory volumes: tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, and residual volume. This air allows gasoline trade with the blood to proceed even between the times one inhales fresh air. Vital capacity, the utmost capacity to ventilate the lungs in one breath, is an particularly necessary measure of pulmonary health. Spirometry helps to assess and distinguish between restrictive and obstructive lung disorders.
References - Hoffman RM, Stone SN, Hunt WC, et al: Effects of misattribution in assigning cause of death on prostate cancer mortality rates, Ann Epidemiol 13(6):450-454, 2003.
- Giannantoni A, Rossi A, Mearini E, et al: Botulinum toxin A for overactive bladder and detrusor muscle overactivity in patients with Parkinsonis disease and multiple system atrophy, J Urol 182:1453n1457, 2009.
- Stein JP, Hertz J, Nichols PW: Urethral recurrence in a woman after continent orthotopic urinary diversion for bladder cancer, Urology 71(4):755.e1n755. e2, 2008.
|
|