"Purchase 20mg levitra oral jelly mastercard, impotence female."By: Lilja Bjork Solnes, M.B.A., M.D. - Program Director, Diagnostic Radiology Residency
- Assistant Professor of Radiology and Radiological Science
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/5251718/lilja-solnes
Cheap levitra oral jelly 20 mg onlineIt is hoped that figuring out particular genes inflicting vertigo syndromes will result in a greater understanding of the mechanisms and also create the chance to develop specific remedies in the future. Though most individuals report nonspecific types of dizziness, nearly 25% of those individuals report true vertigo. Dizziness is more widespread among females and older folks and has essential healthcare utilization implications as a outcome of up to 80% of sufferers with dizziness seek medical care sooner or later. Hearing loss affects roughly 16% of adults (age >18 years) within the United States (Lethbridge-Cejku et al. Men are more generally affected than girls, and the prevalence of hearing loss increases dramatically with age, in order that by age seventy five, nearly 50% of the population reviews listening to loss, which is a typical reason for disability. The most common kind of listening to loss is sensorineural, and each idiopathic presbycusis and noise-induced forms are widespread etiologies. Endolymph fills up the fluid-filled sac and is separated by a membrane from the perilymph. These fluids primarily differ of their composition of potassium and sodium, with the endolymph resembling intracellular fluid with a excessive potassium and low sodium content, and perilymph resembling extracellular fluids with a low potassium and excessive sodium content material. Thin straight arrows point out the course of slow elements; thick straight arrows point out the course of quick parts; curved arrows show the path of endolymph flow within the horizontal semicircular canals. The cochlea senses sound waves after they travel by way of the external auditory canal and are amplified by the tympanic membrane and ossicles of the middle ear (Baloh and Kerber, 2011). The stapes, the last of three ossicles within the middle ear, contacts the oval window, which directs the forces associated with sound waves alongside the basilar membrane of the cochlea. These forces stimulate the hair cells, which in flip generate neural alerts in the auditory nerve. The auditory nerve enters the lateral brainstem at the pontomedullary junction and synapses within the cochlear nucleus. Some projections journey from the superior olivary advanced to the inferior colliculus by way of the lateral lemnisci, and others terminate in one of the nuclei of the lateral lemniscus. Next, fibers travel to the ipsilateral medial geniculate body, after which auditory radiations move via the posterior limb of the interior capsule to attain the auditory cortex of the temporal lobe. The peripheral vestibular system is composed of three semicircular canals, the utricle and saccule, and the vestibular element of the eighth cranial nerve (Baloh and Kerber, 2011). Each semicircular canal has a sensory epithelium known as the crista; the sensory epithelium of the utricle and saccule is known as the macule. The semicircular canals sense angular movements, and the utricle and saccule sense linear movements. Two of the semicircular canals (anterior and posterior) are oriented within the vertical airplane almost orthogonal to one another; the third canal is oriented within the horizontal plane (horizontal canal). The crista of every canal is activated by movement occurring within the aircraft of that canal. Signals originating from the horizontal semicircular canal then move via the medial longitudinal fasciculus along the ground of the fourth ventricle to the abducens nuclei in the middle brainstem and the ocular motor complex in the rostral brainstem. The anterior (also referred to because the superior) and posterior canal impulses cross from the vestibular nuclei to the ocular motor nucleus and trochlear nucleus, triggering eye movements roughly in the aircraft of every canal. A key function is that when vestibular alerts depart the vestibular nuclei they divide into vertical, horizontal, and torsional elements. As a result, a lesion of central vestibular pathways may cause a pure vertical, pure torsional, or pure horizontal nystagmus. The main vestibular afferent nerve fibers maintain a constant baseline firing rate of motion potentials. When the baseline fee from every ear is symmetrical (or an asymmetry has been centrally compensated), the eyes stay stationary. With an uncompensated asymmetry in the firing fee, resulting from either increased or decreased activity on one facet, slow ocular deviation outcomes. The aircraft by which the eyes deviate as a end result of vestibular stimulation depends on the mix of canals which are stimulated (Table forty six. This explains why a whole unilateral peripheral vestibular system can be surgically destroyed and sufferers only expertise vertigo for a number of days to weeks. Other common examination measures to contemplate in particular person patients include a visible evaluation (adequate vision is essential for balance) and a musculoskeletal inspection (significant arthritis can impair gait). The cranial nerves should be completely assessed in sufferers complaining of dizziness. The most necessary a part of the examination is the ocular motor examination (described in more detail in the Neuro-otological Examination section). A posterior fossa mass can impair facial sensation and the corneal reflex on one facet. Assessing facial power and symmetry is important due to the close anatomical relationship between the seventh and eighth cranial nerves. The decrease cranial nerves should also be carefully inspected by observing palatal elevation, tongue protrusion, and trapezius and sternocleidomastoid power. The general motor examination determines power in each muscle group and likewise assesses bulk and tone. Increased tone or cogwheel rigidity could be the primary finding in a affected person with an early neurodegenerative dysfunction. The peripheral sensory examination is important as a end result of a peripheral neuropathy may cause a nonspecific dizziness or imbalance. One should think about the traditional lower in vibratory sensation and absence of ankle jerks that may happen in aged patients. Coordination is a crucial a half of the neurological examination in sufferers with dizziness as a outcome of problems characterised by ataxia can current with the principal symptom of dizziness. Often, sufferers have problem describing the exact symptom skilled, so the onus is on the clinician to elicit pertinent data. No clinician should ever be satisfied to report the complaint simply as "dizziness. Because affected person descriptions about dizziness could be unreliable and inconsistent (Newman-Toker et al. The physician should also ask the following questions: Is the symptom fixed or episodic, are there accompanying signs, how did it start (gradual, sudden, and so on. If episodic, what was the length and frequency of assaults, and were there triggers Identifying orthostatic drops in blood strain could be diagnostic within the appropriate medical setting. Orthostatic hypotension might be the commonest basic medical explanation for dizziness among patients referred to neurologists. Neuro-otologicalExamination the neuro-otological examination is a specialty examination expanding upon certain features of the general neurological examination and also contains an audio-vestibular evaluation. Ocular Motor (see Chapter 44) step one in assessing ocular motor perform is to search for spontaneous involuntary actions of the eyes. The examiner asks the patient to look straight ahead while observing for nystagmus or saccadic intrusions. Nystagmus is characterized by a slow- and fast-phase part and is classed as spontaneous, gaze-evoked, or positional. The course of nystagmus is conventionally described by the path of the quick part, which is the path it seems to be "beating" towards.
Syndromes - Medicines to treat the effects of the poison
- If you find yourself becoming annoyed or angry with your baby, put him in the crib and leave the room. Try to calm down. Call someone for support.
- Retinoblastoma
- Benzodiazepines such as diazepam (Valium) or lorazepam (Ativan) to decrease agitation, seizure-like movements, and muscle stiffness
- Corn
- Kawasaki disease
- Complete blood count (CBC) with white blood cell differential
- Endoscopic esophageal ultrasound (EUS) with biopsy
- Decreased appetite
- Insomnia
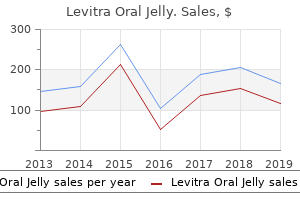
Order 20mg levitra oral jelly with amexThe higher plexus, C5 and C6, mostly is affected, though the lower plexus can be concerned. Sensory nerve motion potentials could also be misplaced distally in a plexopathy, however not in a radiculopathy, because of its preganglionic location, leaving the distal branches of the sensory neurons intact. The brachial and lumbar plexuses are in proximity to the areas that might be infiltrated by tumors, including those involving the lymph nodes, lungs, kidneys, and other stomach organs. Neoplastic plexus compression or infiltration manifests as a progressive painful monoparesis. Limb actions that stretch the plexus elicit pain, and the affected person tends to maintain the limb motionless to keep away from exacerbating the ache. Neoplastic infiltration of the brachial plexus often includes the decrease plexus, C8 to T1. Radiation remedy in the region of the plexus can produce progressive dysfunction. Diabetic amyotrophy is a lumbar plexopathy affecting axons mainly forming the femoral nerve. Although a length-dependent diabetic peripheral neuropathy may be an accompanying function, the femoral distribution signs and signs overshadow the opposite findings. Patients finally enhance, though the restoration often is prolonged and incomplete. It is difficult to study nerve conduction of the femoral nerve, so this check is diagnostically helpful provided that outcomes are regular. Progressive weakness develops over months to years and may ultimately plateau with out further worsening. Onset normally is in young maturity, on the age of roughly 20 years, and men are predominantly affected. A poliomyelitis-like syndrome may finish up from viruses other than the poliovirus itself, including West Nile virus. The sickness normally manifests with acute asymmetrical weakness after an preliminary section of encephalitic signs together with headache, meningeal indicators, and probably confusion or seizures. Common presentation is predominant unilateral weakness, cramping, fasciculations and losing in the hand and arm, but the legs may be affected. Neuronopathies Neuronal degenerations often affect multiple particular person nerve distributions and usually contain more than one limb. Monomelic amyotrophy is a situation by which motoneurons of 1 limb degenerate; typically the distribution suggests involvement of specific motoneuron columns in the spinal twine. Some important points in the differential analysis with such shows are considered subsequent. The deficit of migraine evolves in preserving with the migration of spreading despair throughout the cerebral cortex- thus, over minutes the deficit marches from hand up arm to face, for example. Weakness with migraine usually precedes headache however could accompany headache or may even not be related to headache in some situations. Seizure is recommended by abrupt onset and offset of the deficit, and any related signs of decreased response or twitching. Note that acute lesions will not be related to hyperreflexia and upgoing plantar response- these reflex alterations take time to develop. Brainstem lesions are commonly related to cranial nerve deficits, especially diplopia from disturbance of ocular motor facilities. Spinal wire lesions normally produce bilateral deficits below the level of the lesion, with each motor and sensory involvement. With weak point in the intrinsic muscular tissues of the hand, the cause may be a lesion of the median nerve, ulnar nerve, brachial plexus, or cerebral cortex. Most of the intrinsic muscular tissues of the hand are innervated by the ulnar nerve, so an isolated distal ulnar lesion produces profound lack of use of the hand. This lesion must be differentiated from a lateral frontocentral cerebral lesion which, if located within the hand region, produces prominent loss of unbiased digit use. A median nerve lesion produces impaired hand perform due to lack of function of the finger and wrist flexors greater than of the intrinsic muscle tissue of the hand. With stabilization of the hand, intact function of ulnar- and radial-innervated muscles could be demonstrated to rule out lesions at or above the plexus. Lower brachial plexus lesions produce dysfunction of the median- and ulnar-innervated intrinsic muscular tissues of the hand and likewise could have an effect on the lengthy finger flexors. This dramatic loss of function may be mistaken for central weakness, because the deficit spans peripheral nerve distributions. A small cerebral cortical lesion can produce incapability to use the hand, with out signs of different deficit. The mixture of cupping of the outstretched hand and pronator drift strongly suggests a central lesion. Peroneal nerve palsy ends in weak spot of foot dorsiflexion and eversion, with relative preservation of different motor features. Weakness of foot inversion suggests a cerebral lesion, as a result of it is a tibial nerve operate and never expected with peroneal palsy. Cerebral lesions producing lower leg weakness often cause upgoing plantar response and hyperactivity of the Achilles tendon reflex, despite little clinical proof of gastrocnemius muscle involvement. This article discusses monoplegia rather than paraplegia (see Chapter 24), but with leg weak point, you will need to differentiate between lower spinal wire dysfunction and cauda equina compression, between upper spinal twine involvement and cervical spondylotic myelopathy, and between these problems and midline cerebral lesions producing leg weakness. Cauda equina lesions normally are as a end result of acute disk herniations, spondylosis, or tumors in the lumbosacral spinal canal. The lumbar and sacral nerve roots are compressed, resulting initially in a depolarizing block however later axonal degeneration, which produces motor and sensory loss. Pain, sensory loss, and weakness sometimes are worsened by standing and relieved by flexing the lumbar backbone. Spondylotic myelopathy is compression of the spinal twine by degenerative spondylosis, normally within the cervical area. Differentiation among cauda equina, spinal twine, and cortical lesions can be tricky however in general the following guidelines apply: � Bowel and bladder incontinence can develop with all three locations however is more widespread with cauda equina lesions. Cauda equina lesions are associated with depressed reflexes, whereas spinal twine and cerebral lesions are characterized by hyperactive reflexes and upgoing plantar responses. Radial neuropathy manifests with weakness of the wrist extensors, which if extreme can lead to destabilization of the intrinsic muscle tissue of the hand and lengthy finger flexors; these median- and ulnar-innervated muscle tissue require opposition from radial-innervated extensors for correct perform. Therefore, the deficit appears more extensive than could be expected on the idea of a radial lesion alone. A cerebral lesion is suggested; though cerebral lesions span neural distributions, wrist extension may be more obviously affected than grip or finger flexion. Differentiation of radial neuropathy from a cerebral lesion is dependent upon demonstration of intact median and ulnar nerve perform by the examiner, following stabilization of the finger flexors and wrist. Also, corticospinal tract signs and other indicators of cortical injury (aphasia or neglect) should be looked for in a affected person with a potential cerebral infarct. The underlying dysfunction in leg weak spot could additionally be peroneal nerve palsy or a lesion of the paramedian cerebral cortex.
Purchase 20mg levitra oral jelly mastercardEach stage contributes sensory and motor function, however that of upper centers is extra complicated and dispersed inside the nervous system. Lower degree motor gait issues are as a result of diseases of the muscle and peripheral nerves that produce muscle weak point. Lower level sensory gait disorders comply with lack of one of many three fundamental senses necessary for gait and stability: proprioception, imaginative and prescient, and vestibular sensation. Myopathic Weakness and Gait Weakness of proximal leg and hip-girdle muscles interferes with stabilizing the pelvis and legs on the trunk during all phases of the gait cycle. Failure to stabilize the pelvis produces exaggerated rotation of the pelvis with every step and a waddling gait. The hips are barely flexed on account of weakness of hip extension, and an exaggerated lumbar lordosis occurs. A myopathy is the commonest cause of proximal muscle weak spot, but neurogenic weakness of proximal muscle tissue can also produce this clinical image. Joint position sense must be examined for defects of proprioception in the ataxic patient or awkward posturing of the foot. Other signs similar to a supranuclear gaze palsy, ataxia, and frontal lobe release indicators should be sought the place relevant. Inability to draw a circle with the foot could indicate dyspraxia as seen in corticobasal syndromes. Neurogenic Weakness and Gait Muscle weak point of peripheral nerve origin, as in a neuropathy, sometimes affects distal leg muscular tissues and leads to a steppage gait. The patient lifts the leg and foot high above the ground with every step because of weakness of ankle dorsiflexion and foot drop. When this clinical image is confined to one leg (unilateral foot drop), a standard peroneal or sciatic nerve palsy or an L5 radiculopathy is the standard trigger. Less frequent is foot drop caused by myopathic weak spot, as within the scapuloperoneal syndromes. A femoral neuropathy, as in diabetes mellitus, produces weakness of knee extension and buckling of the knee when strolling or standing. Progressive muscular atrophy in motor neuron disease or a quadriceps myopathy brought on by inclusion physique myositis could end in comparable focal weakness. A patient with cerebellar gait ataxia caused by a vermis lesion may carry out the heel-to-shin check normally when supine but is ataxic when strolling. The discovering of regular muscle energy, muscle tone, and tendon reflexes is common in dystonic syndromes during which an motion dystonia causes irregular posturing of the feet solely when walking. A dystonic gait may be evident solely when running or strolling ahead however not when strolling backward. Gegenhalten (paratonia), with or with out brisk tendon reflexes, may be the solely abnormal signal in the recumbent patient with a frontal lobe lesion, hydrocephalus, or diffuse cerebrovascular disease who is totally unable to stroll when standing. Such sufferers perform the heel-shin take a look at and make bicycling movements of their legs usually when lying on a bed. A related discrepancy can be seen in spastic paraplegia brought on by hereditary spastic paraplegia, cerebral palsy (Little disease), or cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Minor changes in muscle tone, power, and tendon reflexes are evident through the supine examination, in contrast to profound leg spasticity when standing and trying to stroll. The leg tremor of orthostatic tremor solely appears during weight bearing, especially when standing still. Sensory Ataxia Loss of proprioceptive enter and joint position sense from the lower limbs deprives the patient of data of the place of the legs and toes in area, the progress of ongoing movement, the state of muscle contraction, and finer particulars of the feel of the surface on which the affected person is strolling. Patients with sensory ataxia undertake a wide base and advance cautiously, taking slow steps underneath visible steerage. The sole of the foot strikes the ground forcibly with a slapping sound (slapping gait). The absence of visual information when walking at evening or in the course of the Romberg take a look at leads to imbalance and falls. Sensory ataxia is the outcomes of deafferentation because of interruption of large-diameter proprioceptive afferent fibers in peripheral neuropathies, posterior root or dorsal root ganglionopathies, and dorsal column lesions. Paradoxically, unsteadiness and veering whereas working could additionally be much less evident than when walking in acute vestibulopathy. In general, patients with an acute vestibulopathy favor to lie nonetheless to reduce the signs of acute vestibular imbalance. In chronic vestibular failure, gait may be normal, though unsteadiness can be unmasked throughout eye closure and rotation of the pinnacle from side to facet while walking. Acute vestibular imbalance in the lateral medullary syndrome results in tilt and veering toward the side of the lesion (lateropulsion). Other distinguishing features embody changes in muscle tone, such as spasticity in hereditary spastic paraparesis and rigidity in dystonic paraparesis. In young children, the excellence is important as a result of a proportion of such patients could be treated successfully with levodopa (discussed in the following sections). Cerebellar Ataxia Disease of the midline cerebellar constructions, the vermis, and anterior lobe produces loss of truncal balance, elevated physique sway, dysequilibrium, and gait ataxia. When standing, the patient adopts a wide-based stance; the legs are stiffly extended and the hips slightly flexed to crouch forward and decrease truncal sway. Midline cerebellar pathologies embrace structural lesions (masses, hemorrhage), paraneoplastic syndromes, and malnutrition in alcoholism. This combination of truncal gait ataxia and truncal tremor is characteristic of some late-onset anterior lobe cerebellar degenerations. Lesions of the cerebellar flocculonodular lobe (the vestibulocerebellum) exhibit multidirectional body sway, dysequilibrium, and extreme impairment of body and truncal movement. Standing and even sitting may be inconceivable, though when mendacity down, the heel-shin take a look at could appear regular, and higher limb perform may be relatively preserved. Limb ataxia because of involvement of the cerebellar hemispheres is characterised by a decomposition of normal leg movement. Steps are irregular and variable in timing (dyssynergia), size, and path (dysmetria). These defects are accentuated when attempting to walk heel to toe in a straight line. Vascular illness and mass lesions are generally liable for hemisphere lesions. Cerebellar gait ataxia is exacerbated by the speedy postural adjustments needed to change direction, turn a nook or avoid obstacles, and when stopping or starting to stroll. Eye closure could heighten nervousness about falling and improve physique sway, but not to the extent noticed in a sensory ataxia. Episodic ataxias produce periods of impaired gait that typically final seconds to hours.
Buy generic levitra oral jelly 20 mgTo carry out these, a tuning fork (256 Hz or 512 Hz) is gently struck on a tough rubber pad, the elbow, or the knee about two-thirds of the way along the tine. To conduct the Weber take a look at, the bottom of the vibrating fork is placed on the vertex (top or crown of the head), bridge of the nostril, upper incisors, or brow. Patients typically experience brief episodes of vertigo when getting in and out of bed, turning in bed, bending down and straightening up, or extending the head again to lookup. As famous earlier, the condition is brought on when calcium carbonate debris dislodged from the otoconial membrane inadvertently enters a semicircular canal. The debris may be free-floating throughout the affected canal (canalithiasis) or caught towards the cupula (cupulolithiasis). Once the particles is out of the canal, sufferers are instructed to avoid excessive head positions to prevent the particles from re-entering the canal. Meniere Disease Meniere illness is characterized by recurrent assaults of vertigo related to auditory signs (hearing loss, tinnitus, aural fullness) throughout assaults. Thus the term vestibular Meniere disease, previously used for patients with recurrent episodes of vertigo however no listening to loss, is not used. Though often a dysfunction involving just one ear, Meniere illness turns into bilateral in about one-third of sufferers. Endolymphatic hydrops, or growth of the endolymph relative to the perilymph, is considered the etiology, although the underlying trigger is unclear. Additionally, the attribute histopathological modifications of endolymphatic hydrops have been identified in temporal bone specimens of sufferers with no medical history of Meniere disease (Merchant et al. Some sufferers with well-documented Meniere disease expertise abrupt episodes of falling to the bottom, with out loss of consciousness or related neurological signs. These episodes have been known as otolithic catastrophes of Tumarkin due to the suspicion that they symbolize acute stimulation of the otoliths. The bedside interictal examination of patients with Meniere illness may determine asymmetrical hearing, but the head-thrust test is often regular. Treatment is initially directed toward an aggressive low-salt diet and diuretics, though the proof for these therapies is poor. Sectioning of the vestibular nerve and destruction of the labyrinth are different procedures (Minor et al. Patients with this disorder report recurrent episodes of extreme vertigo with out auditory signs creating years after a severe unilateral hearing loss attributable to a viral or bacterial infection. The oval and round windows direct the forces associated with sound waves into the cochlea and along the spiral basilar membrane. A break within the bony capsule of the semicircular canals can redirect some of the sound or strain to the semicircular canals causing vestibular activation, a phenomenon known as Tullio phenomenon. Surgically repairing the defect can be tried if the patient is debilitated by the signs, but many patients do properly with conservative management. Other vestibular fistulae can result from trauma or erosion of a cholesteatoma into the horizontal semicircular canal. Other Peripheral Disorders There are many other peripheral vestibular causes of vertigo, however most are uncommon. Vertigo usually follows a blow to the top, even and not using a corresponding temporal bone fracture. This so-called labyrinthine concussion outcomes from the susceptibility of the delicate structures of the internal ear to blunt trauma. The bilateral vestibular loss often goes unrecognized because the vestibular symptoms could be overshadowed by auditory or different symptoms. Although essentially the most distinguished vestibular signs of bilateral vestibulopathy are oscillopsia and imbalance, some nonspecific dizziness and vertigo attacks may occur as well. Vestibular schwannomas sometimes present with slowly progressive unilateral hearing loss, however hardly ever vertigo can occur. Finally, any dysfunction affecting the skull base, corresponding to sarcoidosis, lymphoma, bacterial and fungal infections, or carcinomatous meningitis, could cause both unilateral or bilateral peripheral vestibular symptoms. Vestibular Paroxysmia Vestibular paroxysmia is characterised by transient (seconds to minutes) episodes of vertigo, occurring suddenly without any obvious set off (Hufner et al. The disorder could also be analogous to hemifacial spasm and trigeminal neuralgia, which are felt to be as a end result of spontaneous discharges from a partially damaged nerve. In sufferers with vestibular paroxysmia, unilateral dysfunction can typically be recognized on vestibular or auditory testing. However, many asymptomatic topics have a standard vessel mendacity on the eighth nerve (usually the anterior inferior cerebellar artery), and most vestibular paroxysmia patients have a favorable course with conservative or medicine management (Hufner et al. Medications associated with a discount in episodes include carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, and gabapentin (Hufner et al. Because central issues can mimic peripheral vestibular disorders, the simplest method in patients with isolated dizziness is first to rule out common peripheral causes. Vestibular Fistulae Superior canal dehiscence was first described in 1998 (Minor et al. As the name implies, dehiscence of the bone overlying the superior canal results in a fistula between the superior canal and the middle cranial fossa. Normally the Brainstem or Cerebellar Ischemia/Infarction Ischemia affecting vestibular pathways inside the brainstem or cerebellum usually causes vertigo. Brainstem ischemia is often accompanied by other neurological indicators and Neuro-otology: Diagnosis and Management of Neuro-otological Disorders 593 symptoms, as a outcome of motor and sensory pathways are in close proximity to vestibular pathways. Central causes of nystagmus can sometimes carefully mimic the peripheral vestibular sample of spontaneous nystagmus (Lee et al. Epilepsy Vestibular signs are widespread with focal seizures, particularly those originating from the temporal and parietal lobes. The key to differentiating vertigo with seizures from different causes of vertigo is that seizures are almost invariably related to an altered stage of consciousness. Episodic vertigo as an isolated manifestation of a focal seizure is a rarity if it happens at all. The key to the prognosis is to find lesions disseminated in time and area within the nervous system. VertigoinInheritedDisorders the scientific analysis of patients presenting with dizziness has historically hinged on the historical past of current sickness and examination. However, with the current rapid advances in molecular biology, it has turn out to be obvious that many causes of vertigo have a powerful genetic element. Because of this, acquiring a complete household history is essential, particularly in patients and not utilizing a specific prognosis for their dizziness. Since the signs of those familial disorders are sometimes not debilitating and may be extremely variable, merely asking the patient about a family history on the time of the appointment will not be sufficient. The affected person ought to be instructed to specifically interview other members of the family concerning the prevalence of those signs. Migraine Migraine is a heterogeneous genetic dysfunction characterised by headaches in addition to many other neurological signs. Linkage analysis has identified a variety of chromosomal loci in frequent types of migraine, but no specific genes have been found. Dizziness has long been known to happen amongst patients with migraine complications, and benign recurrent vertigo is normally a migraine equivalent as a result of no different indicators or symptoms develop over time, the neurological examination remains regular, and a household or personal historical past of migraine complications is widespread, as are typical migraine triggers.
20 mg levitra oral jelly for saleA very complete analysis of the assorted neurological dysfunctions ensuing from cerebellar pathology could be present in a recent publication (Manto et al. Detailed description of particular cerebellar disorders could be discovered elsewhere on this guide. SymptomsinPatientswithAtaxia Gait Disturbances Patients with cerebellar and sensory ataxia often current with abnormalities of gait. The preliminary signs may be a way of insecurity while strolling, particularly when performing acts that require a bit extra skill, corresponding to turning or balancing on a narrow ledge. Even earlier than gait turns into abnormal, sufferers might notice problems with specialized abilities similar to snowboarding, bicycling, or climbing. Patients might report the sense of imbalance as dizziness, but the sensation is extra like being on a ship rather than vertigo. Patients and household notice that the patient feels more secure with the toes progressively apart. An enhance in imbalance when visible cues are removed suggests a sensory element to the ataxia. Limb Ataxia Ataxic diseases cause quite lots of symptoms within the upper limbs, resulting from incoordination and tremor. Patients report clumsiness with actions similar to writing, choosing up objects, and buttoning. Patients may expertise head tremor and truncal instability leading to oscillatory actions of the top and trunk whereas sitting or standing (titubation). Lateralized cerebellar lesions cause ipsilateral signs and indicators, whereas generalized cerebellar lesions give rise to extra symmetrical symptomatology. To some extent, indicators and signs have a relation to the location of the lesions in the cerebellum (Stoodley and Schmahmann, 2010; Timmann et al. Ataxias of stance and gait are correlated with lesions in the medial and intermediate cerebellum: oculomotor features with medial, dysarthria with intermediate, and limb ataxia with lateral cerebellar lesions (Timmann et al. Stoodley and Schmahmann (2010) also level out that such lesion/symptom correlation could be extended to the proposed cognitive and limbic features of cerebellar function as properly, with anterior lobe lesions correlating with the traditional motor abnormalities and posterior lobe lesions with cognitive changes. Acute cerebellar lesions often produce extreme abnormalities early but might present outstanding recovery with time. Recovery could also be much less optimum when the deep cerebellar nuclei are involved (Timmann et al. Chronic progres- Dysarthria and Bulbar Symptoms Ataxic ailments of cerebellar origin lead to slurred speech and abnormalities of pitch and quantity control (scanning speech). Dysphagia may result from incoordination of swallowing muscles, and patients report strangling and choking. Visual Symptoms Patients could expertise blurriness or a way of environmental movements as a result of cerebellar ocular oscillations associated with cerebellar illness. They could report other symptoms of sensory pathway disease similar to paresthesias and numbness. Lesions of the cerebellum can cause deficits involving gait and stance, limb incoordination, muscle tone, speech, and the oculomotor system. The term dysmetria refers to an inaccuracy of movement by which the desired target is both under-reached (hypometria) or over-reached (hypermetria). Holmes considered dysmetria as a disturbance of the speed, vary, and pressure of movement. Kinetic, or intention, tremor manifests as oscillations of the limb that happen throughout a voluntary motion intended to reach a target; the tremor typically will increase in amplitude because the target is reached. The oscillations appear to result from instability on the proximal somewhat than distal portions of the limb and are sometimes perpendicular to the axis of movement. Cerebellar lesions can give rise to a postural tremor initiated by keeping the arms outstretched or pointing the fingers steadily at each other. In the legs, maintaining one heel on the other knee can bring out such a tremor. Also, a extreme tremor in the upper limbs that has both an intention and postural component can seem in cerebellar outflow tract disease. This cerebellar outflow tremor is usually seen in multiple sclerosis, Wilson illness, and midbrain strokes. The time period dysdiadochokinesia refers to irregularity of the rhythm and amplitude of fast alternating movements. Simple tapping duties such as the index finger on the thumb crease or the feet on the floor can even detect the disturbance in rhythm (dysrhythmokinesis). Stance and Gait Patients with cerebellar illness initially experience an increase in body sway when the toes are positioned collectively; the trunk moves excessively within the sideways direction (lateropulsion). With extra extreme disease, sufferers experience the increased sway even with regular stance and study that stability is best with toes apart. Healthy persons often have a foot spread of less than 12 cm throughout regular stance. Patients with cerebellar illness tend to have a a lot larger foot spread during quiet stance (Manto, 2002). In the clinic, one can detect even refined problems with balance by asking the patient to do a tandem stance or stand on one foot; regular adults can do these maneuvers for no less than 30 seconds. The Romberg take a look at is usually positive in patients with cerebellar ataxia, although this tends to be extra prominent in sufferers with proprioceptive or vestibular lesions. Many sufferers experience rhythmic oscillations of the trunk and head known as titubation. Severe truncal ataxia also can end in inability to sit upright with out again help. Ataxic gait is characterized by a widened base and an irregular staggering look resembling alcoholic intoxication. Ataxic gait disturbance could be detected even earlier by testing tandem gait; sufferers with cerebellar lesions lose their capability to do heel-totoe walking in a straight line. Limb Incoordination the cerebellum performs a task in controlling the pressure and timing of limb actions and cerebellar pathology causes errors in velocity, rhythm, and management of limb movements. A variety of scientific exams have been designed to test limb incoordination and the presence of tremor typically associated with cerebellar lesions. Action tremor can be examined by placing the arms in the outstretched position and also by asking the affected person to point the index fingers at one another at about chest level, separated by about 1 cm. Rapid alternating movements are examined by asking the patient to supinate and pronate the forearm within the unsupported place. This can be done by having the affected person alternately tap the palm and dorsum of one hand on the palm of the opposite (stationary) hand or on the thigh. In the lower limbs, the heel-to-shin maneuver is finished by having the affected person deliver the heel of the leg being tested to the alternative knee and sliding it in a straight line down the anterior aspect of the tibia to the ankle. Having the patient relaxation the heel on the other knee for a period of time can elicit tremor in the leg. The incapability of sufferers to check forearm motion in the rebound test is often mentioned to end result from hypotonia however might produce other explanations.
Big Marigold (Tagetes). Levitra Oral Jelly. - Colds, stomach pain, cough, menstrual disorders, mumps, ulcers, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Tagetes.
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Tagetes work?
- What is Tagetes?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96266
Purchase levitra oral jelly with a visaAids and appliances similar to ankle�foot orthoses to forestall footdrop, canes, walkers, and wheelchairs can improve mobility and limit handicap. Changes to the home and work environment-a ramp or stair raise, widening of doorways to permit wheelchair entry, rails for the bathtub and toilet, replacement of the tub with a shower and bathe chair-can be of nice assist to the affected person. Only the ingenuity of clinicians and biomechanical engineers, the supply of technology, and the price restrict the scope of such appliances. Computer-controlled motorized body and lower-limb braces could enable paraplegic patients to stroll (Hochberg et al. In the early phases, the patient may simply want enlarged handles on tools, pens, and utensils to compensate for a weak hand grip, or a cane to assist with walking. Speech remedy, a communication board, or a computer with specialized software program might help when speech is severely impaired. Weight loss and choking from dysphagia could necessitate a percutaneous gastrostomy. An incentive spirometer and an artificial cough machine can defend respiratory perform (see Respiratory Failure later within the chapter). If the patient decides to not use a ventilator, end-of-life counseling and hospice care are needed. Consider, for example, a patient with incapacitating ache in a single leg from carcinoma infiltrating the lumbosacral plexus on one aspect. Surgical interruption of ache pathways is considered the ultimate option to relieve ache from carcinomatous infiltration of the lumbosacral plexus. Such procedures embody surgical or chemical posterior rhizotomy, contralateral anterolateral spinothalamic tractotomy in the midthoracic area, and stereotactic contralateral thalamotomy. Tachyphylaxis for narcotics can occur, and the oral dose of narcotics required to management pain could rise quickly in patients who reside for a number of months. Antidepressant medication are of benefit in many continual pain syndromes by blocking the neurochemical transmitter mechanisms of central nervous system pain pathways, as well as treating melancholy. Many patients are resistant to taking antidepressant medicine for ache because they insist that the ache is real and not from despair; the effectiveness of antidepressant medication for pain management is some extent that should be clarified in such cases. Paresthesias typically end result from injury to the large-diameter myelinated axons in the peripheral nerves or posterior columns of the spinal cord. Weakness the management of weak point, considered more fully in Chapter 57, is a major part of neurological rehabilitation. For instance, weak spot of flexion of the ankle due to Charcot�Marie�Tooth disease could also be treated with a triple arthrodesis of the foot. Most neuromuscular situations benefit from exercise, although fatigue limits the amount of train that might be tolerated. This section outlines the final principles that govern management of those symptoms. Medications similar to baclofen, tizanidine, and botulinum toxin injections reduce spasticity and may enhance perform in upper motor neuron problems. A weighted cuff (wrist weight) positioned on an ataxic limb may reduce kinetic tremor; the added inertia reduces the amplitude of the involuntary movement throughout feeding and other activities of every day dwelling that require coordinated motion. Gait ataxia is finest managed with using walking aids corresponding to a cane, walker, wheelchair, and other measures designed to forestall fall-related injuries. Displacing the center of gravity ahead improves the gait of elderly sufferers, whose lack of postural reflexes causes retropulsion and falls. Increasing the peak of the heels on the sneakers and lowering the walker so the affected person should stoop ahead displaces the middle of gravity forward. Conversely, extreme involuntary movements, such as chorea and stereotypies, typically decrease with medication that deplete dopamine or block dopamine receptors. Botulinum toxin injections are considered the remedy of selection for many focal dystonias and in addition may be effective for motion disorders together with tremors, tics, and circumstances related to irregular muscle contractions. Stereotactic surgery, significantly high-frequency deep mind stimulation, is now a longtime therapeutic technique in patients with severe motion problems that continue to be troublesome or disabling regardless of optimal medical therapy. By the time evidence of hypoxia and hypercapnia seems within the blood, the patient could additionally be bordering on acute respiratory collapse. Reduced important capability, patient distress, and a great data of the disease are higher methods of judging impending respiratory failure (Hutchinson and Whyte, 2008). A affected person with Duchenne muscular dystrophy and a vital capability of 600 mL may survive for a quantity of years with out dyspnea. A affected person with myasthenia gravis who has a vital capacity of 1200 mL but is anxious, sweating, and complaining of dyspnea is at critical risk for the development of fatal respiratory paralysis. With borderline respiratory perform, sleep or sedation could produce carbon dioxide retention and narcosis, resulting in further respiratory suppression and demise. Respiratory failure was as soon as invariably fatal but nows commonly handled by noninvasive positive-pressure ventilation in the early levels and by intubation and positive-pressure air flow within the terminal phases (Radunovic et al. In Western countries, many sufferers think about life on a ventilator unacceptable, and the neurologist should discuss quality-of-life points with the affected person and family earlier than intubation. In these issues, the choice of a competent affected person or the healthcare surrogate (in instances of an incompetent patient or one with whom communication is impossible) holds primacy. Patients who decide against Aphasia and Dysarthria Treatment of language issues is, in precept, similar to that of limb weakness. Speech therapy can enhance aphasia by retraining contralateral speech and nonspeech areas of the mind to compensate for the effects of damaged speech facilities. If the lesion is restricted, some features of language function may be preserved and so provide a direct mechanism for communication. With speech therapy, dysarthric sufferers can study to slow their delivery and emphasize words, thereby enhancing the clarity of speech. Respiratory Failure Respiratory failure may develop in several neurological diseases (Box fifty three. A neurologist or a pulmonary specialist who is relatively inexperienced in neurological problems affecting respiration might underestimate the warning signs of potentially deadly respiratory failure. Even if sufferers have ready a dwelling will, they will be taken by emergency providers to a hospital emergency division and be intubated except proper arrangements are in place for end-of-life care at house, normally through hospice services. For patients who determine to request ventilator assist, medical well being insurance and financial issues should be considered. Patients with a tracheostomy should be capable of discuss using a valved tracheostomy tube or a partially inflated cuff, however many lose bulbar capabilities and need to use communication devices corresponding to computer systems or letter boards. Quality of life often becomes a problem when ventilator dependency turns into permanent. In many patients, the prognosis turns into clear within a relatively quick time, as with stroke and coma. The authorized and moral points are extra complicated with an awake and competent affected person who requests that the ventilator be switched off. Although the authorized methods in many parts of the world accept that such requests fall beneath the right of the patient to refuse medical remedy, involvement of a hospital ethics committee is strongly recommended. If the affected person opts for life-support measures, an elective tracheostomy and intermittent positive-pressure air flow should be offered at the first indicators of terminal respiratory failure. They should be referred to home hospice services, and when terminal respiratory misery seems, home therapy with oxygen, morphine, and sedation will be supplied, regardless of the danger that this may hasten death.
Buy levitra oral jelly cheap onlineMost (90%) spinal meningiomas are intradural, but extradural extension additionally occurs. Ependymomas are extra widespread in males and in about 50% of circumstances contain the decrease spinal twine in the area of the conus medullaris and cauda equina. Ependymomas are normally nicely demarcated and will exhibit a T1 and T2 hypointense pseudocapsule. This is important from a surgical standpoint, because these tumors may often be removed with minimal injury to the encircling twine parenchyma. On T1-weighted photographs, ependymomas are often isointense to the spinal wire or, hardly ever, hypointense. The tumor may have a hemorrhagic element as nicely, during which case the sign characteristic is normally heterogeneous, relying on the stage of the hemorrhage. Ependymomas are sometimes associated with a rostral or caudal cyst, which is hypointense on T1 and hyperintense on T2-weighted images. With gadolinium, intense homogeneous enhancement is seen within the solid portion of the tumor. Although the tumor margin is normally poorly outlined, subtotal resection is usually possible. A cyst or syringomyelic Structural Imaging utilizing Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography 450. Neurofibromas are characteristic for neurofibromatosis sort 1 and are often multiple, whereas schwannomas are uncommon in neurofibromatosis kind 1 and are often solitary. The tumor may cause enlargement of the neural foramen, and the intraspinal portion could displace/compress the spinal twine. Neurofibromas and schwannomas have similar sign characteristics however are typically totally different in form: schwannomas end in eccentric enlargement of the nerve root, whereas neurofibromas cause diffuse thickening. Epidermoid and dermoid cysts, teratomas, and lipomas represent 1% to 2% of all primary spinal tumors. Their presence warrants evaluation for different possible developmental abnormalities corresponding to spina bifida or diastematomyelia. Teratomas are of mixed and variable sign depth depending on their tissue contents. A, Sagittal postcontrast picture demonstrates outstanding enlargement of two neural foramina because of neurofibromatous enlargement of the exiting nerve roots (arrows). B, Axial T1-weighted picture reveals enlarged nerve root because of neurofibroma (arrow). Note the plexiform neurofibroma (arrowheads) in the left paraspinal muscle, which is simple to miss on this noncontrast image. C, Axial T1-weighted postcontrast image higher reveals the enhancing enlarged nerve root (arrow) and the plexiform neurofibroma (arrowheads). A, Sagittal T2-weighted picture demonstrates a hypointense extramedullary dural-based mass lesion that causes marked spinal cord compression (arrow). B, Sagittal T1-weighted postcontrast image reveals an extramedullary dural-based mass lesion in a similar location. A, Sagittal T1-weighted image reveals prominent enlargement of the cervical and upper thoracic twine because of a T1-hypointense intramedullary tumor. C, Sagittal T1-weighted postcontrast image reveals a patchy heterogeneous pattern of enhancement. Lung and breast cancer are the most common sources of intramedullary metastases, but lymphoma, colorectal cancer, and renal cell cancer may also metastasize to the wire. Metastases have some choice for the conus medullaris however may be multiple in 10% of circumstances and involve other wire segments as nicely. Their signal intensity varies; mucus-containing breast or colon most cancers metastases could be hyperintense on noncontrast T1-weighted images. On postcontrast pictures, intense enhancement is seen, which can be homogeneous or ringlike. Associated edema is incessantly seen as surrounding T1 hypointensity and T2 hyperintensity. Their blood provide to the wire is supplemented by segmental anterior and posterior radicular feeder arteries that, originating in posterior intercostal arteries from the aorta, pass by way of the neural foramina alongside the nerve roots. Additional medullary feeder arteries arising from segmental spinal arteries supplement the spinal wire circulation, the biggest of which is the good radicular artery of Adamkiewicz, getting into approximately at the stage of T11. Severe hypotension or occlusion of those key feeding branches may find yourself in watershed infarctions in these areas. In the subacute phase, areas of gadolinium enhancement could also be seen within the ischemic lesion. Intramedullary arteriovenous malformations have an intramedullary nidus, generally with extension to the subpial zone. On T2-weighted pictures, hyperintense sign is seen that may represent edema, ischemia, gliosis, or a combination of those, however hypointense signal zones because of move voids and blood degradation products can also be encountered. After gadolinium administration, the nidus and vessels improve, and sometimes cord parenchymal enhancement can be seen. On T2-weighted pictures, twine hyperintensity could also be present, and with gadolinium enhancing, pial and epidural vessels are seen. In this malformation, the arterial blood is drained via a dilated intradural vein. T2-weighted pictures may also reveal hypointense flow voids corresponding to dilated pial veins. A hypointense move void comparable to the fistula can also be visualized, but the best imaging modality remains spinal angiography. Cavernous malformations might current as intramedullary lesions inside the spinal twine as nicely as intra-axial lesions of the mind. A, Sagittal T2-weighted image demonstrates a lesion with blended sign depth, containing multiple hypointense circulate voids of assorted sizes, consistent with a vascular malformation (arrows). B, Axial T2-weighted picture reveals that this malformation has a prominent intramedullary element as properly (small arrows). With gradient echo techniques, cavernomas seem as extra outstanding areas of hypointensity ("blooming"), owing to the sensitivity of this pulse sequence to magnetic subject distortion by paramagnetic blood merchandise. Neurological emergency happens when the an infection proceeds to the epidural space, resulting in abscess formation that may end up in spinal cord compression. The most typical pathogen liable for discitis and osteomyelitis is Staphylococcus aureus. The most typical route of transmission is hematogenous, and in these instances the lumbar backbone is involved most regularly, normally at the L3/4 or L4/5 levels. Contiguous unfold of infection can also occur, and postoperative causes (such as after instrumentation) have been documented as properly.
20 mg levitra oral jelly saleMuscle stretch reflexes may also provide helpful info with regard to the first degree of harm, because the affected segmental reflex is typically depressed or absent, and caudal reflexes are hyperactive. For occasion, when a lesion is at the C4�C6 level, a radicular sample of ache and sensory signs might usually involve the radial facet of the arm, forearm, and hand. In addition, the biceps and brachioradialis muscle stretch reflexes may be depressed or absent, especially when the C5�C6 levels are involved. In distinction, lesions on the C7�T1 level usually present with pain and sensory impairments over the ulnar side of the upper extremity, together with the arm, forearm, and hand. Motor deficits associated to affected myotomes generally involve elbow extension, the intrinsic hand muscle tissue, and the triceps reflex. If segmental nerve roots and the spinal cord are compressed by a herniated disk or space-occupying lesion at the C5�C6 stage, for instance, a decreased brachioradialis reflex may mirror a C6 radiculopathy, whereas a brisk and hyperactive finger flexor reflex reflects an higher motoneuron syndrome. ThoracicLevels Traumatic spinal twine damage on the thoracic degree often produces a whole lesion. The segmental degree of harm is finest decided by a careful sensory examination of dermatomes. Useful scientific landmarks are the nipple line for the T4 dermatome and the umbilicus for the T10 dermatome. Pain might comply with a radicular sample around the chest or stomach, similar to the segmental levels of damage. Sensory testing of pin, temperature, pressure, and light touch appreciation might decide essentially the most caudal dermatome of normal sensation, in addition to a zone of partial preservation. The sensory testing ought to embody evaluation of dermatomes of the left and right side of the body, with comparisons of homologous ranges. In addition to a mixture of at-level pain, sensory deficits, and muscular weakness, autonomic dysfunction may develop from long-tract involvement and embody urinary retention, bladder�sphincter dyssynergia, and bladder hyper-reflexia. A decrease motoneuron injury presentation with higher extremity muscular weak point and atrophy can also be a part of the medical presentation. When the spinal cord is compressed by epidural or subdural space-occupying lesions, spastic weak spot of higher and lower extremities typically follows. An harm or illness process affecting the higher cervical spinal wire can also compromise breathing. Normal respiration requires useful use of the diaphragm muscle, which is innervated by the phrenic nerve. Motoneurons contributing to the phrenic nerve are located within the cervical spinal wire and contribute efferent axons to the C3�C5 ventral roots. Therefore, complete accidents affecting the spinal wire above the C3 segment will compromise the operate of the diaphragm, and respiratory failure could follow. ConusMedullarisandCaudaEquina the conus medullaris of the spinal twine terminates roughly at the degree of the L1 vertebra, although the exact location of the tip of the conus may show marked variability among topics. This anatomical side of the spinal wire is essential as a outcome of backbone trauma commonly takes place at the thoracolumbar junction, and the extent of such injuries is very variable (Kingwell et al. However, some sufferers with conus medullaris injuries exhibit a mixed higher and lower motoneuron syndrome. In distinction, a cauda equina damage that lesions lumbosacral roots under the level of the conus medullaris is a pure decrease motoneuron syndrome. Cauda equina injuries current with decrease extremity weak point, areflexia and decreased muscle tone, and variable sensory deficits. The correlation between presenting symptoms and localization of the underlying lesion is most exact for the extramedullary pathological processes. Pain is regularly related to spinal cord accidents, along with autonomic impairments that may affect blood pressure and coronary heart rate, bladder, bowel, sexual, and cardiorespiratory capabilities. The kind and severity of autonomic dysfunction depends on the location of pathology and severity of the spinal twine injury. International spinal wire harm societies suggest a scientific strategy to doc remaining autonomic function after a spinal wire injury (Alexander et al. L2 PainSyndromes Distinct pain syndromes might develop on account of compression, irritation, or damage to the vertebral column, ligaments, the dura mater, nerve roots, dorsal horn, and ascending spinal cord sensory tracts. Affected limb and pelvic floor muscles develop flaccid weak spot, and electromyography shows denervation after either a conus medullaris or cauda equina damage, especially following anatomically full lesions. Both conus medullaris and cauda equina accidents are associated with bladder, bowel, and sexual dysfunction. Urodynamic evaluations sometimes reveal detrusor areflexia, and a rectal exam identifies a flaccid anal sphincter. In addition, the bulbocavernosus reflex is typically absent or diminished, and reflexogenic erection in males is commonly lost. Burst fractures and fracture dislocations are frequent accidents to the spinal column that end in neurological deficits, suggesting a conus medullaris or cauda equina involvement. Following trauma to the thoracolumbar backbone, imaging studies can be utilized to assess spinal stability and identify detailed aspects of backbone fractures, including the presence and site of bone fragments, spinal canal encroachment, epidural hematomas, and herniated disks. A lumbar spinal stenosis because of a congenitally smalldiameter spinal canal or central disk and spondylotic narrowing a number of levels below L1 might present with a refined course. Over months to years, decrease extremity numbness or ache, normally in an L3�S1 single or multiradicular sample, accompanies standing and strolling, often progressively progressing to limit strolling distance. Pain is usually accompanied by weak spot, however sufferers is in all probability not conscious of their deficit. Clinical insight into this analysis and the upper degree of cauda compression is gained by a handbook muscle examination after a couple of minutes of being supine, followed by having the topic stroll for about 500 toes, and then instantly retesting power. Transient paresis or higher paresis within the affected Localized neck or again pain could end result from irritation or harm to innervated backbone buildings together with ligaments, periosteum, and dura. The pain is usually deep and aching, might vary with a change in place, and infrequently becomes worse from increased load or weight bearing on affected constructions. Percussion or palpation over the backbone might in some patients worsen the native ache. When the injured or diseased spine structures are irritated, secondary signs might develop and include muscle spasm and a more diffusely situated pain. Musculoligamentous sources of pain usually persist for greater than every week publish backbone surgery and develop with compensatory overuse of joints and muscular tissues. ProjectedPain A pathological process involving the facet joints may be experienced as focal or radiating ache in an upper or lower extremity. Straining or coughing may increase the depth and severity of radicular ache. Nerve root irritation may result in sensory and motor deficits following the identical dermatome and myotome distribution because the affected nerve root. CentralNeurogenicPain Paresthesia, dysesthesia, allodynia, and hyperalgesia accompany injury to the spinal wire in at least half of sufferers, as nicely as after thalamocortical stroke. At-level pain is primarily derived from native mobile and neuroplastic changes within the dorsal horn and sensory roots on the segments of harm. Below-level pain is positioned in physique segments receiving innervation from the spinal wire caudal to the lesioned segments.

Buy levitra oral jelly 20 mg without a prescriptionRight-sided lesions predominate amongst reported instances of the thalamic pain syndrome. Patients reporting pain due to brainstem infarction usually have involvement of pontine or medullary constructions. About 25% sufferers with dorsolateral medullary infarction develop ipsilateral facial pain, particularly when the lesion includes the spinal trigeminal tract. Pharmacological and rehabilitative procedures are efficient in solely about 38% of sufferers. For neuropathic pain, medicines corresponding to gabapentin, amitriptyline, and nortriptyline could ease the pain in some sufferers. Dorsal root entry zone lesions and dorsal rhizotomy have also been used with limited success. Appropriate administration of bowel or bladder dysfunction might assist ease visceral ache. If an ascending syrinx is current, surgical drainage may be efficient in relieving the ache. Pain can have several totally different qualities, such as stabbing, throbbing, burning, or cramping. This ache could additionally be related to a sure place or movement of the phantom and could also be elicited or exacerbated by a spread of physical components. It is extra more likely to happen if the person had persistent pain earlier than the amputation. Pain within the phantom is often just like the pain felt within the limb earlier than amputation. Phantom ache is commonest after the amputation of an arm or leg, but it may also occur after the surgical removal of different physique elements similar to breast, rectum, penis, testicle, eye, tongue, or enamel. About 30% of persons with amputation report the sensation of telescoping, the retraction of the phantom towards the residual limb, and in lots of circumstances the disappearance of the phantom into the limb. Recent evidence means that telescoping is related to extra phantom-limb ache. Phantom-limb pain is often confused with pain in the area adjoining to the amputated physique half. Patients might report extreme "knife-stabbing" or sharp pain at the end of the amputated limb. Formation of a neuroma or strain lesions of the stump could exacerbate stump pain. Changes along the neuroaxis might contribute to the expertise of phantom-limb pain. Spinal mechanisms are characterized by increased excitability of the dorsal horn neurons, discount of inhibitory processes, and structural adjustments at the central nerve endings of the primary sensory neurons, interneurons, and the projection neurons. Supraspinal adjustments associated to phantom-limb ache involve the brainstem, thalamus, and cortex. Reorganization of the somatosensory cortex of the human cerebral cortex in amputees has been supported by findings from a quantity of imaging research. People with arm or hand amputations show a shift of the mouth into the hand representation in the main somatosensory cortex (Woodhouse, 2005). Studies in human amputees have proven that reorganizational changes also occur at the thalamic degree and are carefully related to the perception of phantom limbs and phantom-limb ache. Neuroma in the stump could also be extra liable for stump ache than phantom-limb pain. However, irregular input originating from a neuroma within the residual limb might enhance the amount of central reorganization, enhancing the chance of phantom-limb ache. Psychological elements play a job within the modulation of phantom-limb pain; the pain may be exacerbated by stress. Patients who lack coping strategies, concern the worst, or obtain less social assist are most likely to report extra phantom-limb ache. The prevalence of pain on this disease is higher than initially anticipated; some research estimate it to be up to 86% (Bermejo et al. The majority of patients (87%) with central ache had signs located in the legs, whereas 31% were within the arms. Lamotrigine, gabapentin, oxcarbazepine, and other anticonvulsants may also be used. Painful "burning" dysesthesia may be treated with tricyclic antidepressants or carbamazepine. In extreme cases, intrathecal baclofen and botulinum toxin injections merit consideration. Pain due to subcutaneous injections of -interferons or glatiramer acetate could additionally be decreased by optimizing the PrinciplesofPainManagement 741 Treatment for phantom-limb ache is troublesome. Although tricyclic antidepressants and sodium channel blockers are remedies of alternative for neuropathic pain, no controlled research exist of these brokers for phantom-limb pain. Opioids, calcitonin, and ketamine have proven to be effective in decreasing phantom-limb pain in managed studies. A most good factor about about 30% has been reported from therapies similar to local anesthesia, far-infrared rays, sympathectomy, dorsal root entry-zone lesions, cordotomy, rhizotomy, neurostimulation methods, or pharmacological interventions similar to anticonvulsants, barbiturates, antidepressants, neuroleptics, and muscle relaxants. However, current advances in fundamental scientific research and medical research have supplied clinicians with more insight regarding the mechanism and clinical features of chronic pain circumstances. Advances in clinical applied sciences have provided new hope within the treatment of some refractory ache conditions previously regarded as impossible. With a mix of multidisciplinary pain remedy modalities, a majority of ache circumstances could also be alleviated or managed. The future of ache administration requires extra physicians, together with neurologists, to contribute diagnostic and therapeutic abilities to fulfill the needs of patients. A randomized, controlled examine evaluating a lidocaine patch, a placebo patch, and anesthetic injection for therapy of trigger factors in sufferers with myofascial pain syndrome: evaluation of ache and somatic pain thresholds. Efficacy and safety of milnacipran one hundred mg/day in sufferers with fibromyalgia: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Peripheral nerve blocks and trigger point injections in headache management� a scientific evaluate and recommendations for future analysis. Intrathecal opioid therapy for continual nonmalignant ache: a retrospective cohort research with 3-year follow-up. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-period, crossover, pilot trial of lamotrigine in sufferers with central ache because of a quantity of sclerosis. Peripheral and central sensitization in remote spinal wire areas contribute to central neuropathic pain after spinal cord harm. Mexiletine therapy for chronic pain: survival analysis identifies elements predicting clinical success. Mechanism-based therapy in continual neuropathic ache: the function of antidepressants. Systematic evaluation of diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic utility of lumbar side joint interventions. Recommendations for the pharmacological management of neuropathic ache: an summary and literature update. Elevated cerebrospinal fluid substance p concentrations in posttraumatic stress dysfunction and main despair.
Levitra oral jelly 20 mg on lineThe sensory profile is an assessment tool in the form of a long questionnaire which addresses, in part, a few of the larger sensory processing, and without making a definitive analysis, may be helpful for figuring out patients who could have difficulty with sensory processing (Brown et al. While initially developed to be used in youngsters, an grownup sensory profile evaluation is now in use. Infants with low delivery weight and with neonatal insult seem to be at elevated risk for sensory processing disorder (Gill et al. Not surprisingly, kids with autism also exhibit increased threat for this (Puts et al. Clinical manifestations of sensory processing disorders can include misinterpretation of sensory knowledge resulting in poorly organized motor output and impaired incorporation of sensory stimuli in studying. This can have an effect on not simply responses to audio and visual stimuli however to almost any modality, trigger deficiency or extra cognitive response to sensory stimulation, or even intensify a drive to get sensory inputs. Such misdiagnosis is particularly common with thalamic infarction and plexus dysfunction. Of note, embellished sensory or motor loss, though apparent to the examiner, could additionally be superimposed on an actual neurological deficit. The affected person may be unintentionally helping the examiner but essentially ruining the credibility of the report. In general, nevertheless, medical presentations suggesting functional sensory loss embrace: � Sensory loss exactly splitting the midline, with a minimal transition zone � Circumferential sensory loss around the physique or an extremity � Failure to understand vibration with a precise demarcation � Loss of imaginative and prescient or hearing on the same aspect of the physique as for the cutaneous sensory deficit � Total anesthesia. The discrepancies in whole anesthesia may be failure to perceive any sensory stimulus on an extremity that strikes perfectly nicely. Third, if the anesthetic limb is an arm, analyzing for sensory abnormality whereas the arms are folded across the chest may be complicated for the malingering affected person, especially if carried out shortly. Patients with diabetes who present with distal sensory loss of subacute onset with hyporeflexia are assumed to have additional growth of diabetic neuropathy. Careful nerve conductions and follow-up bodily and electrophysiological exams are essential. Experienced neurologists have sometimes misdiagnosed a patient with paraparesis and lower body sensory loss with spinal wire lesion who finally are recognized as having a cerebral lesion, particularly bilateral anterior cerebral artery infarction from a common arterial trunk or aneurysm, or midline-region mass lesion. Also, if the examiner notes cognitive or behavioral abnormalities, the brain must be studied. Sensory integration, sensory processing, and sensory modulation disorders: putative functional neuroanatomic underpinnings. Pyridoxineinduced toxicity in rats: a stereological quantification of the sensory neuropathy. Stroke induces long-lasting deficits in the temporal fidelity of sensory processing within the somatosensory cortex. Birth and developmental correlates of delivery weight in a pattern of children with potential sensory processing dysfunction. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: scientific features, prognosis, prevention and treatment strategies. Central post-stroke ache: scientific characteristics, pathophysiology, and administration. Pathogenesis of syringomyelia associated with Chiari kind 1 malformation: evaluation of evidences and proposal of a model new speculation. Neck mobility is best assessed by testing for movement in each of the principle planes of motion, flexion and extension, lateral flexion to the proper and left, and rotation to the proper and left. Normally in flexion, the chin can touch the sternum, and in rotation the chin can approximate the point of the shoulder. Dysfunction affecting the ascending sensory tracts within the spinal cord could generate ache or paresthesias in the arm(s) or down the trunk and lower limbs. An electric shock-like sensation provoked by neck flexion and spreading to the arms, down the spine, and even into the legs is thought to originate within the posterior columns of the cervical spinal twine (Lhermitte sign). Sharp, superficial, burning pain or itching points to dysfunction in the spinothalamic system, whereas deep, aching, boring ache with paresthesias of tightness, squeezing, or a sense of swelling suggests dysfunction within the posterior column system. The sensory signs point out the dysfunctional tract but are poor segmental localizers. Brachialgia (arm pain) aggravated by neck motion, coughing, or sneezing suggests radiculopathy and when these trigger features are present one may be fairly certain that the ache is radicular in origin. Nerve root ache is often lancinating in character, but it could possibly current as a uninteresting ache in the arm. Repetitive sudden shooting pains radiating from the occipital region to the temporal areas or vertex suggest the prognosis of occipital neuralgia. There may be native tenderness over the greater or lesser occipital nerve, and a local injection of corticosteroid plus native anesthetic is each diagnostic and therapeutic. Failure to reply suggests that the craniovertebral junction space should be imaged. Ulnar nerve entrapment causes numbness or ache radiating down the medial facet of the arm to the little and ring fingers. Symptoms are sometimes worse at night when the affected person sleeps with a flexed elbow, they usually could interrupt sleep. Ulnar paresthesias are also triggered by pressure on the nerve when resting the elbow on the arm of a chair or desk. Tapping on the nerve in the ulnar groove at the elbow may evoke a tingly electrical sensation within the little and ring fingers- Tinel sign. Median nerve entrapment within the carpal tunnel classically awakens the patient from sleep with numbness and tingling within the thumb, index, and center fingers, which is relieved by "shaking out" the hand. Pain generated in the median nerve could be sharp and lancinating and radiates to the thumb, index, and center fingers. While entrapment in the carpal tunnel is frequent, occasionally the location of entrapment is on the elbow as the nerve passes under the pronator muscle. Infiltrative or inflammatory lesions of the brachial plexus produce severe brachialgia radiating down the Evaluation of the affected person with arm and/or neck ache is predicated on a careful historical past and medical examination. Diagnosis of the frequent causes and a therapy plan can nearly at all times be achieved in the workplace earlier than laboratory investigation, however further research may be required if the patient fails to enhance or has different particular indications for imaging or electrical research. A helpful strategy is to consider the prognosis when it comes to pain-sensitive structures in the neck and upper limbs. These constructions may be a part of the nervous system or may contain joints, muscles, and tendons. Neurological causes must be thought-about primarily based on the innervation of the neck and arm, and non-neurological causes are based mostly on dysfunction of the opposite anatomical structures of the arm or neck. Because nerve root irritation generates neck muscle spasm, this sort of ache is normally lumped into the "neurological" class. Some primarily non-neurological circumstances have neurological problems and are grouped on this chapter as "in-between" problems. The pain could radiate upward to the occipital region and over the top of the pinnacle to the bifrontal space. It is often described as fixed, aching, or bursting, or as a good band or stress sensation on high of the head. Radiation to the ulnar two fingers suggests that the origin is within the decrease brachial plexus, and radiation to the upper arm, forearm, and thumb suggests an upper plexopathy.
References - Cary KC, Beck SD, Bihrle R, et al: Outcomes of post-chemotherapy retroperitoneal lymph node dissection following high-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant, J Urol 185:e237, 2011.
- Sakakibara R, Hattori T, Boku K, et al: Micturitional disturbance in neuro- Behcetis syndrome, Auton Neurosci 83:86n89, 2000.
- Paraiso MF, Falcone T, Walters MD: Laparoscopic surgery for genuine stress incontinence, Int Urogynecol J 10:237n247, 1999.
- Kumar R, Smith G: Dorsal lumbotomy incision for pediatric pyeloplasty?a good alternative, Pediatr Surg Int 15(8):562-564, 1999.
- Koszutski T, Kudela G, Mikosinski M, et al: Quadruplication of dystopic kidney in combination with ureteral cyst, J Pediatr Surg 43(12):e13ne15, 2008.
|
|