"Cefadroxil 250mg on-line, antibiotic 5 day."By: J. Matthew Brennan, MD - Associate Professor of Medicine
- Member in the Duke Clinical Research Institute
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/j-matthew-brennan-md
Order 250 mg cefadroxilA few additional brokers are available to deal with poisoning by metals apart from mercury, similar to calcium disodium edetate for lead and cadmium and deferoxamine for iron. Some, similar to edetate, additionally aggressively take away very important nutrient metals, similar to calcium and zinc. Selectivity is essential in the selection of the chelator, which must be matched for the heavy steel and circumstances of remedy. Subsequently, dimercaprol was found to be an lively chelator of assorted heavy metals. Dimercaprol is ready as a 10% resolution in a peanut oil car (beware of peanut allergy! Dimercaprol is used with calcium disodium edetate in protocols for remedy of lead poisoning. The drug is normally injected two to 3 times a day initially, with doses petering out to a few times a day over about 10 days. The dimercaprol�mercury advanced (actually two dimercaprol molecules to a single mercury atom) is excreted within the urine, which have to be stored alkaline to avoid dissociation of the conjugate. Succimer (meso-2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid) is structurally just like dimercaprol. This drug has the benefit of being effective after oral administration and being much less poisonous than dimercaprol. The dose for lead chelation is 10 mg/kg every 8 hours for 5 days, then 10 mg/kg each 12 hours for 14 days. In animal studies, succimer was simpler than dimercaprol in assuaging acute toxicity and preventing distribution of orally administered mercury from mercuric chloride, notably to the mind. In addition, oral administration was more efficient than parenteral administration in lowering retention and organ deposition of oral mercuric chloride, probably because of decreased intestinal uptake of the mercuric chloride. Penicillamine (3-mercapto-d-valine) is a highly efficient chelator of copper and is of primary importance within the administration of Wilson illness (hepatolenticular degeneration). In basic, 1 to 2 g/day is run as needed for therapy of mercury poisoning. Calcium disodium edetate advanced is a chelator for divalent and trivalent metals that can displace calcium from the molecule. Typically, these metals include lead, zinc, cadmium, manganese, iron, and mercury. Calcium edetate disodium is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is given intramuscularly or intravenously. Calcium disodium edetate can worsen symptoms of severe lead poisoning, similar to cerebral edema and renal tubular necrosis, and in high doses can lead to severe zinc deficiency. The most well-liked route is intramuscular; acute iron intoxication remedy includes 1 g as an preliminary dose, followed by 500 mg every four hours for 2 doses and additional doses of 500 mg each 4 to 12 hours as wanted based on clinical response. Exposure to elemental or inorganic mercury could be handled with dimercaprol (higher mercury levels) or penicillamine (lower mercury levels). For short-chain natural mercurials corresponding to methylmercury, chelation remedy is ineffective, and dimercaprol is contraindicated as a end result of it concentrates mercury within the brain. Gases Perhaps no different toxic air pollution concern stirs such common concern as air pollution because gaseous pollutants are dispersed over broad areas, and inhalation exposure is insidious. Significant regulatory effort is dedicated to decreasing air pollution by the Clean Air Act, and Ozone Ozone (O3) is an odorless, colorless fuel composed of three oxygen atoms. Because of its relative insolubility, impressed O3 is carried deep into the lung, the place it oxidizes membranes within the alveoli. O3 irritates lung airways and causes inflammation, decreased lung capacity, and elevated susceptibility to respiratory diseases such as pneumonia and bronchitis. Oxidation merchandise arising from O3 reactions with lung proteins or lipids initiate numerous mobile responses, together with technology of cytokines and expression of adhesion molecules. These responses promote an inflow of inflammatory cells to the lung in the absence of a pathogenic challenge, resulting in modification of mobile tight junctions, elevated lung permeability, and improvement of edema. Individuals with preexisting respiratory problems, similar to asthma or persistent obstructive pulmonary disease, are most weak. Repeated exposure to O3 air pollution for several months could trigger everlasting lung harm. On dissolution, it varieties sulfurous acid, which is extremely irritating to the nasopharyngeal and respiratory tracts. Acute exposure causes dryness of the nostril and throat and a lower in tidal respiratory volume. Patients have famous fast dental destruction, lack of restorations, and increased sensitivity of tooth to temperature change. Exposure most often happens by way of inhalation; absorption through the pores and skin is also a standard route of exposure. Compounds that are properly absorbed, similar to benzene or toluene, can produce important systemic toxicity. A major threat from ingestion is the potential for pneumonitis because of emesis and aspiration. Regardless of the positioning of absorption, the great lipid solubility of this group of compounds permits them to cross the blood�brain barrier readily. Chronic publicity to decrease concentrations of those chemicals produces poisonous effects characteristic of the individual compounds. Chlorinated solvents Dichloromethane, otherwise often identified as methylene chloride, is a standard solvent in paint remover and is used for liquid�liquid extraction in laboratories. Evidence of its carcinogenicity, obtained in mice, seems to be related to toxic metabolites shaped by glutathione-S-transferase and could additionally be specific to the very excessive exercise and localization of this enzyme in this species. Carbon tetrachloride is metabolized in the liver to a highly reactive free radical metabolite that, within the presence of oxygen, reacts with proteins and lipids. The ensuing hepatotoxicity might take days to develop and is accompanied by severe renal toxicity. Compounds that enhance the speed of carbon tetrachloride biotransformation, corresponding to cytochrome P450 enzyme inducers, improve the hazard of toxicity. In an analogous manner, perchloroethylene (also often recognized as tetrachloroethylene) has been found to produce reactive metabolites that are thought to produce renal toxicity. This compound has additionally been related to an increased danger of oral, laryngeal, and esophageal most cancers in workers occupationally exposed to dry-cleaning processes that use perchloroethylene. Liquids and Vapors the natural liquid that presents the best risks to humans is ethanol. The toxicologic profile of this compound is exclusive among natural liquids and is presented intimately in Chapter 39. Considered in this section are the natural solvents, together with hydrocarbons and chlorinated compounds, and methyl methacrylate (because of its common use in dentistry). Solvents Although transient publicity to solvents might occur within the house, more significant exposure most commonly occurs in the office. Benzene Benzene is one other widely used industrial solvent generally encountered in petroleum distillates corresponding to gasoline.
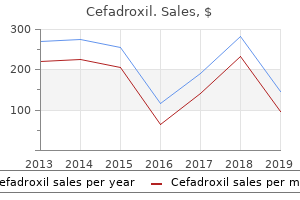
Cheap cefadroxil 250 mg without a prescriptionThese modifications cut back the overall myocardial oxygen requirement and limit the depth, extent, and duration of myocardial ischemia. The combination of the antiarrhythmic and anti-ischemic actions of blockers contributes to a good impact on survival rate after myocardial infarction. In addition, the uses of those compounds within the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias and hypertension are discussed in Chapters 19 and 23. Discussion right here is limited to the function that these drugs play in the management of angina pectoris. Some of essentially the most frequently used agents for this function include propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol, and nadolol. Consideration should be given to the dosage used, nonetheless, as a outcome of all -blocking medication have nonselective effects at higher dosages (see Chapter 9). Adverse Effects As talked about in Chapter 9, blockade of receptors could cause bronchoconstriction or prevent the normal response to insulin-produced hypoglycemia in vulnerable patients. These issues are less extreme with the extra selective 1 blockers, corresponding to metoprolol, which have been used with out severe adverse effects in many sufferers with bronchospastic disease. Drugs corresponding to metoprolol are 1-selective, not 1-specific, nevertheless, and are able to eliciting bronchospasm in prone patients. Because of the association between 2-adrenergic receptors and glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver, 1-selective blockers are associated with less risk of hypoglycemic reactions in diabetics than the nonselective receptor blockers. For this reason, dosages ought to be gradually elevated until concentrations providing therapeutic effects within the management of angina are reached. The sudden discontinuance of blockers has been implicated in rebound overstimulation of the guts, worsening of angina, and myocardial infarction. Pharmacologic Effects Because exercise and emotional stress are attainable precipitating factors in angina. The blockade of adrenergic responses could be helpful in the treatment of this situation. Effects of blockers that are useful in treating angina embody decreased heart fee and safety from reflex tachycardia, depressed myocardial contractility, decreased cardiac output, and reduced blood strain. The constructions of different dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (most generally amlodipine) resemble the structure of nifedipine. Many of these compounds are efficient within the prophylactic remedy of continual secure exertional angina, variant angina, and unstable angina. They have additionally proved to be helpful in the treatment of other cardiovascular issues, similar to supraventricular tachyarrhythmias and hypertension (see Chapters 19 and 23). Chemistry and Classification Verapamil is a diphenylalkylamine spinoff and the one member of its type clinically out there. Dihydropyridines are characterised by their outstanding arterial vasodilatory properties, decreased direct results, and larger oblique results on the heart. Diltiazem, particularly at higher doses, has been proven to depress the Na+, or fast, channels. They may additionally be concerned in regulating sinus node automaticity by altering diastolic depolarization. By this mechanism, they scale back intracellular Ca2+ activity and interfere with the replenishment of Ca2+ stores in vascular clean muscle. The degree of binding is influenced by the practical state of the channel (resting, open, or inactivated) in a fashion much like the use dependency described for native anesthetics and Na+ channels (see Chapter 14). Their motion on coronary vessels is particularly distinguished in vessels that bear transient vasospasm in variant angina. The vasodilator action in massive measure explains their use as antianginals and antihypertensives. For verapamil and diltiazem, the direct cardiac effects normally predominate (Table 21-2). They inhibit Ca2+ flux in cardiac and smooth muscle and are effective in the treatment of stable angina because of their coronary vasodilator impact, adverse inotropic and chronotropic effects (for verapamil and diltiazem), enhancement of diastolic rest of the left ventricle (primarily verapamil and diltiazem), and hypotensive effect mediated via peripheral arterial dilation. These results lead to an increase in coronary blood circulate and myocardial perfusion with a decrease in myocardial oxygen demand. Verapamil and diltiazem are transformed partially to energetic metabolites; biotransformation of nifedipine causes complete inactivation. Clinically and histologically resembles that seen with phenytoin, nevertheless it occurs much less typically and normally less severely than with phenytoin. The dosage of ranolazine must be limited when given with verapamil or diltiazem because these drugs are inclined to inhibit the metabolism of ranolazine. Chemistry and pharmacologic effects Ranolazine is a piperazine by-product that inhibits the late Na+ present of the plasma membrane (see Chapter 19). Inhibition of the late sodium current reduces sodium�calcium change, thereby decreasing intracellular calcium and diastolic wall rigidity. This drug exerts its antianginal and anti-ischemic effects with out reducing heart rate or blood strain. The drug can be utilized together with different antianginal medication or sometimes as monotherapy. Adverse effects Constipation, nausea, dizziness, and headache are the most common adverse results. Ivabradine Ivabradine is discussed in Chapter 20 in relation to its use in heart failure. The reduction in heart price results in less cardiac work and enhanced time spent in diastole with longer profusion time for the myocardium. Absorption, fate, and excretion Ranolazine is administered twice a day by mouth in an extended-release preparation. They reduced the response of the sympathetic nervous system, cause vasodilation of blood vessels together with the microvasculature, and enhance conditions in coronary heart failure. This has the useful effect of lowering coronary artery illness and angina pectoris. Their motion is to forestall platelet aggregation and adhesion, thus reducing the chance of platelet clots. Certain anticoagulants corresponding to low-molecular-weight heparins are used prophylactically to scale back coronary ischemia. The latter motion causes the smooth muscle cell to hyperpolarize and loosen up, resulting in vasodilation of blood vessels. Trimetazidine has the distinctive action of inhibiting beta-oxidation and metabolism of fatty acids. Fatty acids are the popular power source of the cardiac cells; however, this vitality supply requires appreciable oxygen. Because these situations typically arise in the dental operatory, dentists must pay consideration to the signs and treatment of angina. Although nitroglycerin tablets are actually stabilized against breakdown, unused tablets should be discarded 3 months after the original bottle has been opened due to oxidation, volatilization, and adsorption of the drug to the wall of the container. In most instances, anginal ache subsides rapidly (2 to three minutes), and the affected person may have a headache or a stinging sensation under the tongue or each. As a precaution, sufferers should be handled fastidiously, be fully knowledgeable in regards to the procedure, and in the event that they really feel it needed, be given prophylactic medicine.
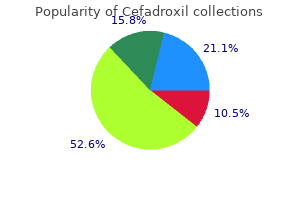
Cefadroxil 250mg on-lineAnother important determinant of the onset, severity, and period of the withdrawal syndrome is the half-life of the particular drug. Drugs with comparatively quick halflives (8 to 30 hours) tend to produce a severe withdrawal syndrome that develops fairly rapidly. Drugs with longer half-lives (40 to a hundred hours) produce a slower onset however less severe withdrawal syndrome of long period. The withdrawal syndrome after cessation of sedative-hypnotics resembles that seen after alcohol withdrawal. After a normally symptomless period (8 to 18 hours after the last dose), the individual exhibits rising symptoms of hysteria, insomnia, agitation, and confusion. Coarse tremors within the face and arms; dilation of the pupils; and will increase in respiratory rate, heart rate, and blood stress might happen. These signs turn into more severe in the course of the first 24 to 30 hours of drug withdrawal. By the third or fourth day, main manifestations of abstinence might develop, which embrace delirium, hallucinations, agitation, hyperthermia, convulsions, and nonspecific symptoms of anxiety. Symptoms associated with benzodiazepine withdrawal additionally happen; these are persistent tinnitus (8 months), muscle twitching, paresthesias, visual disturbances, and confusion and depersonalization. Reports of xerostomia and ache in the jaws and teeth have specific dental significance. One or extra grand mal convulsions lasting lower than 3 minutes might occur, with consciousness being regained inside 5 minutes. Delirium develops progressively over 2 to four days and is heralded by a period of insomnia. Delirium is characterised by confusion, disorientation of time and place, nightmares, and vivid auditory and visible hallucinations. Paranoid delusions with excessive worry and agitation may develop, especially at night ("night terrors"). This withdrawal psychosis may be attributable to rebound speedy eye motion sleep, which, having been suppressed during the interval of intoxication, intrudes into the waking state. A steady marked hyperthermia is a life-threatening problem that, if not instantly and vigorously treated, may (along with agitation) lead to fatal exhaustion and cardiovascular collapse. After the acute withdrawal syndrome, restoration is gradual but complete after approximately eight days, though residual weak spot could also be noted for 6 to 12 weeks. Abrupt withdrawal from massive doses of sedative-hypnotics can precipitate a severe, life-threatening withdrawal syndrome that has a major mortality fee. The withdrawal syndrome from sedative-hypnotics could additionally be extra extreme than withdrawal attributable to opioids. Tolerance develops to sedative-hypnotic medicine, and partial cross-tolerance additionally happens among the various medicine on this class. Tolerance is often full to doses of short-acting barbiturates of up to 500 mg/day, but doses of greater than 800 mg/day are related to signs of intoxication. The onset of tolerance to benzodiazepines in people develops slowly, starting in three to 5 days, with maximal tolerance in 7 to 10 days. Much of the tolerance to large doses of short-acting barbiturates is associated with hepatic enzyme induction that results in enhanced barbiturate elimination. This metabolic tolerance plays much less heroin and morphine; it relieves opioid cravings in mildly to reasonably addicted individuals and produces less respiratory despair and withdrawal signs than the full agonist methadone. Older sedative-hypnotic medication, together with barbiturates, glutethimide, and the broadly abused however not approved drug methaqualone, have substantial abuse potential. Benzodiazepines and associated medication are now probably the most generally used sedative-hypnotic and antianxiety medication. Sedative-hypnotic medicine are available from illicit sources and by prescription abuse when giant quantities of the medication are accrued by drug abusers visiting totally different prescribers. Pharmacologic Effects the signs of intoxication with sedative-hypnotic and antianxiety drugs are much like indicators produced by alcohol: drowsiness, impairment of motor coordination, ataxia, and slurred speech. Sluggishness, problem in reasoning, temper swings, and irritability are additionally seen. Subjective results embody sensations of well-being, euphoria, and typically stimulation. The next day the abuser may expertise nervousness, nervousness, tremor, headache, and insomnia. Abuse Characteristics the degree of addiction with sedative-hypnotic medicine is dependent upon the dose of the drug, the frequency of administration, and the period of drug use. Sedative-hypnotic drugs differ in onset and length of action (short-acting and long-acting barbiturates and benzodiazepines are available). Addiction is mostly associated with abuse of short-acting medicine, corresponding to secobarbital, pentobarbital, oxazepam, and lorazepam. Dependence on longer appearing agents, such as phenobarbital and chlordiazepoxide, is much less frequent. Initial exposure to sedative-hypnotics might occur when the drug is prescribed to relieve nervousness or insomnia. The dose is slowly increased, and the abuser could turn into preoccupied with acquiring and utilizing the drug. So-called date rape medication, similar to hydroxybutyrate, a metabolite of -aminobutyric acid, and the prescription benzodiazepine flunitrazepam ("roofies") are also subject to misuse. Both medicine have related effects as sedative-hypnotics; nonetheless, their rapid oral absorption, onset of action, and talent to cause anterograde amnesia have resulted in their surreptitious use as sedatives to facilitate rape of unwitting individuals. The onset and severity of the abstinence syndrome also depend, partially, on the dose and the period of drug use. For occasion, some physical dependence is more doubtless to occur with daily doses of secobarbital in excess of four hundred mg for about 90 days or more. Coma may develop with progressive deterioration of respiration and blood pressure. Therapy is mainly supportive, consisting of oxygen administered by synthetic respiration and fluids or pressor brokers (or both) to maintain circulation. For barbiturates, osmotic diuretics with sodium bicarbonate are also used to alkalinize the urine and hasten elimination of the drug. The benzodiazepine receptor antagonist flumazenil has been used particularly to block poisonous effects in the remedy of acute benzodiazepine overdose. Withdrawal from persistent therapeutic abuse of sedative-hypnotic medicine is related to drug craving, nausea and belly cramps, tachycardia, palpitation, and generalized seizures. Panic attacks and disorientation could occur, progressing to paranoid psychosis with aggression, delusions, and visual hallucinations. Treatment consists of substitution with a long-acting sedative-hypnotic drug, such as phenobarbital, followed by a modest day by day reduction in the upkeep dose. Seizures represent a medical emergency and are handled by quick administration of diazepam, pentobarbital, or carbamazepine. Withdrawal from sedative-hypnotic drugs ought to be carried out in a hospital setting because life-threatening complications may develop. Abuse characteristics Patterns of oral use are usually intermittent and contain decrease doses causing milder results.
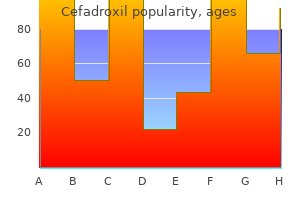
Proven 250 mg cefadroxilMortality rate: 5% to 8%; mostly ensuing from ventilator-associated pneumonia 6. Pathophysiology and epidemiology; inflammatory (macrophage-dependent) demyelination of nerve roots and peripheral nerves; immune-mediated illness presumably triggered by an influenza-like infection or different viral infections; prevalence 1 to 2 per 100,000 (6�7 per a hundred,000 in those >70 y/o); affects males more than females; 30% to 50% have relapsing-remitting course. Symmetric, affecting each motor and sensory fibers with muscle weak point and sensory loss c. In those larger than 50 y/o, extra males than women and more incessantly have thymomas f. Distribution of weak spot: ocular and facial weak point in 40% to 50% at presentation and 85% in some unspecified time in the future iii. Symptoms normally start in the course of the first 24 hours after start and should final for several weeks. Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita on account of lack of fetal movement in utero vi. Difficulty in feeding, generalized weak point, respiratory difficulties, weak cry, and facial weak spot vii. Etiologies (A)Medications (1)D-penicillamine (2)Aminoglycosides (3)Quinidine (4)Procainamide (5)Beta blockers (6)Synthroid (7)Lithium (8)Chlorpromazine (B)Infection ii. If unsure if myasthenic disaster versus cholinergic disaster, use Tensilon (edrophonium chloride) take a look at problem. Physical exam: ptosis with extended upgaze or decremental weak spot after repetitive exercise (particularly proximal muscles) c. Purified protein by-product of tuberculin (before initiating immunosuppressant treatment) vi. Thymectomy: in sufferers with or with out the presence of thymoma (but with different thymic abnormalities such as hyperplasia); sometimes recommended between ages eight and 55 years; maximal response 1 to four years after thymectomy c. Overmedication leading to miosis, elevated salivation, diarrhea, cramps, fasciculations ii. Treatment: withdrawal of anticholinesterase medicines underneath shut remark B. Paraneoplastic situation: 50% to 66% have most cancers, significantly small-cell (oat) lung carcinoma; onset of Lambert-Eaton typically precedes analysis of most cancers by 9 to 12 months. Erectile dysfunction, decreased lacrimation and sweating, orthostatism, and abnormal pupillary light reflexes additionally present f. Food-borne botulism: 1,000 instances per 12 months worldwide; usually homecanned greens; most related to type A spores ii. The most typical form is wound botulism and then that associated with subcutaneous heroin use. Neurotoxins types A, B, and E are the standard cause, but, not often, varieties F and G can be symptomatic. May cause a delayed neuropathy or myelopathy starting 1 to three weeks after acute exposure iv. Pathology: degeneration of the anterior horn cells and corticospinal tracts; Bunina bodies: intracytoplasmic, eosinophilic inclusions in anterior horn cells; muscle biopsy: fascicular atrophy, neurogenic atrophy (small angulated fibers) three. Hands could also be affected early, usually asymmetrically, after which the illness generalizes to involve the legs and bulbar muscular tissues (dysphagia, dysarthria, sialorrhea). A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized research of vitamin E plus riluzole versus riluzole alone showed no effect on survival after 12 months of therapy, however patients given vitamin E had been less prone to progress from the milder to the more severe state. Anti-epileptic medicine with delicate glutamate inhibitory properties (such as gabapentin and topiramate) have been ineffective in well-designed trials. Placement of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube may enhance survival price and quality of life. Weakness of the arms and legs can develop later, however signs can also remain restricted for years. Dysarthria and dysphagia appear first, followed by limb weak point; tongue fasciculations are current along with absent reflexes. Clinical features: age of onset is often after 40 years; normally starts as a slowly progressive spastic gait that later stabilizes; sufferers not often lose the power to stroll with a cane or some other help; sphincter is normally preserved, but spastic bladder can occur not often. Postpolio syndrome: sufferers usually complain of fatigue, as properly as a decline in practical talents, decades after the initial poliovirus an infection; pyridostigmine has been previously studied, with mixed outcomes. In addition to meningoencephalitis, West Nile virus is associated with a decrease motor neuron paralytic syndrome. Most of the cases had fever, meningitis, or encephalitis, and one-half had flaccid weak point that progressed over 3 to eight days; the weak point tended to be proximal and uneven. Histology implies degeneration and some regeneration however no proof of irregular storage products. Pathophysiology: deletion or duplication at Xp21 in 60% to 70% of cases; abnormality of dystrophin (a cytoskeletal protein situated in or near the plasma membrane and appears to be associated with membrane glycoproteins that link it to laminin on the external floor of the muscle fiber; when dystrophin is absent, the sarcolemma becomes unstable with subsequent excessive inflow of calcium because of harm, which causes muscle necrosis) ii. Clinical (A)X-linked recessive trait with females as carriers (B)Some carriers have delicate manifestations. Initially involves the muscles of the face and trapezius, pectoralis, biceps, and triceps; muscles of the decrease extremities are affected much later. Typically begins within the 2nd to third decade with pelvic involvement and soon spreads to contain shoulders (face spared) v. Clinical options (A)Primary form (1)Myotonia -delayed muscle leisure after contraction (2)Weakness and wasting affecting facial muscular tissues and distal limb muscle tissue (Hatchet Facies) (3)Long face with wasting of the masseter and temporal muscle tissue (4)Thin neck with losing of the sternocleidomastoids (5)Frontal balding in males (6)Cataracts (7)Cardiomyopathy with conduction defects (8)Gastrointestinal motility disturbances-cholecystitis, dysphagia, constipation, urinary tract symptoms (9)Multiple endocrinopathies (a)Hyperinsulinism, hardly ever diabetes (b)Adrenal atrophy (c)Infertility in girls (d)Testicular atrophy: growth hormone secretion disturbances (10)Low intelligence or dementia (11)Excessive daytime sleepiness (B)Congenital form i. Characterized by myotonia (90% of affected individuals) and muscle symptoms-weakness, ache, and stiffness (82%), and less generally by cardiac conduction defects, iridescent posterior subcapsular cataracts ("Christmas tree" cataracts), insulin-insensitive kind 2 diabetes mellitus, and testicular failure. Although myotonia has been reported during the first decade in some cases, onset is often within the third decade, mostly with fluctuating myalgia and with weak point of the neck and finger flexors. Subsequently, weakness happens in the elbow extensors and the hip flexors and extensors. Notably, facial weakness and weak spot of the ankle dorsiflexors are much less generally seen. Progressive ptosis and dysphagia develop late in life, with or with out extraocular muscle weak point. Pathology: muscle biopsy-variation of fiber measurement, occasional, inner nuclei, small angulated fibers, and an intermyofibrillary network with moth-eaten look when stained with oxidative enzymes 7. Unlike most dystrophies, predominantly impacts distal muscle tissue of higher extremities and lower extremities iii. Weakness typically begins in intrinsic hand muscular tissues, adopted by dorsiflexors of the wrist and foot. Pathophysiology: most have X-linked inheritance (but rare households have autosomal dominance). Clinical: weak point develops in humeroperoneal muscle tissue; early contractures with marked restriction of neck and elbow flexion; also cardiac abnormalities causing atrial fibrillation and a sluggish ventricular fee. Infection because of undercooked pork containing encysted larvae of Trichinella spiralis b. Post-initial gastroenteritis may have invasion of skeletal muscle tissue, however weak point is mainly limited to muscle tissue innervated by cranial nerves (tongue, masseters, extraocular muscle tissue, oropharynx, and so on).
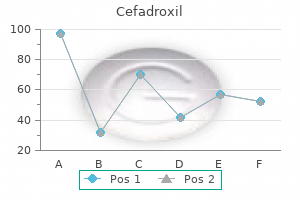
Buy 250mg cefadroxil with amexPsychosis might develop within 1 to 5 days after starting drug use and often lasts 6 to 7 days. The commonest signs are delusions of persecution; auditory, tactile, and especially visible hallucinations; and hyperactivity. Paranoia, hallucinations, and terror reactions result in hostility and difficulty in controlling rage. Amphetamine abusers display a high incidence of unpremeditated, unprovoked, and weird acts of violence and assaultive and even homicidal behavior. After amphetamine use is discontinued, confusion, delusions, and lack of reminiscence might persist for several weeks or months. Treatment of toxicity is predicated on enhancing the elimination of the drug from the body. Acidification of the urine with ammonium chloride increases the speed of urinary excretion of amphetamine and causes speedy discount of psychotic symptoms. Cocaine hydrochloride normally is inhaled as a "line" of powder containing 20 to 30 mg of the drug. It produces a maximum impact in 15 to 20 minutes and a duration of impact lasting 1 hour or more. Nasal mucosal vasoconstriction and paralysis of membrane cilia forestall full absorption by this route, and measurable cocaine remains on the nasal mucosa for three hours after use. Snorting of cocaine in answer produces effects in 5 to quarter-hour that last 2 to four hours. The mixture, referred to as a "speedball," is used to attenuate the extreme stimulation attributable to large doses of cocaine. The smoking of cocaine requires conversion of the hydrochloride salt of the drug to the freebase form. The salt form, when heated, decomposes earlier than the vaporization temperature is reached. Smokers might manufacture their own freebase by dissolving the salt in an alkaline solution and extracting the alkaloid with a solvent similar to ether. Since the mid-1980s, the freebase type Cocaine the leaves of the coca plant, which contain up to 1. The Andean Indians have chewed coca leaves, blended with an alkaline substance to promote launch of cocaine, for many years. Although peak blood concentrations of ninety five ng/mL are achieved, little drug-induced euphoria is reported among Andean Indians who chew coca leaves. The leaves are used to make cocaine paste (30% to 90% cocaine), which is transformed to pure cocaine hydrochloride, primarily in South America. Many samples of avenue cocaine apparently comprise adulterants corresponding to amphetamines, mannitol, or lidocaine. The local anesthetic procaine shares some traits with cocaine and may produce euphoria. Smokers common 100 mg of base with each smoke, rising to 250 mg with fast tolerance improvement. Smoking could also be repeated every 5 minutes, with consumption in compulsive abusers totaling 1. Smoking freebase cocaine has become the preferred method for administration of this drug, and much like methamphetamine freebase, the freebase type of cocaine has contributed considerably to the rise in its abuse. Used intranasally as a low-dose recreational drug, cocaine produces average addiction. Cocaine shares with different addictive medicine a reinforcing property that leads to speedy acquisition of self-administration habits. Cocaine enhances dopaminergic activity at the latter web site by blocking dopamine uptake by nerve endings. This endogenous reward system is normally activated by responding to physiologic imperatives corresponding to hunger, thirst, and intercourse drive. Cocaine instantly stimulates this reward circuitry, dominating motivation for essential physiologic needs. Frequent use resulting in fixed cocaine concentrations within the physique does cause tolerance, nevertheless. Withdrawal results in depression, dysphoria, social withdrawal, yearning for the drug, urge for food disturbances, tremor, and muscle pain. Such withdrawal phenomena could additionally be extreme enough to stop some abusers from stopping the drug, despite the very fact that poisonous delirium could develop with continued drug use. Oral diazepam has been helpful in treating withdrawal nervousness; psychotherapy or cautious use of tricyclic antidepressants is beneficial for prolonged despair. Abrupt will increase in arterial blood pressure, occurring inside minutes of intranasal use of cocaine, have resulted in subarachnoid hemorrhage, significantly in people with aneurysms of cerebral vessels. One case of deadly rupture of the ascending aorta was reported in an individual with preexisting persistent hypertension who had smoked freebase cocaine. Acute cardiac occasions could happen even with leisure intranasal use of cocaine in individuals with out predisposing cardiac disease. Hepatotoxicity, with medical findings of elevated titers of serum transaminases and jaundice, has been reported in chronic cocaine abusers. Such liver damage could occur in plasma cholinesterase�deficient people, in whom cocaine metabolism is shunted by way of hepatic oxidative pathways, resulting within the manufacturing of cytolytic superoxides. A significantly increased rate of spontaneous abortion has been noted in pregnant women. Because cocaine can cross the placental barrier, infants born to cocaine abusers may exhibit tremulousness. Frequent intranasal use leads to persistent rhinitis and rhinorrhea, atrophy of the nasal mucosa, loss of sense of scent, and necrosis and perforation of the nasal septum. These adjustments, occurring because of continual ischemia, should alert the clinician to potential intranasal cocaine abuse. Bruxism and temporomandibular joint problems are additionally extra frequent in cocaine abusers. Death from cocaine overdose often is attributable to generalized convulsions, respiratory failure, or cardiac arrhythmias. Deaths have occurred with each route of cocaine administration and could also be so fast that remedy comes too late. Because cocaine is metabolized by plasma esterases, individuals with low cholinesterase exercise are at excessive danger of cocaine fatality. Synthetic cathinones interact with monoamine transporters on nerve cells analogously to other psychostimulant drugs and thus produce desirable subjective effects similar to these attributable to amphetamine or cocaine. At excessive doses or extended use, artificial cathinones can cause psychosis, tachycardia, hyperthermia, and death. The syndrome is characterised by intense anxiety, incapability to focus, stereotyped compulsive conduct, paranoid delusions, and violent loss of impulse control.
Cheap cefadroxil 250mg on linePrognosis (A)Mortality of untreated instances is 70%; mortality for acyclovir-treated neonates is 15%. Gabapentin, pregabalin, and different anticonvulsants, antidepressants, and topical brokers are used for therapy of neuralgic ache. In immunocompromised individuals, small- and mediumsized vessels are involved, causing deep infarctions. Acute illness is normally asymptomatic; can current as nonspecific febrile sickness or infectious mononucleosis. Infection can also happen perinatally throughout passage by way of infected birth canal or breastfeeding. Louis encephalitis West Nile virus Japanese encephalitis California encephalitis Powassan Colorado tick fever Midwestern and northeastern June to September United States, southern Canada North-central United States, jap Canada United States and Canadian Rocky Mountains Spring, summer March to September a. Louis encephalitis virus (1)Clinical an infection in less than 1% (a)Encephalitis (60%) (b)Aseptic meningitis (15%) (c)Influenza-like illness (d)Nonconvulsive status epilepticus might happen more frequently than with different arbovirus infections. Orbivirus (A)Colorado tick fever virus (1)Clinical: fever, headache, myalgia, anorexia, nausea, and rash (similar to symptoms of Rocky Mountain spotted fever), adopted by aseptic meningitis (2)Treatment: supportive care solely (3)Prognosis: mortality rare three. Worldwide, 50,000 to 60,000 die yearly (but just one to 2 per yr in United States) c. Incubation: 1 week to years (shortest after an infection to the head and neck), often 1 to 3 months ii. Prodrome: headache, malaise, sore throat, nausea/vomiting, and/or belly ache iii. Furious = agitated encephalitis (A)80% of human rabies cases (B)Confusion, anxiousness, agitation, hallucinations, dysphagia, hydrophobia, hypersalivation, autonomic hyperactivity, and seizures (C)Death secondary to muscle spasms involving diaphragm or accent respiratory muscular tissues that lead to respiratory arrest or coma iv. Symptomatic (A)Supportive care only (B)Place in isolation as a end result of rabies virus is current in body fluids. Cognitive decline, visible subject deficits, cranial neuropathies, sensory deficits, motor deficits, speech disturbances, and ataxia progressing to dementia; headaches, extrapyramidal syndromes, and seizures are uncommon. Pathology: oligodendrocytes contain eosinophilic intranuclear inclusions; bizarre astrocytes. Non-polio enteroviruses (coxsackie, echovirus, human enterovirus 68-71) are the most common cause of aseptic viral meningitis. Usually occur in late summer time and fall (A)Polioviruses (1)Clinical (a)Usually restricted signs or asymptomatic (b)Neurologic manifestations (i)Aseptic meningitis (8%) (ii)Paralytic poliomyelitis (1%) [1]Usually due to poliovirus kind 1 [2]Prodrome of fever, headache, vomiting, myalgia, and meningeal indicators [3]Acute flaccid paralysis seems inside 1 to 2 days due to involvement of alpha motor neurons in the spinal twine. Post�polio syndrome is a late complication in 25% of sufferers because of exacerbation of motor weak spot 30 to forty years after an infection. Measles vaccination has been linked with acute encephalopathy and everlasting neurologic deficits. Postviral encephalomyelitis (A)1/1,000 circumstances of measles (B)Seen within 2 weeks after rash seems (C)Usually <10 y/o (D)Headache, irritability, seizures, somnolence, or coma; sometimes paralysis, ataxia, choreoathetosis, or incontinence (E)Treatment: supportive care (f)Prognosis: mortality = 10% to 15%; neurologic sequelae = 20% to 60% iii. Measles inclusion physique encephalitis (A)Rapidly progressive neurodegeneration (B)Develops 1 to 6 months after infection (C)Patients normally have deficiency of cell-mediated immunity or are immunocompromised. Sequelae: psychological retardation, cataracts, sensorineural listening to loss, irregular tone and posture, congenital heart illness iii. Progressive rubella panencephalitis: follows congenital or childhood rubella, with neurological deterioration progressing to demise in the second decade of life d. Diagnosis: prenatal analysis possible by way of amniotic fluid or rubella-specific IgM in fetal blood. Opportunistic infections and malignancies of the nervous system (A)Most opportunistic infections are as a outcome of reactivation of latent an infection. Infection acquired by the bite or inoculation of contaminated vector feces into the pores and skin or mucous membranes 2. Clinical: preliminary fever, headache, and malaise followed by rash and neurological symptoms three. Neurological symptoms: agitated delirium related to pyramidal tract signs and neck stiffness adopted by seizures and brainstem dysfunction ii. Other methods: thrombocytopenia, hyponatremia, increased liver perform checks and creatinine, myocarditis c. Spreads from animals to people by inhalation of the infected dust or by handling infected animals; primarily an occupational illness, mainly affecting shepherds and farmers iii. Direct extension of sinusitis (40%); otitis, facial infection, or dental infection (5%) ii. Generalized septicemia (30%): often a quantity of abscesses; seen in pulmonary infections, bacterial endocarditis iii. Common organisms: aerobic and anaerobic streptococci, staphylococci, Bacteroides, Enterobacteriaceae, and anaerobic organisms c. Initial cerebritis adopted by central necrosis with surrounding vasogenic edema followed by capsule formation 2. Immunocompromised patients and sufferers with congenital coronary heart disease extra susceptible three. Antibiotics: third-generation cephalosporin with metronidazole and vancomycin if Staphylococcus suspected b. Cranial epidural abscess Source of an infection: local unfold from cranial infection or after trauma or surgical procedure Common organisms: S. Source of an infection: native unfold from cranial an infection or after trauma or surgery 2. Caused by the neurotoxins of gram-positive spore-forming anaerobes Clostridium botulinum and, in uncommon instances, Clostridium butyricum and Clostridium baratii b. Eight distinct type of botulism toxins; neurotoxins varieties A, B, and E are most regularly liable for illness in people, whereas sorts F and G have been reported solely sometimes. Irreversible binding to the presynaptic membrane of cholinergic nerve endings within the neuromuscular junction, parasympathetic and sympathetic ganglia ii. Symptoms 12 to 38 hours after ingestion of meals as a result of ingestion of preformed toxin ii. Descending weakness from cranial nerves (ptosis, diplopia, blurred imaginative and prescient, dysphagia, and dysarthria) to proximal muscle tissue, including respiratory muscle tissue iii. Autonomic signs: dilated pupils, dry mouth, urinary retention, ileus, vomiting, abdominal cramping, constipation b. Constipation, lethargy, hypotonia, poor sucking, weak cry, poorly reactive pupils, respiratory misery iii. Antitoxin: human-derived botulinum immunoglobulin for infants and equine serum botulism antitoxin for kids older than 1 year and adults c. Systemic: primary involvement of lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow, but almost every organ could additionally be involved. Neuropathology: granulomas, demyelination, thickening of leptomeninges, angiitis, mycotic aneurysms, and degeneration of anterior horn cells 3. Systemic: chills, fever, headache, generalized weak spot, muscle ache, and arthralgias with lymphadenopathy b. Prevention: keep away from consumption of undercooked meat and unpasteurized dairy products.
Purchase cefadroxil mastercardOral cephalosporins are usually well absorbed, with all except cefadroxil and cefprozil having their absorption delayed, but not reduced, by meals. Plasma protein binding is 10% for cephalexin, 25% for cefaclor, 8% to 17% for cephradine, and 80% to 90% for cefazolin and cefoxitin. Excretion of most cephalosporins takes place primarily by glomerular filtration and energetic tubular secretion within the kidney. The serum half-life is 50 to eighty minutes for cephalexin, forty eight to eighty minutes for cephradine, and 35 to 54 minutes for cefaclor. In sufferers with end-stage renal disease, these half-lives might improve to 19 to 22 hours for cephalexin, eight to 15 hours for cephradine, and 2 to three hours for cefaclor. Firstgeneration medicine are used to treat infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. A subset of second era medication represented by cefoxitin has good activity in opposition to many gram-negative anaerobes. Third-generation drugs have turn out to be prominent within the remedy of significant gram-negative coccal and bacillary infections. They are very useful in treating meningitis, pneumonia, gonorrhea, and sepsis from delicate organisms. Cephalosporins are often given with aminoglycosides for gram-negative bacilli infections. There are vital particular person variations between members of the third-generation drugs, and never all indications apply to every member. Cefepime is resistant to many -lactamases and is efficient in treating some gram-negative bacilli that produce -lactamases. Ceftaroline has exercise in opposition to methicillin-resistant staphylococci as nicely as several gram-negative organisms (see Table 33-6). Cephalosporins have good activity in opposition to many orofacial pathogens but limited exercise towards oral anaerobes. Serious antagonistic reactions associated with cephalosporins are uncommon, with the main concern being the potential for cross-allergy with penicillins. Less widespread antagonistic reactions include transient increases in liver enzymes, nephrotoxicity, reversible neutropenia, eosinophilia and thrombocytopenia, aseptic meningitis, and disulfiram-like reactions associated with cephalosporins with the methylthiotetrazole side chain. The inherent allergic potential of cephalosporins along with their cross-allergenicity with penicillins is of main concern. Cutaneous allergic reactions to cephalosporins (rash, pruritus, urticaria) are commonly reported to occur in 1% to 3% of sufferers. Anaphylactic reactions to cephalosporins seem to be rare, with an incidence ranging from 0. In 9388 sufferers without a historical past of penicillin allergy given cephalosporins, two anaphylactic reactions have been reported (0. In a retrospective study of 350,000 adverse drug reactions, six deadly cases of cephalosporin-induced anaphylaxis were reported, with three of the six cases in patients with a history of penicillin allergy. The problem of cross-sensitivity between the cephalosporins and penicillins has by no means been satisfactorily resolved. Penicillin-allergic individuals may have a fourfold larger danger of allergy to cephalosporins than individuals not allergic to penicillins; however, penicillin-allergic individuals have a three to four times higher risk of allergy to any drug. No pores and skin test is on the market to detect cephalosporin allergy, and expertise with desensitization is limited and not standardized. Antacids, H2 histamine receptor antagonists, proton pump inhibitors, as properly as iron supplements may scale back the oral absorption of some cephalosporins. Some cephalosporins similar to cefotetan may induce a disulfiram response with ethanol and will trigger hypoprothrombinemia. Nephrotoxicity could also be seen with the mixture of cephalosporins with aminoglycosides or loop diuretics. Cephalosporins are contraindicated in sufferers allergic to these medication and in individuals with a historical past of extreme penicillin reactions or a positive pores and skin check reaction to the penicillin minor determinant mixture. Carbapenems are derivatives of thienamycin (from Streptomyces cattleya) and differ from penicillins by the alternative of the sulfur by a methylene group in the five-membered ring of the -lactams. Currently, four carbapenems can be found for parenteral use within the United States: imipenem, meropenem, ertapenem, and doripenem. Imipenem is combined with cilastatin to cut back the hydrolysis of imipenem by renal dehydropeptidase. Aztreonam is a monocyclic -lactam (monobactam) lacking the thiazolidine ring of penicillin. Aztreonam induces -lactamase production and could also be synergistic with the renal toxicity and ototoxicity of aminoglycosides. Erythromycin is active in opposition to gram-positive aerobic/facultative staphylococci and streptococci, gram-negative anaerobes (M. Erythromycin, as derived from Streptomyces erythreus, was introduced in 1952, and azithromycin and clarithromycin had been introduced in 1991 and 1992, respectively. Azithromycin is a 15-membered macrolide with an added nitrogen and N-methylation (making it technically an azalide), whereas clarithromycin is fashioned by the alkylation of a hydroxyl group of erythromycin (a 14-membered ring). Bioavailability ranges from 10% for dirithromycin to 40% to 50% for azithromycin, clarithromycin, and erythromycin. The time to most blood concentrations of the macrolides after oral administration is about 2 hours. Impaired renal perform might cut back the excretion of the macrolides, with the elimination half-life of erythromycin growing from 1. Clarithromycin and erythromycin are primarily eliminated in the urine, and azithromycin is primarily eliminated within the bile, although erythromycin may also endure important biliary excretion. The average serum half-lives are 68 hours for azithromycin, 3 to 7 hours for clarithromycin, and 1. A outstanding property of macrolides and highly fat-soluble tetracyclines and clindamycin is selective uptake by phagocytic cells and fibroblasts, which perform as repository drug depots and as a drug supply system to areas of irritation and infection. These cells concentrate *Specific macrolide(s) for many indications are listed in Table 33-5. Other macrolide resistance mechanisms embody energetic efflux genes encoding for transport efflux proteins and an esterification gene that codes for inactivation of the macrolides by phosphorylation and glycosylation. Motilin is a regulatory peptide of the gastrointestinal tract that stimulates enzyme secretions by the abdomen and pancreas and induces strong phasic contractions of the abdomen. The most important agonists of the motilin receptor are the 14-membered macrolides (erythromycin); azithromycin and clarithromycin are lesser stimulants. Approximately 30 instances have been reported of macrolide-induced hearing loss, with a minimal of two instances judged to be irreversible. Most appear to be related to erythromycin doses exceeding 4 g/day or from accumulation of lesser doses in sufferers with impaired renal or hepatic function. In patients with renal impairment, the dose of erythromycin must be no greater than 1. All macrolides induce ototoxicity, presumably by an impact on the auditory nerve pathways, and tinnitus has been observed even with therapeutic doses of azithromycin. Stevens-Johnson syndrome (erythema multiforme) could occur with erythromycin along with a hypersensitivity syndrome related to azithromycin and clarithromycin consisting of fever, rash, hepatitis, interstitial nephritis, oliguria, and xerostomia.
Order cefadroxil 250mg fast deliveryChanges in pharmacokinetics of toxicants are a frequent foundation for altered dose�response relationships. Known influences embody elevated toxicant bioactivation by enzyme induction, similar to occurs in certain variants of cytochrome P450 with exposure to phenobarbital or polychlorinated biphenyls. Conversely, inhibition of metabolic clearance is possible with interacting chemical substances, rising the pharmacodynamic motion of medicine and chemicals. The cytochrome P450 isozyme 3A4 is an important enzyme in human drug metabolism, and its presence within the intestine and liver subjects it to inhibition by many medicine and dietary components, such as grapefruit juice. Conversely, substances are sometimes less poisonous by the oral route when administered with meals as a consequence of less speedy absorption. The time and frequency of administration could be important in altering dose�response relationships via functional adjustments. Many compounds induce tolerance upon repeated administration, whereas others can become extra poisonous with carefully repeated administration. Receptor densities and sensitivity could differ with time or as a consequence of earlier publicity. An example of the latter is the wellknown tolerance that develops to long-term administration of opioids. Recognition and understanding of relevant aspects of human variety derived from useful genomic analyses offer potential for therapeutic features. These efforts have spawned new phrases, including pharmacogenetics, representing characterized genetic differences in drug metabolism and disposition, and pharmacogenomics, used to describe the broad spectrum of genes that have an effect on drug response (see Chapter 4). A summary is available that describes progress in figuring out genetic polymorphisms relevant to drug action and disposition. Similar advances are prone to be utilized to perceive genetic differences that end in poisonous results except for those who arise throughout drug remedy. Approximately 400 million people worldwide exhibit a heritable deficiency in the cytoplasmic enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. High human exposures trigger a dermatologic toxicity often identified as chloracne in some people. The penalties of metabolism of medication and chemical substances after ingestion are extraordinarily important. The following example illustrates the importance of understanding toxic effects relative to drug metabolism. Terfenadine is a nonsedating histamine H1 receptor antagonist that was broadly used for reduction of signs of seasonal allergy. This drug was removed from the market as a result of research revealed cardiotoxicity when terfenadine was given with erythromycin. Of explicit significance to the interpretation of toxicologic research are interspecies differences, which can confound understanding and interpretation of outcomes from animal models. Well-known differences in physiology, metabolic charges, pharmacokinetics of toxicant metabolism and excretion, and sites of toxicant motion mediate these interspecies differences. Advances involving physiologically based mostly pharmacokinetic modeling and use of predictive, mechanistically based biomarkers offer promise of augmenting, or in some circumstances obviating, conventional toxicity testing. Acute versus Chronic Toxicity Toxicity could be categorised by the period of time required for improvement of the opposed effect. For this function, the time period acute describes toxicity with a sudden onset, whereas chronic indicates a protracted latency or period. In epidemiology, this classification usually describes the time between exposure and onset of toxicity. Intoxication is an acute effect that outcomes from ingestion of a giant amount of ethanol over a short time. Alternatively, the progressive, diffuse architectural injury to the liver often identified as cirrhosis happens over years with chronic ethanol publicity. In experimental toxicology, these phrases are used to discuss with experimental paradigms involving the duration of remedy or exposure. Acute testing typically describes a single treatment, whereas continual toxicity testing usually includes dosing or feeding a chemical over the lifetime of a species, as in a rodent carcinogenicity bioassay. If exposure occurs repeatedly at intervals extra frequent than the time required to get rid of a toxicant, the fabric accumulates within the physique throughout the period of exposure. Although every publicity could also be less than toxic, accumulation might produce toxic concentrations if publicity continues for adequate time. The main determinant is the rapidity of elimination relative to the frequency and magnitude of publicity. Slowly eliminated toxicants, similar to lipophilic chemical compounds or materials readily certain in tissues, have the best potential for accumulation. Chronic toxicity could exhibit little or no apparent relationship to acute toxicity. Of the many examples of continual toxicity, carcinogenesis presently is of nice concern in society. Precancerous mobile changes occur and develop slowly and will remain undetected over lengthy durations. Periodic dental examinations typically play a significant function in detection of cancers of the oral cavity. Knowledge of affected person habits with adverse potential health results, such because the link between tobacco use and prevalence of oral lesions, assists the dental practitioner in being vigilant against such persistent toxicity. Local versus Systemic Effects Toxic results can happen at a web site of exposure, similar to dermal contact, or at some website distant from the point of chemical contact or entry. Local effects dependent on utilized concentration are usually diminished by dilution with physiologic fluids and diffusion within tissue away from the site of software. If the effect is caused by reversible interaction with a receptor, such as that of a neighborhood anesthetic, the impact is attenuated by diffusion, and the system is returned to a extra normal state because the drug dissociates from receptors. This phenomenon is routinely used in dental follow with the inclusion of epinephrine with native anesthetics, corresponding to lidocaine, to limit native blood flow and lengthen period of native anesthetic motion. For toxicants that act via destruction of normal cellular architecture, corresponding to a caustic agent, return to normality requires repair of membranes and mobile buildings. Systemic results are facilitated by transport within the body fluids and could also be influenced by metabolism. Depending on whether or not biotransformation prompts a protoxicant or detoxifies a toxicant, the consequences of systemic processing can enhance or attenuate toxicity. Compounds may be more or less poisonous by the oral route than by different means of systemic publicity, as the first-pass impact of intestine or liver serves to activate or take away toxicants before distribution in the systemic circulation. Chemically Related Toxicants Understanding of chemical toxicity requires data of associated chemical compounds which may be present as impurities because of manufacturing or exist as a outcome of environmental results. Although dioxin existed at low part-per-million ranges within the herbicide mixture, the extreme toxicity of this contaminant in certain species created grave concern for contaminated areas.
References - Pulido JE, Furth SL, Zderic SA, et al: Renal parenchymal area and risk of ESRD in boys with posterior urethral valves, Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 9(3):499n505, 2014.
- Tang K, Xu Z, Xia D, et al: Early outcomes of thulium laser versus transurethral resection of the prostate for managing benign prostatic hyperplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies, J Endourol 28(1):65n72, 2014.
- von der Maase H, Specht L, Jacobsen GK, et al: Surveillance following orchidectomy for stage I seminoma of the testis, Eur J Cancer 29A:1931n1934, 1993.
- Jha S, Gray T: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact of native tissue repair for pelvic organ prolapse on sexual function, Int Urogynecol J 26(3):321n327, 2015.
- Abdel-Aziz KF, Anderson JK, Svatek R, et al: Laparoscopic and open retroperitoneal lymph-node dissection for clinical stage I nonseminomatous germ-cell testis tumors, J Endourol 20:627n631, 2006.
|
|

