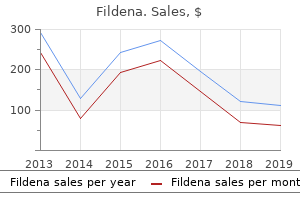
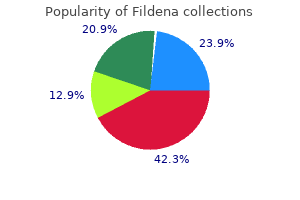
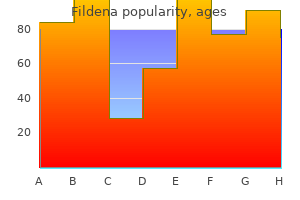
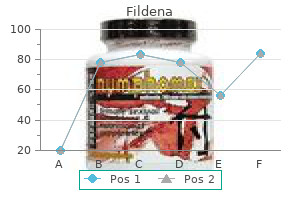
"Discount 100mg fildena free shipping, erectile dysfunction treatment old age."By: Peter Bartlett Bressler, MD - Associate Professor of Medicine
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/peter-bartlett-bressler-md
Discount 50 mg fildena visaHypocalcemic focal seizures in a one-month-old toddler of a mother with a low circulating degree of vitamin D. Accidental intoxication of the fetus with native anesthetic drug during caudal anesthesia. Plasma levels of lidocaine (Xylocaine) in mother and newborn following obstetrical conduction anesthesia: scientific applications. Brain tissue ranges in a deadly case of neonatal mepivacaine (Carbocaine) poisoning. Blood concentration of mepivacaine and lidocaine in mother and child after epidural anesthesia. Diagnosis, remedy, and follow-up of neonatal mepivacaine intoxication secondary to paracervical and pudendal blocks throughout labor. Pathogenesis of seizures occurring during restoration of plasma tonicity to normal in animals previously chronically hypernatremic. The incidence of seizures after rehydration of hypernatremic rabbits with intravenous or advert libitum oral fluids. Atypical shows of pyridoxinedependent seizures: a treatable cause of intractable epilepsy in infants. Focal status epilepticus as atypical presentation of pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy. Prevalence of pyridoxine dependent seizures in south Indian children with early onset intractable epilepsy: a hospital based mostly prospective study. Pyridoxine-dependent seizures: a household phenotype that results in severe cognitive deficits, regardless of treatment regime. Vitamin Responsive Conditions in Paediatric Neurology International Review of Child Neurology Series. Vitamin B6-dependency of glutamic acid decarboxylase in the kidney from a patient with vitamin B6 dependent convulsion. Seizures and paroxysmal occasions: signs pointing to the prognosis of pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy and pyridoxine phosphate oxidase deficiency. Pyridoxine-dependent seizures in Dutch sufferers: analysis by elevated urinary alphaaminoadipic semialdehyde ranges. Folinic acid-responsive seizures presenting as breakthrough seizures in a 3-month-old boy. Defective glucose transport throughout the blood-brain barrier as a cause of persistent hypoglycorrhachia, seizures, and developmental delay. A patient with dysfunction of glucose transport at the blood-brain barrier however regular cytochalasin B binding and immunological reactivity to glucose transporter protein on erythrocyte membranes [abstract]. Defective glucose transport throughout brain tissue limitations: a newly recognized neurological syndrome. Seizure characterization and electroencephalographic features in Glut-1 deficiency syndrome. Benign familial neonatal convulsions: evidence for clinical and genetic heterogeneity. Confirmation of linkage of benign familial neonatal convulsions to D20S19 and D20S20. Neonate with benign familial neonatal convulsions: recorded generalized and focal seizures. Benign familial neonatal-infantile seizures: characterization of a brand new sodium channelopathy. Detection of seizure exercise within the paralyzed neonate using continuous monitoring. Bilateral tonic-clonic epileptic seizures in non-benign familial neonatal convulsions. The early-infantile epileptic encephalopathy with suppression-burst: developmental aspects. Clinical and electroencephalographical follow-up study of early myoclonic encephalopathy. Early epileptic encephalopathy with suppression bursts and olivary-dentate dysplasia. Intrauterineonset myoclonic encephalopathy related to cerebral cortical dysgenesis. A case of Ohtahara syndrome with olivary-dentate dysplasia and agenesis of mamillary bodies. Early-infantile epileptic encephalopathy with suppression-bursts, Ohtahara syndrome; its overview referring to our sixteen circumstances. Clinical and laboratory findings in twins with neonatal epileptic encephalopathy mimicking aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Molecular bases and clinical spectrum of early childish epileptic encephalopathies. Genotype-phenotype correlations in neonatal epilepsies attributable to mutations within the voltage sensor of K(v)7. Early-onset epileptic encephalopathy brought on by gain-of-function mutations within the voltage sensor of Kv7. Migrating partial seizures in infancy: increasing the phenotype of a uncommon seizure syndrome. Mutational scanning of potassium, sodium and chloride ion channels in malignant migrating partial seizures in infancy. A case of malignant migrating partial seizures in infancy as a continuum of childish epileptic encephalopathy. The temporal evolution of electrographic seizure burden in neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Subclinical seizures identified by postoperative electroencephalographic monitoring are frequent after neonatal cardiac surgical procedure. The precise ictal and interictal period of electroencephalographic neonatal seizures. Engineering elements of the quantified amplitude-integrated electroencephalogram in neonatal cerebral monitoring. Three-channel electroencephalogram montage in neonatal seizure detection and quantification. Amplitude-integrated electroencephalography interpretation during therapeutic hypothermia: an educational program and novel teaching tool. Impact of amplitude-integrated electroencephalograms on clinical look after neonates with seizures. Neonatal seizures in very preterm and really low birthweight infants: mortality and handicaps at two years of age in a nationwide cohort. To treat or not to treat: a survey of present medical follow towards neonatal seizures. Prophylactic phenobarbital administration after resolution of neonatal seizures: survey of present apply.
Black Walnut. Fildena. - Are there any interactions with medications?
- How does Black Walnut work?
- Dosing considerations for Black Walnut.
- What is Black Walnut?
- Leukemia and infections such as diphtheria, syphilis, intestinal worms; use as a gargle; and skin wounds.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96630
Purchase discount fildenaMore common within the newborn interval is tonic deviation of the eyes to one facet as a manifestation of seizure (accompanied typically by nice jerking actions of the deviated eyes) or of a postictal state. Vertical gaze palsies are rare in the newborn; I even have seen only defects of upward gaze with ensuing downward deviation, as noted earlier. These abnormalities have occurred on the premise of presumed pretectal involvement by a massively dilated third ventricle (posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus or congenital aqueductal stenosis), main acute intraventricular hemorrhage, kernicterus, posterior fossa hemorrhage, or hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Episodic (paroxysmal) downward deviation of the eyes lasting for several seconds could occur in the absence of overt neurological disease after which resolve by 1 to 6 months of age. Paroxysmal downward deviation can also occur later in the first yr, especially in preterm infants with extreme injury (periventricular leukomalacia) of posterior cerebral white matter and, maybe, connections to the pretectal area. Paroxysmal upgaze, characterised by episodes of tonic upgaze of 15 to 30 seconds, has been documented as early as the first week of life but usually has its onset at roughly 6 months of age and is later typically associated with minor cognitive deficits and ataxia. The multidirectional nature of the movements is the important criterion for distinction from seizure. I have observed opsoclonus and ocular flutter (jerking similar to that of opsoclonus but confined to the horizontal plane) in infants with maple syrup urine disease, nonketotic and ketotic hyperglycinemia, and posterior fossa hemorrhage. Nystagmus with onset at delivery or the primary few days of life ought to suggest the prognosis of congenital nystagmus. The horizontal nature of the nystagmus persists with vertical gaze, an necessary diagnostic level. The familial selection could additionally be both autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked recessive. The oscillations in an affected member of the family may be so reduced as to have been missed up to now. Visual impairment is present in the minority of patients, and static neurological deficits are present in the majority of nonfamilial (but not familial) instances with visual impairment. Because nystagmus could be observed, albeit uncommonly, in the new child with severe visual deficit or with diencephalic or brain stem lesions. A transient, idiopathic nystagmus has been described in early infancy, with disappearance at a imply age of 8 months. The commonest pathological substrate is hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, particularly with infarction in the distribution of the middle cerebral artery, and less commonly cerebral contusion (with or with out subdural hemorrhage). The purpose for this apparent facial sparing may relate to the chance that, throughout normal improvement of the corticobulbar system, there are ipsilateral terminations of every corticobulbar tract that are eradicated postnatally by selective elimination of axonal processes and of synapses (see Chapter 7) however that are retained when the normal contralateral enter is lost. Rare causes of injury to the facial nerve involve compression from a posterior fossa hematoma, whether intracerebellar or extraparenchymal. In nerve accidents, the higher in addition to the decrease face is usually affected, and eye closure is notably poor. Note, at relaxation, on the affected side (right) the widened palpebal fissure, flattened nasolabial fold, and depressed corner of the mouth. Facial weak spot secondary to disturbance of the cerebrum is usually more apparent with the baby at rest or in the course of the first movements of spontaneous facial features and could also be completely inapparent in the course of the full actions of crying. Nuclear, cranial nerve, neuromuscular, or muscular lesions, nevertheless, are usually more obvious throughout elicited facial motion, such as a cry or grimace. A easy classification of the kinds of facial weak spot that may occur within the neonatal interval is supplied, in accordance with the level of the lesion, in Table 9. Each of those specific disorders is discussed in more element in other related chapters of this book. Difficulty with eye closure, flattened nasolabial fold, issue sucking, and drooling are prominent features. In view of the relative frequency of mind stem nuclear harm with perinatal asphyxia, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy could also be associated with bilateral weakness of each the upper and decrease face. Bilateral facial weakness-often with ptosis, dysphagia, and generalized hypotonia-may accompany both the neonatal transient or congenital sorts of myasthenia gravis (see Chapter 32). Diagnosis within the new child is made greatest by observing the response to neostigmine or edrophonium. In the former, extra widespread variety of myasthenia gravis, the mother also has the disorder. In addition to facial diplegia, the infant with childish botulism exhibits unreactive pupils, dysphagia, peripheral weak point, hypotonia, and constipation. Hereditary forms of deafness are common and account for roughly 50% of all instances of congenital eb oo ks fre. Definition of serious hearing loss within the newborn infant by clinical examination is difficult. However, detection or a minimum of severe suspicion of main hearing deficits is usually possible. In addition to the absence of startle and extra refined responses to sound, a sometimes valuable clue to a critical listening to deficit within the alert young infant is apparent visual hyperattentiveness and constant startle when the examiner approaches the kid shortly from the periphery. The use of mind stem auditory evoked potentials is of main worth (see Chapter 10). Universal neonatal screening (relative to selected screening) has been proven to lead to the sooner prognosis of listening to loss and faster intervention. Early prognosis is important because language development is benefited by early corrective efforts and impaired by delay in correction. Unfortunately this mnemonic neglects the extra class of the time period toddler subjected to apparent hypoxic-ischemic insults, a category I have added to Table 9. Injury to cochlear nuclei secondary to marked hyperbilirubinemia is an uncommon isolated reason for extreme listening to loss (see Chapter 26). Results of studies of untimely infants recommend that less marked elevations of serum bilirubin stage (<20 mg/dL) exert at least an essential additive effect in the genesis of sensorineural hearing loss. Many different hereditary syndromes related to deafness current later in infancy and childhood. Of these, the primary two are autosomal recessive issues and the latter two are autosomal dominant. Autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked recessive, and mitochondrial inheritances are acknowledged. The gene encodes a connexin protein involved in gap junctions and perhaps potassium inflow for mechanosensory transduction in mind cells. These problems usually could be distinguished on medical grounds by recognition of different features (see Chapter 33). Restricted weak point of the face is attribute of hypoplasia of the depressor anguli oris muscle (see Chapter 33). In this disorder, the corner of the mouth is unable to retract and to be depressed. The abnormal audiograms of all 24 youngsters, 8 to 10 years of age, with neurosensory listening to loss have been averaged.
Discount 100mg fildena free shippingSmall intragenic deletions/insertions and nonsense, missense, and splice website mutations. Unlike the scenario with problems of the cerebrum and other central causes of hypotonia, weak point is equally extreme. Only minimal movements at hips and shoulders may be elicited within the presence of energetic movements of hands and ft. Muscle atrophy can be severe and generalized, though the severity could additionally be tough to recognize fully within the newborn. Indeed the alternative of atrophied muscle by connective tissue may additional hinder the appreciation of atrophy. These options relate to weak point of the intercostal oo oo ks re ks fre fre ks f ok s oo oo oo ks fre. Contractures of the limbs, usually solely at wrists and ankles, are evident in 10% to 20% of infants with onset in utero or within the first month of life. Thus extraocular actions are normal, and facial motility is comparatively nicely preserved. Indeed, the pathetic image of a bright-eyed, almost completely paralyzed infant is attribute of Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. Sucking and swallowing are affected early in the course in roughly half of instances. Fasciculations and atrophy of the tongue, scientific indicators in anterior horn cell problems of barely later onset, are obvious in only about one-third to one-half of sufferers, with the illness occurring at delivery or in the first month. Both these capabilities could be anticipated to be affected with major spinal cord illness, and sensory operate with peripheral nerve disease. Total areflexia and absence of ptosis, ophthalmoplegia, and facial weak point rule towards a wide range of primary diseases of muscle. When subject is supine, observe the frog-leg positioning of the legs and the dearth of traction response (B) and the lag of head (C), with makes an attempt by the examiner to pull the toddler to a sitting position. Infants with clinical onsets after 2 months of age have clearly longer median and maximum survival occasions. Characteristically, pronounced atrophy of all fibers of each varieties inside entire fascicles of muscle. Motor nerve conduction velocities are usually regular, though in particularly extreme disease, a slight reduction may be noticed. In contrast, the sensory nerve action potentials are normal, which underscores the motor neuron nature of the illness. These complications are caused by aspiration because of faulty swallowing, hypoventilation due to impaired intercostal muscle operate, and impaired clearing of tracheal secretions secondary to weak or absent cough because of weak abdominal muscle tissue. This virtual absence of signs of terminal axonal sprouting and reinnervation (see Chapter 30) is probably indicative of the severe, fulminating course of involving anterior horn cells that causes widespread elimination before such compensatory attempts can occur. Hypertrophy of predominantly sort I fibers, usually in clusters, is an extra attribute function. The discovering that these hypertrophic fibers typically happen in clusters suggests the potential of reinnervation. The distribution of the histopathological findings parallels the generalized pattern of muscle weak point; the diaphragm is co. Note the clear neurogenic sample of grouped atrophy and hypertrophic fibers, with modest enhance in endomysial connective tissue. Enhanced apoptosis of anterior horn cell neurons is probably the most prominent function during fetal life. The degenerative modifications consist significantly of central chromatolysis, characterised by rounded and distended neuronal cell our bodies with eccentric nuclei and Nissl substance displaced to the periphery. Frequent aspiration of the oropharynx is required, and normally cessation of oral feedings and establishment of tube feeding are required before long to guarantee adequate diet. Indeed, when dysphagia turns into severe enough to preclude reasonable nutrition and is sophisticated by frequent aspirations, many clinicians recommend gastrostomy or gastrojejunostomy feeding. Radiographs of the chest are useful in demonstrating the chest deformity, the thin ribs characteristic of extreme congenital neuromuscular illness,117-119 and the marked atrophy of muscle. The motor nucleus of nerve V is affected in approximately 70% of circumstances, and the abducens nucleus is involved in fewer than 50% of circumstances. Hypoxic adjustments are often noticed in hippocampal neurons and Purkinje cells of cerebellum. The motor nerves exhibit the changes anticipated from a lack of anterior horn cells. Indeed, the glial proliferation may be so conspicuous that some workers have attributed to it a pathogenetic position. The glial response consists of each microglia and astrocytes and is particularly outstanding in the ventral aspect of the anterior horns. Surveillance for respiratory infection have to be diligent, as a result of this complication is the standard mode of demise for these unlucky babies. In severe Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, my strategy is foremost to provide emotional support to the mother and father and to guarantee as a lot comfort as attainable for the infant. I point out to the family our current understanding of the dire outcome and suggest cautious consideration to oral-pharyngeal secretions, measures to guarantee adequate diet, and diligent remedy of respiratory infections. Between 1 and 6 months of age, respiratory misery secondary to diaphragmatic paralysis becomes obvious, and progressive major distal lower limb weak spot ensues. Motor, sensory, and autonomic disturbances develop; these infants turn into ventilator dependent. Respiratory failure and progressive weakness result in demise within the first days to weeks in most infants. However, some instances with predominance of bone fractures probably are autosomal recessive. Among neuroprotectors, olesoxime, a mitochondrial pore modulator that enhances motor neuron survival in tradition, may be effective in stabilizing the illness, however riluzole and gabapentin have proven combined outcomes. I choose to use the term neurogenic arthrogryposis multiplex congenita for the clearly nonprogressive forms of arthrogryposis related to anterior horn cell or peripheral nerve illness. By far the commonest variety is amyoplasia congenita, in all probability associated typically to a dysgenetic disturbance of anterior horn cells, described in Chapter 31. Thus as a result of this and different generalized types of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita secondary to anterior horn cell have been discussed, I consider on this section solely the localized varieties. A few sufferers later developed indicators within the upper extremities and fasciculations of the tongue after a quantity of years. Infants require ventilatory assist at a median age of 6 months, and death in one giant sequence (n = 168) occurred at a median age of approximately 9 months. In the localized varieties, the potential for a correctable structural lesion of the cervical cord or the lumbosacral wire and cauda equina ought to be ruled out by applicable studies. Large vacuoles, often confluent, are obvious when commonplace fixation procedures co.
Order discount fildena on linePreferential blood flow enhance to the mind stem in reasonable neonatal hypoxia: reversal by naloxone. Cerebrovascular hemodynamics throughout and after recovery from acute asphyxia within the new child dog. Cerebral blood move throughout experimental hypoxaemia and ischaemia within the new child piglet. Blood circulate and metabolism throughout and after repeated partial brain ischemia in neonatal piglets. Cerebral hemodynamics on near-infrared spectroscopy in hypoxia and ischemia in younger animal studies. Changes in cerebral cyclic nucleotides and cerebral blood move throughout prolonged asphyxia and recovery in new child pigs. Cerebral ischemia/ reperfusion increases endothelial nitric oxide synthase degree by an indomethacin-sensitive mechanism. The impact of antioxidative mixture remedy on submit hypoxic-ischemic perfusion, metabolism, and electrical exercise of the new child mind. Acute hypoxia increases S100beta protein in affiliation with blood flow redistribution away from peripheral circulations in fetal sheep. The regional distribution and determinants of myocardial blood circulate throughout asphyxia in the fetal lamb. Effects of anoxia on cerebral blood move in the rat mind: proof for a job of adenosine in autoregulation. Effects of hypoxia on beta-endorphin and beta-lipotropin launch in fetal, new child, and maternal sheep. Plasma beta-endorphin in perinatal asphyxia and respiratory difficulties in new child infants. The effects of hypoxia on (methionine) enkephalin peptide and catecholamine launch in fetal sheep. Delayed seizures occurring with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in the fetal sheep. Brain metabolism and intracellular pH throughout ischaemia and hypoxia: an in vivo 31 P and 1H nuclear magnetic resonance examine within the lamb. Acid homeostasis following partial ischemia in neonatal mind measured in vivo by 31P and 1 H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Decreased cerebral blood circulate after administration of sodium bicarbonate within the distressed newborn infant. Alterations in cerebral blood circulate in preterm infants with intraventricular hemorrhage. Paper offered at: Second International Conference, Fetal and Neonatal Physiological Measurements1984; Oxford, United Kingdom. Preservation of single-flash visual evoked potentials at very low cerebral oxygen delivery in preterm infants. Carbon dioxide-related changes in cerebral blood quantity and cerebral blood move in mechanically ventilated preterm neonates: comparability of close to infrared spectrophotometry and 133Xenon clearance. Aminophylline reduces cerebral blood move in secure, preterm infants without affecting the visible evoked potential. Effect of cerebral blood flow and cerebrovascular autoregulation on the distribution, kind and extent of cerebral harm. Topographic features of lactic acid accumulation in brain tissue during circulatory arrest. Comparison of electrical impedance and 133xenon clearance for the assessment of cerebral blood circulate within the new child infant. Perfusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the brain: strategies and utility in youngsters. Noninvasive measurements of regional cerebral perfusion in preterm and time period neonates by magnetic resonance arterial spin labeling. Cerebral blood flow requirement for brain viability in new child infants is lower than in adults. Cerebral blood circulate increases over the primary three days of life in extraordinarily preterm neonates. Cerebral oxygenation correlates with mean arterial strain in critically unwell premature infants. Cerebral intravascular oxygenation correlates with mean arterial pressure in critically unwell premature infants. Cerebral oxygenation and cerebral oxygen extraction within the preterm infant: the impact of respiratory distress syndrome. The relationship between cardiac output, cerebral electrical exercise, cerebral fractional oxygen extraction and peripheral blood circulate in untimely new child infants. Cross-spectral analysis of cerebral autoregulation dynamics in high threat preterm infants during the perinatal interval. Relationship between cerebrovascular dysautoregulation and arterial blood stress within the untimely toddler. Cerebral autoregulation in the preterm newborn using near-infrared spectroscopy: a comparability of time-domain and frequency-domain analyses. Continuous dedication of optimum cerebral perfusion stress in traumatic brain damage. Early low cardiac output is related to compromised electroencephalographic activity in very preterm infants. Relationship between blood strain, cerebral electrical activity, cerebral fractional oxygen extraction, and peripheral blood move in very low start weight new child infants. Role of O2hemoglobin affinity within the regulation of cerebral blood flow in fetal sheep. Blood viscosity during the neonatal interval: the role of plasma and pink blood cell sort. Changes in cerebral, renal and mesenteric blood flow velocity during steady and bolus infusion of indomethacin. Responsiveness of human toddler cerebral arteries to sympathetic nerve stimulation and vasoactive agents. Intrinsic tone of cerebral artery segments of human infants between 23 weeks of gestation and term. Does caffeine impair cerebral oxygenation and blood circulate velocity in preterm infants Higher neonatal cerebral blood flow correlates with worse childhood neurologic end result. Cerebral artery Doppler ultrasonography for prediction of end result after perinatal asphyxia.
Order fildena 150mg onlineRadial glial progenitors could give rise to a glial restricted progenitor that then generates astrocytes or oligodendrocytes. Proliferation of glia, in contrast to that of neurons, additionally could happen locally, throughout and after migration. Microglial cells play key roles during brain development, involving vascularization,229 apoptosis,128 axonal development,sixty six and later myelination. Many wonderful critiques of the application of those measures are available236-240 and are discussed in different related chapters on this e-book (see especially Chapters 10 and 16). This part focuses on studies relevant to regular development in the fetal and neonatal intervals. Because of the principal application of those measures to preterm infants, the great preponderance of data includes brain improvement primarily over the interval from 28 to 40 postconceptional weeks. The last half of human gestation is an important time in astrocyte formation in the human cerebral cortex and white matter. The mobile bases for these increases doubtless mirror all features of the organizational events described earlier, significantly the events involving cortical arrival of late migrating neurons, neuronal differentiation, neurite outgrowth, axonal growth, premyelination oligodendroglial occasions, lamination, and gyrification (see earlier). The multiplicity of effectors of the volumetric increases makes it troublesome to delineate the relative importance of every, not only when it comes to regular organizational events, but additionally as causes of impaired volumetric development (see the section on problems of organizational events). Cortical surface area will increase roughly 12% per week in the course of the premature interval. However, in addition to the forces generated by development of cerebral cortical floor area, cortical folding probably depends re fre. The lower values of the preterm infants studied at time period (closed circles) recommend a deleterious effect of prematurity on this process (see textual content for details). However, an extra anatomical determinant, especially later in the third trimester, may reflect axonal ensheathment by premyelinating oligodendrocytes. As noted earlier the latter course of is particularly energetic presently,213,214 and experimental research have delineated such a interval of premyelination anisotropy. Axial diffusivity increases in fiber tracts with axonal growth, and radial diffusivity declines in tracts as premyelinating oligodendroglial ensheathment occurs. Advanced magnetic resonance imaging methods within the preterm brain: methods and applications. This decline in functional connectivity could result from more and more particular practical connectivity. The shade maps display the course of individual fibers: right to left (red), anterior to posterior (green), and superior to inferior (blue). This organization has the impact of limiting water displacement parallel to the cortical floor more than displacement orthogonal to it, leading to diffusion ellipsoids which are nonspherical with their main axes oriented radially (arrows). This has the impact of proscribing water displacement more uniformly in all instructions. As a result, the diffusion ellipsoids are spherical, and not using a most popular orientation. Short corticocortical connections are obvious initially, and longer corticocortical connections develop towards time period. Unfortunately, little is understood about issues of this part of neural maturation. This ignorance is triggered primarily by the inadequacy of standard neuropathologic methods to evaluate the complex circuitry and synaptic connections of human brain. Combining these research with diffusion tensor tractography offers an insight into the fiber tracts doubtless concerned in interconnecting numerous elements of the growing brain. Note variations in the crossover point for regression lines for gray and white matter throughout regions. Cortical grey and adjacent white matter reveal synchronous maturation in very preterm infants. Although the latter uncertainties often persist, in recent years, the arrival of superior immunocytochemical methodologies, the delineation of molecular genetic defects, and the utilization of genetically manipulated animals have offered new insights into the identification and the basis of organizational issues. If these lesions disrupt the subplate neurons or their axonal collaterals to subcortical or cortical sites, the capabilities described earlier can be impaired, and the impact on cortical neuronal improvement and on quite a lot of crucial projection systems might be enormous. Indeed, the main portion of the striking improve in cerebral cortical quantity within the last trimester of gestation consists of the in depth elaboration of the afferent fibers, previously "waiting" involved with subplate neurons, as they enter the cerebral cortex. The position of subplate neuronal injury within the encephalopathy of prematurity is discussed in Chapters 14 and 15. In addition, subplate neuronal pathology has been instructed in quite a lot of other neurological disorders, together with epilepsy, autism, and schizophrenia beyond the neonatal period. Drug-resistant epilepsy is commonly accompanied by extreme cortical dysplasias, during which massive groups of cells are additionally abnormally located throughout the cerebral white matter. Following proper wrist movement, localized useful exercise was recognized in all infants within the contralateral (left) major somatosensory cortex. Excessive numbers of interstitial white matter neurons have been reported in post-mortem analyses of the brains of patients with schizophrenia and autism. These abnormal patterns embrace focal cortical dysplasia and the four-layered types of lissencephaly and polymicrogyria that are mentioned intimately in Chapter 6. Layer-specific markers have provided insight into the neurobiology of those patterns. A major aim in developmental neuropathology is to develop a panel of markers to analyze all neuron varieties and their distribution within the human neocortex to elucidate abnormalities in the place and number of every neuron kind in cortical malformations, in addition to in metabolic and degenerative illnesses that involve selective loss of particular neuron varieties. Huttenlocher,seventy four,270 utilizing the Golgi method and quantitative estimation of dendritic branching, initially studied 11 brains from individuals with severe mental retardation of unknown cause. In six of those brains, extreme defects within the number, size, and spatial arrangement of dendritic branching and in dendritic spines, the websites of synaptic contacts, have been demonstrated. Other gyral abnormalities embrace maldevelopment of particular person gyri and/or lobes, ensuing, for example, in small superior temporal gyri in Down syndrome. Insight into a serious mechanism in the production of such defects was provided first by the work of Purpura and colleagues. Ultrastructural studies showed an aberration of microtubules with loss of the identical old parallel array of these constructions. These findings indicated that a disturbance of cytoskeletal constructions, so crucial for maintenance of cell shape and for outgrowth of dendrites and axons, may cause a severe dendritic abnormality and marked neurologic disturbance. There is a scarcity of social interaction, with avoidance of eye contact, in addition to deficits in verbal and nonverbal communication, emotional control, and understanding the feelings of others. Using complete exome sequencing, evaluation of rare coding variation in 3871 autism circumstances and 9937 controls implicated 22 autosomal genes, in addition to a set of 107 autosomal genes strongly enriched for these prone to affect risk. These organizational occasions heart mainly, however not solely, on total mind development, synaptogenesis, lamination, and axonal connectivity. Still, the survival rate of people with Down syndrome has dramatically elevated from less than 50% through the mid-1990s to 95% within the early 2000s with a current median life expectancy of 60 years. The emergence of lamination, for instance, is both delayed and disorganized, notable after 20 to 21 weeks of gestation and over the next 7 to 10 weeks. This sequence of excessive preliminary branching adopted by deficits is much like that seen in sure animal fashions of impaired dendritic improvement.
Buy discount fildena 150mgRetrospective, multicentric study of a hundred and eighty children with cytochrome C oxidase deficiency. Pyruvate dehydrogenase advanced deficiency: biochemical and immunoblot evaluation of cultured pores and skin fibroblasts. Intracerebral distribution of mitochondrial abnormalities in 21 circumstances of infantile spongy dystrophy. Combined deficiencies of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complicated and enzymes of the respiratory chain in mitochondrial myopathies. Familial mitochondrial encephalopathy with fetal ultrasonographic ventriculomegaly and intracerebral calcifications. New familial mitochondrial encephalopathy with macrocephaly, cardiomyopathy, and Complex I deficiency. Necrotizing encephalopathy and macrocephaly with mitochondrial complex I deficiency. Long-term consequence and scientific spectrum of seventy three pediatric sufferers with mitochondrial illnesses. Mitochondrial depletion causes neonatal-onset Leigh syndrome, myopathy, and renal tubulopathy. Neonatal onset of mitochondrial problems in 129 sufferers: clinical and laboratory characteristics and a model new approach to analysis. Clinical and radiologic enhancements in mitochondrial encephalomyelopathy following sodium dichloroacetate remedy. Regional variation in mind lactate in Leigh syndrome by localized 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Analysis of the mitochondrial encoded subunits of advanced I in 20 patients with a fancy I deficiency. Free-thiamine is a potential biomarker of thiamine transporter-2 deficiency: a treatable reason for Leigh syndrome. Cerebral white matter involvement in youngsters with mitochondrial encephalopathies. Cerebral white matter disease in kids could additionally be caused by mitochondrial respiratory chain deficiency. Long-term follow-up of neonatal mitochondrial cytopathies: a research of 57 patients. L-serine synthesis within the central nervous system: a review on serine deficiency disorders. Congenital microcephaly and seizures due to 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase deficiency: outcome of remedy with amino acids. Infantile serine niosynthesis defect because of phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase deficiency: variability in phenotype and therapy response, novel mutations, and diagnostic challenges. Hypomyelination and reversible white matter attenuation in 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase deficiency. Prenatal and early postnatal therapy in 3-phosphoglycerate-dehydrogenase deficiency. Neurological presentation in pdiatric patients with congenital disorders of glycosylation type 1. Congenital dysfunction of glycosylation kind Ia: a clinicopathological report of a new child infant with cerebellar pathology. Successful prenatal mannose therapy for congenital dysfunction of glycosylation-Ia in mice. Neurological roles for phosphomannomutase kind 2 in a new Drosophila congenital dysfunction of glycosylation illness model. Predominant cerebellar volume loss as a neuroradiologic characteristic of pediatric respiratory chain defects. The syndrome of autosomal recessive pontocerebellar hypoplasia, microcephaly, and extrapyramidal dyskinesia (pontocerebellar hypoplasia sort 2): compiled knowledge from 10 pedigrees. Congenital pontocerebellar atrophy in three sufferers: clinical, radiologic and etiologic concerns. A syndrome of autosomal recessive pontocerebellar hypoplasia with white matter abnormalities and protracted course in two brothers. Three siblings of fatal infantile encephalopathy with olivopontocerebellar hypoplasia and microcephaly. Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency: medical options, drug therapy and follow-up. Clinical and biochemical features of aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Volpe Neuromuscular problems could cause dramatic disability in the neonatal period. In this context, neuromuscular problems are thought-about those that predominantly contain the motor system, from its origins within the cerebral cortex to its termination within the muscle. This article and the subsequent three chapters are concerned with neuromuscular disorders. In this text, the motor system is described by means of its anatomical and physiological organization; special extra emphasis is placed on the development and biochemical options of muscle. Also, the evaluation of problems of the motor system in the newborn and the diagnostic studies used of their diagnostic investigation are reviewed in detail. This system descends by way of the posterior limb of the inner capsule, the cerebral peduncles, and the pontine tegmentum; it decussates in the ventral medulla and then descends in the lateral column of the spinal wire. In the following discussion, the main components of the central and peripheral nervous techniques that are necessary for the management of movement and tone are briefly reviewed. The discussion is organized within the framework used within the next three chapters for the categorization of diseases that disturb muscle power and tone within the human toddler. The system of basal ganglia, typically categorized by the less precise time period extrapyramidal system, principally consists of 5 major nuclear plenty: caudate, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra. The main afferent facilities are the caudate and putamen (the corpus striatum), and the major efferent middle is the globus pallidus. Output from the globus pallidus is relayed to the cortical motor neurons principally by means of the thalamus. Efferent connections are conveyed principally by way of the superior cerebellar peduncle to the purple nucleus (and then to the rubrospinal tract), the vestibular nuclei (and then to the vestibulospinal tract), and the thalamus (and then to cerebral cortical motor neurons). Thus the management of motion and tone by the cerebellum is in the end by way of different motor methods. The hypotonia observed in cerebellar disease may be mediated primarily by decreased muscle fusimotor activity. The other major elements of the motor system include the rubrospinal, reticulospinal, and vestibulospinal tracts, typically collectively known as the bulbospinal tracts. Other Components co Corticospinal and Corticobulbar Tracts m Control of muscle energy and tone begins in the central nervous system at levels above the decrease motor neuron (Box 30. This control is mediated largely by the major motor efferent system-the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts-often termed the pyramidal system because most of these tracts originate in the pyramidal cells of the motor cortex of the cerebrum.
Syndromes - Recognize signs of unresolved stress in your child.
- Numbness to hot, cold, and pain
- A dye (contrast) is injected into an artery or vein.
- Sick sinus syndrome
- Reduced blood pressure (caused by rapid heart rate)
- Necrosis (holes) in the skin or underlying tissues
- Behcet syndrome
Purchase fildena 25mg otcAtrophy and flaccid weak point of upper extremities and the proximal and distal muscle groups have been marked, and flexor contractures on the elbow and interphalangeal joints have been apparent. Onset in utero was suggested by the presence of flexion contractures, and onset in the first trimester was suggested by the presence of poorly fashioned palmar creases. The nature of the intrauterine insult to cervical anterior horn cells was not clear. The concurrence of fasciculations of the tongue and issue sucking, crying, and swallowing further mimics this major anterior horn cell degeneration. However, a number of scientific features assist distinguish Pompe illness from Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. Second, the tongue, though weak and maybe even fasciculating, is normally massive in Pompe disease because of the glycogen accumulation, unlike the small, atrophic tongue of Werdnig-Hoffmann disease. Third, the skeletal muscular tissues, though weak, are often prominent in Pompe illness, because of glycogen accumulation. Most sufferers have preserved tendon reflexes early in the clinical course and later have complete areflexia. The illness is related to glycogen deposition in anterior horn cells (as properly as in skeletal and cardiac muscle, liver, and brain), and with putting weak point and hypotonia in early infancy. H&E shows massive vacuoles in all fibers (A, arrows) that stain intensely with the acid phosphatase response (B). The neuropathology of Pompe disease is fre fre fre eb oo ks ks oo oo ks ks oo oo eb o eb eb ok sf are used. An extra characteristic function is irritability of muscle with the prevalence of pseudomyotonic bursts of discharges. The large R waves on electrocardiography are significantly helpful signs in analysis. Attempts to replenish alpha-glucosidase by bone marrow transplantation have been unsuccessful. The accumulation of glycogen within the anterior horn cells is probably the most putting change. Only one case has been reported within the United States within the roughly forty years for the explanation that widespread use of. Neonatal poliomyelitis is brought on by infection of neurons by poliovirus, a basic neurotropic virus. The demonstration of maternal viremia and placental an infection and the recovery of virus from meconium of stillborn infants of diseased moms assist the concept of intrauterine an infection by transplacental mechanisms. Because of the incubation interval for poliomyelitis, infants affected after approximately 10 days of age presumably were contaminated during supply by contamination with contaminated stool or by postnatal publicity. The neuropathological features within the newborn are often more extreme than within the grownup. Neuronal necrosis, neuronophagia, and perivascular cuffing with inflammatory cells contain neurons of the anterior horns, motor nuclei of the brain stem, roof nuclei of the cerebellum, diencephalon, and motor cortex of the cerebrum. Moreover, contractures can evolve quickly, and care should be taken to avoid the postnatal improvement of arthrogryposis multiplex. In addition, approximately nine cases per 12 months of poliomyelitis brought on by vaccine-related poliovirus nonetheless happen within the United States. Indeed, the only neonatal case reported up to now three a long time on this nation acquired the an infection by contact with a just lately vaccinated infant with diarrhea. In many cases, an additional feature, related to proliferation of Schwann cells and fibroblasts, is "onion bulb" formation, with proof of demyelination-remyelination. However, the extra frequent consideration of problems of peripheral nerve as the cause for motor deficits in neonatal sufferers, the extra frequent use of refined techniques for finding out nerve histology, similar to electron microscopy, and the explosion in utility of molecular genetics lead to the conclusion that disease at this stage might be considerably more common than was beforehand suspected. The categorization is somewhat arbitrary as a end result of out there reports recommend some overlap, as nicely as the need for extra definitive technique of research. However, this series of terms was coined earlier than the availability of genetic testing and now could cause confusion. All infants had neonatal clinical options and congenital neuropathy with hypomyelination, with or with out onion bulbs, on nerve biopsy. The last of these is expounded to a connexin-32 defect and almost at all times presents clinically in childhood. The purely hypomyelinative cases are attributable to either de novo dominant or autosomal recessive mutations. The dominant neurological options within the neonatal interval are hypotonia and weak point. Involvement normally is generalized, and the distal greater than proximal involvement attribute of peripheral nerve illness has been tough to demonstrate in the newborn interval. Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita has been a characteristic in numerous instances and may be very prominent (see Table 32. Involvement of the sensory system is a priceless feature to elicit for identification of neuropathy. Elicitation of sensory deficits in the neonatal patient requires very careful examination (see Chapter 9). Definitive analysis of the sensory system usually also requires electrophysiological data (see later discussion). Most sufferers (70%) never stroll, and solely 11% finally achieve this unassisted (see Table 32. Approximately 40% of infants die, and a transparent relation to severity of illness, as reflected within the presence or absence of evidence for demyelination-remyelination. Thus roughly 85% of infants with absence of onion bulbs have died, whereas 81% of those with onion bulbs survive (see Table 32. Three reports of infants with the medical electrophysiological and pathological features of congenital hypomyelinating polyneuropathy who improved spontaneously after months and had been normal or markedly improved at 18 or 19 months and 9 years, respectively, raised the risk of a transient, reversible type of this dysfunction. Some scientific clues to the prognosis of congenital hypomeylinating polyneuropathies, and related genes and phenotypes, are proven in Table 32. The sural nerve, which has a limited distribution over the pores and skin of the foot, is usually chosen for biopsy. Also, the invention of mutations in numerous genes in patients with congenital polyneuropathies has allowed for molecular prognosis of these problems (see earlier). If any myelin is present, large-diameter nerve fibers, which usually are heavily myelinated, are conspicuous by the paucity of myelination. The normal proportion between diameter size and thickness of myelin sheath thus is misplaced. No indicators of myelin destruction could be discerned; the lack of a demyelinating course of is supported by biochemical research, which confirmed no accumulation of ldl cholesterol ester, the chemical hallmark of demyelination. Accompanying these changes may be a modest proliferation of Schwann cells and endoneurial fibroblasts.

Fildena 150mg low priceIn an earlier sequence, though 9% of infants with seizures skilled hypoglycemia, in none was the metabolic defect the only potential etiological issue. The first peak, which takes place in the first 2 to three days of life, happens most frequently in low-birth-weight newborns, each of average and below-average weight for his or her gestational age, and in infants of diabetic moms. In an earlier series, 13% of the infants with seizures exhibited hypocalcemia, however as with hypoglycemia, the metabolic defect was not the only co. Paracervical and pudendal blocks have been the commonest forms of maternal analgesia concerned in the well-documented instances of fetal injection. The discovering that infants with intoxication enhance over the first 24 to 48 hours (if properly supported) additional distinguishes the disorder from severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. The remedy required depends, in part, on the time of recognition of the intoxication; the half-life of the drug in blood is roughly 8 to 10 hours. Early hypocalcemia may be a situation associated with neonatal seizures somewhat than the cause. Classically, these hypocalcemic newborns are giant, full-term infants who avidly devour a milk preparation with a suboptimal ratio of phosphorus to calcium and phosphorus to magnesium. Hypomagnesemia is a frequent accompaniment, or, extra not often, could additionally be present without hypocalcemia. The convulsive phenomena are often focal, both clinically and electroencephalographically. Later-onset hypocalcemic seizures are associated extra generally with endocrinopathy (maternal hyperparathyroidism, neonatal hypoparathyroidism) or with congenital heart illness (with or without DiGeorge syndrome). Because calcium levels additionally could also be low, the mistaken prognosis of primary hypocalcemia may be made. Parenteral administration of magnesium prevents the seizures and early infantile death. Metabolic disturbances apart from hypoglycemia and deficiency of divalent cations are unusual causes of seizures in the new child (see Table 12. These metabolic disturbances are all mentioned rather more extensively in Chapters 27 to 29. Hyponatremia could result in seizures and sometimes happens with inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion in the context of bacterial meningitis, intracranial hemorrhage, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, or excessive consumption of water. The latter could happen in a baby with minor gastrointestinal difficulties with inappropriate dilution of method or excess water (in place of formula) consumption. Seizures typically end result during the correction of hypernatremia if markedly hypotonic solutions are used, perhaps secondary to the development of intracellular edema. Disturbances of amino acid or organic acid metabolism could result in neonatal seizures, just about always within the context of other neurological options. Hyperammonemia or acidosis (or both) mostly accompanies these disturbances. Although not strictly a "metabolic" disturbance, peroxisomal illness, especially Zellweger syndrome or neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy, related to elevations of blood levels of very-long-chain fatty acids and different biochemical adjustments, is related to extreme neonatal seizures, brought on by associated cerebral neuronal migrational defects. Pyridoxine dependency, a disturbance in pyridoxine metabolism, may produce severe seizures which would possibly be recalcitrant to traditional therapy (see Chapter 29). Seizures are usually multifocal clonic and recalcitrant to all therapeutic modalities. There is an associated newborn encephalopathy, which may manifest as hyperalertness, tremulousness, or hypothermia. Generalized tonic-clonic seizures, a rare form of neonatal seizure, have been described in newborns with pyridoxine dependency. Clinical research additionally point out that the disorder might start after days or even weeks; that the seizures might respond initially to anticonvulsant drugs; and that doses of pyridoxine larger than 100 mg may be essential to cease the seizures. Subsequently complete control of seizures on pyridoxine monotherapy and recurrence on withdrawal established the prognosis. Most infants have exhibited subsequent intellectual incapacity regardless of remedy from the primary days of life. Nevertheless, early remedy may decrease the chance or severity, or both, of intellectual deficit; indeed, eight of the 10 reported infants with normal intellect were recognized and handled within the first month of life. However, many infants treated in the first month still exhibit cognitive deficits later. Intrauterine therapy by maternal pyridoxine supplementation could also be necessary to prevent fetal brain injury. Glutamate could lead to neuronal harm by excitotoxic mechanisms and to oligodendroglial damage by free radical mechanisms. Intrauterine onset of anatomical disturbance is suggested by the fetal imaging discovering of partial hypoplasia of the corpus callosum. The medical presentation typically includes fetal seizures, and infants are often premature and exhibit an encephalopathy as well as seizures. The discharges have subsided (4 minutes earlier), and the patient exhibits regular sleep background with early sleep spindles appearing within the tracing. The seizures respond to oral folinic acid at doses starting from 2 to 20 mg twice every day; the bottom doses have been used within the neonatal interval. A dysfunction of glucose transport from blood to brain is important to recognize as a outcome of immediate remedy can result in the cessation of seizures and to improved neurological development. Approximately 25% of cases have had onset of seizures within the first 2 months of life. The impaired glucose transport is related to a defect of the glucose transporter (Glut1) liable for the facilitative diffusion of glucose throughout the blood-brain endothelial barrier and throughout the neuronal plasma membrane. Treatment with a ketogenic food regimen, which supplies usable metabolic gas for brain vitality metabolism not transported by the glucose transporter, is generally efficient in leading to seizure management and will blunt the impaired neurological growth that may be a consistent characteristic of the disease. However, in general, the beneficial impact of the ketogenic diet is most obvious for seizure management. Characteristic features are a extreme neonatal-onset epileptic encephalopathy and diabetes mellitus, related to a channelopathy involving the endocrine pancreas and the mind. The depolarization results in Ca2+ inflow and thereby to physiological insulin launch. This mechanism serves to regulate insulin launch moment-by-moment in response to blood glucose. However, sulfonylurea, an oral hypoglycemic agent, binds to the channel, promoting closure and physiological insulin launch. Prompt recognition and remedy of this syndrome with oral hypoglycemic brokers and not systemic insulin administration are important for a great neurological consequence. The seizures most often are focal clonic, focal tonic, or apneic and should occur with a frequency of 10 to 20 per day or higher. The disorder is often self-limited, with cessation of seizures in 1 to 12 months. This syndrome is an eb As described earlier, most neonatal seizures characterize acute symptomatic (provoked) seizures, however there are uncommon newborns with epilepsy. The current International League Against Epilepsy classification system defines several electroclinical syndromes with onset in the neonatal and infantile durations. An epilepsy syndrome was defined as "a posh of scientific features, indicators, and symptoms that collectively outline a distinctive, recognizable medical disorder. The traditional time of onset of seizures in this setting is the primary a number of days of life.
Order fildena with amexMinocycline prevents glutamate-induced apoptosis of cerebellar granule neurons by differential regulation of p38 and Akt pathways. Antioxidant properties of minocycline: neuroprotection in an oxidative stress assay and direct radical-scavenging activity. Minocycline inhibits neuronal death and glial activation induced by beta-amyloid peptide in rat hippocampus. Maturational change within the cortical response to hypoperfusion injury in the fetal sheep. A new mannequin of white matter injury in neonatal rats with bilateral carotid artery occlusion. Induction of antenatal periventricular leukomalacia by hemorrhagic hypotension in the chronically instrumented fetal sheep. Hypoxia-ischemia depletes the rat perinatal subventricular zone of oligodendrocyte progenitors and neural stem cells. Chronic ischemia preferentially causes white matter injury within the neonatal rat mind. Analyses of things contributing to vulnerability to antenatal periventricular leukomalacia induced by hemorrhagic hypotension in chronically instrumented fetal sheep. White matter damage following systemic endotoxemia or asphyxia within the fetal sheep. Gestational hypoxia induces white matter damage in neonatal rats: a brand new mannequin of periventricular leukomalacia. Selective vulnerability of preterm white matter to oxidative harm defined by F(2)isoprostanes. Hypoxia-ischemia preferentially triggers glutamate depletion from oligodendroglia and axons in perinatal cerebral white matter. Susceptibility of the neonatal feline telencephalic white matter to a lipopolysaccharide. Intrauterine infection induces programmed cell demise in rabbit periventricular white matter. Experimentally induced intrauterine infection causes fetal mind white matter lesions in rabbits. Cytokine induction in fetal rat brains and brain harm in neonatal rats after maternal lipopolysaccharide administration. Differential roles of tumor necrosis factor- and interleukin-1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced mind injury within the neonatal rat. Patterns of cerebral inflammatory response in a rabbit model of intrauterine infection-mediated mind lesion. Disturbance of oligodendrocyte improvement, hypomyelination and white matter injury in the neonatal rat brain after intracerebral injection of lipopolysaccharide. No phenotype associated with established lipopolysaccharide model for cerebral palsy. Long-term changes in blood-brain barrier permeability and white matter following extended systemic inflammation in early improvement in the rat. Endotoxemia severely impacts circulation during normoxia and asphyxia in immature fetal sheep. Increase in endogenous mind superoxide dismutase as a potential mechanism of lipopolysaccharide-induced brain ischemic tolerance. Protective effect of glial cells against lipopolysaccharide-mediated blood-brain barrier injury. Cooperation between toll-like receptor 2 and 4 within the brain of mice challenged with cell wall components derived from gram-negative and gram-positive micro organism. Toll-like receptor four: the missing hyperlink of the cerebral innate immune response triggered by circulating gram-negative bacterial cell wall elements. Polyamines play a critical role within the management of the innate immune response within the mouse central nervous system. Determining the fetal inflammatory response in an experimental mannequin of intrauterine inflammation in rats. Innate immunity and toll-like receptors: clinical implications of fundamental science research. Innate immune sensing of pathogens and danger indicators by cell surface Toll-like receptors. Evolution of neuropathologic abnormalities related to blood-brain barrier breakdown in transgenic mice expressing interleukin-6 in astrocytes. Murine tumor necrosis issue alpha is transported from blood to mind within the mouse. The blood-brain barrier and its function in immune privilege within the central nervous system. Systemic cytokine administration can have an effect on blood-brain barrier permeability in the rat. Antioxidants attenuate acute toxicity of tumor necrosis factor-alpha induced by brain damage in rat. Blood-brain barrier changes following intracerebral injection of human recombinant tumor necrosis factor- within the rat. Hypoxia increases production of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis issue by human mononuclear cells. Exacerbation of ischemic brain harm by localized striatal injection of interleukin-1 in the rat. Cytokine modulation of glial glutamate uptake: a potential involvement of nitric oxide. Cystine deprivation induces oligodendroglial demise: rescue by free radical scavengers and by a diffusible glial issue. Developmental differences in H2O2-induced oligodendrocyte cell death: position of glutathione, mitogen-activated protein kinases and caspase three. Novel position of Vitamin K in stopping oxidative injury to creating oligodendrocytes and neurons. Hypoxic/Ischemic insult alters ferritin expression and myelination in neonatal rat brains. Iron supplementation aggravates periventricular cystic white matter lesions in newborn mice. Ventriculomegaly, delayed myelination, white matter hypoplasia, and "periventricular" leukomalacia. Non-proteinbound iron is elevated in cerebrospinal fluid from preterm infants with posthemorrhagic ventricular dilation. Blood transfusion increases radical selling non-transferrin sure iron in preterm infants. Total hydroperoxide and superior oxidation protein merchandise in preterm hypoxic infants. Oxidative stress in erythrocytes from untimely and full-term infants throughout their first seventy two h of life. Macrophages: their myelinotrophic or neurotoxic actions depend on tissue oxidative stress.
Discount 25 mg fildena visaThe vasodilation is mediated by a Ca2+-activated K+ channel on vascular smooth muscle. Adenosine, administered on the perivascular aspect of pial arteries, leads to a concentration-dependent vasodilation. Prostaglandins, notably prostaglandins E and F2, lead to cerebral vasodilation. The concentrations of those compounds increase in response to cerebral ischemia, and brokers that inhibit prostaglandin biosynthesis. Prostaglandins appear to be of cerebral hemodynamic importance in immature animals (see later discussion). Increases in perivascular osmolarity have a vasodilating impact, and decreases have a vasoconstricting effect. Blood flows to the cerebral cortex had been roughly 5- to 10-fold of these to subcortical white matter. These regional differences have been confirmed in research of the perinatal rabbit, lamb, piglet, and puppy. Cerebral autoregulation appears to be operative over a broad range of arterial blood strain within the preterm and term fetal lamb, the neonatal lamb, and the neonatal dog. The autoregulatory range of blood pressures varies barely amongst species and experimental situations. The curve for the preterm lamb differs from that for the term or neonatal lamb in two respects. Second, and maybe extra strikingly, the traditional arterial blood stress in the preterm lamb could be very close to or on the decrease autoregulatory limit. Indeed, within the preterm lamb at 80% of gestation, normal arterial blood stress is just 5 to 10 mm Hg above the decrease limit of the curve, in distinction to the state of affairs in older animals. In a subsequent research that included preterm fetal lambs at roughly 65% gestation. One report shows that morphine infusions in neonatal piglets result in an upregulation of the vasoconstrictor, endothelin-1, and its receptors. Stated in one other method, the observations recommend that the margin of security, at least in the preterm fetus, and to a lesser extent within the time period fetus, is small at the decrease end of the autoregulatory curve and factors to vulnerability to ischemic brain harm with modest hypotension, particularly within the preterm animal. Vulnerability to hypertension additionally might outcome as a outcome of little change occurs within the upper restrict of the autoregulatory vary throughout a quick developmental period (third trimester within the lamb and the human) when regular arterial blood stress increases markedly. Autoregulation within the term fetal lamb and within the newborn lamb has been proven to be sensitive to hypoxia. The limited vasodilatory response in cerebral white matter may have implications for the vulnerability of this region to hypoxic-ischemic damage. Regional cerebral blood flow after hemorrhagic hypotension in the preterm, near-term, and new child lamb. The modestly hypercarbic animals had essentially the most favorable hemodynamic, biochemical, and neuropathological outcomes. These observations again suggest that cerebral white matter has limited vasodilatory capability and thereby has implications for the vulnerability of this region to hypoxic-ischemic harm within the preterm infant (see later discussion and Chapter 15). However, the findings point out that the myogenic properties of the major cerebral vessels themselves should be considered within the analysis of mechanisms of adjustments in cerebral hemodynamics. Brain metabolic correlates of hypoxic-ischemic cerebral necrosis in mid-gestational sheep fetuses: significance of hypotension. Recall that brain adenosine concentrations increase with hypoxia and seizures; both conditions require will increase in substrate influx to mind. However, in neonatal animals, prostanoids exert results which may be different from these observed in the grownup. Prostaglandins additionally attenuate the vasoconstrictor responses of norepinephrine and are the apparent mediators of the vasodilatory responses of endogenous opiates. As a consequence of those important roles, indomethacin, via its inhibition of cyclooxygenase and thereby prostanoid biosynthesis, might have a variety of necessary cerebral hemodynamic results which are vasoconstrictive. After asphyxia, critical extra circulatory results develop, and indeed from the medical standpoint, these postinsult results are as essential, if no more so, than these occurring during asphyxia (Table 13. In general, the increase in blood flow is most marked in mind stem constructions and is least obvious in cerebral white matter. This common pattern was documented within the fetal lamb, neonatal lamb, and neonatal puppy. This lower within the fraction of move to mind stem may impair the try to preserve important brain stem facilities. A probably conclusion from this work is that with hypoxia or asphyxia, the function of endogenous opiates is to suppress the cerebral price of oxygen consumption, with the related decrease in ks fre fre. In large half, this impact is related to a diminution in cardiac output,a hundred,196 probably secondary to an effect on the myocardium. This redistribution of blood flow is paying homage to the diving reflex noticed in aquatic animals and seems designed to defend probably the most crucial and vulnerable organs. Vascular autoregulation in these term fetal animals appeared to be very sensitive to asphyxia. The probably mechanism relates likely to the hypoxemia and hypercapnia which may be the hallmarks of perinatal asphyxia. The sensitivity of the autoregulatory system in the fetal and neonatal brain to these alterations in blood fuel levels was described earlier (see the section on autoregulation). The implications of these knowledge for ischemic harm to perinatal mind are obvious. The burst in launch of endogenous opiates with hypoxia and asphyxia and the well-known suppression of cerebral neural exercise and oxygen consumption by endogenous opiates support this notion. The principal experimental models used have been near-term fetal sheep and neonatal piglets and rat pups, and the insults have primarily consisted of hypoxia-ischemia and, less generally, asphyxia. Moreover, superoxide anion, a consequence of reperfusion after asphyxia (see earlier), might lead to a disturbance of cerebrovascular autoregulation by way of stimulation of vasodilation. Changes in total cerebral hemoglobin (tHb), oxygenated hemoglobin (HbO2), and cytochrome oxidase (CytO2) have been measured by near-infrared spectroscopy. Note the 2 phases of cerebral vasodilation and elevated cerebral blood circulate, as assessed by the hemoglobin alerts; the early improve happens within the first 2 to 3 hours after ischemia, and the delayed enhance occurs from 12 to 48 hours. The delayed improve in move is accompanied by a decline in CytO2, consistent with impaired mitochondrial oxygenation. This improve is related to evidence of impaired mitochondrial oxygenation (as assessed by mind levels of oxidized cytochrome c), with the cellular energy failure, and with neuropathological proof for neuronal and white matter damage. The delayed hyperemia, its association with energy failure, and its correlation with severity of mind harm have additionally been noticed in asphyxiated human infants (Chapters 18 to 20). Symbols (n = 7) represent responses to changes in blood stress in particular person asphyxiated lambs (n = 7).
References - Savory JG, Hsu B, Laquian IR, et al: Discrimination between NL1- and NL2- mediated nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor, Mol Cell Biol 19(2):1025n1037, 1999.
- Beck SD, Lalka SG: Long-term results after inferior vena caval resection during retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy for metastatic germ cell cancer, J Vasc Surg 28(5):808n814, 1998.
- Hansel DE, Rini BI: Molecular genetics of hereditary renal cancer: new genes and diagnostic and therapeutic opportunities, Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 8:895n905, 2008.
- Wells SA, Wheeler KM, Mithqal A, et al: Percutaneous microwave ablation of T1a and T1b renal cell carcinoma: short-term efficacy and complications with emphasis on tumor complexity and single session treatment, Abdom Radiol 41:1203n1211, 2016.
|
|