"Order cheap elimite on line, acne types."By: Jonathan Tze-Wei Ho, M.A., M.D. - Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/10003132/jonathan-ho
Order cheap elimite lineIt results in circulatory changes and will progress to muscle atrophy, contractures, pale pores and skin, and lack of hair on the extremity. The knee is positioned in a barely bent, recumbent position for the often used anterolateral entry. The patella is pulled laterally and the puncture is made mid-patella or above with the needle getting into the joint beneath the surface of the patella. To be succesful of fill the knee joint with a small quantity of dissolved contrast medium, compression is applied to the soft tissues 15�20 cm above the joint cavity with an elastic bandage to prevent entry of the distinction medium into the suprapatellar recess. After the injection, lively and passive actions of the knee joint are carried out a quantity of occasions to obtain uniform distribution in the joint. On delayed sequences, nevertheless, an enhancement impact in cartilaginous areas with altered intrachondral structures can be noticed. This is attributable to diffusion of distinction materials into the hyaline cartilage, though the thickness and floor of the cartilage may still appear regular in grade I lesions. Management and prognosis of these osteochondral lesions depend upon the soundness of the fragment within its bony crater and the status of the overlying articular cartilage. Imaging is critical to confirm the scientific diagnosis and to localize these our bodies before surgical procedure, because intra-articular bodies could also be missed throughout arthroscopy. Radiography and traditional tomography are helpful only when radiopaque intra-articular our bodies are current. Fast spin echo is most popular over standard spin echo because of the decreased metallic artifact seen with quick spin echo. Use of thinner 3 mm sections reduces quantity averaging artifacts and provides better delineation of the neoalignment. Plica Synovialis the three plicae of the knee (suprapatellar plica, medial patellar plica and infrapatellar plica) are remnants of the embryologic synovium that separate the joint into completely different compartments throughout gestation. Partial plical remnants are sometimes recognized at arthroscopy however are incidental findings with out medical significance. Some plicae could persist into adult life and cause anterior knee pain, clicking, catching or locking of the knee when these plicae turn out to be inflamed and thickened by trauma or overuse. The mediopatellar plica which extends from beneath the quadriceps and slides over the medial femoral condyle with knee movement is of great pathologic significance. Differentiation between knee accidents and mediopatellar plica is essential to keep away from unnecessary arthroscopy. Graft Impingement Graft impingement occurs when the graft abnormally contacts both the wall or the roof of the intercondylar notch. The distal two-thirds of the graft show increased sign depth on T2W pictures;86 however, that is by no means fluid signal depth not like in graft rupture. One of the most important etiologies inflicting extension lag is localized anterior arthrofibrosis. The bluish discoloration of this rounded lesion resembles an eyeball on arthroscopy and has been named the cyclops lesion. On T1 and proton density weighted images, nodular intermediate signal intensity mass is seen at the anterior distal facet of the graft in the intercondylar notch. On T2-weighted images the nodule has a heterogeneous but predominantly low signal intensity. Autologous chondrocyte implantation entails harvesting chondrocytes from the relative nonweight bearing surfaces similar to intercondylar notch. The chondrocytes are grown ex vivo and changed into the periosteal lined site of the cartilage defect. From 13 weeks to 3 years the maturation stage entails reworking of the collagen framework resulting in firm hyaline tissue. Magnetic resonance and arthroscopy are complementary examinations for follow-up of autologous chondrocyte implants in knee. This is especially important when larger than 25% of the meniscus is removed during which the remaining meniscus can seem foreshortened with an irregular margin. The specificity of those findings for meniscal retear is lower than that for tears in nonoperative menisci. Several research have reported an accuracy of 66�80% in the postoperative meniscus. It can also be extremely useful in imaging the postoperative knee and in figuring out the response to therapy. By pondering like an arthroscopist, one can present a more clinically related report and by doing so add value to the work-up of a affected person with any knee pathology. Postoperative Articular Cartilage the development of latest cartilage repair procedures that transplant or probably reform hyaline like articular cartilage has led to an correct noninvasive analysis of the cartilage lesions following repair procedures. Magnetic resonance imaging has been used to assess incorporation of grafts, assess vascularity of grafts consider the congruency between the graft and the native cartilage and bone and assess the donor website. Value of short echo time quick spin echo utilizing excessive performance gradients versus standard spin echo imaging for the detection of meniscal tears. The high sign depth meniscus of the knee magnetic resonance analysis and in vivo correlation. Bone bruises on magnetic resonance imaging analysis of anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Pellegrini Stieda disease: A heterogeneous dysfunction not synonymous with ossification/calcification of the tibial collateral ligament� anatomic and imaging investigation. Magnetic resonance imaging of a rupture of the medial head of the gastrocnemius muscle. Hyaline cartilage truncation artifact as a reason for trilaminar look with fats suppressed three dimensional spoiled gradient recalled sequences. Subchondral Bone Marrow Edema in sufferers with degeneration of the articular cartilage of the knee joint. Characteristics magnetic resonance imaging entheseal changes of knee synovitis in spondyloarthropathy. Subchondral insufficiency fracture of the femoral head and medial femoral condyle. Magnetic resonance imaging in planning limb salvage surgery for primary malignant tumours of bone. Postoperative evaluation of the knee after autologous chondrocyte implantation: What Radiologists Need to Know. The pelvis is answerable for transferring the weight of the whole body to each the ft and on the similar time, it allows for extensive hip motion. Diagnostic imaging has a significant position within the analysis and staging of illness. Early diagnosis is potent of delaying the onset of arthritis and the requirement of whole hip alternative. The hip is a ball and socket joint which features stability by the anterolateral orientation of the acetabulum and the anterior position of the femoral head with regard to the femoral shaft.
Purchase generic elimite pillsVarieties of embolizing agents have been used, corresponding to gelatin sponge, stainless-steel coil, n-butyl cyanoacrylate, absolute alcohol, autologus blood clot. Technique for delivery of absolute alocohol to renal artery consists of balloon occlusion technique and superselective technique. In superselective technique, endhole catheter is superior superselectively into lobar braches and the alcohol is injected to stop reflux. Mechanism of motion of alcohol proposed to be mixture of perivasculat necrosis, sludging of erythrocytes in small arteries and glomeruli and endothelial harm. Injection fee of 1�5 mL/sec, leads to perivascular necrosis, sludging of erythrocytes in small arteries and glomeruli indicating direct tissue toxicity. Embolization with absolute ethanol ought to be carried out fastidiously because of the vigorous thrombosis it causes by denaturing proteins. It may even permeate the tissues and causes injury to adjoining structures, corresponding to nerves and bowel. Transcatheter Embolization of Renal Pseudoaneurysms Incidence Incidence of aneurysm formation differs for the various etiologies of renal artery aneurysms. Other causes of aneurysm formation embody fibromuscular dysplasia, polyarteritis nodosa, amphetamine abuse, angiomyolipoma (either with or with out associated tuberous sclerosis) and neurofibromatosis. Selective injection should be carried out to identify the feeding vessel or vessels. Many embolization methods could be utilized in this setting relying factors like the sort, number, and placement of the aneurysms. Sometime, aneurysms of the primary renal artery perhaps amenable to stent graft placement, thus allowing distal perfusion to be maintained. However, till stent graft placement is perfected, surgical repair by resection, aneurysmorraphy, and autotransplantation is more commonly performed on this setting. In the presence of a quantity of aneurysms from a lesion, similar to an angiomyolipoma, a mix of particle and coil embolization can be carried out. However, pregnant women are extra vulnerable to rupture which has similarities to splenic artery aneurysms rupture. Anatomic/Physiologic Considerations the vascular provide to the kidney is considered endorgan, and hence, infarction is frequent after embolization. Superselective embolization is advisable in all cases of renal artery embolization until partial or total nephrectomy is deliberate. The use of superselective strategies results in little or no ischemia, and there are minor chances of inducing renal failure. Embolization of End-stage Kidney the nonfunctional kidney could manifest by ache, hypertension, albuminuria and other symptoms. Complications In uncommon instances, dissection or perforation of the renal arteries and their branches can happen. Both dissection flaps and rupture could be instantly controlled with balloon tamponade. Although dissection flaps can usually be tacked down, rupture typically requires emergent surgery. Even perforation of smaller department vessels can happen if a guidewire is passed too far into the periphery. The embolization material is injected cautiously through an endhole catheter beneath fluoroscopic control to avoid reflux into the aorta. There is subsequently residual opacification of the parenchyma of the embolized kidney. Patients have to be then fastidiously monitored for 24 hours and stored in the hospital until their ache and any related pyrexia has settled. Majority of those symptoms are self-limited and are resolve without any specific remedy. Rarely, there could additionally be main issues like renal failure, renal abscess and testicular infarction. The results of embolization are fairly encouraging in most of the clinical situations. Arteriovenous fistulas and malformations acquired arteriovenous fistulas within the kidney are normally the end result of trauma, particularly percutaneous biopsy. These lesions encompass quite a few dilated, tortuous vessels within the subepithelium of the amassing system. When symptomatic, they normally present with gross hematuria and less generally are related to hypertension or an belly bruit. At angiography, an arteriovenous fistula produces dilatation of the feeding branch and early filling of the draining vein. Transcatheter embolization is the primary line of therapy for most of these lesions. The frequent indications for therapy are menorrhagia leading to anemia, belly ache, uterine enlargement with mass effect, infertility and late miscarriages. The varied causes of postpartum hemorrhage are abnormal placentation, retained products of conception, start canal laceration, uterine atony or rupture of uterus. All such catastrophic bleeding situations may be handled by angiographic embolization of uterine artery through the use of numerous embolizing supplies. Only symptomatic sufferers in whom different causes for disease have been excluded (including a recent Papanicolaou test) should bear this treatment. The intervention radiologist is obligated to become the first physician caring for the affected person in Preprocedure session, hospital recovery, and all outpatient management. Regardless of the location of fibroids, bilateral embolization is important to prevent development of collateral vessels. The interventionalist should be observant of variant arterial anatomy and necessary collateral vessels. In most instances, the ovarian arteries contribute to fibroids by way of anastomoses with the main uterine artery. In about 10% of patients, the uterine artery is the main blood provide to the ovary, or the ovarian artery has vital direct communication with the fibroid. Embolization of these vessels theoretically increases the risk of ovarian infarction and infertility. A postembolization syndrome consisting of ache, nausea and vomiting, and low-grade fever is to be expected. Follow-up is completed by the interventionalist, together with routine clinic evaluation at 1�3 weeks after the process. Selective catheterization of the anterior divisions of the interior iliac arteries is carried out with a cobra or ultra-long reverse-curve. Once the uterine artery is recognized and selected, angiography reveals the markedly dilated spiral arteries feeding the uterus. In some circumstances, the descending portion of the uterine artery could be engaged with the 5 French diagnostic catheter. However, vasospasm could also be a problem, in order that coaxial placement of a microcatheter directed well into the uterine artery often is required.
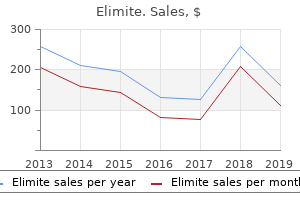
Order cheap elimite on lineT2-weighted images are helpful in distinguishing a simple renal cyst from other lesions. A homogeneous hyperintense lesion on T2 with a skinny wall and no enhancement is a renal easy cyst. All 3 phases of renal excretion are obtained after contrast and subtraction photographs could also be obtained to determine, share of enhancement. Angiography Renal angiography, as soon as a fundamental component within the prognosis of renal lots, is of little worth now. Angiography may be an alternative alternative to open biopsy in analysis of infiltrating renal neoplasm. Retrograde and Antegrade Pyelography Retrograde and antegrade pyelography could also be used for small urothelial tumors, for better mucosal element. It accounts for 85% of all malignant renal tumors and about 3% of all recognized neoplasms. Superficial tumors can invade and breach the renal capsule and instantly contain perirenal fat, adrenal gland and adjacent organs. Metastasis often occurs in regional nodes, invasion of cisterna chylii can lead to hilar and supraclavicular nodes. Systemic dissemination can take place into liver, bone, adrenal, reverse kidney or mind in decreasing order of frequency. They sometimes appear as variegated, expansile, cortical plenty with areas of necrosis, hemorrhage, cystic change and calcification (15%). They appear as homogeneous, hypovascular, gentle tissue cortical lots with foci of calcification. The tumor is typically giant at presentation, homogeneous without necrosis or hemorrhage. The chromophobe type is related to the least malignant potential and best prognosis. Tumors that are hyperechoic with echogenicity much like renal sinus fats happen and account for one third of tumors beneath 3 cm in diameter, these mimic angiomyolipoma. Features that recommend a malignancy is an echopoor rim and small cysts inside the tumor. If the tumor is cystic, it presents as a unilocular cystic mass in about 50% of such instances. Features, similar to irregular thickened walls, echoes and calcification favour malignancy. In 30%, the appearance is of a multilocular cystic mass with intervening stable areas, which may calcify. Doppler An abnormal Doppler signal may be seen within the ipsilateral renal artery as a rise in velocity, spectral broadening and turbulence. Intraoperative ultrasound is being used in nephron sparing surgery to delineate exact extent of the mass and venous thrombi. Computed Tomography Ultrasound Renal adenocarcinoma is detected as a properly encapsulated strong mass. Clear cell carcinomas enhance to a higher diploma than different subtypes of malignant lesions, especially papillary carcinoma. The criterion of 1 cm as a threshold has proved to be unsuccessful in differentiating reactive nodes from metastatic adenopathy. Based on T1-weighted images, a 15�20% enhancement on scans 3�5 minutes after gadolinium is considered diagnostic. Subtraction (gadoliniumenhanced fat-suppressed T1-weighted images�unenhanced fat-suppressed T1-weighted image) is an easy, reliable method. Enhancing papillary projections at periphery of a cystic hemorrhagic mass are seen. Angioinfarction has a limited role, in massive tumors and as palliative process to management pain, hematuria in inoperable/ unfit for surgery sufferers. False-positive results have additionally been seen in patients with benign inflammatory means of the kidney or benign tumors. Flurodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography could have a job in evaluating distant metastasis and in the differentiation between recurrence and posttreatment changes. Staging of Renal Cell Carcinoma7-11 Staging is a crucial element of evaluation of a patient with renal mass. Some signs like stranding of perinephric fats fascial thickening, obliteration/blurring of fat, adrenal involvement, seen collaterals are thought-about suggestive for extracapsular unfold. Perinephric stranding might outcome from edema, congestion and obliteration of fat could additionally be because of mass impact. If tumor extends only into subdiaphragmatic cava, then a flank method is adequate. On the right aspect it might be tough to distinguish between intraluminal tumor thrombus and extrinsic caval compression caused by a big primary tumor or enlarged lymph nodes. Falsepositive charges of 58% have been reported, nevertheless, when a size criterion of 1 cm is used, owing to reactive or different benign nodal disease. These false-positives are more frequent in patients with tumor involvement of the renal vein and tumor necrosis. A regular node will take up this particle and create a drop in T2 sign, whereas no drop in signal is seen in metastatic nodes. Bone scan is carried out only in patients with bone ache or raised alkaline phosphatase. Bone scan may be adverse because the lytic metastasis produce little osteoblastic reaction. Follow-up Most recurrences occur inside 3 years with a median relapse time of 1�2 years. Normal buildings might migrate into the renal fossa after nephrectomy and should simulate recurrent tumor. The liver, ascending colon, 2nd a part of duodenum, pancreatic head and small bowel may migrate into the right aspect. Flurodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography may also play a role in follow up with a high constructive predictive worth. Renal sparing surgery is now turning into a extensively accepted technique for removing small cancers. These sufferers have a decreased danger of continual renal insufficiency and proteinuria. The central tumors are tougher to ablate than the peripheral exophytic ones. It has been suggested that stage quite than tumor grade is the main prognostic issue for urothelial tumor of the higher tract.
Elimite 30 gm overnight deliveryCircumcaval Ureter Circumcaval ureter outcomes when the supracardinal vein persists and types the major portion of the inferior vena cava. The typical pattern on urography is a tortuous, dilated proximal right ureter and related hydronephrosis. Primary megaureter may be seen in both youngsters and adults and typically stays asymptomatic in many circumstances. Acquired Ureteric Obstruction the causes of acquired ureteric obstruction may be intraluminal or extraluminal. Tissue slough: Necrosed papilla and cholesteaotoma can slough and trigger obstruction of ureter with proximal dilatation. Fungus ball: Most fungus balls or mycetomas are attributable to Candida albicans and Aspergillus. Intraluminal Causes Abnormalities might develop throughout the ureteral lumen with none attachment to the uroepithelial lining. The common causes are calculi, blood clots, tissue slough, fungus ball and foreign materials. Ureteric Calculus Approximately 90% of urinary stones contain calcium (calcium oxalate, magnesium ammo nium phosphate) and 10% are calcium free (uric acid, cystine and xanthine). Oxalate and cystine calculi are radiopaque; nonetheless, pure uric acid calculi are radiolucent on plain radiography. Calculi within the ureters may be troublesome to visualize on plain Xrays in view of the fact that a 3rd of the ureter could overlie bone. Strong echoes with a sharply marginated acoustic shadow are the distinguishing features that distinguish stones from different filling defects in the ureter. Computed tomography performs a major role in the differential analysis of nonopaque filling defects within the ureter. Stones which may be nonopaque (uric acid) or faintly opaque (cystine) are visualized as dense as calcium containing stones; nonetheless, their precise attenuation values are lower than calcium stones. Noncontrast contiguous sections from kidney to bladder permit identification of the ureter in addition to obstructing calculus. Blood clots exhibit radiographic options which may be frequent to different nonradiopaque lesions. When clot persists as a mass of fibrin, calcification may develop that resembles stones or uroepithelial tumors. Intramural Causes Ureteral Tumors Primary ureteral tumors are relatively rare, accounting for about 1% of all urinary tract tumors. Males are affected greater than females with the usual age of presentation being in the 5th�8th decades. Certain epidemiological elements have been associated with elevated danger for growth of transitional cell carcinoma. Tobacco, espresso, artificial sweetener, chronic irritation and an infection are further danger factors. Squamous cell carcinoma happens in older age and is usually related to continual infection and leukoplakia of urinary tract. Sonography: Tumors of the ureter could also be seen as a delicate tissue mass located at the distal finish of a barely dilated ureter. The tumor could project into the ureteric lumen with circumferential or eccentric mural thickening. The lesion can present as a cell, clean, cylindrical, barely cellular, filling defect. Secondary Tumors and Contiguous Infiltration these are more widespread than main ureteric tumors. Direct extension of tumor from primary websites such as cervix, prostate and bladder can cause ureteric obstruction. Some tumors invoke an intense periureteric desmoplastic reaction causing ureteric obstruction. In such circumstances, imaging could demonstrate a soft tissue mass like retro peritoneal fibrosis. The frequent primaries responsible are melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, breast, lung and prostate. The most commonest is a papilloma which presents as a solitary filling defect connected to the ureter by a stalk. Inflammatory Lesions of Ureter Inflammatory conditions of the ureter include a wide variety of problems. Primary inflammation of the ureter is rare in the absence of systemic or regional disease in urinary tract, retroperitoneum, pelvis or peritoneum. Inflammation of ureteral wall could originate from inflammatory parts excreted in the urine, hematogenous embo lism or contiguous unfold from adjoining areas throughout the urinary tract and abdomen. The common responses of the ureter to irritation are loss of ureteric peristalsis, dilatation, Nonepithelial Tumors Fibroepithelial polyp is the most typical nonepithelial tumor. These sometimes occur in patients within the 20�40 years age Chapter 110 Imaging of Obstructive Uropathy and Diseases of Ureter 1749 ulceration, irregularity, pseudopolyposis, edema and desmo plasia resulting in stricture and calcification. This information dietary supplements that from other scientific diagnostic tools including urinalysis, urine culture, urine cytology and cystoureteroscopy. Malakoplakia: It is a benign chronic granulomatous disorder more generally seen in ladies than males. It may be seen at any level of the urinary tract however has a predilection for the bladder and lower ureter. It is seen in affiliation with chronic Escherichia coli or Proteus mirabilis infection and is discovered extra regularly in diabetics and immunosuppresed patients. On urography, the lesions are rounded to flat, coalescent filling defects lending an irregular contour to the ureteral margin. Ureteritis cystica: this disease entity is normally asymptomatic but could current with hematuria or signs of urinary tract an infection. Histologically, this condition consists of a number of, small, subepithelial, fluidfilled cysts within the ureteric wall. The typical radiographic appearance is that of a quantity of, small, filling defects with scalloping of the ureteral margin. The differential diagnosis includes air bubbles, hemorrhage into ureteric wall, and papillary neoplasm. Leukoplakia: Leukoplakia is a rare inflammatory condition which more generally involves the urinary bladder than the ureter. It results from squamous metaplasia of the urothelium and is regularly associated with continual urinary tract an infection or lengthy standing stone disease. Schistosomiasis: Schistosomiasis is a continual indolent infestation attributable to the trematode Schistosoma hematobium. The parasite lays its eggs within the veins of the bladder and decrease ureter stimulating continual inflammatory response leading to cystitis and ureteritis and finally scarring and calcification. Schistosomiasis generally affects the bladder and ureteric involvement is seen in onethird of patients.
Purchase elimite 30gm fast deliveryFibromatosis refers to a family of soft tissue lesions characterized by intermediate malignant potential, i. The fibromatosis are categorised on the premise of their anatomic location as both superficial or deep. The deep or musculoaponeurotic fibromatosis embody extra-abdominal, abdominal, intra-abdominal and extremity fibromatosis. The descriptive term desmoid tumor was coined to emphasize the band-like or tendon-like character of the lesion ("Desmos" which means band or tendon). These masses of fibromatoses are normally solitary though synchronous multicentric lesions could happen. Bone involvement could also be seen within the form of a stress erosion, scalloping without invasion or destruction, or stimulation of periosteum producing a "frond-like" periosteal reaction. The heterogeneous sign displays various proportions of collagen, spindle cells and mucopolysaccharide throughout the tumor. Those fibrous tumors which are hypocellular tumors with dense collagenous components have lower T2 signal depth while those with greater cellularity or larger quantities of extracellular myxoid matrix have greater signal depth. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, commonly known as referred to as inflammatory pseudotumor commonly happens in the orbit but additionally at other websites, such as lung, trachea, cranium base and thyroid. These tumors may be related to fibrosing mediastinitis and retroperitoneal fibrosis. Histologically the tumors show myofibroblastic spindle cells and an inflammatory infiltrate comprising of plasma cells, lymphocytes, and eosinophils. Extraorbital pseudotumors are much less aware of steroid remedy than orbital pseudotumors and may present perineural spread. Fibrohistiocytic Tumors the classification of this group is of tumors is controversial and is currently beneath revision. This lesion may also happen as second malignancy at websites of previous surgery/radiotherapy. The lesion is often of intermediate T1 sign depth, heterogeneously high T2 sign intensity with enhancement of the strong parts with a gadolinium contrast agent. Leiomyoma There are two groups within leiomyoma, one being the pelvic tumor seen in females and the other being tumors occurring in deep delicate tissues of both sex. These are reported as well-defined plenty that are slightly hyperintense to muscle on T1W pictures and with heterogeneous high sign depth on T2W photographs. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a rare tumor seen in middle-age adults but in addition reported in kids, generally found on the trunk or proximal extremities. The web site of origin of the tumor is dermis, nevertheless it spreads domestically into the deeper tissues. Clinical presentation is of slow-growing subcutaneous plaque or nodule with overlying pores and skin discoloration simulating a vascular lesion. Chapter 199 Imaging of Soft Tissue Lesions 3317 Rhabdomyosarcoma Rhabdomyosarcoma accounts for greater than half of softtissue sarcomas seen in kids. This tumor is believed to come up from primitive mesenchymal cells which are committed to become striated muscle. The histological variants of the tumor embrace embryonal, alveolar, and pleomorphic variants. The lesion may have an affiliation with syndromes corresponding to Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and neurofibromatosis. Hemangiopericytoma was earlier included in this category however is now considered to be extra intently related to solitary fibrous tumors. These uncommon tumors happen in the extremities as cutaneous nodules and occasionally within the sinonasal cavity. Mesenchymal Chondrosarcoma these are uncommon tumors occurring in 2nd or 3rd decades of life. Synovial Sarcoma Synovial sarcoma is the fourth commonest soft tissue tumor and affects the extremities, significantly across the knee joint (popliteal fossa) in majority of the instances. These lesions embody schwannoma, neurofibroma, and malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor. This signal is seen in lesions involving massive nerve trunks and not in lesions of small nerves. Plexiform neurofibroma exhibits diffuse nerve thickening, typically including nerve branches, producing a serpentine appearance on imaging and reflecting the irregular, convoluted gross look. Diffuse neurofibromas infiltrate the subcutaneous tissues and appear as fine linear branching lesions. Classically, the nerve is eccentric to the mass (although throughout the capsule) in schwannoma, rather than being central or obliterated by the mass as in neurofibroma. Neurogenic neoplasms present a sign depth similar to or slightly larger than that of skeletal muscle on T1-weighted imaging. They are aggressive neoplasms with excessive recurrence charges with frequent metastases to the lungs. Intratumoral hemorrhage, adjoining bone destruction and lymphadenopathy may also be seen. Magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography within the evaluation of soft tissue tumours of the extremities. Diffusion-weighted imaging of sentimental tissue tumors: usefulness of the obvious diffusion coefficient for differential analysis. Diffusionweighted echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of tumor cellularity in sufferers with soft-tissue sarcomas. The fats pad sign following elbow trauma in adults: Its usefulness and reliability in suspecting occult fracture. Hemangiomas and vascular malformations in infants and youngsters: a classification Chapter 199 Imaging of Soft Tissue Lesions primarily based on endothelial traits. High spatial resolution is required to establish microcalcifications measuring within the order of a hundred m. Grids are used for all mammographic research to scale back scattered radiation and to increase contrast, especially in the dense or thick breast. Modern mammography machines automatically choose target/filter combination, kVp and tube present according to breast density and the thickness of the compressed breast. Mammography is the one screening modality, which has been confirmed to scale back mortality from breast most cancers by way of early detection. The mammography tools and approach used should take into account the broad variation in breast measurement, variation within the relative quantities of fats, glandular and stromal tissue current, and the low inherent distinction between normal and abnormal breast tissue. The spectrum is refined additional by including filters on the source of the X-ray beam to take away the very low energy photons that are more doubtless to be absorbed in the breast and never contribute within the image formation. Modern mammography machines routinely choose target/filter mixture, kVp and tube present according to breast density and the thickness of the compressed breast Chapter 200 A Systematic Approach to Imaging of Breast Lesions 3323 X-ray spectrum for big breasts to provide adequate penetration and stop excessive radiation.
Pix Liquida (Pine). Elimite. - Upper and lower respiratory tract swelling (inflammation), mild muscle pain, nerve pain, blood pressure problems, common colds, cough or bronchitis, and fevers.
- How does Pine work?
- What is Pine?
- Dosing considerations for Pine.
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96143
Discount elimite 30gm amexWhile a multimodality method is commonly required to come to a last conclusion, the strengths and weaknesses of every approach should be known in order that both conventional and newer methods can be used to the utmost advantage of sufferers. Availability, price effectiveness and radiation dose are a number of the different essential components determining the selection of the imaging modality whereas investigating varied clinical problems. This article will focus on the current status of standard radiological procedures vis-�-vis the newer strategies in frequent medical situations. Patients suspected to have urolithiasis may present with acute flank ache, hematuria or recurrent urinary tract infections. However, the diagnostic accuracy of plain movie for the detection of urinary tract calculus depends on the chemical composition of the stone, its measurement, location, overlying bowel gasoline shadows and technical quality of the film. However, plain movies are nonetheless good as baseline research and for follow-up of stone disease post-treatment. Painless hematuria is another main urological drawback which wants evaluation of each renal parenchyma and urothelium to rule out urinary tract malignancy. There is presence of left hydroureteronephrosis with renal and ureteric calculi (arrows) urogram was a small urothelial tumor that was not detected in an unopacified section. The purpose of imaging is to diagnose any underlying congenital renal anomaly which will predispose to recurrent urinary tract infections and detect the presence of renal scarring and vesicoureteric reflux. Using T2-weighted (static-fluid urography) and distinction enhanced dynamic T1-weighted sequences (excretory urography), photographs of sufficient diagnostic quality can be obtained in infants with oral sedation. The sensitivity of detecting stones, strictures and congenital ureteropelvic junction obstructions was sixty eight. The sensitivity of detecting ureteral calculi is approach dependent, with greater sensitivity being reported for excretory urography than for staticfluid urography. Precise info of number of ureters, site of becoming a member of in case of duplication of ureter and vascular anatomy is obligatory before donor selection. However, in international locations corresponding to ours, a blanket substitution may not be possible due to value issue and availability. Photograpy of renal calculus: Description an adjustable modification in the focus tube. Visualization of the kidney and urinary tract on roentgenograms via intravenous administration of a new contrast: Uroselectan. Can ultrasound replace the intravenous urogram in preliminary investigation of renal tract disease Evaluation of asymptomatic microscopic hematuria in adults: the American Urological Association best follow coverage. Patient evaluation, cytology, voided markers, imaging, cystoscopy, nephrology analysis, and follow-up. Multidetector computed tomography urography for diagnosing higher urinary tract urothelial tumor. Paediatric urinary tract infection and the necessity of complete urological imaging. With fashionable instrumentation, bedside sonography and guided procedures could be carried out on even the most seriously sick sufferers. Although no specific preparation is required for scanning the kidneys, fasting optimises the visualization. Evaluation of the renal vessels is augmented by adequate affected person hydration and a full bladder is important for visualising the lower ureters, vesicoureteric junction and the bladder. The left kidney is more difficult to visualize because fuel in small bowel and splenic flexure intervene with the anterior or anterolateral approach. Some of the common indications for evaluating the higher urinary tract are: z Evaluation of collecting system obstruction z Evaluation of suspected or known nephrolithiasis z Evaluation of cystic renal illness z Detection of a renal or perirenal mass lesion z Characterization of a renal mass lesion z Guidance for diagnostic or therapeutic interventional procedures. It is surrounded by a fibrous capsule which demarcates it from the encompassing perirenal fats. However, if the renal cortex is brighter than the liver, it strongly suggests the presence of illness. Medullary pyramids are seen as echopoor oval areas evenly distributed across the inner margin of the cortex. The renal sinus incorporates the calyces, infundibulum, a portion of the renal pelvis, fibrous tissue, fats, vessels and lymphatics. When Normal Sonographic Appearance the kidneys lie retroperitoneally on both side of the backbone enclosed in fascial layers. However, in well-hydrated patients it might be slightly distended with echo free urine. The length of the normal adult kidney is usually 10�12 cm but can vary from 7 to 14 cm in patients with regular renal operate (Table 2). On sonography the longest cranio-caudal size is imaged by rotating the probe round its vertical axis. For more correct measurement of renal size, a renal volume assessment can be made, both by measuring the realm of kidney in serial slices and subsequently calculating the volume or through the use of the modified 3D ellipsoid formulation. The exact worth is probably not as important as consistency so that changes in volume over a period of time could be measured. The medullary pyramids appear disproportionately massive and are very poorly reflective. Sagittal sonogram reveals central parenchyma separating the higher and lower moieties. There is delicate dilatation of upper moiety Table 1: Differences between neonatal and adult kidney Neonatal Contour Cortex reflectivity Medullary reflectivity Sinus Collecting system Lobed ++ � Echo poor Apparent Adult Smooth + � Echogenic Inapparent Table 2: Normal kidney size in adults (cm) Adult female Left kidney Right kidney eleven (9. Normal Variations the kidneys could vary in position due to ptosis or an ectopic location. The most common website for the ectopic kidney is the pelvis, the place it might be tough to detect, as it can be obscured by bowel gas. A hypertrophied column of Bertin is a standard variant and represents unresorbed polar parenchyma from one or each of the two subkidneys that fuse to type the conventional kidney. Sagittal sonogram demonstrating the echogenic line (arrowhead) that extends from the renal sinus to the perinephric fat hilum. Accessory renal arteries might come up from the aorta in as many as 20% individuals, either superior or inferior to the primary renal artery. The renal arteries sometimes divide into anterior and posterior divisions that lie anterior and posterior to the renal pelvis, respectively. These divisions give rise to the segmental arteries which branch further within the renal sinus, forming interlobar arteries that penetrate the renal parenchyma. These terminate in arcuate arteries that curve across the corticomedullary junction giving rise to cortical branches. Occasionally it might be tough to differentiate a small avascular tumour from a hypertrophied column of Bertini when additional investigations maybe required. It was thought to symbolize connective tissue on the junction of the development of anterior and posterior components of the kidney. However, subsequent reassessment means that this line represents an extension into the parenchyma of hilar/sinus fats in sufferers with a deep renal sinus, quite than a real aircraft of fusion between embryological components. An enhance in fats content of the renal sinus can occur in overweight people, in renal sinus lipomatosis, and in cases of parenchymal atrophy. A mild distension of the accumulating system can occur because of physiological filling.
Purchase 30 gm elimite otcIf vasovagal response happens, she should be instantly positioned in a supine position with ft raised and pulse and blood strain monitored. Strict aseptic precautions in the course of the biopsy are important to decrease the chances of infection. A good compression after the biopsy and patient compliance of the post-biopsy instructions are important to reduce the probabilities of main hematoma formation. Although issues of breast biopsy are uncommon, psychological influence of breast biopsy is necessary. In less than 2% instances, a tiny round opacity could develop, which is seen in only one view of the mammogram. A fiducial (marker), normally a vitamin E capsule, can be placed in one of many holes. Depth is decided by counting the sagittal slices between needle holder and the lesion. The lesion and fiducial are localized and bar and columns moved to align the needle holder with the lesion for efficiency of biopsy. The patient needs to be moved in and out of the gantry several times in the course of the biopsy, making it cumbersome and time consuming. Histopathological Correlation Core biopsy is a reliable method of analysis of breast abnormalities. However, steps must be taken to achieve absolute best accuracy of the process. Accurate target setting and relationship of the needle with the lesion must be verified on imaging throughout breast biopsy. Whenever relevant, specimen radiography must be accomplished to verify presence of calcifications in the harvested samples. After biopsy, the outcomes of the biopsy ought to at all times be correlated with imaging findings. A rebiopsy is essential if the pattern is taken into account inadequate for definitive pathological diagnosis. It can also be being used for high-risk screening and preoperative staging of breast cancer. Imaging histologic-discordance occurs in 3�7% of core biopsies and malignancy is found in about one-fourth of those cases on surgical excision. Close audit of the biopsy results at an individual center should be regularly carried out to keep the standard and accuracy of breast biopsy. Overall, malignant outcomes are expected in 20�40% of all breast biopsies performed. With improvement of correct percutaneous core biopsy strategies, hookwire localization is now hardly ever performed for preliminary diagnosis. Hookwire localization prior to breast conservation surgical procedure helps to exactly resect the most cancers with clear margins. Indications of hookwire localization for diagnostic surgical excision biopsy include nonavailability of stereotactic biopsy facility or re-biopsy after inconclusive or discordant percutaneous core breast biopsy. It can also be beneficial for biopsy of vaguely outlined breast abnormalities lesions; corresponding to suspicious focal asymmetry or architectural distortion with out associated mass. Needle localization for excision biopsy helps to achieve correct lesion retrieval with minimal elimination of breast parenchyma. Early preoperative localization procedures had been performed using numerous types of dyes, corresponding to methylene blue or evans blue, combined with iodinated distinction. The dye was injected within the lesion through a needle introduced underneath mammographic guidance. However, spread of the dye and amount of tissue stained was unpredictable, leading to missed lesions or excision of a lot larger breast tissue than really required. Charcoal powder was also used as an alternative of aqueous dyes, in order to restrict the spread over massive area, but this was additionally not very accurate. Accuracy and reliability of preoperative needle localization significantly improved after the development of varied needle�hookwire combos. It consists of a 20 G needle and a thin flexible wire which may be introduced via it. After right needle placement, the hookwire is introduced and needle withdrawn over it. A modification of this hook-wire has a thick stiffened phase simply proximal to the hook. This rigid phase of wire is helpful to the surgeon because it allows manual palpation of the target lesion intraoperatively. Some variations of hookwire have double folded hook forming a barb, which prevent their displacement with in or out of the breast. Another kind of needle hookwire meeting has a retractable curved J-tip instead of the angled hook. If final hookwire position is unsatisfactory, the curved part of the wire may be retracted back into the needle and repositioning can be performed. The needle stays in the breast after deployment and it supplies a stiff guide to the surgeon. However, it might even be carried out under ultrasound steerage if the lesion is clearly defined on ultrasound. There are radiopaque alphanumeric centimeter markers on the margins of the window. The fenestrated compression plate has rows of multiple small spherical holes, like a sieve, as an alternative of a single open window. Both digital and film primarily based mammography machines are appropriate for needle localization. However, digital methods are most popular as photographs at every step are instantly out there and procedure is therefore much sooner. Technique Films on the basis of which needle localization has been recommended are reviewed and acceptable guiding modality and approach is chosen. Informed consent inclusive of needle localization and excision is often obtained by the surgeon. Mammographic needle localization is carried out with the patient in a sitting place. An approximate area of lesion, based mostly on the baseline movies, is marked on the pores and skin and breast is positioned in the craniocaudal view. The breast is compressed with the alpha-numeric window compression plate, with pores and skin mark within the heart. If the lesion is seen well within the window, its x and y axis location is determined using the alpha-numeric markers in the picture. The point is marked on the pores and skin at the crossing of similar coordinates, as seen on the compression plate. Availability of movable cross-hair shadow marker in the mild beam of mammography unit is significantly useful to mark the precise point on the skin.
Purchase elimite with paypalFat is quickly distinguished from different gentle tissues provided a main X-ray beam of decrease power is used, i. Density differences can additionally be maximized utilizing postprocessing in digital radiography. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Magnetic resonance imaging has emerged as the popular modality for imaging delicate tissue lesions. Technique: Positioning of affected person and the selection of correct floor coils for the study of soppy tissue lesions is crucial to decrease movement artifacts and to obtain optimal sign to noise ratio. Evaluation of trunk and thighs is most efficacious utilizing the physique coil with the affected person supine. If a gluteal gentle tissue lesion is suspected, susceptible position may be useful to keep away from distortion of the posterior delicate tissues. The body coil also allows comparability of each lower extremities and might provide full evaluation of the complete osseous or gentle tissue area of curiosity. New sequences have been developed to decrease the examination time or enhance the specificity. Fast spin echo T2-weighted sequences give a strong T2-weighted picture and save time. To be used adequately, a fats presaturation technique must be employed with this sequence. Gradient echo imaging is a helpful complement in demonstrating hemosiderin due to its greater magnetic susceptibility. Gradient echo pictures can also be higher in some cases to reveal the lesion fat interface and to detect small surrounding vessels. In equivocal instances contrast enhancement could also be useful in distinguishing cystic from stable lesions, and thus identifying essentially the most acceptable web site for biopsy. A majority of sentimental tissue masses have a nonspecific low to intermediate signal on T1 and excessive sign on T2-weighted pictures. A right histologic analysis based on imaging research alone is achieved in perhaps solely 25�30% of cases. Investigators, nonetheless, feel that this proportion is rising and finally will approach the range of 75�90%. Simple cystic lesions (ganglion, meniscal cyst, bursa, fats necrosis, lymphocele) have a attribute homogeneous, very low and really excessive signal on T1 and T2-weighted pictures, respectively. Conversely, some delicate tissue lots (scar/fibrous tissue), persistent hematoma, aggressive fibromata, pigmented villonodular synovitis, aneurysm and vascular malformation present a low sign or signal void on each sequences. There are situations, nevertheless, during which a specific prognosis may be made or strongly suspected. Some delicate tissue masses (lipoma, subacute hematoma, hemangioma, intralesional hemorrhage and well-differentiated liposarcoma) show a characteristic high-signal on T1 and T2-weighted images. Lipoma, aggressive fibromatosis (desmoids), nerve sheath tumors, myxomas and gentle tissue secondaries are most likely to be multiple. Infection can also mimic a malignant gentle tissue tumor and clinical history is necessary in this regard. A vital proportion of malignant soft tissue tumors may have well-defined margins with a so known as pseudocapsule and comparatively homogeneous signal depth. It is essential that the complete extent of any gentle tissue mass along with its relationship to the adjacent joint and surrounding anatomical buildings be clearly demonstrated. If the lesion enhances, a tumor ought to be suspected and biopsy of the enhancing space be obtained. The staging of sentimental tissue sarcomas is set by the dimensions of the tumor, the histologic grade, and lymph nodal unfold or distant metastases. There is, however, difficulty in separating the adjustments related to recent remedy, particularly radiotherapy. Radiotherapy might end in soft tissue trabeculation, improve in fatty marrow in addition to focal marrow abnormalities. Rarely, patients may develop radiation-induced malignancies in the irradiated field. Chemotherapy-induced hemorrhage may end in a rise in the dimension of the mass. Recurrent tumor seems as a discrete nodule or mass with sign traits that characteristically mirror these of the original tumor. Use of unenhanced T1-weighted fatsuppressed and gradient-echo sequences helps differentiate post-treatment hemorrhage from tumor recurrence. The locations embody intramuscular, intermuscular, subcutaneous,and intra-articular/periarticular. An intensive lesion may be multicompartmental and the differential prognosis of such lesions is angiomatous lesions, neurofibromatosis, fibromatosis, lipomatosis, myxoma (Mazabraud syndrome), metastases, or lymphoma. An intracompartmental lesion refers to one which has not crossed any pure anatomic boundaries. These boundaries may be cortical bone, articular cartilage, joint capsule, main fascial aircraft, tendon, or ligament. Idiopathic calcification or calcinosis in previously normal tissues with normal serum ranges. Metastatic calcification is usually widespread, fairly symmetrical and bilateral in distribution. Dystrophic calcification is often limited to the positioning of harm and tends to be extra focal and asymmetrically distributed. Substances on the pores and skin, corresponding to lead ointment or pigments used in tattoos, might trigger confusing opacities. Abnormal tissue calcification can be subdivided into three main classes (Table 2). Metastatic in previously undamaged tissues, with elevated serum of calcium and phosphate levels. Arterial and cartilaginous calcifications are nicely acknowledged in hyperparathyroidism. Arterial calcification is frequently seen in sufferers on renal dialysis and on this group one may discover quite gross periarticular calcification just like the looks of tumoral calcinosis. This could occur with comparatively regular values of serum calcium and seems to be related to the rising levels of serum phosphate. A severe form of the illness affecting children underneath 10 years of age causes intensive muscle harm and fibrosis with significantly widespread calcification. Radiographically, gentle tissue calcification is indistinguishable from idiopathic calcinosis universalis. In the latter situation the diagnostic areas are arms and toes, where soft tissue calcification is related to attribute shortening of the first, fourth and fifth metacarpals and metatarsals. Of the parasitic infestations, cysticercosis cellulosae is the most common trigger of soft tissue calcification, seen in Asian subcontinent. They seem to have a predilection for skeletal muscle, subcutaneous tissue and mind.
References - Allsbrook WC Jr, Mangold KA, Johnson MH, et al: Interobserver reproducibility of Gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma: urologic pathologists, Hum Pathol 32(1):74n80, 2001.
- Goessl C, Knispel HH, Millar K, et al: Is routine excretory urography necessary at first diagnosis of bladder cancer?, J Urol 157:480n481, 1997.
- Frutiger P: Zur Fruhentwicklung der Ductus paramesonephrici und des Mullerschen Hugels beim Menschen, Acta Anat (Basel) 72(j):233-245, 1969.
- Abdollah F, Ye Z, Miller DC, et al: Understanding the use of prostate biopsy among men with limited life expectance in a statewide quality improvement collaborative, Eur Urol 70:854n861, 2016.
|
|