"Buy 250mg chloroquine with visa, treatment 4 toilet infection."By: J. Matthew Brennan, MD - Associate Professor of Medicine
- Member in the Duke Clinical Research Institute
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/j-matthew-brennan-md
Best 250mg chloroquineUnderstanding the administration of these extreme diabetic foot problems is key, as most foot infections and other issues are preventable, or no much less than treatable (8). Prevention of Diabetes Foot Complications Vascular problems are a major reason for morbidity and mortality in diabetic sufferers. These outcome from interactions between systemic metabolic abnormalities such as hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, genetic and epigenetic modulators, and local tissue responses to poisonous metabolites. Infection can proceed rapidly and the end-stage of tissue death is shortly reached. Thus, the window of opportunity for intervention is limited and is often missed (10). Optimal management of glycemic control, hypertension, dyslipidemia, smoking cessation, weight management, use of antiplatelet brokers, and addressing different modifiable risk components are important to prevent or slow any progression of those and different vascular problems (10,11). The first step in prevention is identifying the "at-risk" inhabitants during the complete foot evaluation. Emollient - twice daily use of urea-based heel balm to prevent drying & cracking of ft 7. Deterioration � consider if that is an acute Diabetic foot drawback and refer if necessary. High arch in the extra common distal sensorimotor neuropathy is associated with plantar ulceration Abscesses (may monitor to dorsum) Subluxed bone in Charcot neuroarthropathy Heel ulcer - normally neuropathic, and often pressure-related. Ensure good heel protection in all patients confined to bed (a) Thin, dry (non-sweating) skin Posterior tibial pulse Prominent veins in neuropathy Ischemic ulcer/necrosis Interdigital infection Dorsalis pedis pulse Ischemic ulcer/necrosis Sausage toe (b) Digital gangrene Onychogryphosis. Document all findings including completing daily foot inspection chart (Table 40-1). In sufferers with intensive ulceration, document with medical pictures as soon as possible. In addition, all patients with diabetes ought to have their ft inspected at each visit (including inpatient admission). Foot examination should embrace general inspection of pores and skin integrity, and musculoskeletal deformities. The characteristic clawing seen in motor nerve dysfunction is as a result of of the differential lack of energy between the extensor muscle tissue and the flexor muscle tissue resulting in areas of high plantar pressures (leading to callus and increased risk of ulcer) and an increased risk of the dorsal features of the toes rubbing towards the within of the toe field of a shoe. At least one different assessment (pinprick or temperature [smallfiber function], vibration or ankle reflexes [large-fiber function]) should be carried out (6,9,10). Management of High-Risk Patients All patients with diabetes and particularly these with high-risk foot conditions. Appropriate footwear (including orthotist review) and footwear behaviors at home (and also in the hospital setting) ought to be outlined. Regular podiatry evaluation as needed is important and clear instructions on how and when to access urgent/emergency foot care is crucial. The presence of important limb ischemia may improve the level of severity In Uninfected 1 2 Classification and Diagnosis Over the previous three a long time, a number of schemes for classification of the most common diabetic foot issues have been printed. In which diabetic patients with a foot wound should I suspect an infection, and how ought to I classify it Every foot wound in a diabetic patient must be thought of as probably contaminated, notably if the affected person is at high danger as a end result of the presence of peripheral neuropathy or arterial illness. Clinicians should assess the patient at three totally different levels: first, the affected person as a complete; then the affected limb; and, finally, the wound. If not out there, the clinicians in cost of the patient ought to attempt to coordinate obtaining and deploying the recommendation of all the key specialists required. Which sufferers with a diabetic foot infection ought to I hospitalize, and what criteria should they meet before I discharge them Hospitalization should be thought-about in case of extreme infection, average an infection and issues. When and how ought to I acquire specimen(s) for culture from a patient with a diabetic foot wound After careful cleaning and wound debridement, obtain the sample from deep tissue by biopsy or curettage or by aspiration of purulent secretions, if in any respect attainable. Select an empiric routine primarily based on the likeliest pathogens and identified native antibiotic sensitivity patterns and consider modifying it based mostly on the medical response to therapy and the results of culture and sensitivity checks. The selection of an empiric antibiotic routine also wants to be based on the severity of the infection (Table 40-4) and other elements (Table 40-5). How should I diagnose and treat osteomyelitis of the foot in a affected person with diabetes In any infected, deep, or large foot ulcer, notably if the lesion is continual or overlies a bony prominence, think about the potential of osteomyelitis. When a definitive diagnosis of osteomyelitis is required, clinicians should obtain a bone specimen for microbiological and histopathological analysis. Treating osteomyelitis nearly always requires antibiotic therapy, which can be effective alone but is usually mixed with no much less than some surgical resection of necrotic and contaminated bone. An elective amputation may be appropriate in a number of situations, similar to irreversible lack of limb perform, recurrence of the wound regardless of enough preventive administration, or the need for an unacceptably extended or intensive hospital management. What types of wound care strategies and dressings are applicable for diabetic foot wounds Adequate administration of a wound should embody correct cleansing, followed by debridement of callus and necrotic tissue and pressure offloading. The clinician ought to measure the important signs, palpate for pedal pulses, examine for peripheral neuropathy and debride and probe any open wounds. The presence of any of those findings ought to immediate speedy session with an skilled foot surgeon. In addition to primary hematology and blood chemistry tests, virtually all patients with a foot wound ought to have a plain radiograph of the foot to look for the presence of fuel, a international physique or bone lesions. Similarly, the presence of a deep gentle tissue abscess or osteomyelitis additionally requires surgical analysis. Multidisciplinary Teams and Clinical Pathways Early and continued care supplied by a multidisciplinary staff has been repeatedly proven to be associated with higher outcomes in inpatient, in addition to outpatient, settings and to reduce likelihood of major lower extremity amputation. The key criterion for membership is less the specific specialty of the members than their expertise and interest (6, 15). However, even in resource-rich nations the existence and acceptable referral to multidisciplinary foot teams may be deficient. Despite these undesirable deficits in care, having a strong diabetic foot care pathway with clear antibiotic protocols in place enables nearly all of patients in the hospital setting to get quick acceptable treatment with a transparent plan of motion. Infected wounds, nonetheless, nearly at all times Acute Diabetic Foot Species quantity Strict anaerobes Enterobacteriaceae Pseudomonas spp. The colonizing bacterial species are depending on the chronicity of the ulcer and the age of the wound. Species numbers enhance ensuing in the evolution from a monomicrobial to a polymicrobial community (18). Obtaining a tissue sample for tradition from any clinically infected wound, preferably before initiating empirical antibiotic remedy, is a crucial step toward making certain an acceptable agent is chosen. Specimens of deep tissue obtained by biopsy or curettage, or aspirations of purulent secretions are extra apt to develop the true pathogens and less prone to yield colonizing microorganisms. Blood cultures are rarely constructive, besides in patients with proof of systemic sepsis.
Order 250mg chloroquine otcClinical features and administration of splenic artery pseudoaneurysm: case series and cumulative evaluate of literature. A first case report of the successful laparoscopic restore of a splenic artery aneurysm. Jaundice secondary to hepatic artery aneurysm: radiological look and medical features. Celiac artery aneurysms: historic (1745�1949) versus contemporary (1950�1984) variations in etiology and clinical significance. Uncommon splanchnic artery aneurysms: pancreaticoduodenal, gastroduodenal, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric, and colic. Diagnosis and administration of aneurysms involving the superior mesenteric artery and its branches: a report of 4 instances. Massive gastrointestinal hemorrhage attributable to rupture of a jejunal branch artery aneurysm. True aneurysms of the pancreaticoduodenal artery: profitable non-operative administration. Gastroduodenal and pancreaticoduodenal artery aneurysms: a complication of pancreatitis causing spontaneous gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Arterial problems of pancreatitis: diagnostic and therapeutic features in 104 cases. Treatment of pancreatic pseudoaneurysm with percutaneous transabdominal thrombin injection. Contemporary management of splanchnic and renal artery aneurysms: results of endovascular compared with open surgery from two European vascular centers. Invariably, such people are on a number of antihypertensive medication with continued issue in controlling their blood strain. The chosen intervention depends on the extent of aortic and renal artery illness, and on whether or not a simultaneous aortic reconstruction is to be undertaken. The traditional surgical exposure when performing an endarterectomy of the renal artery is an anterior one via the bottom of the mesocolon and root of the mesentery, 245 246 Surgical administration of grownup and pediatric renovascular hypertension except when enterprise a direct isolated renal artery endarterectomy, by which case a medial visceral rotation is undertaken. A supraumbilical transverse abdominal incision is most well-liked, prolonged from one anterior axillary line to the opposite for bilateral reconstructions, and to the ipsilateral posterior axillary line when treating unilateral disease. The ligament of Treitz is divided and the duodenum together with the pancreas is then mobilized and retracted into the higher abdomen with the assist of a set retractor. The underlying renal arteries are skeletonized from their aortic origin to past their branching and the apparent plaque. Small nonparenchymal arterial branches, corresponding to these to the adrenal gland, could also be transected and ligated close to the renal artery. This requires division of the periaortic diaphragmatic crura, which are transected perpendicular to their fibers and the aorta with electrocautery. Axial aortorenal endarterectomy this is the commonest method of normalizing renal blood flow in circumstances of aortic spillover renal artery plaque. Arterial clamping is achieved with low-pressure (30�70 g/cm2) microvascular Heifetz clamps. This type of endarterectomy is particularly suited when (b) (a) (c) Axial aortorenal endarterectomy using a vertical aortotomy, extending from the level of the superior mesenteric artery to the anterior aorta onto the infrarenal aorta (a). Bilateral proximal arteriosclerotic stenoses preoperatively (b) and postendarterectomy (c). An endarterectomy airplane is developed between the diseased and normal outer aortic media and this airplane is extended circumferentially. Aortic tacking sutures could often be wanted to secure the residual plaque to the deeper aortic media and stop a later aortic dissection. Renal artery endarterectomy is accomplished by sustaining light traction on the aortic plaque and its extension into the renal artery, whereas simultaneously pushing the everted inside arterial wall away from the plaque. This kind of endarterectomy may be simpler to perform if the aortic plaque is transected into lateral halves. A well-defined renal artery end point usually occurs with distal feathering of the plaque. The aortotomy is closed with a continuous cardiovascular suture after irrigating the endarterectomized aorta and renal arteries to take away any small items of debris. Once the aortotomy has been closed, circulation is restored first through the aorta to the decrease extremities, then to the kidneys. This lessens the danger of renal embolization of any materials loosened by the higher aortic clamp. Intraoperative duplex scanning or directional Doppler examination is undertaken to assess the adequacy of the endarterectomy. If a preocclusive intimal flap is suspected, a separate renal artery incision ought to be made past the tip point of the plaque. The elevated distal plaque is then removed or tacked down and the arteriotomy is closed, often with a vein patch to forestall narrowing of the artery. The endarterectomy is facilitated by everting each renal artery while sustaining mild traction on the plaque. A soft-jaw clamp may then be positioned on the graft, and renal blood circulate is restored while the distal graft anastomosis is completed. Direct renal artery endarterectomy Direct renal artery endarterectomy could additionally be undertaken for focal, unilateral renal atherosclerotic narrowing occurring independently of extensive aortic atherosclerosis. Once systemic anticoagulation and vascular management are achieved, an anterior renal arteriotomy is carried out and prolonged proximally into the aorta and distally past the renal artery plaque. Following elimination of the plaque, a vein or prosthetic patch graft closure of the arteriotomy is undertaken. Occasional sufferers with ostial disease may be finest served by reimplantation of a transected renal artery after eversion endarterectomy. This method is nicely suited to Transaortic renal artery endarterectomy Transaortic renal artery endarterectomy for arteriosclerotic renal artery stenotic disease is usually carried out in sufferers requiring a concomitant aortic reconstruction. Vascular control is obtained in the identical manner as undertaken with the axial approach, besides that placement of the distal aortic clamp is determined by the type and extent of aortic aneurysmal or occlusive disease being treated. An eversion endarterectomy is performed in a standard manner and the endarterectomized artery is then reimplanted onto the prosthetic graft in instances of a concomitant aortic reconstruction or immediately into the native aorta in other instances. The renal artery is dissected about its circumference from near its aortic origin to its proximal branches. The most direct route for right-sided aortorenal grafts is in a retrocaval place. This branch is incised alongside its lumen adjoining to the mother or father vein in order that a common orifice is created between the principle trunk and its branch. In each circumstances, the resultant generous circumference lessens the likelihood of anastomotic narrowing and permits for a comparatively perpendicular origin of the vein graft from the aorta. Graftto-aortic anastomoses are carried out utilizing a nice working cardiovascular suture. Management of stenotic disease affecting multiple main renal arteries or widely separated segmental branches could require separate implantations of the arteries right into a single conduit. This is normally Aortorenal bypass procedures Aortorenal bypass procedures for both arteriosclerotic and fibrodysplastic renal artery stenoses were the usual of care in lots of practices through the Nineteen Seventies. The infrarenal aorta is dissected about its circumference below the origin of the renal arteries, recognizing that ligation and transection of the lumbar veins and arteries could also be undertaken with out consequence, if necessary.
Buy 250mg chloroquine with visaA extra simple strategy is to divide measured serum glucose (in mmol/L) by four; and add this number to measured serum sodium stage to get hold of the corrected serum sodium stage. Serum potassium levels may also be low, normal, or elevated, regardless of whole body potassium depletion resulting from protracted polyuria and vomiting (1). However, leukocytosis with cell counts >25,000 mm3 could designate infection and applicable evaluation is indicated. Starvation ketosis and alcoholic ketoacidosis are distinguished by medical historical past and by plasma glucose concentrations that vary from mildly elevated (rarely >200 mg/dL [11. Severe hypovolemia might manifest as tachycardia (pulse >100 bpm) and/or hypotension (systolic blood stress <100 mmHg). Each has its limitations particularly on preliminary assessment where previous comparator knowledge may not be available. Because of the increasing frequency of diabetes (both recognized and undiagnosed) or stressrelated hyperglycemia, and with the harms related to increased glucose concentrations, glucose must be measured in all unwell sufferers presenting to the hospital. It is also imperative to exclude unknown being pregnant by performing a being pregnant check in applicable patient. As Healthcare providers are involved by the risk of extreme hyperglycemia during acute illness in individuals with diabetes, especially those treated with insulin therapy. Blood glucose concentrations usually enhance throughout sickness due to the release of stress hormones. The directions embrace sustaining traditional food plan, noninsulin therapies, and/or insulin regimen each time potential. Persons with diabetes, who experience nausea or vomiting, ought to provoke the sick-day meals plan. In patients handled with insulin, blood glucose and ketone (if available) monitoring must be carried out as beneficial. If the blood glucose focus is >250 mg/dL (14 mmol/L) on two consecutive exams regardless of following the sick day rules, individuals with diabetes are really helpful to contact their clinician because of the potential must complement their present insulin routine with short- or rapid-acting insulin as essential. The particular person have to be instructed to contact their healthcare supplier when the blood glucose is persistently raised. The majority of these "gentle" conditions might be managed in the community or outpatient setting. However, this determination has to bear in mind varied factors together with medical. These aims often are achieved via the administration of low-dose (0. Frequent laboratory measurements of creatinine, and serum electrolyte ranges ought to be accomplished to guide fluid and electrolyte substitute. It is essential to substitute fluid and electrolytes and correct pH whereas bringing the blood glucose concentration to a traditional level. A sudden change in the osmolality of extracellular fluid also can happen when blood glucose ranges are lowered too rapidly, and this could cause cerebral edema. Serum potassium levels typically fall as acidosis is corrected and potassium strikes from the extracellular into the intracellular compartment, but once more, this may be due to the rate of insulin infusion being too high as glucose concentrations drop (19). Identification and treatment of the underlying trigger, such as infection, are also necessary. The mean period of treatment till blood glucose is <250 mg/dL (14 mmol/L) and ketoacidosis (pH >7. Check capillary glucose and serum/urine ketones to confirm hyperglycemia and ketonemia/ketonuria. Fifty items of short-acting insulin or rapid-acting insulin made up to 50 ml with 0. Subcutaneous injections of long-acting insulin ought to be continued if the affected person is already utilizing these agents. Re-assessment of cardiovascular status at 12 hours is mandatory, further fluid could also be required Reproduced with permission from John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Measure venous blood gasoline for pH, bicarbonate and potassium at 60 minutes, 2 hours and a pair of hourly thereafter. Where available, the diabetes inpatient staff ought to ideally be concerned as early as is practical after admission. Even when specific hospital pointers can be found, adherence to and use of these are variable amongst inpatient teams. Other objectives includes identifying and treating the underlying trigger; prevent arterial or venous thrombosis; forestall other potential complications. The goal of the preliminary therapy is growth of the intra and extravascular quantity and to restore peripheral perfusion. Measurement or calculation of osmolality must be undertaken each hour initially and the rate of fluid substitute adjusted to guarantee a positive fluid balance adequate to promote a gradual decline in osmolality. Urinary fluid losses may be appreciable as a result of osmotic diuresis which may persist for hours as glucose concentrations slowly decrease. The fall in osmolality with the lowering of blood glucose and shift of water into the intracellular house inevitably results in a rise in serum sodium. Provided plasma glucose is declining at a protected price, for example, no more than ninety mg/dL/hr (5 mmol/L/hr), this will be accompanied by a rise in serum sodium, but a fall in osmolality. Serum sodium concentrations ought to be regularly monitored, and the concentration of sodium in fluids adjusted to promote a gradual decline in corrected serum sodium. The purpose of therapy should be to exchange roughly 50% of estimated fluid loss throughout the first 12 hr and the remainder within the following 12 hours, although this will, in part, be determined by the preliminary severity, and the degree of renal impairment and related comorbidities, which may limit the velocity of correction. Insulin treatment previous to sufficient fluid alternative may end in cardiovascular collapse as water moves out of the intravascular house, with a ensuing decline in intravascular quantity. Insulin could additionally be started at this point, or if already in place the infusion rate increased (increased by 1 unit/hr). A blood glucose target of between 180 and 270 mg/dL (10 and 15 mmol/L) is an inexpensive objective in the first 24 hours. If the blood glucose falls below 250 mg/dL (14 mmol/L), begin 10% dextrose at 125 ml/h and proceed the zero. For patients with beforehand undiagnosed diabetes or who have been nicely controlled on oral agents, switching from insulin to the appropriate non-insulin remedy must be thought of after a period of stability. In addition, greater progesterone ranges in pregnancy induce a respiratory alkalosis that results in a compensatory metabolic acidosis which reduces buffering capability. However, prevention of those states is at all times preferred and this requires appropriate education of sufferers, carers, and healthcare practitioners on an ongoing foundation. The challenges posed with the use of insulin in hospitalized sufferers happen all through all areas of this care setting. Guidelines and recommendations for laboratory evaluation in the prognosis and administration of diabetes mellitus. Blood ketones: measurement, interpretation, limitations and utility within the management of diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetic emergencies: ketoacidosis, hyperglycaemic hyperosmolar state and hypoglycaemia. Update on prognosis, pathogenesis and administration of ketosis-prone Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: a possible complication of remedy with sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition.
Buy chloroquine on lineWhen the best pleural area is entered throughout mobilization of the aorta, a chest tube should be inserted in the postoperative setting. Finally, to prevent chyle leak, it could be helpful to ligate the thoracic duct at a number of locations within the distal thorax. This can be prevented by ensuring sufficient hydration and cardiac output, minimizing infectious issues, and allowing permissive hypertension. Case examples 279 anastomosis, and noteworthy atherosclerotic modifications at the distal anastomotic website. She was discharged in satisfactory condition on postoperative day 6, with out issues. Case example 2 A 51-year-old man presented with a previous historical past of an acute kind B aortic dissection difficult by visceral ischemia for which a bowel resection and an iliacsuperior mesenteric artery bypass was carried out. He had an extensive medical historical past, including hypertension, dyslipidemia, and kind B dissection. Furthermore, he had a history of substance abuse including alcohol, cocaine, and tobacco (former smoker). The affected person was inspired to remain substance-free to scale back the danger of aortic issues. This affected person met the thresholds of surgical restore because the diameter of the descending thoracic aorta had a most of 5. His preoperative workup included cardiac catheterization, which suggested normal pulmonary artery pressures, preserved cardiac output, and gentle nonobstructive coronary artery disease. His ankle�brachial pressure indexes, carotid duplex scanning, and pulmonary operate checks had been excellent. His postoperative course was without problems and he was discharged in passable condition on postoperative day eight. Synchronous and metachronous thoracic aneurysms in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms. Female and aged abdominal aortic aneurysm patients more generally have concurrent thoracic aortic aneurysm. Longterm outcomes from a 12-year expertise with endovascular therapy for thoracic aortic disease. Resection of the descending thoracic aorta: outcomes after use of hypothermic circulatory arrest. Strategies to handle paraplegia danger after endovascular stent repair of descending thoracic aortic aneurysms. Stenting of this vessel has not proven outcomes corresponding to endarterectomy with patch angioplasty, significantly in crucial limb ischemia. In addition, the increased complexity of surgical intervention following stent thrombosis makes the endovascular option less interesting. Iliac artery endarterectomy is carried out much less generally due to the favorable outcomes of endovascular procedures, which are also relatively much less invasive. However, in choose circumstances iliac artery endarterectomy is advantageous, and may be an necessary adjunct procedure. One example is localized iliac artery endarterectomy for the donor iliac artery of an iliofemoral bypass. Mukherjee and Inahara reported a 5-year patency of 94%,1 whereas Ballotta and collaborators reported an 8-year primary patency of 96% and assisted patency of 100%. It can be used to optimize inflow or outflow to the arterial system of the extremity, or as an isolated therapy for regional illness. Sharafuddin and collaborators confirmed 75% � 17% primary patency, or 92% � 12% assisted patency at forty months for the hybrid method. Familiarity with femoral triangle anatomy is of utmost significance for the vascular surgeon. The proximal side of the sartorius muscle delineates the lateral border of the 281 282 Common femoral and iliac artery endarterectomy femoral triangle. The medial border of the femoral triangle is fashioned by the adductor longus muscle, which originates from the superior ramus of the pubis, and inserts into the femur as it runs laterally. The procedure can be done under general or epidural anesthesia, or local anesthesia with sedation. The benefit of a longitudinal incision is doubtlessly better exposure and the potential for proximal or distal extension as wanted. A transverse incision could be more cosmetically appealing, and it has been reported that it could have decrease postoperative wound complications when compared to a longitudinal incision. The transverse incision must be positioned simply distal to the medial side of the place the inguinal ligament is assumed to be, using the anterior superior iliac backbone and the pubic tubercle as landmarks for the course of the inguinal ligament. The longitudinal incision is on the midpoint of the inguinal ligament, extending from the ligament as far distally as is critical. For exterior iliac artery publicity, an oblique incision below the umbilicus, lateral to the rectus muscle and directed toward the flank ought to be used. A longitudinal incision is made at the midpoint of the inguinal ligament, extending from the ligament as far distally as is necessary. In instances the place no pulse is palpated, the floor landmarks described earlier should provide an enough information. Usually, a 5�10-cm-long incision is adequate, depending on the extent of dissection and body habitus of the patient. After pores and skin incision, the dissection is carried down through the subcutaneous tissues with electrocautery. When the femoral sheath is encountered, the authors primarily use sharp dissection with Metzenbaum scissors. The dissection is kept near the artery to avoid injuring the adjacent constructions. On event, native vessels are severely diseased and software of a clamp may be hazardous. In this example, intravascular management of the artery with the use of balloon occlusion proximally, distally, or both, may be of worth. The arteriotomy is then prolonged utilizing Potts scissors proximally and distally till a comparatively disease-free section of the vessel is seen. Longitudinal 6-0 sutures are placed at the proximal and distal edges to stop flap elevation and reduce its profile to blood circulate. Care should be taken at the proximal and distal end of the plaque to ensure easy transition and avoid a significant intimal flap, especially at the distal extent of the endarterectomy. A residual intimal flap can lead to antegrade dissection and possible arterial occlusion. After hemostasis is passable, the wound is closed in multiple layers to obliterate potential lifeless area that may accumulate into a lymphocele or a hematoma.
Discount 250mg chloroquine otcReconstruction the reconstructive phases are like conventional strategies of open degenerative aortic aneurysm restore. Curved, heavy iliac clamps are placed first, adopted by a curved aortic clamp placed suprarenal for the juxtarenal restore. The aneurysm is opened, the thrombus is eliminated, lumbar bleeding is managed, and a graft is sewn end-to-end in a normal style. The thoracoabdominal method involves a two-body cavity exposure with the affected person turned 60 levels on the chest and forty five levels at the hip, with an "S" incision via the eighth intercostal space from a left-side up position. The dissection can be retroperitoneal or the parietal peritoneum can be opened, followed by an prolonged left medial visceral rotation. As a outcome, the anatomic nuances of inflammatory aortic aneurysms are even much less regularly encountered than in the past. Familiarity with these and their influence on the chance of open restore of inflammatory aortic aneurysms continues to be worthy of research and evaluate by vascular surgeons. This permits the surgeon to reliably control the aorta and its surrounding structures, stopping injury to vascular and visceral structures. Appropriate retractor set-up is prime to the exposure course of and ultimate security and success. Adequate lateral and superior retraction of the upper abdominal wall and lower rib cage with sequential advancement of deep self-retaining retractor blades is needed. Attempts at duodenal dissection of the inflammatory aneurysm risks injury and perforation of the duodenum. It must be left intact until the proximal and distal dissections are full and ideally till after the aneurysm is clamped and opened. If essential for enough publicity, the duodenum can be dissected off the aneurysm wall with a No. The goal of therapy is to exclude the aneurysm from the circulation and to protect adequate perfusion to the organs. With open restore, the aneurysm may be ligated or resected with distal organ revascularization. When revascularization is performed, a direct arterio-arterial anastomosis or aortic reimplantation may be carried out. In saccular aneurysms, aneurysmorrhaphy with excision of the diseased portion of the vessel wall could be carried out, though recurrence is greater. Most agree that "true" aneurysms ought to be handled provided that symptomatic or if their size exceeds 2 cm; in distinction, most pseudoaneurysms advantage remedy until very small and secure. An essential benefit of axial imaging over angiography is that it permits examination of adjoining intra-abdominal organs. The celiac axis originates from the anterior floor of the proximal stomach aorta because it passes between the diaphragmatic crura at the stage of the 12th thoracic vertebra. These branches and their tributaries provide the blood provide for the abdomen, liver, spleen, portions of the pancreas, and the proximal duodenum. The splenic artery gives off the dorsal pancreatic artery, left gastroepiploic artery, and quick gastric arteries before completing its tortuous course towards the spleen. It travels behind the neck of the pancreas, in entrance of the uncinate process and over the third portion of the duodenum. If undetected, such lesser sac hematomas finally rupture into the peritoneal cavity and can cause fatal bleeding. Treatment of sufferers with asymptomatic aneurysms >2 cm in diameter is indicated if the procedural danger is suitable. Proximal or midportion aneurysms are treated with resection or ligation; revascularization is usually not required as a outcome of the distal splenic artery fills via collaterals from the brief gastric arteries. When distal aneurysms are situated inside the pancreatic parenchyma, distal pancreatectomy could also be needed. Hepatic artery aneurysms 235 artery anastomotic reconstruction and 5 with distal pancreatectomy). The afferent and efferent vessels from the aneurysm are ligated to exclude blood flow from the sac. The pancreas may also have to be mobilized to better expose the splenic artery coursing just superior and posterior to its physique and tail. Recurrent episodes of pancreatitis, especially with formation of pseudocysts, which may erode into the artery, can produce pseudoaneurysms in this location. Each vessel is then suture-ligated from throughout the sac with monofilament polypropylene suture. When cysts involve the distal body or tail of the pancreas, it may be preferable to carry out a distal pancreatectomy, removing the diseased pancreas, pseudocyst, and aneurysmal artery all at once. Historically, aneurysms close to the hilum of the spleen have been handled with splenectomy. To provide higher exposure, the spleen may must be mobilized by taking down a few of its ligamentous attachments to the diaphragm, colon, or kidney. If technically possible, aneurysmorrhaphy, ligation exclusion, or aneurysm excision are all preferred strategies of remedy over splenectomy. If the aneurysm is saccular, a vascular stapler could additionally be utilized across its base, though this will go away behind a part of the aneurysmal wall as a source for recurrence. Laparoscopic ultrasonography is helpful to localize the aneurysm and establish its tributaries. Such exact localization minimizes dissection near the pancreas and pancreatitis. The basic triad of stomach pain, hemobilia, and obstructive jaundice, reflecting a ruptured intrahepatic aneurysm, is seen in less than one-third of cases. Current management suggestions embody therapy of all symptomatic aneurysms and, in good operative candidates, all true aneurysms >2 cm or with fast development. Surgical publicity is obtained via both a proper subcostal or upper midline laparotomy incision. More distal lesions may be discovered within the portal triad working in the hepatoduodenal ligament. Exposure may be particularly challenging when treating aneurysms associated with vital inflammation. Saccular aneurysms involving lower than half of the vessel circumference could be resected and the ensuing arteriotomy closed either primarily or with a vein patch. Arterial reconstruction can often be carried out with an interposition graft between the remaining proximal and distal parts of the hepatic artery. The ends of the graft in addition to the artery must be spatulated so as not to cause a narrowing within the lumen at the anastomosis. Alternatively, a bypass graft with influx from the aorta or right renal artery to the remaining distal hepatic artery may additionally be carried out. Intrahepatic aneurysms are mostly treated by endovascular means with coil or particle embolization. The commonest anatomic predistribution includes the move disturbances associated with the common celiacomesenteric trunk, seen in zero. The celiac trunk and supraceliac aorta are finest exposed by performing a left medial visceral rotation or by publicity through the lesser sac.
Buy chloroquine nowA more trendy functional check involves exercising the affected person and demonstrating the "second wind" phenomenon. Management Acute severe rhabdomyolysis should be treated with prompt fluid (normal saline) alternative and renal support as required. Patients should be given recommendation on secure types of exercise and tips on how to obtain the "second wind" phenomenon. Patients sometimes develop myalgia/muscle stiffness/rhabdomyolysis after extra extended train, for instance, playing sport or marathon operating. Prolonged fasting, chilly publicity, intercurrent infection and even emotional stress are other well-recognized precipitants. Symptoms may last for a quantity of weeks following an acute assault, however sufferers could also be completely asymptomatic, with regular muscle energy on examination, between attacks. Encephalopathy Acute encephalopathy is a rapid decrease in acutely aware degree (over hours or days), not secondary to ictal or syncopal episodes. Patients may present with a change in personality (often agitated/aggressive), confusion, lethargy, drowsiness or coma. Neurological findings may embrace secondary seizures, irregular posturing, abnormal gait and poor coordination. A metabolic trigger is a risk in any grownup who presents with encephalopathy: consideration ought to be given to hyperammonemia, hypoglycemia, and metabolic acidosis. A historical past of previous unexplained episodes of confusion or agitation, or uncommon dietary habits such as protein aversion, ought to be sought from family and friends. By far the most typical cause of hyperammonemia in adults is hepatic disease, often related to portosystemic shunting. Once this has been excluded as a trigger, then consideration must be given to different causes, and defects of the urea cycle are essential among these (4). Hyperammonemia also can occur in fatty acid oxidation issues or natural acidemias (5), but in these situations first presentation often happens in infancy/childhood rather than in maturity. Valproate is an natural acid and may inhibit the urea cycle, precipitating hyperammonemia. Valproate therapy may be the trigger for metabolic decompensation in individuals with a beforehand unknown urea cycle defect. In the emergency setting, the vast majority of circumstances of metabolic acidosis are because of lactic acidosis secondary to hypoxia and tissue hypoperfusion, or diabetic ketoacidosis. Most often these shall be drugs or poisons, but if the event has been triggered by metabolic stress somewhat than toxin ingestion, an underlying organic acidemia is a chance. Long-term administration would require enter from a specialist middle to guarantee acceptable dietary advice (including supplementation of vitamins and minerals in those on a restricted diet) and titration of oral medicines to ensure optimum metabolic management. In organic acidemias, therapy can additionally be primarily based on prevention of catabolism, restriction of protein and removing of poisonous metabolites (6). Intravenous carnitine is used to conjugate poisonous fatty acid derivatives and metronidazole can reduce propionate manufacturing by intestine microbiota. These exams should be discussed along with your native specialist laboratory to guarantee the right sample conditions and transport. The aims of therapy are to reduce catabolism and ammonia manufacturing and to decrease plasma ammonia before cerebral edema develops. Intravenous arginine and ammonia scavengers (sodium Case Study A 28-year-old girl attended her local emergency division three times over the course of a week. The week earlier than she had had what appeared to be a viral sickness with "flu-like" signs, headache, and ear pain. She then started to behave oddly, staring blankly and not responding to questions. Her companion brought her to the hospital and a analysis of ear infection was made. It was felt her symptoms were secondary to an an infection and she was once more discharged. She had a better degree from her residence country and was learning English and dealing as a waitress. She had had surgery as a baby Endocrine and Metabolic Emergencies in Inherited Metabolic Diseases for cleft palate. This operation was uneventful, but after further surgery on her ear she developed impaired steadiness and vomiting within the postoperative interval, accompanied by strange habits: she was found showering in her garments. Initial investigations included regular blood rely, renal and liver operate tests, thyroid operate, and C-reactive protein. As viral encephalitis had been excluded, other causes of encephalopathy were considered. The concurrence of gastrointestinal symptoms and behavioral/psychiatric features raise the potential of acute porphyria or hyperammonemia. Urine natural acids, taken through the acute part of her illness, got here again per week later exhibiting an orotate/creatinine ratio of 31 mol/mmol (0�5), according to a prognosis of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. This is an X-linked dysfunction, so all male sufferers presenting in adrenal disaster should be asked a few household history of leukodystrophy and/or spastic paraparesis. Stroke Stroke or stroke-like occasions can happen in a selection of metabolic issues, together with Fabry disease, homocystinuria, mitochondrial issues, natural acidemias, and urea cycle defects. In some of these conditions, stroke is as a result of of cerebrovascular events, but in others cerebral infarction is secondary to energy deficiency and/or toxic effects of metabolites, so-called metabolic stroke. Fabry Disease Fabry disease is an X-linked disorder attributable to deficiency of the enzyme alphagalactosidaseA (-Gal A). Lachmann related to pyrexia, angiokeratomas in the bathing trunk space and cornea verticillata are attribute. Renal, cardiac, and cerebrovascular diseases are the most important sources of morbidity and mortality. Male patients typically have more severe signs at an earlier age then heterozygote females, who may remain asymptomatic. Nonetheless, the prevalence of Fabry illness in populations of patients presenting with stroke is low. Diagnosis If there are scientific features or a household history suggestive of Fabry, analysis in males is made by measuring -Gal A enzyme activity in plasma, isolated leukocytes, and/or cultured cells. Management Enzyme alternative therapy is out there and an oral chaperone remedy has recently been licensed in Europe. Symptomatic parasthesiae, renal and cardiac disease are treated as per standard guidelines. Classical clinical manifestations contain the attention, skeleton, central nervous and vascular methods, but the age of onset, severity, and sort of medical involvement can range broadly amongst affected people. In a large research of the natural historical past of 629 people with homocystinuria, simply over a third had suffered a thromboembolic occasion, with cerebrovascular accidents accounting for a 3rd of these (10). The likelihood of getting any thromboembolic event was about 50% by age 29 years, and was a big causative or contributory factor to death in practically 80% of the sixty four patients who had died. Pregnancy is a particular danger factor for cerebral thrombosis in girls with homocystinuria.
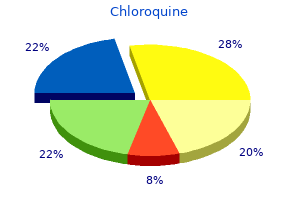
Purchase cheap chloroquine onlineIn the long term, extra intensive managment of hyperglycemia could scale back additional myocardial infarctions and strokes, and a few particular person remedies may offer explicit benefits. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Prospective randomised study of intensive insulin therapy on long-term survival after acute myocardial infarction in sufferers with diabetes mellitus. Effect of rosiglitazone on myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. Long-term results of metformin on metabolism and microvascular and macrovascular disease in sufferers with sort 2 diabetes. Effects of metformin versus glipizide on cardiovascular outcomes in sufferers with kind 2 diabetes and coronary artery illness. The impact of pioglitazone on recurrent myocardial infarction in 2,455 patients with type 2 diabetes and former myocardial infarction. Saxagliptin and cardiovascular outcomes in sufferers with kind 2 diabetes mellitus. Effect of Management of Diabetes and/or Hyperglycemia in Acute Coronary Syndrome, Acute Stroke, and Acute Heart Failure sitagliptin on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. Effect of intensive diabetes administration on macrovascular events and risk components within the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Effects of pioglitazone in patients with kind 2 diabetes with and with out earlier stroke. Intensive glycemic management has no impression on the risk of heart failure in kind 2 diabetic patients: proof from a 37,229 patient meta-analysis. Association between sitagliptin use and heart failure hospitalization and related outcomes in sort 2 diabetes mellitus: secondary analysis of a randomized medical trial. Acute Diabetic Foot Glenn Matfin Key Points r Foot problems are among the many commonest and feared complication of diabetes mellitus and at the second are the leading diabetesrelated cause of hospitalization, as well as the main explanation for decrease extremity amputations. Diabetic foot problems have a major monetary impact on healthcare systems, increased in-hospital occupancy and size of stay. All persons with diabetes must be screened for threat of foot issues on a minimum of an annual basis: these with threat components require regular podiatry, patient schooling, and instruction in foot self-care the commonest foot complication is skin ulceration, which is normally secondary to diabetes-related peripheral neuropathy (with loss of protecting sensation) and fewer usually associated to peripheral arterial illness, or both. Most of the surplus morbidity and mortality in these sufferers is expounded to heart problems, and emphasizes the need for good diabetes and cardiovascular threat administration. Most foot ulcers should heal if pressure is faraway from the ulcer web site, the arterial circulation is enough, and infection is managed and treated aggressively. Glenn Matfin r the r general principles for in-hospital foot care in folks with diabetes ought to apply to all admissions, not just these with lively foot illness. The toes of individuals with diabetes ought to be inspected every day during the hospital keep and r new problems that are recognized ought to be managed along side the specialist diabetic foot multidisciplinary staff (or equivalent). Appropriate ongoing training of sufferers and healthcare suppliers concerning the importance of prevention and early recognition of diabetes-related foot problems is critical. Introduction Foot issues are among the commonest and feared complication of diabetes mellitus and are now the leading diabetesrelated reason for hospitalization, in addition to the most important reason for decrease extremity amputations. Diabetic foot issues have a significant financial influence on healthcare systems, with increased in-hospital occupancy and length of stay. The lifetime danger of a person with diabetes growing a foot ulcer is 15�25%, though when additional data are thought-about, between 19% and 34% of individuals with diabetes are likely to be affected (4). Infection is best defined as an invasion and multiplication of microorganisms in host tissues that induce a host inflammatory response, normally adopted by tissue destruction. Infection is usually the ultimate precipitating reason for decrease extremity amputations, the chance of which is 23 occasions greater in persons with diabetes than these with out. Over 85% of decrease extremity amputations in persons with diabetes are preceded by foot ulceration (4). The common principles for in-hospital foot care in individuals with diabetes ought to apply to all admissions, not just those with energetic foot illness. It is necessary to take the shoes, socks, and any dressings off the ft to inspect any underlying wounds, making certain that stress areas are healthy. The feet should be inspected every day in the course of the hospital stay and new issues Acute Diabetic Foot which are recognized should be managed ideally at the aspect of the specialist diabetic foot multidisciplinary staff (which ought to embrace well timed access to podiatrist, diabetologist, vascular and orthopedic surgeon, interventional radiologist, tissue viability nurse, infectious disease/microbiologist, diabetes educator/nurse, and orthotist). Worryingly, 1 in 75 sufferers with diabetes developed a new foot lesion during their in-hospital keep (1. When the infection is persistent, or the affected person has been treated with antimicrobials, aerobic gram-negative organisms often be part of the gram-positives. In instances of severe an infection, empirical antibiotic remedy should be administrated parenterally and ought to be broad-spectrum, covering staphylococci, streptococci and commonly reported gram-negatives. Obligate anaerobes are nearly always a half of a mixed an infection and normally one accompanied by gangrene or ischemia. These patients should be referred emergently to a multidisciplinary diabetic foot group (or equivalent) (10). Initial empiric antibiotic selections could have to be tailored primarily based on the outcomes of culture and sensitivity exams. If the affected person is clinically responding, it will not be necessary to cowl all isolates, especially comparatively avirulent organisms. Antibiotic therapy want solely be given till decision of the infectious signs and signs and never prolonged until the complete healing of the wound. Surgical Interventions Surgical procedures are needed for most extreme infections and for many average and a few delicate infections. These could vary from minor bedside debridement or incision and drainage, carried out at the bedside or within the clinic, to major operative procedures. Patients with proof of limb ischemia should bear vascular analysis; if blood move is insufficient (based on transcutaneous oxygen measurements or other appropriate studies), consider early revascularization by open surgery or an endovascular approach (19). Tissue sample by curettage or scraping with a scalpel blade after debridement of the wound and washing with water is preferable to superficial swab. Typically 2�4 weeks for non bone infections Treat osteomyelitis for a minimal of six weeks As above suspected osteomyelitis: X-ray and repeat 2�4 weeks. If bone biopsy is required, this ought to be an operative or radiological procedure beneath local anaesthesia. Lytic bone on X-ray is prone to represent osteomyelitis particularly if there are progressive changes over time with no other reason for lytic osteoarthropathy. Suspect osteomyelitis in any ulcer with visible bone or bone that can be easily probed and if an ulcer fails to heal after 6 weeks of acceptable wound care and offloading. Uncomplicated plantar ulcers ought to heal in 6�8 weeks with enough offloading (20). The exterior shock wave system mechanically stimulates the wound and should be used with normal ulcer care.
References - Yeow W-C, Pemberton R, Barker A: Flexible ureterorenoscopy and laser lithotripsy in children, J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg 14:63-65, 2009.
- Dellon AL, Hashemi SS, Tollstrupt TH: Orchialgia after orchiectomy, Plast Reconstr Surg 134:998en999e, 2014.
- Weizer AZ, Joshi D, Daignault S, et al: Performance status is a predictor of overall survival of elderly patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer, J Urol 177:1287n1293, 2007.
- Blandy JP, Tresidder GC: Meatoplasty, Br J Urol 39:633, 1967.
- Gurung PM, Attar KH, Abdul-Rahman A, et al: Long-term outcomes of augmentation ileocystoplasty in patients with spinal cord injury: a minimum of 10 years of follow-up, BJU Int 109:1236n1242, 2012.
|
|