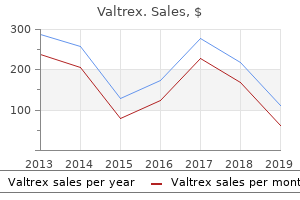
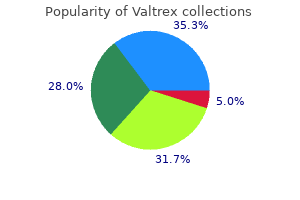
"Cheap 1000 mg valtrex, antiviral treatment and cancer control."By: Noreen A Hynes, M.D., M.P.H. - Director, Geographic Medicine Center of the Division of Infectious Diseases
- Associate Professor of Medicine
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/0010761/noreen-hynes
Discount 1000mg valtrex with visaThree examples of how these cooperative interactions facilitate blood cell responses are described next. Many integrins are constitutively current on the cell surface however interact poorly with their ligands. Cell activation by numerous agonists induces conformational adjustments in integrins in order that they effectively recognize their ligands. The cytoplasmic domains of integrins can exert each optimistic and adverse influences on binding affinity. Binding of particular cytoplasmic proteins to these domains may propagate structural adjustments to the extracellular ligand-binding areas of the integrins. Three-dimensional buildings of integrins suggest that the integrin "headpiece" that accommodates the ligand-binding web site faces down towards the membrane in the inactive conformation and quickly extends upward in a "switchblade"-like opening movement on activation. Low-affinity ligand binding could stabilize some lively conformations of integrins, perhaps explaining why integrins on unactivated cells will sometimes bind to immobilized, multivalent adhesive proteins but to not the same proteins in resolution. Platelet activation, in turn, increases the affinity of platelet integrins for collagen and fibronectin, which stabilizes adhesion. The consequences of such signaling include changes in affinity or avidity of other adhesion receptors for his or her ligands, shape change, secretion, proliferation, synthesis of cytokines and other molecules, and migration. In some cases, binding of a monovalent adhesive ligand to a receptor could induce a signal. More commonly, signaling requires cross-linking of a number of receptors through interactions with multivalent ligands in matrix or on apposing cells. Binding of the same ligand to totally different integrins can mediate completely different responses in the identical cell. Furthermore, ligand binding to the same integrin expressed in different cells can lead to totally different signals. These information recommend that very specific interactions happen between ligand-occupied integrins and intracellular components. At sites of tissue harm or infection, neutrophils first roll on the endothelial cells in postcapillary venules. These transient adhesive interactions are mediated by activation-induced transcription-dependent expression of E- or P-selectin on the endothelial cell floor. Chapter12 CellAdhesion 133 unstimulated platelets to house to the positioning of vascular damage and then be activated by domestically generated mediators. Neutrophil rolling on the endothelium occurs beneath shear forces, just as platelets adhere to subendothelial matrix under shear forces, though the shear circulate in postcapillary venules is lower than that in arterioles. Rolling requires a stability between the formation of selectin�ligand bonds at the forefront of the cell and the dissociation of bonds at the trailing edge of the cell. Whereas shear forces have an result on the lifetimes of selectin�ligand bonds, lower forces prolong lifetimes (catch bonds) and higher forces shorten lifetimes (slip bonds). Catch bonds assist clarify why a minimal shear drive is required to assist leukocyte rolling, significantly through L-selectin. Instead, locally generated inflammatory mediators induce expression of E- or P-selectin on the endothelial cell floor. The requirement for activation of endothelial cells somewhat than leukocytes allows the latter to adhere to vessels solely at the site of vessel inflammation. These alerts cooperate with others directed by engagement of selectin ligands and promote very slow rolling of neutrophils on the surface of activated endothelium. Adhesion of leukocytes to the endothelium disrupts cytoskeletal tethers to the endothelial cadherins; this disruption results in dissociation of homotypical cadherin interactions that usually forestall passage of leukocytes. These bonds strengthen adhesion, and the costimulatory molecules transduce sustained and additional alerts to the T cell that trigger elevated gene transcription, proliferation, and cytokine secretion. Not proven is the redistribution of those adhesion molecules into completely different areas of the contact zone as adhesion strengthens. Additional signals result from binding of 1 integrins on the T cell to adhesive proteins in the extracellular matrix. These molecular contacts are all of low affinity but are highly specific as a outcome of they first require particular antigen presentation to the appropriate T cell. The first principle of those three responses is that the initial adhesive event, though comparatively limited, is very particular. Thus, platelets bind to uncovered subendothelial matrix in injured vessels, neutrophils bind to hyperadhesive endothelium near the location of an infection, and T cells bind to cells presenting particular antigen in secondary lymph nodes. The second principle is that subsequent activation events strengthen cell adhesion and result in further responses similar to secretion, fibrin formation, cellular migration, and release of cytotoxic mediators or cell activation and proliferation. Activation typically outcomes from cooperative signaling by soluble agonists and by binding of ligands to adhesion receptors. Costimulation by multiple indicators can amplify and supply specificity to mobile responses by mechanisms not always possible for particular person mediators. The means of reversing cell adhesion, though much less properly understood, is equally important for the management of cell conduct. Some molecules such as the selectins can be proteolytically cleaved or internalized. Genetic deficiencies in the leukocyte 2 integrins (as in leukocyte adhesion deficiency-1) are related to frequent severe bacterial infections and a failure of neutrophils to enter the infected tissues. Similar symptoms are seen in patients with a congenital defect in fucose metabolism that prevents synthesis of the carbohydrate ligands for selectins (leukocyte adhesion deficiency-2). A recently recognized set of patients has each hemorrhagic signs and life-threatening infections (leukocyte adhesion deficiency-3). The molecular mechanism is attributable to mutations in an intracellular protein kindlin-3, which binds to 1, 2, and three integrin cytoplasmic tails upon cell activation. For example, erythrocytes from patients with sickle cell anemia adhere to one another, to leukocytes, and to the endothelium, contributing to vasoocclusive crises. These adhesive occasions may reflect, partially, the expression of integrins and selectin ligands not usually discovered on mature erythrocytes. Inappropriate adhesion and activation of platelets on uncovered atherosclerotic plaques could contribute to thrombosis and acute ischemic coronary artery syndromes. Dysregulated expression of selectins on the endothelium of ischemic blood vessels throughout myocardial infarction or shock might contribute to neutrophilmediated tissue necrosis after reperfusion of the vessel. Mediators released whereas the neutrophils are adherent within the reperfused vessels may activate integrin operate, strengthening adhesion and producing additional indicators that release harmful oxygen radicals and proteases within the vasculature. Finally, malignant cells appear to use molecules usually used for adhesion of blood cells to promote metastatic spread via interactions with platelets, endothelial cells, and extravascular matrix. These examples underscore the significance of proper regulation of adhesion molecule expression within the physiology of blood cells. Accomplishing these tasks requires continuous motion of billions of motile immune cells that roam all through the physique along distinct nonrandom site visitors routes from one tissue to another utilizing blood and lymphatic vessels as avenues for fast entry. Migratory pathways characteristic for distinct immune cell subsets are integral components of their practical make-up determined within the process of cell differentiation and activation.
Diseases - Granulomatous rosacea
- Exudative retinopathy familial, autosomal dominant
- Pfeiffer Singer Zschiesche syndrome
- Sialuria, French type
- Microcephaly microcornea syndrome Seemanova type
- Spellacy gibbs watts syndrome
- Holmes Benacerraf syndrome
- Trichinosis
Cheap 1000 mg valtrexType I hypersensitivity (immediate-reaction hypersensitivity) is an inborn capability to overproduce IgE in response to an allergen. Matching donor and recipient tissues and utilizing immunosuppressive medication can reduce a tissue rejection response. Autoimmune disorders may result from a previous viral an infection, defective T cell growth, or response to a nonself antigen that resembles a self antigen. Trace the general pathway of lymph from the interstitial areas to the bloodstream. Tissue fluid types as a result of filtration from blood capillaries exceeding, whereas lymph types as a result of increasing in the tissue fluid. Discuss how a low-grade fever of quick period may be a pure response to infection. List three kinds of T cells, and describe the perform of each in the immune response. Match the major kinds of antibodies with their perform and/or where each is found. IgA (1) associated with allergic reactions (2) important in B cell activation, on B. IgE (4) effective towards micro organism, viruses, and toxins in plasma and tissue fluids (5) present in exocrine secretions, including breast milk 26. Why is injecting a substance into the skin similar to injecting it into the lymphatic system How can the removal of enlarged lymph nodes for microscopic examination aid in diagnosing certain illnesses Some dad and mom keep their preschoolers away from different children to prevent them from catching diseases. Why does vaccination present long-lasting protection in opposition to a disease, while gamma globulin (IgG) provides only short-term protection Why is a transplant consisting of fetal tissue much less more probably to provoke an immune rejection response than tissue from an adult Connect Integrated Activity Can you differentiate between an allergic response, an autoimmune response, and an immune deficiency Anatomy & Physiology Revealed Go extra in depth into the human body by exploring the lymphatic organs. Not the entire cells in an grownup physique are human; about half are microorganisms traditionally referred to as microflora, but extra recently called the microbiome. The "human oral microbiome," for example, includes greater than 600 species that can reside within the mouth. The different finish of the digestive tract houses the "distal intestine microbiome," which includes more than 6,800 species. Our "intestine" residents also synthesize nutritional vitamins and amino acids, and break down sure toxins and drugs. We can use data of our gut microbiome to improve health, as a outcome of illness can alter the bacterial populations within us. An strategy referred to as probiotics provides micro organism to foods to forestall certain infections. For instance, certain Lactobacillus strains added to yogurt help defend in opposition to Salmonella foodborne an infection. As public stool banks are screening donations and offering them to physicians, scientific trials are evaluating tips on how to greatest deliver the fabric: fresh or frozen, and by enema, nasogastric tube, or capsule. Analysis of the bacterial genomes within the stool of handled sufferers indicates that fecal transplant treats diarrhea. The structure of its wall, the method it strikes meals, and its innervation are comparable all through its length. Structure of the Wall the wall of the alimentary canal consists of four distinct layers which are developed to totally different degrees from region to area. Although the four-layered construction persists throughout the alimentary canal, sure regions are specialized for particular functions. Mucosa (mu-kosah), or mucous membrane (mukus membrn): Surface epithelium, underlying connective tissue, and a small amount of smooth muscle form Digestion (di-jestyun) is the mechanical and chemical breakdown of meals and the absorption of the ensuing vitamins by cells. Mechanical digestion breaks large pieces of meals into smaller ones with out altering their chemical composition. The digestive system consists of the alimentary canal (ali-mentar-e kah-nal), extending from the mouth to the anus, and several accessory organs that secrete into the canal substances which might be utilized in digestion. The alimentary canal (from starting to end) consists of the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, abdomen, small gut, giant gut, rectum, and anus. The accessory organs embody the salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas (fig. Overall, the digestive system is a tube, open at both ends, that has an inside surface area of 186 sq. meters. These include companies, resorts, food service corporations, neighborhood businesses, colleges, senior facilities, health-care amenities, prisons, and eating places. Registered dietitians also can have careers in research or educating different health-care professionals, or open their own businesses. In some areas the mucosa is folded, with tiny projections that reach into the passageway, or lumen (lumen), of the digestive tube. The mucosa protects the tissues beneath it, secretes into the lumen, and absorbs substances from the food regimen. Submucosa (submu-kosah): the submucosa incorporates appreciable unfastened connective tissue as properly as glands, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves. Muscularis: this layer, which provides movements of the tube, consists of two layers of easy muscle tissue. Coordinated contractions of each muscle layers trigger movement of substances via the tube. Serosa (sro-sah), or serous layer (serus laer): the layer of epithelium on the outside of the tube with the connective tissue beneath it compose the serous layer. Mixing occurs when easy muscle in small segments of the tube contracts rhythmically (fig. For example, when the stomach is full, waves of muscular contractions transfer along its partitions from one end to the other. In the small gut, a process known as segmentation aids mixing by alternately contracting and stress-free the graceful muscle in nonadjacent segments of the organ. As the peristaltic wave moves alongside the tube, it pushes the tubular contents ahead of it (fig. Describe how several varieties of tooth are adapted for various features, and record the components of a tooth. The mouth receives food and begins digestion by mechanically breaking up stable particles into smaller items and mixing them with saliva. Mucous membrane covers the tongue, and a membranous fold called the lingual frenulum (linggwahl frenu-lum) connects the midline of the tongue to the floor of the mouth.
Order valtrex 500 mg otcWhile the placenta is forming from the chorion, a second membrane, known as the amnion (amne-on), develops around the embryo (fig. Fluid, referred to as amniotic fluid, fills the house between the amnion and the embryonic disc. The amniotic fluid allows the embryo to grow freely with out compression by surrounding tissues. The margins of the amnion fold in such a means as to enclose the embryo in the amnion and amniotic fluid. The amnion envelops the tissues on the underside of the embryo, notably the connecting stalk, by which the embryo is attached to the chorion and the creating placenta. The umbilical wire originates at the umbilicus of the embryo and inserts into the center of the placenta (fig. Chorion Umbilical twine Allantois Amnion It suspends the embryo within the amniotic cavity. The umbilical cord contains three blood vessels-two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein-that transport blood between the embryo and the placenta (fig. In addition to the chorion and amnion, two different extraembryonic membranes type during development-the yolk sac and the allantois (see fig. It varieties blood cells in the early levels of improvement and offers rise to the cells that later become sex cells. The allantois (ah-lanto-is) varieties in the course of the third week as a tube extending from the early yolk sac into the connecting stalk of the embryo. The disc-shaped area where the chorion still contacts the uterine wall develops into the placenta. The embryonic portion of the placenta is composed of the chorion and its villi; the maternal portion consists of the world of the uterine wall (decidua basalis) where the villi connect (fig. The absolutely formed placenta is a reddish-brown disc about 22 centimeters in diameter and 2. A thin placental membrane separates embryonic blood within the capillary of a chorionic villus from maternal blood in a lacuna. This membrane consists of the epithelium of the chorionic villus and the endothelium of the capillary contained in the villus. Umbilical arteries transport oxygen-poor blood away from the embryo, and the umbilical vein returns oxygenrich blood to the embryo. Various substances also cross the placental membrane by lively transport and pinocytosis. Mesodermal cells kind all forms of muscle tissue, bone tissue, bone marrow, blood, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, inside reproductive organs, kidneys, and the epithelial linings of the physique cavities. Endodermal cells produce the epithelial linings of the digestive tract, respiratory tract, urinary bladder, and urethra. During the fourth week of development, a part of the flat embryonic disc becomes cylindrical to kind the neural tube, which can become the central nervous system. By the end of the second week, the inner cell mass has flattened into an embryonic disc with two distinct layers-an outer ectoderm and an inside endoderm. A brief time later the ectoderm and endoderm fold, and a third layer of cells, the mesoderm, types between them. All organs kind from these three cell layers, referred to as the first germ layers (primar-e jerm laerz), in a course of referred to as organogenesis (see fig. The twoweek embryo, with its three main germ layers, is recognized as a gastrula (gastroo-lah). However, because the embryo and the encompassing chorion enlarge, only villi that contact the endometrium endure. The others degenerate, and the areas of the chorion where they have been connected turn out to be clean. The region of the chorion still in touch with the uterine wall is restricted to the placenta. If a pregnant woman repeatedly ingests an addictive substance that crosses the placenta, her new child could suffer from withdrawal symptoms when quantities of the chemical the fetus was accustomed to receiving all of a sudden plummet after birth. Newborn addiction can happen with certain medicine of abuse, similar to heroin, and with certain prescription drugs used to treat nervousness. By the start of the eighth week, the embryo is about 25 millimeters long and weighs lower than a gram (fig. It is probably the most important interval of development, when all the important external and inside physique parts form. Factors that cause congenital malformations by affecting an embryo are referred to as teratogens. Such brokers include medication, viruses, radiation, and even massive amounts of otherwise healthful substances, similar to fat-soluble vitamins. The particular nature of a delivery defect reflects the constructions creating when the injury occurs. The time during prenatal improvement when a genetic mutation or exposure to a teratogen can alter a particular structure known as its important interval. In distinction, the mind is delicate all through development and even into childhood, so its crucial period may be very long. This is why many start defects are related to the brain, resulting in mental impairment. In the seventh month, the pores and skin turns into smoother as fat is deposited in subcutaneous tissues. In the final trimester, fetal mind cells rapidly kind networks, as organs specialize and grow. In the male, the testes descend from areas close to the developing kidneys, through the inguinal canal, and into the scrotum. The digestive and respiratory techniques mature last, which is why premature infants could have issue digesting milk and respiration. Approximately 266 days after a single sperm fertilized an egg, a child is ready to be born. The pores and skin has lost its downy hair, but sebum and dead epidermal cells still coat it. The fetus is usually positioned the different means up, with its head towards the cervix, as shown in figure 20. Fetal Stage the fetal stage begins at the finish of the eighth week of development and lasts until birth. During this period, the fetus (fetus) grows quickly and body proportions change significantly. At the start of the fetal stage, the pinnacle is disproportionately giant and the decrease limbs are brief. By the twelfth week the exterior reproductive organs are distinguishable as male or female.

Cheap valtrex 500mg amexBecause the lipid bilayer membrane basically has the bodily properties of a soap bubble, it would rapidly be emulsified within the circulation. Strength and order are offered to the lipid bilayer by the hexagonal arrays of the extremely helical protein spectrin, which types a latticework underlying the membrane. These protein�protein interactions appear to be crucial for holding the latticework collectively in what has been described because the "horizontal" dimension that allows resistance to shear stress. The involvement of intermediate-length actin fibers and the variability of binding affinities by phosphorylation state appear to provide some flexibility and pliability at these factors of interaction. Strength in the "vertical" dimension is provided by extra molecules or additional binding features of the same molecule, whereby the latticework is attached to the lipid bilayer. For probably the most part, the physiologically necessary attachments appear to be indirect. Linkage is mediated via the interaction of the adaptor proteins, such as ankyrin and protein 4. These proteins traverse and are embedded in the lipid bilayer, providing a agency anchor. A attainable additional stabilizing function for the Rh protein complicated has been advised. These seem to end in half from the buildup of small amounts of oxygen harm to membrane structures. The altered areas are sensed by the reticuloendothelial cells during passage of the erythrocytes via the liver and spleen. Progressive lack of membrane floor by the use of the pitting phenomenon ought to ultimately trigger the growing older erythrocyte to assume a more rigid spherical form. A sphere is inevitably far much less distensible and much much less able to passing through small apertures than a disk, especially within the sluggish and tortuous circulation of the spleen. The finish product would be spherocytes incapable of traversing the splenic vascular mattress and escaping engulfment by the reticuloendothelial cell. Higher order aggregates appear to be recognized by an endogenous isoantibody possessed by all people. The aggregates would then be certain by antibody and be eliminated by the reticuloendothelial cells as antigen�antibody complexes, utilizing the same means used by reticuloendothelial cells to acknowledge any immune advanced. All three of the proposed mechanisms are interrelated by their inception with oxidative injury. Increasing phosphatidyl serine publicity and lowered aminophospholipid translocase activity throughout aging would possibly induce oxidative injury to the cell. Chief among these is the technology of oblique or unconjugated bilirubin, the byproduct of heme catabolism occurring inside the reticuloendothelial cells. These portions are enormous-almost 2 kilos of Hb are current in the physique of a fairly sized human at any given time. Otherwise, the caloric and biosynthetic assets needed to substitute every day losses of Hb can be prohibitive. The mobile content of blood influences its viscosity; in particular, the hemodynamics are adversely compromised by the presence of too many circulating erythrocytes as a result of blood viscosity correlates especially with hematocrit. This concentration is close to the solubility limit of Hb in physiologic options. HemoglobinStructure the Hb tetramer consists of two pairs of unlike globin polypeptide chains, each associated with a heme group. Normal Hb has two -globin and two non�-globin chains; the interplay of these chains is answerable for the quaternary structure of the Hb molecule and normal oxygen transport. Functionally, the second exon of each globin gene encodes the main component of the heme-binding pocket, and the and non- contacts are regulated by the third exon. The behavior of Hb is set by its primary construction, the covalent linking of amino acids to kind the polypeptide globin. The higher order constructions of Hb rely upon the sequence of amino acid residues that make up the globin chain. Globin folds into a tertiary construction such that polar or charged amino acids are positioned on the exterior of the molecule and the heme ring resides in a hydrophobic niche between the E and F helices. There are eight helical segments, A by way of H, separated by quick stretches from which the -helix is absent. These nonhelical segments allow folding of the polypeptide on itself and are sometimes dictated by the presence of prolyl residues, that are usually unable to participate within the formation of -helices. These residues happen at parts of the molecule which might be critical for its stability and performance, similar to heme binding residues, hydrophobic amino acids of the interior of the molecule, and sure subunit contacts at the 1�2 interface. The introduction of prolyl residues into -helical segments by mutation results in interruption of the -helix and instability of the resulting Hb molecule. This folding pattern locations polar residues exteriorly and provides a hydrophobic niche for the heme ring between the E and F helices. Numerous noncovalent bonds are formed between the heme and surrounding amino acid residues of globin. An iron atom within the heart of the porphyrin ring forms an necessary bond with the F8 or proximal histidine and thru the linked oxygen with the E7 or distal histidine residue. Folding of globin and affiliation of chains into dimers and tetramers was as quickly as thought to happen spontaneously. The motion of particular person globin chains, as properly as the movement of globin chains relative to one another throughout oxygenation and deoxygenation, gives Hb its distinctive usefulness as a respiratory protein. HemoglobinFunction Evolution has honed the Hb tetramer into a molecule ideally suited for its tasks. Because human Hb should behave differently than that of altitude dwelling species or species inhabiting hypoxic locales, many various variants of the same fundamental molecular design have advanced. Because of the exigencies of molecular evolution, we discover in the genome of all animals, together with humans, makes an attempt by nature to propagate a variety of completely different globin genes. The % saturation of hemoglobin (Hb) with oxygen at totally different oxygen tensions is depicted by the pink sigmoidal curve. Heterotopic modifiers of Hb function can shift the curve leftward by increasing or rightward by reducing its oxygen affinity. All of those, however, share the properties of highly reversible oxygen binding and excessive solubility in cytoplasm. We know extra in regards to the operate of Hb than about virtually any other protein, and the data of this mechanism offers a wonderful and intellectually satisfying end result to a long time of study by many investigators. The sigmoidal shape of this curve is a results of interplay among the many subunits of Hb. Communication inside the tetramer known as heme�heme interplay or cooperativity. Myoglobin, a heme-containing protein with nearly the identical tertiary construction as globin, exists in muscle as a monomer.
White Squill (Squill). Valtrex. - What is Squill?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Squill.
- Abnormal heart rhythm and other heart problems, fluid retention, bronchitis, asthma, whooping cough, thinning mucus, or inducing vomiting.
- How does Squill work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96725
Cheap valtrex 500mg fast deliveryFor this reason, folks can donate elements of their livers to folks in liver failure, if the tissues of donor and recipient are appropriate. Storage Blood filtering Detoxification Secretion Composition of Bile Bile (bl) is a yellowish-green liquid constantly secreted from hepatic cells. In addition to water, bile contains bile salts, bile pigments (bilirubin and biliverdin), ldl cholesterol, and electrolytes. Of these, bile salts are the most abundant and are the one bile elements which have a digestive function. Bile pigments are breakdown products of hemoglobin from pink blood cells and are normally secreted within the bile (see section 12. Bile duct Bile ductule Bile canaliculi Jaundice, a yellowing of the pores and skin and mucous membranes due to accumulation of bile pigment, has a number of causes. In hemolytic jaundice purple blood cells are destroyed too rapidly, as happens with an incompatible blood transfusion or a blood an infection. About half 1,000,000 individuals develop hepatitis in the United States every year, and 6,000 die of the illness. Acute hepatitis might at first resemble the flu, producing mild headache, low fever, fatigue, lack of urge for food, nausea and vomiting, and generally stiff joints. By the top of the primary week, extra distinctive symptoms come up: a rash, pain within the higher proper quadrant of the abdomen, dark and foamy urine, and pale feces. The pores and skin and sclera of the eyes turn yellow due to accumulating bile pigments (jaundice). Great fatigue may proceed for two or three weeks, after which progressively the individual begins to really feel higher. In a uncommon acute type referred to as fulminant hepatitis, symptoms are sudden and severe, along with altered conduct and character. Only rarely does hepatitis result from alcoholism, autoimmunity, or the usage of sure medicine. The viral sorts are categorised as follows: Hepatitis A spreads by contact with food or objects contaminated with virus-containing feces, including diapers. V Hepatitis B spreads by contact with virus-containing body fluids, such as blood, saliva, or semen. It could additionally be transmitted by blood transfusions, hypodermic needles, or sexual exercise. This virus is primarily transmitted in blood- by sharing razors or needles, from pregnant lady to fetus, or via blood transfusions or use of blood merchandise. As many as 60% of individuals infected with the hepatitis C virus suffer persistent signs. Hepatitis D an infection happens in individuals already infected with the hepatitis B virus. Hepatitis G an infection is rare however accounts for a significant proportion of instances of fulminant hepatitis. In folks with wholesome immune systems, the virus produces symptoms so delicate that they will not be noticed. Treatment with a quantity of new medication, used in mixture to block viral activity in several methods, is now simpler, quicker, and with fewer unwanted effects, than older drugs corresponding to interferon and ribavirin. The gallbladder is lined with epithelial cells and has a strong layer of easy muscle in its wall. The gallbladder shops bile between meals, reabsorbs water to concentrate bile, and contracts to release bile into the small intestine. It connects to the cystic duct (sistik dukt), which in turn joins the frequent hepatic duct (figs. The widespread hepatic duct and cystic duct join to type the bile duct (common bile duct). It leads to the duodenum the place the hepatopancreatic sphincter guards its exit (figs. Because this sphincter usually remains contracted, bile collects in the bile duct. Cholesterol in bile might precipitate underneath sure circumstances and type crystals referred to as gallstones (fig. Gallstones within the bile duct might block bile circulate into the small gut and cause appreciable ache. A surgical process called a cholecystectomy can take away the gallbladder when gallstones are obstructive. The surgical procedure can typically be carried out with a laparoscope (small, lit probe) on an outpatient foundation. The intestinal mucosa releases this hormone in response to proteins and fat in the small gut. Bile salts have an result on fat globules (clumped molecules of fats) very related to a soap or detergent would have an effect on them. That is, bile salts break fats globules into smaller droplets which might be more soluble in water. This action, known as emulsification (e-muls-f-kashun), greatly will increase the entire floor space of the fatty substance. Fat-splitting enzymes (lipases) can then digest the fat molecules extra successfully. Bile salts also improve absorption of fatty acids, ldl cholesterol, and the fat-soluble nutritional vitamins A, D, E, and K. The small intestine is a tubular organ that extends from the pyloric sphincter to the start of the massive gut. With its many loops and coils, the small intestine fills a lot of the belly cavity (see fig. The small intestine receives chyme from the stomach and secretions from the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder. It completes digestion of the nutrients in chyme, absorbs the products of digestion, and transports the residue to the massive gut. It follows a C-shaped path as it passes anterior to the right kidney and the upper three lumbar vertebrae. The the rest of the small intestine is cell and lies free within the peritoneal cavity. The proximal two-fifths of this portion of the small intestine is the jejunum (j-joonum), and the remainder is the ileum (ile-um). A double-layered fold of peritoneal membrane known as mesentery (mesen-tere) suspends the jejunum and ileum from the posterior abdominal wall (figs. The mesentery supports the blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels that offer the intestinal wall. A filmy, double fold of peritoneal membrane called the larger omentum drapes like an apron from the abdomen over the transverse colon and the folds of the small gut (fig. If the wall of the alimentary canal turns into contaminated, cells from the omentum could adhere to the infected region, serving to to wall off the realm. Structure of the Small Intestinal Wall the inside surface of the small intestine all through its size appears velvety due to many tiny projections of mucous membrane known as intestinal villi (vili) (figs.
Buy cheap valtrex 1000mg lineWhen used to estimate physique iron shops, all of the available indirect measures are influenced not only by total physique iron stores but additionally by the results of acute or continual modifications in plasma hepcidin (see field on Control of Iron Homeostasis by Hepcidin and Ferroportin). Measurement of the plasma ferritin concentration supplies probably the most useful indirect estimate of body iron stores. Characteristic values for some clinically available indicators of iron status are shown. In iron overload, the diagonal traces are supposed to illustrate will increase in extra storage iron from the conventional vary of 1 g or less to as much as 40 to 50 g. Under physiologic circumstances, hepatic hepcidin production coordinates physique iron provide with iron want. Decrements in plasma hepcidin concentration increase the quantity of ferroportin, producing an increase in plasma iron concentration as a consequence of enhanced delivery from macrophages, mobilization of storage iron from hepatocytes, and elevated dietary iron absorption from enterocytes. In addition to the effects of physique iron shops, hepcidin manufacturing is stimulated by infection, irritation, mobile damage, or malignancy and inhibited by hypoxemia or increased erythropoietic demand. Although hepcidin is the central regulator of iron homeostasis, hypoxia inducible issue 2 and the iron regulatory protein/iron-responsive component system modulate intestinal iron absorption (see Chapter 35). In the absence of complicating factors, plasma ferritin concentrations lower with depletion of storage iron and enhance with storage iron accumulation (see field on Plasma Ferritin Concentrations). Measurement of the plasma transferrin receptor focus is useful in detecting tissue iron deficiency. A majority of plasma transferrin receptors are derived from the erythroid marrow, and their focus is determined primarily by erythroid marrow exercise. While decreased levels of circulating soluble transferrin receptor are found in patients with erythroid hypoplasia (aplastic anemia, persistent renal failure), increased levels are present in sufferers with erythroid hyperplasia (thalassemia major, sickle cell anemia, anemia with ineffective erythropoiesis, persistent hemolytic anemia). The plasma transferrin receptor focus reflects the whole body mass of tissue receptor; thus, within the absence of different conditions causing erythroid hyperplasia, a rise in plasma transferrin receptor concentration provides a sensitive, quantitative measure of tissue iron deficiency. In specific, measurement of plasma transferrin receptor focus may assist differentiate between the anemia of iron deficiency and the anemia related to continual inflammatory problems. Although the plasma ferritin focus may be disproportionately elevated in relation to iron shops in sufferers with irritation or liver illness, the plasma transferrin receptor focus seems to be much less affected by these problems and to present a more dependable laboratory indicator of iron deficiency. The erythrocyte zinc protoporphyrin supplies an indicator of iron supply to erythroid precursors. Levels are also increased in many sideroblastic anemias and particularly with persistent lead or other heavy metal poisoning. Iron shops are normally assessed on the aspirate as opposed to the biopsy because the decalcification process required for processing the biopsy leaches out the iron and might lead to a false conclusion of absent stores. This can show iron stores (blue reaction product), particularly within the cytoplasm of macrophages and histiocytes (A�B). Iron can be seen within the cytoplasm of some nucleated purple blood cells (tiny blue cytoplasmic specks), which would allow these cells to be designated sideroblasts (C). These are in contrast to red blood cell precursors with irregular iron accumulation across the nucleus, or "ring sideroblasts" (C, inset). Hemosiderin containing iron could be seen on the Wright-stained aspirate smears as a darkish brown or black pigment in histiocytes (D), but generally an iron stain is required to affirm the presence of iron stores. When parenteral iron therapy is run, the marrow aspirate can typically present coarse iron deposits, regularly in lengthy streaks (E). PlasmaFerritinConcentrations Plasma ferritin concentrations are helpful within the detection of both iron deficiency and iron overload. Plasma ferritin concentrations decline with storage iron depletion; a plasma ferritin focus less than 12 mg/L is just about diagnostic of absence of iron shops. The solely recognized circumstances which will decrease the plasma ferritin concentration independently of a lower in iron stores are hypothyroidism and ascorbate deficiency, but these conditions solely hardly ever trigger problems in clinical interpretation. Increased plasma ferritin concentrations may indicate elevated storage iron, but numerous disorders may enhance the plasma ferritin stage independently of the physique iron store. Thus fever, acute infections, rheumatoid arthritis, and different continual inflammatory problems elevate the plasma ferritin concentration. Both acute and continual injury to the liver, in addition to to different ferritin-rich tissues, might increase plasma ferritin focus through an inflammatory course of or by releasing tissue ferritins from broken parenchymal cells. After iron shops are exhausted, lack of iron limits the production of hemoglobin and different metabolically energetic compounds that require iron as a constituent or cofactor. A number of mechanisms coordinate the speed of erythropoiesis with iron availability (see Chapter 35). Without iron supplementation, most women will become iron-deficient throughout pregnancy. Overall, the iron requirement for an individual contains not solely the iron needed to replenish physiologic losses and meet the calls for of progress and pregnancy but also any additional quantities wanted to exchange pathologic losses. Physiologic iron losses typically are restricted to the small quantities of iron contained within the urine, bile, and sweat; shedding of iron-containing cells from the gut, urinary tract, and pores and skin; occult gastrointestinal blood loss; and, in ladies, uterine losses throughout menstruation and pregnancy. The median total iron loss with being pregnant is roughly 600 mg, or virtually 2 mg/d over the 280 days of gestation. The commonest pathologic cause of elevated iron requirements leading to iron deficiency is blood loss. Within the gastrointestinal tract, any hemorrhagic lesion may result in blood loss, and the accountable lesion could additionally be asymptomatic. Iron deficiency often is the first signal of an occult gastrointestinal malignancy or different unrecognized conditions such as coeliac illness, or autoimmune, atrophic, or Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Chronic ingestion of medicine similar to alcohol, salicylates, steroids, and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory medicine might trigger or contribute to blood loss. Worldwide, essentially the most frequent cause of gastrointestinal blood loss is hookworm an infection,6 however other helminthic infections, similar to Schistosoma mansoni and Schistosoma japonicum, and extreme Trichuris trichiura an infection additionally may be responsible. In girls of childbearing age, genitourinary blood loss with menstruation adds to iron requirements. Uncommonly, respiratory tract blood loss ensuing from chronic recurrent hemoptysis of any cause produces iron deficiency. In infants, youngsters, and adolescents, the necessity for iron for development could exceed the provision available from food regimen and stores. With rapid development through the first 12 months of life, the body weights of term infants usually triple, and iron necessities are at excessive levels. Iron requirements decline as progress slows during the second year of life and into childhood however rise again with the adolescent development spurt. Without supplemental iron, pregnancy entails the net loss of the equivalent of 1200 to 1500 mL of blood. In some instances, an insufficient provide of iron may contribute to the event of iron deficiency. For older kids, males, and postmenopausal girls, the restricted availability of dietary iron is almost by no means the only rationalization for iron deficiency, and other causes, particularly blood loss, must be considered. Impaired absorption of iron in itself infrequently is the only source of iron deficiency. Nonetheless, in sufferers in whom analysis fails to establish a source of blood loss, in addition to in those unresponsive to oral iron remedy, celiac disease, autoimmune, atrophic, or H.
1000 mg valtrex free shippingKidney failure to excrete acids Excessive production of acidic ketones as in diabetes mellitus Accumulation of nonrespiratory acids Alkalosis the symptoms of alkalosis embrace light-headedness, agitation, dizziness, and tingling sensations. In extreme instances, impulses could also be triggered spontaneously on motor neurons, and muscles may respond with tetanic contractions (see section eight. The two main types of alkalosis are respiratory alkalosis and metabolic alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis results from extreme lack of carbon dioxide and consequent lack of carbonic acid. Respiratory alkalosis develops as a outcome of hyperventilation (described in part sixteen. Hyperventilation could happen in periods of hysteria or may accompany fever or poisoning from salicylates, corresponding to aspirin. At excessive altitudes, hyperventilation could additionally be a response to low oxygen partial strain. Musicians might hyperventilate to provide the big quantity of air needed to play sustained passages on wind instruments. In each case, fast, deep respiratory depletes carbon dioxide, and the pH of physique fluids increases. Chemical buffers, corresponding to hemoglobin, that release hydrogen ions resist the increase in pH. The decrease ranges of carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions stimulate the respiratory middle to a lesser degree. At the identical time, the kidneys lower their secretion of hydrogen ions, and the urine becomes alkaline as bases are excreted. Metabolic alkalosis can also develop because of ingesting too much antacid, such as sodium bicarbonate to relieve the signs of indigestion. Compensation for metabolic alkalosis includes a decrease in the respiration price and depth, which in turn ends in an increased concentration of carbon dioxide within the blood. What is the distinction between a respiratory acid-base disturbance and a metabolic acid-base disturbance The intracellular fluid compartment contains the fluids and electrolytes cell membranes enclose. The extracellular fluid compartment contains all of the fluids and electrolytes outside cell membranes. Extracellular fluids have excessive concentrations of sodium, chloride, calcium, and bicarbonate ions, with less potassium, magnesium, phosphate, and sulfate ions. Intracellular fluid accommodates high concentrations of potassium, magnesium, and phosphate ions. It additionally has a greater concentration of sulfate ions and lesser concentrations of sodium, chloride, calcium, and bicarbonate ions than does extracellular fluid. Water is lost in urine, feces, and sweat, and by evaporation from the pores and skin and lungs. The distal convoluted tubules of the nephrons and the accumulating ducts are the effectors of the control system that regulate water output. The electrolytes of best importance to cellular capabilities in body fluids dissociate to launch ions of sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, sulfate, phosphate, bicarbonate, and hydrogen. These ions are obtained in foods and beverages or as by-products of metabolic processes. Concentrations of sodium, potassium, and calcium ions in physique fluids are significantly necessary. The mechanisms that management positively charged ions secondarily regulate negatively charged ions. Chemical buffer systems (1) Buffer systems convert strong acids into weaker acids or strong bases into weaker bases. Respiratory acidosis outcomes from increased ranges of carbon dioxide and carbonic acid. Metabolic acidosis outcomes from accumulation of non-respiratory acids or lack of bases. Prepare a list of sources of regular water gain and loss to illustrate how the input of water equals the output of water. List five sources of hydrogen ions in body fluids, and name an acid that originates from every supply. Explain how the respiratory system and the kidneys perform within the regulation of acid-base stability. After eating an undercooked hamburger, a twenty-five-yearold male developed diarrhea as a result of infection with a strain of Escherichia coli that produces a shigatoxin. Connect Integrated Activity Can you expect the effects of several types of fluid and electrolyte imbalances Intrigued, the young woman submitted a health history, had a checkup, and a month later acquired a call. For two weeks Sherrie injected herself in the thigh with a drug that acts like gonadotropin-releasing hormone, suppressing release of an egg from an ovary (ovulation). This second drug mimicked folliclestimulating hormone, and it triggered a number of ovarian follicles, the buildings that contain creating eggs, to mature. Finally, injections of luteinizing hormone introduced the eggs close to being released. Then, at a health-care facility, Sherrie received pain treatment and lightweight sedation. A needle inserted through her vaginal wall retrieved a dozen mature eggs from the surface of her ovary. When a sperm and an oocyte join at fertilization, the quantity of genetic information held in forty six chromosomes is restored. An extra perform of the reproductive techniques is the secretion of hormones important to the event and upkeep of reproductive organs and the regulation of reproductive functions. She or he can do bodily exams, prescribe medicines, and order and interpret medical tests to present a analysis. A nurse-midwife is a registered nurse who has a graduate diploma in midwifery from an accredited program, and has American Midwifery Certification Board approval. Because infants born at residence face higher dangers of issues, patients are fastidiously screened and plans are made so that a doctor can arrive or the affected person can be transported to a hospital within minutes. Risk factors that rule out a home delivery include evidence of twins or breech presentation (buttocks first), earlier cesarean part supply, diabetes, high blood pressure, and being previous the due date. But emergencies, such because the placenta detaching or the umbilical twine previous the baby, are unpredictable. Describe the structure and function(s) of every a half of the male reproductive system. The major sex organs (gonads) of the male reproductive system are the two testes, in which sperm cells develop and the male sex hormones are synthesized. The accent intercourse organs (secondary sex organs) of the male reproductive system are the interior and external reproductive organs (fig. The paired testes are the first sex organs, and the other reproductive structures, both internal and external, are accessory sex organs. A lobule accommodates one to four extremely coiled, convoluted seminiferous tubules (sem-nifer-us tooblz), each approximately 70 centimeters lengthy uncoiled.

Order valtrex 1000 mg with visaHowever, not like the motor pathways of the somatic nervous system, which usually embody a single neuron between the mind or spinal twine and a skeletal muscle, these of the autonomic system embody two neurons (fig. The cell physique of the first neuron, the preganglionic neuron, is positioned within the mind or spinal wire. From there, they lead outward in cranial or sacral nerves to terminal ganglia positioned close to or in various viscera. The relatively short postganglionic fibers continue from the ganglia to particular muscular tissues or glands in these viscera. Decreasing sympathetic stimulation relaxes the muscular walls of the vessels, which will increase the diameter of the vessels (dilates). Control of Autonomic Activity Autonomic Neurotransmitters the preganglionic fibers of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions all secrete acetylcholine and are due to this fact called cholinergic fibers (kolin-erjik fiberz). The completely different postganglionic neurotransmitters cause the completely different results that the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions have on their effector organs. Most organs obtain innervation from each sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions, normally with opposing actions. For example, parasympathetic activity increases activity of the digestive system, whereas sympathetic exercise decreases it. Similarly, sympathetic stimulation will increase heart rate, however parasympathetic action slows coronary heart price. For instance, the sympathetic division regulates the diameter of most blood vessels, which lack parasympathetic innervation. For example, management facilities in the medulla oblongata for cardiac, vasomotor, and respiratory actions obtain sensory impulses from viscera on vagus nerve fibers and use autonomic nerve pathways to stimulate motor responses in the heart, blood vessels, and lungs. Similarly, the hypothalamus helps regulate body temperature, starvation, thirst, and water and electrolyte balance by influencing autonomic pathways. Specific facilities in the brain, including the limbic system and the cerebral cortex, can affect the autonomic nervous system. A acquainted example involving the parasympathetic division is salivating at the anticipation of eating. An instance involving the sympathetic division is the rise in heart fee and blood strain when one turns into agitated or upset. How do the divisions of the autonomic nervous system regulate visceral actions Two preparations of parasympathetic postganglionic fibers are found in both the cranial and sacral portions. Similarly, sympathetic paravertebral and collateral ganglia are present in both the thoracic and lumbar portions. Skeletal System Bones protect the brain and spinal cord and assist maintain plasma calcium, which is important to neuron perform. Muscular System the nervous system controls movement and processes details about the position of body parts. Respiratory System the nervous system alters respiratory exercise to control oxygen ranges and blood pH. Urinary System the nervous system plays a role in urine manufacturing and elimination. Cardiovascular System the nervous system helps control blood circulate and blood pressure. Reproductive System the nervous system plays a task in egg and sperm formation, sexual pleasure, childbirth, and nursing. Nervous tissue includes neurons, which are the structural and useful models of the nervous system, and neuroglia. Organs of the nervous system are divided into the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. Sensory functions contain sensory receptors that detect inner and external changes. Integrative features collect sensory data and make decisions that motor functions carry out. Neuroglia within the central nervous system embody microglial cells, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and ependymal cells. A single axon arises from the cell physique and could additionally be enclosed in a myelin sheath and a neurilemma. Neurons are categorised functionally as sensory neurons, interneurons, or motor neurons. A presynaptic neuron conducts an impulse into a synapse; a postsynaptic neuron or other cell responds. A neurotransmitter is released when an impulse reaches the synaptic knob on the end of an axon. A neurotransmitter reaching the postsynaptic neuron membrane is either excitatory or inhibitory. Channels in cell membranes that enable passage of some ions however not others set up variations in the concentrations of particular ions inside and outdoors a neuron. A excessive focus of sodium ions is exterior a cell membrane, and a excessive concentration of potassium ions is inside. In a resting cell, more constructive ions go away than enter, so the skin of the cell membrane develops a positive cost, whereas the within develops a adverse charge. At threshold, sodium channels open, and sodium ions diffuse inward, depolarizing the membrane. At almost the identical time, potassium channels open, and potassium ions diffuse outward, repolarizing the membrane. Many motion potentials can happen in a neuron without disrupting the ion concentrations. Unmyelinated axons conduct motion potentials uninterrupted along their entire lengths. Axons with bigger diameters conduct impulses faster than those with smaller diameters. An motion potential occurs in an all-or-none method whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity is applied to an axon. The web effect of synaptic knobs communicating with a neuron is determined by which knobs are activated from second to moment. Neurotransmitters embody acetylcholine, biogenic amines, amino acids, and peptides. A synaptic knob releases neurotransmitters when an action potential will increase membrane permeability to calcium ions. After being released, neurotransmitters are decomposed or faraway from synaptic clefts. A neuron is facilitated when repeated impulse conduction will increase its release of neurotransmitter in response to a single impulse. Convergence enables impulses from totally different sources to have an additive impact on a neuron. Impulses occurring on a neuron of a neuronal pool usually synapse with several other neurons.
Purchase 1000mg valtrex otcAs the cells near the tip of their three-month life span, however, they turn out to be more fragile. The cells could sustain damage merely passing through capillaries, particularly these in active muscular tissues that should withstand sturdy forces. Macrophages phagocytize and destroy broken pink blood cells, primarily within the liver and spleen. Hemoglobin molecules liberated from red blood cells break down into their 4 part polypeptide "globin" chains, every surrounding a heme group. The blood might transport the iron, mixed with a protein, to the hematopoietic tissue in red bone marrow to be reused in synthesizing new hemoglobin. About 80% of the iron is saved in the liver within the form of an iron-protein advanced. Biliverdin ultimately is converted to an orange-yellow pigment known as of either of those nutritional vitamins. The body reuses a lot of the iron released by the decomposition of hemoglobin from broken purple blood cells. A deficiency of pink blood cells or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin they include ends in a situation referred to as anemia. This reduces the oxygen-carrying capability of the blood, and the affected individual might appear pale and lack energy. A pregnant girl could have a traditional variety of pink blood cells, but she develops a relative anemia because her plasma quantity increases as a result of fluid retention. Biliverdin and bilirubin are secreted in the bile as bile pigments (see part 15. In jaundice (icterus), accumulation of bilirubin turns the pores and skin and eyes yellowish. This condition may be the result of immature liver cells that ineffectively secrete bilirubin into the bile. Treatment includes publicity to fluorescent mild, which breaks down bilirubin in the tissues, and feedings that promote bowel actions. In hospital nurseries, babies being handled for physiological jaundice lie under "bili lights," clad only in diapers and protective goggles. The therapeutic impact of fluorescent light was found in the Fifties, when an astute nurse famous that jaundiced infants improved after sun publicity, besides within the areas their diapers coated. Erythropoietin stimulates target cells in the pink bone marrow to increase the production of pink blood cells, which carry oxygen to tissues. White Blood Cells White blood cells, also known as leukocytes (luko-stz), shield towards illness. Interleukins are numbered, whereas most colonystimulating factors are named for the cell population they stimulate. For instance, leukocytes with granular cytoplasm are referred to as granulocytes, whereas these without cytoplasmic granules are known as agranulocytes (see fig. Neutrophils (nutro-filz) have fine cytoplasmic granules that seem mild purple in impartial stain. The nucleus of an older neutrophil is lobed and consists of two to five sections (segments, so these cells are generally called segs) related by skinny strands of chromatin (fig. Neutrophils account for 54% to 62% of the leukocytes in a typical blood sample from an grownup. Eosinophils (eo-sino-filz) include coarse, uniformly sized cytoplasmic granules that seem deep red in acid stain (fig. Lymphocytes are formed within the organs of the lymphatic system, in addition to in the red bone marrow (see section 14. Monocytes (mono-stz), the most important blood cells, are two to thrice larger in diameter than purple blood cells (fig. They normally make up 3% to 9% of the leukocytes in a blood sample and reside for several weeks and even months. A typical lymphocyte has a large, round nucleus surrounded by a thin rim of cytoplasm (fig. Which hormones are needed for differentiation of white blood cells from hematopoietic stem cells within the pink bone marrow List the five forms of white blood cells, and explain how they differ from each other. Functions of White Blood Cells White blood cells shield towards infection in numerous ways. Some leukocytes phagocytize bacterial cells within the physique, and others produce proteins (antibodies) that destroy or disable overseas particles. Leukocytes can squeeze between the cells that kind the partitions of the smallest blood vessels. This motion, known as diapedesis (diah-pe-desis), permits the white blood cells to depart the circulation (fig. Once outdoors the blood, they transfer via interstitial spaces utilizing a type of selfpropulsion referred to as amoeboid motion. Monocytes leave the bloodstream and specialize further to turn out to be macrophages that phagocytize bacteria, lifeless cells, and different particles in the tissues. Both of these phagocytes comprise many lysosomes, that are organelles crammed with digestive enzymes that break down organic molecules in captured micro organism, vitamins, and wornout organelles. Neutrophils and monocytes might turn into so engorged with digestive merchandise and bacterial toxins that they die. Eosinophils also help control inflammation and allergic reactions by eradicating biochemicals related to these reactions. Basophils migrate to broken tissues, the place they release heparin, which inhibits blood clotting, and histamine, which promotes inflammation. Lymphocytes called B cells, for instance, produce antibodies that assault specific foreign substances that enter the body. White blood cell counts are of clinical curiosity as a result of their number may change in response to irregular situations. A whole variety of white blood cells exceeding 10,500 per microliter of blood constitutes leukocytosis, indicating acute infection, corresponding to appendicitis. The white blood cell depend is greatly elevated in leukemia, as Clinical Application 12. A complete white blood cell rely beneath 3,500 per microliter of blood is called leukopenia. This take a look at is beneficial as a result of the relative proportions of white blood cells may change in particular diseases. The number of neutrophils, for example, usually will increase during bacterial infections. Eosinophils may become more plentiful during certain parasitic infections and allergic reactions.
References - Satoh K, Motomura M, Suzu H, et al: Neurogenic bladder in Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome and its response to 3,4-diaminopyridine, J Neurol Sci 183(1):1n4, 2001.
- Shiraishi K, Naito K: Effects of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, a marker of oxidative stress, on spermatogenesis and expression of p53 protein in male infertility, J Urol 178:1012n1017, 2007.
- Bush WH, Swanson DP: Acute reactions to intravascular contrast media: types, risk factors, recognition, and specific treatment, AJR Am J Roentgenol 157:1153-1161, 1991.
|
|