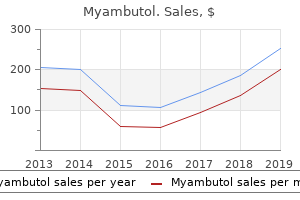
"Cheap myambutol 400 mg on-line, antibiotics for sinus infection and pneumonia."By: J. Matthew Brennan, MD - Associate Professor of Medicine
- Member in the Duke Clinical Research Institute
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/j-matthew-brennan-md
Purchase myambutol 600mg lineThese findings can enhance surgical planning and reduce the chance of intraoperative problems. Delayed imaging of the ureters within the urographic phase is beneficial for detecting congenital ureteral variants or an aberrant course. The indications for imaging in the postoperative interval embrace the detection of vascular problems corresponding to renal artery stenosis, renal vein thrombosis, or ureteral stenosis. High-grade, proximal atherosclerotic stenosis of the proper renal artery in a 74-year-old man. Classic string-of-beads check in each renal arteries caused by alternating dilatations and stenoses in a 22-yearold lady. Fluid collections corresponding to urinomas, hematomas, lymphoceles, and abscesses present intermediate hyperintensity in T2 W sequences. Contrast pooling within the medulla shall be present in sufferers with acute tubular necrosis. This contrasts with malignant retroperitoneal fibrosis, which is hyperintense in fat-suppressed T2 W sequences and reveals only slight gadolinium enhancement. While benign retroperitoneal fibrosis reveals bilateral encasement and medialization of the ureters, malignant retroperitoneal fibrosis usually impacts the ureter on one facet solely. Morphological imaging standards are insufficient for optimistic differentiation between malignant and benign retroperitoneal fibrosis. They are characterised mainly by their enlargement (para-aortic and paracaval nodes > 15 mm, retrocrural nodes > 6 mm). Liposarcoma and lipoma: the signal traits of liposarcomas depend primarily on the proportion of fatty tissue and on tumor grade. Lipomas, on the opposite hand, are homogeneously hyperintense in T1 W sequences with out fats saturation and show variable hyperintensity in T2 W sequences. A key differentiating criterion at imaging is the nodular enhancement that occurs in dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Other potentialities are neuroectodermal tumors such as paragangliomas, extra-adrenal pheochromocytoma, and germ cell tumors (teratoma). The relaxation have an affiliation with lymphomas, aneurysms, and retroperitoneal hematomas. The right ureter has been stented with a double-J catheter to relieve hydronephrosis. Besides nonspecific stomach complaints, which can include ache and digestive issues, paresthesias may also occur relying on the tumor location. Examples are complete or incomplete duplication of the ureters, duplex ureter, and bifid ureter, with an associated duplex kidney on the affected facet. Differentiation of a bifid ureter from a duplex ureter could additionally be tough if the bifid ureters unite at a low degree. The physiologic constriction of the ureter at the stage where it crosses over the iliac vessels is often misinterpreted as irregular narrowing. In the classification of bladder masses, primary plenty arising from the bladder itself must be differentiated from secondary processes that infiltrate the bladder from adjacent organs or metastasize to the bladder from more distant websites. Lung cancer, breast most cancers, and melanoma are the tumors that mostly metastasize to the bladder. The most typical primary bladder tumor is urothelial carcinoma, which arises from the 421 Downloaded by: University of Michigan. Squamous cell cancers are sometimes triggered by an infection with schistosomes (Schistosoma haematobium). These lesions are indistinguishable from primary urothelial carcinoma by imaging alone. Bladder carcinomas are isoechoic to the bladder wall and normally current an undulating surface. If gross hematuria is present, the vascularity of the lesion could be assessed with shade Doppler ultrasound to differentiate between a tumor and possible blood clot. The healthy bladder wall has intermediate sign depth in T1 W sequences and low signal depth in T2 W sequences. More superior phases of bladder carcinoma present with nonspecific B signs (night sweats and weight loss), hydronephrosis, flank and bone pain, and in some instances a palpable decrease belly mass. Rhabdomyosarcoma: this tumor presents comparable symptoms which will include dysuria and pollakiuria, lower belly ache, hematuria, and possible urinary retention, relying on tumor measurement. A potential mass will not be definable until the bladder lumen is sufficiently distended. Urothelial carcinoma most commonly happens within the bladder, however 5% of those tumors arise in the ureter or pelvicalyceal system. Parenchymal enhancement of the best kidney is decreased relative to the left kidney. The enlarged renal pelvis (asterisk) exhibits no enhance in density, whereas contrast medium fills the left renal pelvis (arrow). A urothelial carcinoma of the renal pelvis appears sonographically as a hypoechoic, polypous intraluminal mass that fills the renal pelvis and mainly types a pelvic "forged. Necrosis or calcifications appear as hypoechoic or hyperechoic areas, respectively, giving the mass a heterogeneous look. The tumor shows intermediate sign depth in T2 W sequences and enhances in postcontrast sequences. The medical manifestations of upper urinary tract tumors might embody flank pain, renal or ureteral colic, and hematuria. Because lesions are multifocal in 25 to 30% of circumstances, all parts of the urinary tract must be evaluated. Urinary stones (calculi) are formed within the renal collecting system and should then transfer from the kidney into the ureter. Homogeneously enhancing mass within the renal pelvis (a, b) has obliterated normal hilar constructions (a). Stones within the center third of the ureter or at the junction of the center and lower thirds are related to colicky ache within the again and lateral lower abdomen. With stones at a lower level, the pain radiates to the inguinal and genital areas. Vessel wall�associated calcifications or phleboliths within the lesser pelvis or calcified pelvic lymph nodes could additionally be misinterpreted as ureteral stones. If the persistent portion is positioned just previous the origin of the urachus from the bladder, a bladder diverticulum is fashioned, which can result in lithiasis or recurrent episodes of cystitis. Persistence of the urachus postnatally leads to a patent channel between the bladder and umbilicus, which presents clinically with umbilical drainage. Diagnostic efficacy of contrastenhanced ultrasonography in strong renal parenchymal lesions with most diameters of 5 cm.
Buy discount myambutol 800mg onlineThe scapulae are hypoplastic and the midthoracic vertebrae small with unossified pedicles. The femora had been straight in this patient and campomelic dysplasia was identified clinically at the age of 1. The gene was identified by way of a candidate gene method primarily based on recognition of phenotypic similarities with the spontaneous mouse mutant, droopy ear, that was recognized to be caused by Tbx15 deficiency. However, the craniofacial dysmorphism of Cousin dysplasia differs from campomelic dysplasia, which is characterized by Robin sequence. Defective spinal ossification; missing or markedly delayed ossification of vertebral our bodies. There is a substantial danger of neurologic disease with delayed motor improvement, spasticity, finger contractures, and even tetraplegia. Around age 2�3 years, the extremely abnormal ossification pattern in the hand is kind of pathognomonic. Achondrogenesis sort 2 is tough to differentiate prenatally, as the major discovering in both is extreme deficiency in vertebral physique ossification. The rib cage has a sloping or tented look secondary to vertebral malformations. There is desynchronization of the bone age with a delay in carpal ossification while the phalangeal epiphyses are giant and rounded. There are additionally multiple pseudoepiphyses involving essentially all the tubular bones of the hands. Broad brow with distinguished parietal and frontal bones separated by metopic groove; broad sutures in childhood; delayed closure of the anterior fontanel; small face with extensively spaced eyes; small maxilla. Clavicular hypoplasia ranging from skin dimple to sloping shoulders and strange mobility of the shoulders; narrow chest; small or winged scapulae. Persistence of deciduous tooth; late eruption and impaction of supernumerary everlasting teeth. Less incessantly, funnel chest, spinal deformities, slim pelvis, abnormal gait, hypermobility of joints, muscular hypotonia, quick distal phalanges, hypoplastic nails. Hypoplastic clavicles and underossified cranium have been detected by ultrasound at 14 weeks gestation. Retarded ossification of the skull with partial lack of ossification of the calvaria and cranium base, delayed closure of sutures, and fontanels with multiple Wormian bones; underpneumatization; platybasia; enlarged or deformed foramen magnum because of median cleft of occipital bone. Partial, less frequently total, absence of the clavicles, mostly bilateral, more commonly within the lateral and center thirds; or presence of two fragments of the clavicles with failure to fuse; small, frequently deformed scapulae. Absent ossification of pubic bones in early infancy, underdevelopment of the pubic and inferior portion of ischial bones in childhood; extensive pubic symphysis, sacroiliac junction, and Y-cartilage of the acetabulum; hypoplasia and anterior rotation of the iliac wings; valgus deformity or, much less regularly, varus deformity of the femoral necks. Numerous, massive pseudoepiphyses of metacarpal and metatarsal bones; dysplasia of the middle phalanx of the fifth finger, less regularly also of the second finger; shortening of the distal phalanges; retarded ossification of the carpal and tarsal bones and the vertebral bodies; slim shafts of the tubular bones. Germ-line mosaicism explains pedigrees suggestive of autosomal recessive inheritance. Complications embrace scoliosis, genua valga, habitual dislocation of the shoulder and/or radial head, hip dislocation, and dental anomalies including supernumerary enamel, failure of exfoliation of the first dentition, and malocclusion. Atlantoaxial dislocation induced myelopathy has been observed in a single affected person (Kobayashi et al. Congenital pseudarthrosis or fracture of the clavicle is mostly unilateral and never associated with other skeletal modifications. Yunis-Varon syndrome is characterized by the aplasia/ hypoplasia of thumbs and toes. Smallness of the distal phalanges outcomes from osteolysis and not from hypoplasia as in cleidocranial dysplasia. Cole-Carpenter syndrome: Hypoplastic clavicles are associated with craniosynostosis and elevated bone fragility. Verloes/Lesenfants (2001) described a single patient with hypoplastic clavicles, severe myopia, single central incisor, and peripheral neuropathy. Serum alkaline phosphatase could additionally be low and urinary phosphoethanolamine excretion elevated, elevating the query of hypophosphatasia. Scheuthauer G (1871) Kombination rudimiment�rer Schl�sselbeine mit Anomalien des Sch�dels bei erwachsenen Menschen. Verloes A, Lesenfants S (2001) New syndrome: clavicle hypoplasia, facial dysmorphism, extreme myopia, single central incisor and peripheral neuropathy. Note large calvaria, frontal bossing with melancholy of the midfrontal space due to delayed closure of the metopic suture; ocular hypertelorism; irregular mobility of the shoulder and funnel-shaped chest in Patient 1. Ossification of the calvaria is deficient and multiple Wormian bones are seen in the occipital and parietal bones. The anterior fontanel and coronal and lambdoid sutures are wide open, and numerous Wormian bones are seen in the latter. In both sufferers, father and daughter, the transverse diameter of the calvaria is increased and the facial bones are underdeveloped, giving the pinnacle the looks of an inverted pear. In the grownup affected person, a wide open anterior fontanel and metopic suture and uneven bossing of the left hemicranium are present. In C, lack of osseous fusion of the lateral and the medial two-thirds of the clavicles is shown. Mild hypoplasia of the lateral ends of the slender straight clavicles is current in D. The abnormal look of the scapulae in B, C, and D results in half from their irregular anteversion and partly from true dysplasia. In addition to defective ossification of the pubic and ischial bones, the sacroiliac junction is broad. The bodies of the ilia are almost as wide as the ala, resulting in a characteristic lack of iliac flare. The transverse diameter of the iliac wings is decreased, the sacrosciatic notches are narrow, and the pelvic inlet is small. The femoral heads are incompletely lined by the acetabular roofs, and the femoral necks are quick, broad, and in valgus place. The distal phalanges of the hands and foot are hypoplastic, especially the ungual tufts. In C the middle phalanx of the index finger is short with a coneshaped epiphysis; the metaphysis of the distal phalanx of the middle finger is delta-shaped; the physis of the distal phalanx of the fifth finger is broad. Craniofacial anomalies: large fontanels; bitemporal indentation; sparse scalp hair, eyebrows, and eyelashes; brief, upturned palpebral fissures; proptosis; anteverted nostrils; quick philtrum; low-set ears; thin lips with labiogingival retraction; micrognathia. Developmental delay with central nervous system malformations, including arhinencephaly, callosal agenesis, and vermian dysplasia. Other abnormalities: untimely loss of deciduous teeth; absent nipple; sclerocornea and cataract; congenital coronary heart defect. Hypoplastic or absent distal phalanges of the second to fifth fingers and toes; hypoplasia of the center and proximal phalanges might happen. Variable pelvic dysplasia: slim or flared ilia; supraacetabular notches; horizontal acetabula or hip dislocation with steep acetabula. Most affected individuals succumb from respiratory problems and present with failure to thrive within the neonatal interval or in early infancy. Most surviving kids show severe developmental delay, however some present virtually regular intellectual performance.
Cheap myambutol 400 mg on-lineAs the laser strikes throughout the plate, the trapped electrons in the phosphor are released from the electron traps and migrate back to their resting location. The higher the publicity to the plate, the larger the depth of the light emitted from the plate through the studying process. The light launched is collected by an optical system that sends the sunshine to a tool liable for changing the sunshine into an analog electrical signal. However, when digital expertise is used, consideration to these details becomes extra essential because of the following components. The software processes the complete x-ray eld as a knowledge set; any surprising attenuation of the beam could additionally be included within the calculations for brightness, contrast, and publicity indicator. Failure to align the half to the receptor accurately and collimate the publicity eld correctly could result in poor image quality on initial image display. The technologist should examine the exposure indicator to confirm that the exposure elements used had been in the right range for optimum high quality with the bottom radiation dose to the affected person. The objective of these two supplies is to present a supply of electrons to the thin- lm transistor that collects the electrons in the course of the exposure. Amorphous silicon requires the usage of a scintillator, which produces light when struck by x-ray photons. One different benefit is the potential to produce diagnostic radiographs with lower ranges of exposure. Speci cally, the division needs to set up publicity eld sizes; projections per receptor, if permitted; and uniform processing parameters on all technologist workstations. A frequent example of the physique half, the orientation is l applied to scientific practice relates to chest radiography. Standards have been developed to be certain that all producers and kinds of equipment are able to talk and transmit images and information effectively. Current standards (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) embrace d and H 7 (health level 7). Although standards might not always provide for an instantaneous performance between units, they do allow for decision of connectivity problems. Physicians may view these radiologic pictures from a private laptop at just about any location, including their properties. T eleradiography is the electronic transmission of diagnostic photographs from one location to another for functions of interpretation or consultation. The development of pc purposes in radiologic expertise has led to new profession paths for radiologic technologists. Bit depth: Representative of the number of shades of gray that could be demonstrated by every pixel. Bit depth is determined by the manufacturer and is based on the imaging procedures for which the gear is required. Brightness: the intensity of sunshine that represents the person pixels in the picture on the monitor. Contrast decision: the ability of an imaging system to distinguish between similar tissues. Digital archive: A digital storage and picture management system; in essence, a sophisticated computer system for storage of patient les and images. Edge enhancem ent: the applying of speci c image processing that alters pixel values within the image to make the sides of constructions appear extra outstanding compared with photographs with much less or no edge enhancement. Equalization: the application of speci c picture processing that alters the pixel values across the picture to present a more uniform picture look. Exposure latitude: Range of publicity intensities that may produce an acceptable image. Exposure level: A time period used by sure tools producers to indicate exposure indicator. Postprocessing: Changing or enhancing the electronic picture so that it could be viewed from a different perspective or its diagnostic quality could be improved. Typical capabilities embrace examination order processing, examination scheduling, patient registration, report archiving, lm tracking, and billing. Sm oothing: the applying of speci c image processing to scale back the show of noise in a picture. Spatial resolution: the recorded sharpness of buildings on the image; also could also be referred to as detail, sharpness, or de nition. Window stage: Controls the brightness of a digital picture (within a sure range). Windowing: Adjustment of the window degree and window width (image contrast and brightness) by the consumer. Workstation: A laptop that serves as a digital postprocessing station or an image evaluate station. A complete understanding of radiation protection is crucial for each technologist, but a complete review13 is beyond the scope of this anatomy and positioning text. The primary rules and utilized features of radiation protection, as described on this half, ought to be an integral part of a course in radiographic positioning. Radiologic technologists are the final line of protection between patients and unnecessary radiation exposure, making radiation protection consciousness of primary significance. Although many matters are coated in this part, it is essential to remember that the three handiest ways to protect sufferers and workers from ionizing radiation are: 1. Tim e- Minimize radiation beam-on time Maximize distance from the radiation source of both 2. The most essential quantities for a radiographic technologist to be familiar with are absorbed dose (Gy/ rad) and equal dose (Sv/ rem). Absorbed dose is usually displayed by radiography and uoroscopy tools to assist estimate affected person dose throughout publicity. There are however, quite so much of radiation portions, including exposure, air kerma, absorbed dose, equal dose, and efficient dose, that are de ned subsequent. X and scattered radiation ranges are often indicated by measurements of exposure. For the identical absorbed dose, some types of radiation trigger extra harm than others. The product of the absorbed dose and the radiation weighting factor yields the equivalent dose. Effective dose allows comparisons of the relative threat from numerous imaging procedures. However, just because the United States has been slow to convert to the metric system for different applications, conventional items of radiation measurement such because the roentgen, rad, and rem are nonetheless in common use within the United States. Therefore, dose limits have been established by governing bodies to scale back the chance of adverse effects (T in a position 1. The rationale for the dose limits is to make threat from occupational publicity similar to the dangers for staff in different secure industries (excluding mining and agriculture). The annual dose limit for occupationally exposed staff is 50 m v (5000 mrem) whole-body effective dose equivalent. Higher annual dose limits are utilized for partial body publicity: one hundred fifty mSv (15,000 mrem) for the lens of the attention and 500 mSv (50,000 mrem) for the pores and skin, palms, and toes.
Buy myambutol 600mg amexThe ischial rami are absent in Patient 1, whereas in other patients the ischiopubic synchondroses are extensive. The patella is absent in Patient 1, mildly hypoplastic in Patient 3, and unusually properly shaped in Patient 4. The scapulae are normal in Patients 2 and 4, whereas the left scapular wing is hypoplastic in Patient 3. Minor facial dysmorphism: hypertelorism, depressed nasal bridge, quick nose, and low-set ears. Segmental defects of the thoracic backbone: a number of sagittal clefts or a quantity of butterfly vertebrae; block vertebrae and hemivertebrae in some cases. A "zipper-like appearance" of the spine within the neonatal interval, brought on by absent ossification of the vertebral our bodies and incompletely ossified, partially fused posterior neural arches. Lumbosacral hypoplasia could cause myelopathy and cauda equina syndrome, leading to deformities of the ankle and foot. Campomelic dysplasia: Spinal malformations are predominant in the cervicothoracic backbone somewhat than the thoracolumbosacral area and are much less conspicuous. Hypoplastic scapulae and hypoplastic thoracic vertebral pedicles are discriminating features. Most of the illustrated instances appear to be examples of acampomelic campomelic dysplasia (see Offiah et al. Electronic letter: Surviving campomelic dysplasia has the radiological features of the previously reported ischio-pubic-patella syndrome. Some thoracic vertebral bodies, lower lumbar vertebral our bodies, and the sacrum are unossified. The thoracolumbar vertebral bodies are hypoplastic, and several other lumbar vertebral bodies are unossified. There is progressive caudal narrowing of interpedicular distances in the lumbar spine. The lumbar vertebral bodies have turn out to be ossified, whereas the sacrum stays unossified. Uncommon findings: choanal atresia; atresia of the external auditory canal; absence of the olfactory bulb; elbow dysplasia. Narrow, bell-shaped thorax, sometimes with unossified (fibrocartilaginous) gaps between ossified posterior and anterior ribs; most severely with small remnants of the posterior ribs and full absence of ossification of the anterior ribs. Survivors commonly present with mental deficiency and microcephaly as sequelae of perinatal asphyxia somewhat than syndromic elements. This series show variable manifestations of rib hypoplasia and/or rib gaps in lowering severity. In addition, this affected person showed a quantity of unusual findings, including hypoplasia of the clavicles, scapulae, and ilia. Facial abnormalities: broad brow, deep-set eyes, downslanting palpebral fissures, quick nostril, malar hypoplasia, micrognathia with small mouth and higharched palate, easy and/or dysplastic pinnae with preauricular pits or tags. Urogenital hypoplasia: cryptorchidism, hypoplastic exterior genitalia, vaginal insertion of the urethra. Delayed ossification of the pubes and ischial our bodies; faulty ossification of the acetabulum; central dislocation of the femoral head. Goosecoid was recognized to be a determinant at the Xenopus gastrula organizer area and a segment-polarity determinant in drosophila. However, the differential diagnosis is straightforward due to craniosynostosis and syndactyly in Apert syndrome. The medial acetabular walls are faulty together with central dislocation of the proximal femora. Mild hypertelorism, outstanding, broad open eyes ("gloomy") with periocular fullness, anteverted nares, full lips. The patients have extreme quick stature however otherwise the prognosis is good with relatively few complications reported. Russell-Silver syndrome: the characteristic asymmetry of Russell-Silver syndrome is absent in 3M sufferers and the facial options are different. Many newborns with 3M syndrome are initially identified with achondroplasia previous to radiographic research, thus supporting the view that the analysis of achondroplasia must be radiographically or molecularly confirmed even in so-called typical cases. Le Merrer M, Brauner R, Maroteaux P (1991) Dwarfism with gloomy face: a brand new syndrome with features of 3-M syndrome. This picture shows the outstanding heels which may be typical of 3M syndrome and that may provide a diagnostic clue even within the prenatal interval. Despite a marked reduction in length, the radiographs show solely minor modifications with all bones, including the ribs, being considerably gracile. These radiographs also point out that significant neonatal constipation is a recurrent (unrecognized) characteristic of 3M. The lengthy bones are slender with undermodeling, and thus the metaphyses seem relatively massive. Both patients have slender long bones as nicely as skinny, quick tubular bones with diaphyseal constriction. Microphthalmia, severe hypermetropia, often glaucoma, corneal clouding, retinal calcification, tortuous retinal vessels, pseudopapilledema. Narrowing of the medullary cavities of the tubular bones (medullary stenosis) with regular or increased cortical thickness. Reduced diameter of the shafts of the tubular bones with relative flaring of the metaphyses. Arg569His) is recurrent and probably the most frequent mutation liable for the Kenny-Caffey syndrome. Other mutations in the identical gene lead to Osteocraniostenosis, a condition that has comparable however extra extreme skeletal findings and is normally prenatally or perinatally lethal. Postnatal peak development is insufficient, and the adult height varies between 122 and 152 cm. Hypocalcemia is often observed in infancy and manifests with tetany and hypocalcemic seizures. Children could additionally be mildly affected and radiographic anomalies may be detected by the way within the work-up of short stature. Pubertal delay, hypogonadism, and infertility appear to be frequent in affected males; the exact incidence stays to be decided. The phenotype is comparable but extra sever and often not suitable with extended survival. Sanjad-Sakati syndrome: Tubular stenosis is variably present in Sanjad-Sakati syndrome, however total the radiographic appearance and mineral disturbance are just like Kenny-Caffey dysplasia. Sanjad-Sakati syndrome is characterised by microcephaly and developmental delay, and its inheritance is recessive. The original statement of Kenny, Linarelli, and Caffey described an affected mother and son; indeed, the few instances of dominant transmission have solely concerned affected mothers, not fathers, probably due to infertility in affected males.
Discount 400mg myambutol with mastercardIn younger ladies selected for irradiation of the pelvis, the ovaries are often transposed out of the proposed radiotherapy subject to protect ovarian operate. In that position they could be mistaken for an ovarian mass, lymph node metastasis, recurrence, or peritoneal mass if the surgical history is unknown. Metastases seem as solid gentle tissue plenty, usually positioned within the vagina and parametria or affecting the lymph nodes. Recurrent endometrial carcinoma after main radiotherapy is commonly positioned in the uterus or ovaries. They are divided into three histological subtypes:fifty six Leiomyosarcoma (usually arising in the myometrium). Both scar tissue and recurrent tumor tissue are moderately hyperintense in the unenhanced T2 W sequence. Differentiation is aided by the contrast-enhanced fat-saturated T1 W sequence: scar tissue is hypointense in that sequence due to lack of uptake of contrast medium, while inflammatory or neoplastic tissue concentrates extra contrast medium and is subsequently hyperintense. Suggestive indicators are rapid growth, a big heterogeneous mass, and central necrotic parts. Leiomyosarcoma and endometrial stromal sarcoma at the T1 stage are classified based on tumor dimension, whereas adenosarcoma is classified according to the depth of myometrial invasion (see Table 12. It is often hypointense in the unenhanced T1 W sequence and hyperintense within the T2 W sequence. Some tumors have a pseudocapsule, which is hypointense in T1 W and T2 W sequences. The tumor exhibits intense enhancement with an total heterogeneous appearance and clean margins. Patients could complain of diffuse decrease belly pain or specific ache within the vagina, bladder, or rectum. Primary vulvovaginal lymphoma can be rare, accounting for just 1% of all extranodal lymphomas. Ultrasound is appropriate for native tumor detection but could also be unable to define the full extent of lymphomatous involvement, so sectional imaging is useful. Patients could also be asymptomatic or may complain of irregular vaginal bleeding or nonspecific decrease stomach complaints. The lymphoma, situated in the perineal area, is reasonably hyperintense and has smooth margins however presents a considerably polygonal form. Tumor extends beyond the uterus, within the lesser pelvis Female Pelvis nonspecific strain sensation on the pelvic floor, or persistent discharge (especially with vulvovaginal lymphoma). The diagnostic potentialities depend upon location and extent: Leiomyoma with degenerative changes. Ovarian carcinoma is the sixth most typical malignancy in women, with an incidence of 12 circumstances per 100,000 ladies per 12 months within the United States, and is the leading cause of gynecologic cancer deaths. Ovarian most cancers is often asymptomatic, inflicting a delay in prognosis till the tumor has reached a sophisticated stage. Approximately two-thirds are of epithelial origin, roughly one-fourth are germ-cell tumors, and just 10% are sex cord-stromal tumors (Table 12. Current gynecologic pointers describe transvaginal ultrasound as an important imaging modality for ovarian cancer owing to its excessive availability. It is unsuitable for staging, nevertheless, as it supplies restricted visualization of the pelvis as an entire. Stage T1c is based partly on the presence of malignant cells in ascites, and stage T2c is predicated entirely on that criterion. The ovarian cortex is extra hypointense than the medulla within the unenhanced T2 W sequence. The cortex contains hyperintense mature and immature follicles, which range from 0. Ovarian tumors could additionally be predominantly cystic, could comprise T1c solid elements, or may display combined options (see Table 12. It could additionally be tough to undoubtedly characterize the lesion by imaging because of the similar morphologies of different subtypes, however there are a quantity of suggestive morphological standards that can narrow the differential prognosis for a given tumor. For instance, the detection of papillary development inside a cystic ovarian mass is a powerful predictor of malignancy. Axial T2 W image displays the best ovary with follicles, a thin-walled ovarian cyst, and a hypointense stable central part in the ovary with no criteria of malignancy. Ovarian tumors could also be asymptomatic for an extended time and could also be detected by the way in routine examinations. The anterior portion of the mass features a small stable construction with stippled inner calcifications. A regressive cystic teratoma, additionally confirmed histologically, is noted within the left ovary as an incidental discovering. High-resolution T2 W and unenhanced T1 W sequences, coronal if the lesion is lateral to the uterus, or axial if the lesion is anterior or posterior to the uterus, using a 4- to 5-mm slice thickness across the ovarian lesion. T1 W sequence after administration of contrast medium, with fats saturation, in no much less than two planes. Given its close histological resemblance to papillary serous ovarian carcinoma, the actual number of main fallopian tube cancers is probably underestimated. Reconstruction of the portal venous phase in three planes with a 3- to 5-mm slice thickness is crucial as a result of papillary growth and strong components particularly may not but present enhancement in the arterial part. Hematogenous metastasis is often detected only at a sophisticated stage, the commonest websites being the liver, pleura, vagina, lung, and brain. Increased fluid manufacturing by the tumor may distend the tube into a sausage shape. Unenhanced T2 W picture exhibits a polygonal cystic mass permeated by multiple skinny septa and streaks. It was recognized histologically as mucinous cystadenoma of the left ovary with no evidence of malignancy. A predominantly solid, hypointense structure is famous by the way in the proper ovary, recognized histologically as a dermoid (arrow). Some patients expertise lower stomach ache, which may be boring or colicky, as nicely as vaginal bleeding, discharge, or a palpable mass within the decrease stomach. The cystic and solid components are visualized, however the comparatively poor soft-tissue distinction limits additional differentiation and delineation from adjacent intestinal constructions. Hydrosalpinx, hematosalpinx, or pyosalpinx in a setting of irritation (distinguished by an absence of solid mural modifications; the only adjustments are within the fluid composition, due primarily to blood or debris). The outlines of the uterus, cervix, bladder, urethra, and rectum are clearly outlined. Unenhanced T1 W with fat saturation Hypointense = fatty Dermoid (mature teratoma) Hyperintense = blood or mucin Hemorrhagic cyst Hematosalpinx Mucinous cyst Solid elements
Buy cheap myambutol 800 mgI the area o curiosity consists of the sacrum and/ or coccyx, gonadal shielding or emales is in all probability not attainable without obscuring essential anatomy. Females o childbearing age at all times must be questioned concerning the chance o pregnancy be ore any radiographic examination o the decrease vertebral column is begun. The prone position places the lumbar backbone with its pure lumbar curvature in such a method that the intervertebral disk spaces are virtually parallel to the divergent x-ray beam. This position opens up and provides higher visualization o the margins o the intervertebral disk areas. For example, the lateral position requires a better kV than a supine place as a outcome of o elevated half thickness. Increasing the kV and lowering the mAs accordingly reduces affected person doses or analog (f lm-screen) and digital imaging but produces a lower distinction image with f lm-based imaging. Close collimation is important with a high-kV method to limit the quantity o scatter radiation reaching the picture receptor and, as at all times, to cut back the affected person dose. A clear explanation o this process is required i maximal belief and cooperation are to be obtained rom the patient and guardian. T safe their sa ety, pediatric sufferers should be repeatedly o watched and cared or. Use o immobilization units to support the patient is really helpful to reduce the necessity or the affected person to be held, thus reducing radiation exposure. The chn ica l ctors Fa Because o the excessive incidence o osteoporosis in geriatric sufferers, the kV or mAs may require a decrease. Use o short exposure times (associated with the use o higher mA) is really helpful to scale back the chance o motion. It could additionally be essential to li t the abdominal panniculus adiposus (atty apron) to visualize the crease. Additional density rom adipose tissue and pannicular olds might require an increase in technical actors. An improve in kV to enhance penetration by way of moreover thick tissue may be necessary. The location o the lumbar backbone sacral and coccygeal anatomy might be aligned equally in the common inhabitants o sufferers. Use known external landmarks and previously discussed ideas or identi ying the situation o the anatomy o interest. Reassurance and extra care rom the technologist assist the affected person to eel safe and com ortable. I the examination is per ormed with the patient in the recumbent place, a radiolucent mattress or pad placed on the examination table supplies com ort. Patients with exaggerated kyphosis may be more com ortable i positioned or photographs within the erect place. A big selection o pathologic circumstances is demonstrated on sectional images, including the presence and extent o ractures, disk disease, and neoplastic disease. A radiopharmaceutical-tagged tracer component is injected that concentrates in areas o elevated bone exercise, demonstrating a hot spot on the nuclear drugs picture. In ammatory situations, Paget disease, neoplastic processes, and osteomyelitis also could also be demonstrated on the bone scan. Causes or loss o bone mass (osteoporosis) include long-term steroid use, hyperparathyroidism, estrogen def ciency, advancing age, and li estyle actors. Bone densitometry is correct to within 1%, and the radiation skin dose may be very low. Lesions o the spinal canal, nerve roots, and intervertebral disks are demonstrated. In addition to the superior diagnostic high quality o these modalities, avoidance o invasive puncture and contrast injection is benef cial or the patient. The backbone may turn into utterly rigid because the intervertebral and costovertebral joints use. The superior and in erior sur aces o the vertebral physique are pushed together, producing a wedge-shaped vertebra. For patients with osteoporosis or different vertebral pathologic processes, the orce needed to trigger this racture sort could additionally be minor. Patients wearing lap-type seat belts are in danger as a end result of these belts act as a ulcrum during sudden deceleration. The so t internal half o the intervertebral disk (nucleus pulposus) protrudes by way of the f brous outer layer, urgent on the spinal cord or nerves. It happens most requently on the L4-L5 ranges, inflicting sc at ca (an irritation o the sciatic nerve that passes down the posterior leg). Lor os s describes the normal concave curvature o the lumbar spine and an abnormal or exaggerated concave lumbar curvature. This condition may end result rom being pregnant, weight problems, poor posture, rickets, or tuberculosis o the spine. This condition varies greatly in severity and happens most o ten at L5 (see clinical indications in Chapter 16). It is usually as a end result of a developmental de ect within the pars interarticularis or may result rom spondylolysis or extreme osteoarthritis. Ro utine andSpe cialPo s itio ning Protocols and positioning routines range among acilities, relying on actors similar to administrative buildings and liabilities. T echnologists ought to turn into amiliar with present standards o follow, protocols, and routine or special projections or any acility by which they work. Certain routine and special projections or the lumbar backbone, sacrum, and coccyx are demonstrated and described within the ollowing pages and listed in Appendix B. The erect position could additionally be use ul or demonstrating the natural weightbearing stance o the backbone. This help is strongly recommended to forestall patients rom greedy the sting o the desk, which can outcome of their f ngers being pinched. Po sitio n: Accurate 45� affected person rotation as indicated by open � zygapophyseal joints and the pedicle (eye o the Scottie dog) between the midline and lateral side o the vertebral border. I the pedicle is demonstrated laterally on the vertebral body border with extra o the lamina (body o Scottie dog) demonstrated, this indicates under-rotation. Exp o su re: Clear demonstration o bony margins and � trabecular markings o lumbar vertebrae. High quantities o secondary or scatter radiation are generated as the end result o the half thickness. Close collimation is essential, along with placement o lead masking on tabletop behind patient. Po sitio n: Sacroiliac joints show equal distance rom � backbone, indicating no pelvic rotation.
Buy myambutol 800mg amexNormally, no space exists between the double walls o the pericardial sac or between the parietal and visceral pleura unless pathology is present. The coronary heart is also shown to be situated within the anterior portion o the chest cavity immediately behind the sternum and le t anterior ribs. The esophagus is posterior to the heart, with the descending aorta between the esophagus and the thoracic vertebrae. The proper hemidiaphragm and upper liver are shown inside the best lung region, indicating that this may be a decrease thoracic level picture. Although the technical actors are designed or optimal visualization o the lungs and different so t tissues, the bony thorax can be seen. The thyroid gland, giant blood vessels, and thymus gland are proven in relation to the lungs and coronary heart. The apex (B) o each lung is the rounded higher space above the extent o the clavicles. The apices o the lungs lengthen up into the lower neck area to the extent o T1 (f rst thoracic vertebra). The carina (C) is proven as the point o bi urcation, the lowest margin o the separation o the trachea into the best and le t bronchi. The base (D) o every lung is the lower concave space o each lung that rests on the diaphragm (E). The diaphragm is a muscular partition that separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities. The costophrenic angle (F) re ers to the acute outermost decrease corner o every lung, the place the diaphragm meets the ribs. When positioning or chest radiographs, you need to know the relative areas o the uppermost and lowermost parts o the lungs- the apices and the costophrenic angles, respectively- to ensure that these areas are included on each chest radiograph. Pathology, such as a small amount o uid assortment, could be evident at these costophrenic angles within the erect place. The hilum (hilus) (G), also called the root area, is the central space o every lung, where the bronchi, blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves enter and go away the lungs. Some o the decrease lobe (D) extends above the extent o the hilum (C) posteriorly, whereas some o the higher lobe (B) extends under the hilum anteriorly. Four radiographically important buildings situated within the mediastinum are the (1) thym us gland, (2) coronary heart and great vessels, (3) trachea, and (4) esophagus. At its most improvement, the thymus gland lies above and anterior to the guts and pericardium. It is believed to contribute to the power o the physique to produce antibodies, which serve in rejecting oreign tissue and cells. The coronary heart is positioned posterior to the body o the sternum and anterior to T5 to T8. The nice vessels in the mediastinum are the in erior vena cava and superior vena cava, aorta, and huge pulmonary arteries and veins. The in erior vena cava is a large vein that returns blood rom the decrease hal o the body. The aorta is divided into three components: ascending aorta (coming up out o the heart); arch o the aorta; and descending aorta, which passes via the diaphragm into the stomach, the place it becomes the stomach aorta. The capillary community surrounds the small air sacs, or alveoli, where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged with the blood by way of the thinwalled air sacs. The proximal esophagus is located posterior to the trachea and continues down by way of the mediastinum anterior to the descending aorta till it passes via the diaphragm into the abdomen. Care ul centering is also required on the lateral projection to make certain that the anterior or posterior margins are included on the radiograph. With this construct, the thorax is slender in width and shallow rom ront to back however could be very lengthy in its vertical dimension. L 2 Bre athingMove me nts Movements o the bony thorax throughout inspiration (taking air in) and expiration (expelling air) greatly change the dimensions o the thorax and the thoracic volume. The f rst o these is the vertical diam eter, which is increased primarily by contraction and transferring downward o the diaphragm, increasing the thoracic volume. The ribs swing outward and upward, and this will increase the transverse diameter o the thorax. The third dimension is the anteroposterior diam eter, which is also increased during inspiration by the elevating o the ribs, particularly the second through sixth ribs. When a chest radiograph is taken, the affected person ought to take as deep a breath as possible and then maintain it to aerate the lungs ully. The best method that can be used to determine the degree o inspiration is to observe how ar down the diaphragm has moved by counting the pairs o posterior ribs within the lung space above the diaphragm. T determine this, o start on the top with the f rst rib and rely down to the tenth or eleventh rib posteriorly. The posterior part o each rib, where it joins a thoracic vertebra, is probably the most superior part o the rib. There ore, it might be impossible to reveal 10 ribs above the diaphragm or these chest projections. C Po s itio ningCo ns ide ratio ns Patient preparation or chest radiography consists of the removal o all opaque objects rom the chest and neck regions, including clothes with buttons, snaps, hooks, or any objects that would be visualized on the radiograph as a shadow (radiopaque arti act). T o make positive that all opaque objects are removed rom the chest area, the standard procedure is to ask the affected person to take away all clothes, including bras, necklaces, or different objects around the neck. The affected person then places on a hospital gown, which generally has the opening in the back. Long hair may be seen as an arti act on chest radiographs taken with digital imaging methods. Long hair ought to be drawn up or draped throughout the shoulder to eliminate superimposition throughout the chest anatomy. All radiopaque objects ought to be moved care ully rom the radiographic f eld o interest to stop arti acts rom inter ering with the standard o the diagnostic image. In general, chest radiography makes use of low contrast, described as long-scale contrast, with extra shades o gray. T excessive distinction is clear oo when the center and different mediastinal buildings appear underexposed, even though the lung f elds are su f ciently penetrated. As a basic rule, in chest radiography, the use o excessive kV (>100) requires the use o grids. Su f cient mAs ought to be used to provide or optimum density (brightness) o lungs and mediastinal structures. An anatomic facet marker (le t or right) must be positioned on the picture receptor previous to exposure. I not seen radiographically, the exposure ought to be retaken to guarantee the proper facet o the thorax is identif ed. Reduce patient dose as a lot as attainable via the use o correct radiation safety practices by close collimation and protective shielding.
Buy myambutol onlineExcept for the odontoid process, all parts of the cervical and thoracic vertebrae are underdeveloped. The humeri are very quick and spherical, and the femora are quick with rounded proximal and tapered distal ends. The distal phalanges are well ossified and thick, whereas other phalanges and metatarsals are poorly ossified. The radius is unossified and ulna is bowed in A, whereas the radius and ulna are broad with posterior bowing of the ulna in B and C. Ossification is best preserved within the first and fifth fingers that show grossly misshapen metacarpal bones and hook-shaped distal phalanges. Craniofacial abnormalities together with midface hypoplasia, hypertelorism, depressed nasal bridge, micrognathia, and cleft palate. Abnormal arms with broad distal phalanges, syndactyly, camptodactyly, and prominent interphalangeal joints in later life. Kyphosis or double curve deformity of the cervical spine; broad odontoid process of C2. Small vertebral our bodies and coronal clefts all through the thoracic and lumbar backbone; sagittal clefts in the thoracic area. Disproportionately brief, distally tapered humerus and femur; short and bowed tibia, hypoplastic fibula; occasionally premature ossification of the proximal humeral epiphysis. Short and broad phalanges, notably the proximal phalanges (tombstone-like phalanges); bifid distal phalanx of the thumb in some instances; quick, broad metacarpals; abnormally formed and supernumerary carpal bones later in life. Ventilatory help is often needed, and recurrent respiratory tract infections stay an issue in later childhood. Other medical problems embrace cleft palate, chronic middle ear dysfunction with conductive listening to loss, clubfeet, and dislocated joints. There is scoliosis of the thoracic spine, and the thoracic vertebral our bodies are hypoplastic. Except for delicate bowing of the ulna and tibia, the bones of the forearms and legs are normal. The cervical backbone is kyphotic, and several other midcervical vertebral bodies are unossified. There is kyphosis on the thoracolumbar junction, and the lumbar backbone accommodates coronal clefts at multiple ranges. The iliac wings are flared, and the basilar parts of the iliac bones are slim. The midcervical vertebral bodies are hypoplastic along with exaggerated cervical lordosis and sharp kyphosis of the cervicothoracic junction. A delta-shaped proximal phalanx of the index finger is just like that of filaminopathy A (F). Multiple joint dislocations, notably of the hips, knees, and elbows; knee dislocation commonly presents as genu recurvatum. Craniofacial abnormalities with distinguished brow, low nasal bridge, widely spaced eyes, flattened facies, and cleft uvula and/or palate (in about 50% of cases). Abnormal hands with cylindrical fingers, relatively short metacarpals and spatulate thumbs. Prenatal sonography could detect abnormally positioned limbs in the second trimester of gestation. Multiple joint dislocations, most notably within the hips, knees, and elbows, with secondary epiphyseal deformities. Abnormal spinal curvature with vertebral abnormalities most commonly in the cervical region; generally cervical kyphosis with hypoplasia of the midcervical vertebral our bodies; thick odontoid strategy of C2. Extra calcaneal ossification heart appearing in late infancy or later, fusing with the main ossification heart in childhood. Supernumerary carpal bones; short, generally broad and irregular metacarpal bones; lack of distal tapering of proximal and center phalanges; brief, broad first via fourth distal phalanges; untimely fusion of epiphysis and shaft of the first distal phalanx; bifid distal phalanx of the thumb in some instances. Occasionally epiphyseal (trochlea and capitellum) separation at the elbow and infrequently separation of patellar ossification leading to pseudoarthrosis; untimely ossification of the proximal humeral epiphysis. Gonadal mosaicism happens and leads to recurrence of the dysfunction in kids of unaffected dad and mom. The severest phenotypic ends of Larsen syndrome overlap with these of atelosteogenesis type 3. In such cases, severe laryngotracheomalacia might impose affected people on long-term respiratory assist. Spinal wire compression with early death may outcome from cervical kyphosis, hypermobility of the small vertebral joints, and ligamentous hyperlaxity. Note outstanding forehead, depressed nasal bridge, chest deformity, genu valga, and pes adductus with forefoot torsion. There are a quantity of joint issues, including genu recurvatum, posterior elbow dislocation, hip dislocation, and spinal malalignment (kyphosis of the cervicothoracic junction and irregular thoracic lordosis). The skull is large and dolichocephalic, and the facial bones are relatively small. Note hypoplasia of midcervical vertebral our bodies with kyphosis of the cervicothoracic junction. There are gentle upper thoracic scoliosis and decrease thoracic lordosis with kyphosis at the thoracolumbar junction. However, the acetabular fossae are underdeveloped, the femoral heads are dysplastic, and the femoral necks are in valgus position. The patella is tripartite, and the biggest and smallest segments are superiorly dislocated. There is lateral dislocation of the radial head, which lacks an epiphyseal ossification center. The capitellum of the humerus is comparatively massive, and the trochlea is proximally misplaced. The capitellum and trochlea are separated from the humeral metaphysis (pseudoarthrosis). The radiocapitellar articulation is preserved, whereas the ulnnotrochlear relationship is disrupted. Note clubfeet and undertubulation of the phalanges and to a lesser diploma of the metatarsals. The remnant of double calcaneal ossifications is seen as plantar notch and vertical white line within the calcaneal body. There is premature ossification of the proximal humeral and distal radial epiphyses. The quick tubular bones are brief and thick, but the finding is milder than that seen in A. The distal ends of the primary metacarpals and the proximal and middle phalanges are expanded.
References - Xi X, Zhong P: Dynamic photoelastic study of the transient stress field in solids during shock wave lithotripsy, J Acoust Soc Am 109:1226n1239, 2001.
- Donabedian A: The quality of medical care, Science 200(4344):856-864, 1978.
- Bavendam TG, Star RA, Rodgers GP: Research to improve urological health for women and girls: focus on prevention, J Womens Health (Larchmt) 25(11):1081n1082, 2016.
|
|