"Purchase leflunomide online pills, medicine lake."By: Noreen A Hynes, M.D., M.P.H. - Director, Geographic Medicine Center of the Division of Infectious Diseases
- Associate Professor of Medicine
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/0010761/noreen-hynes
Order leflunomide pills in torontoSuperior vena caval abnormalities: their prevalence fee, associated cardiac abnormalities and angiographic classification in a paediatric inhabitants with congenital heart disease. Case report: saccular aneurysm of the azygos vein simulating a paratracheal tumour. Aneurysm of the left brachiocephalic vein: an unusual reason for mediastinal widening. Benign blood vascular tumors of the mediastinum: report of four instances and review of the literature. Mediastinal hematoma simulating recurrent hodgkin illness throughout systemic chemotherapy. Computed tomography of mediastinal hematoma secondary to uncommon esophageal laceration: a Boerhaave variant. Traumatic disruption of the thoracic aorta: significance of the left apical extrapleural cap. Interstitial pulmonary hemorrhage from mediastinal hematoma secondary to aortic rupture. Optimal surgical management of descending necrotising mediastinitis: our expertise and evaluation of literature. Poststernotomy mediastinitis: a evaluate of standard surgical remedies, vacuum-assisted closure therapy and presentation of the Lund University Hospital mediastinitis algorithm. Use of computed tomography to assess mediastinal complications after median sternotomy. Wandering wires: frequency of sternal wire abnormalities in sufferers with sternal dehiscence. Computed tomography and the idiopathic form of proliferative fibrosing mediastinitis. Idiopathic fibrosis of mediastinum: a dialogue of three instances and review of the literature. Idiopathic fibroinflammatory (fibrosing/sclerosing) lesions of the mediastinum: a research of 30 cases with emphasis on morphologic heterogeneity. Fibrosing mediastinitis causing nonvisualization of one lung on pulmonary scintigraphy. Calcific fibrosing mediastinitis: demonstration of pulmonary vascular obstruction by magnetic resonance imaging. Extra-anatomic bypass of the superior vena 992 References cava after profitable stenting for fibrosing mediastinitis. The differentiation between major and secondary involvement on the chest roentgenogram. Imaging of neuroblastoma in patients recognized by mass screening using urinary catecholamine metabolites. Thoracic neurilemomas: an analysis of computed tomography findings in 36 patients. Imaging of peripheral nerve sheath tumors with pathologic correlation: pictorial evaluate. Neuroblastoma: positron emission tomography with 2-[fluorine-18]-fluoro-2deoxy-D-glucose in contrast with metaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy. Positron emission tomography of schwannomas: emphasizing its potential in preoperative planning. Cross-sectional imaging of paragangliomas of the aortic body and different thoracic branchiomeric paraganglia. Mediastinal paragangliomas (aortic body tumor): a report of four cases and a evaluation of the literature. Retroperitoneal and mediastinal chemodectoma: report of a case and evaluate of the literature. Paraganglioma (pheochromocytoma) of the posterior mediastinum: a case report and 482. Mediastinal parathyroid tumors: expertise with 38 tumors requiring mediastinotomy for elimination. Multiple hyperfunctioning mediastinal parathyroid glands in a patient with tertiary hyperparathyroidism. Combined transmission and (99m) Tc-sestamibi emission tomography for localization of mediastinal parathyroid glands. Localization of ectopic parathyroid glands utilizing technetium-99m sestamibi imaging: comparability with magnetic resonance and computed tomographic imaging. Technetium-99m-tetrofosmin as a model new radiopharmaceutical for myocardial perfusion imaging. Mediastinal emphysema complicating diabetic ketoacidosis: plea for conservative diagnostic method. Pneumomediastinum in diabetic ketoacidosis: comments on mechanism, incidence, and management. Pneumoperitoneum, pneumomediastinum and pneumopericardium following dental extraction. Pneumomediastinum after double-contrast barium enema examination: an indication of colonic perforation. Mediastinal widening: a useful radiographic sign of superior vena cava thrombosis. Pleural effusions in superior vena cava syndrome: prevalence, traits, and proposed pathophysiology. Thymic hyperplasia after high-dose chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation: incidence and significance in patients with breast most cancers. Ultrasound of the normal thymus within the toddler: a simple technique of resolving a scientific dilemma. Use of fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography within the detection of thymoma: a preliminary report. Role of flourine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in thymic pathology. Thymic atrophy and rebound enlargement following chemotherapy for testicular most cancers. Enlargement of the thymus following chemotherapy for non-seminomatous testicular cancer. Regrowth and overgrowth of the thymus after atrophy induced by the oral administration of adrenocorticosteroids to human infants. Case report: transient thymic calcification: affiliation with rebound enlargement. Galliumavid thymic hyperplasia in an grownup after chemotherapy for Hodgkin illness.
Buy cheap leflunomide on linePulmonary issues may precede the prognosis of inflammatory bowel disease, or may occur years after the initial analysis, and even after full colectomy for ulcerative colitis. At the time of prognosis about 50% of sufferers have extraskeletal involvement that primarily affects the skin, retroperitoneum, retroorbital area, heart, hypothalamus/posterior pituitary, and lungs. Lungs are concerned in about 15�30% of patients658,660 with about 30 instances on the planet literature up to 2003. These modifications are distributed along lymphatics and have an result on visceral pleura, interlobular septa, and bronchovascular bundles. Chest radiographic appearances661 encompass diffuse interstitial opacities, usually described as reticular. These modifications generally present a mid- to upper zone predominance and may be accompanied by cysts or honeycomb opacity. These findings are often related to multifocal ground-glass attenuation, and centrilobular nodules. Four patients had evidence of small airways illness with a sample much like that of panbronchiolitis. Parenchymal abnormalities associated with inflammatory bowel illness embody organizing pneumonia,639�642 pulmonary hemorrhage,645 and granulomatous infiltration in Crohn illness. Although physiologic abnormalities are quite widespread on this situation, symptomatic pulmonary involvement is uncommon; in a examine of 411 patients, symptomatic lung disease was found in solely four adults and 4 kids. Hermansky�Pudlak syndrome is an autosomal recessive syndrome characterised by partial oculocutaneous albinism, platelet dysfunction, and accumulation of ceroid in varied tissues together with the lung. The abnormality showed subpleural predominance, but was usually diffusely distributed in the craniocaudal aircraft, with some instances displaying predominance in mid- or decrease lung zones. This condition must be considered in the imaging differential analysis of nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and ordinary interstitial pneumonia. Amyloid has a pathognomonic staining reaction because of its unique structure, binding with Congo red and giving a green birefringence in polarized gentle. In the past the classification of amyloidosis has relied on the identification of varied clinicopathologic entities with major subdivisions into primary/secondary amyloidosis and local/systemic illness. However, current categorization relies on the type of fibrillar protein within the amyloid deposit. Transthyretin is similar as prealbumin, a normal plasma protein that may act as a carrier for thyroxine. Genetically decided mutations substitute amino acids and alter its structure, giving rise to greater than 20 heredofamilial types of amyloidosis. The syndrome is associated with slowly progressive lung fibrosis occurring in individuals aged between 20 and 40 years. A number of these can generate amyloid including atrial natriuretic issue (isolated atrial amyloid) and procalcitonin (medullary carcinoma of the thyroid). A classification of the main medical forms of amyloidosis and amyloid deposition together with the sort of chest involvement is given in Table 11. Broadly speaking the deposition could additionally be generalized (systemic amyloidosis) or it may be localized to a single organ. Difficulties mostly happen with so-called localized illness which, although not systemic, is in plenty of situations clearly not restricted to a single organ. This occurs for example within the chest when lung or airway illness can be accompanied by mediastinal and cervical adenopathy. Should direct involvement by amyloid deposition happen, it takes the type of interstitial parenchymal disease, lymphadenopathy, or pleural illness. There is a 2: 1 male predominance with a mean age at presentation of about 60 years. When urine and blood take a look at outcomes are combined, 89% of patients may have a monoclonal protein. If both belly fat and bone marrow aspiration is adverse, rectal biopsy (80% positive) is recommended, followed if necessary by biopsy of a suspect organ. Patients with cardiac involvement survive 4�6 months, whereas those with out cardiac involvement at the time of diagnosis have a median survival of 30 months. The prevalence of lung involvement pathologically varies considerably in different series. Two studies give a prevalence price of 1�5%,707,710 whereas in others the prevalence approaches 100 percent. The interstitial infiltration is manifest as a diffuse micronodular, reticulonodular, or linear sample with accentuation of bronchovascular constructions. In general nodules are within the 2�4 mm range however larger nodules, a centimeter or more in diameter, are described. Other much less common abnormalities embrace ground-glass opacity, honeycombing, and traction bronchiolectasis. Pleural effusions in amyloidosis are commonly caused by heart failure secondary to myocardial infiltration,707,709 or by nephrotic syndrome. However, amyloid involvement of the pleura is seen pathologically734,735 and undoubtedly once in a while causes pleural effusion. The affected person was thought to have heart failure, but diffuse interstitial lung opacity continued within the face of normal cardiac perform. This combination of findings is suggestive of amyloidosis: differential diagnosis may embrace dendriform pulmonary ossification. The affected person was a 61-year-old man who introduced with neck swelling, cough, and weight reduction. Initial mediastinal and cervical adenopathy was adopted by the development of a large right pleural effusion. There was an IgG gammopathy with biopsy evidence of pleural and nodal amyloidosis but no proof of disease elsewhere. In explicit, a number of circumstances of amyloidosis have been described in patients with Sj�gren syndrome who developed benign or malignant lymphoproliferative disease. These structures are normally concerned independently;716 but very sometimes both are affected collectively. The imply age of patients in a large evaluate was fifty three years, with a range of 16�76 years. Local versus diffuse lesions give rise to endoluminal plenty (amyloidomas) that could be indistinguishable from neoplasms on imaging. If treatment is required, the amyloid deposits may be removed, by intermittent bronchoscopic resection,769 or laser photoresection. Microscopically, lung tissue is changed by eosinophilic amyloid containing nests of plasma cells and lymphocytes surrounded peripherally by a low-grade inflammatory infiltrate with big cells. Bronchioles, alveolar septa, and blood vessels in the region of the tumor usually include amyloid as properly.

Purchase leflunomide online pillsPulmonary infection with Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare leads to air trapping distal to the small airways. Pulmonary lesions due to opportunistic mycobacteria (review consists of 30 circumstances of M. Differentiation of Mycobacterium kansasii infection from Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection: comparison of scientific features, radiological appearance, and end result. Clinical options and follow up of 302 sufferers with Mycobacterium kansasii pulmonary an infection: a 50 year experience. Pulmonary infections attributable to Mycobacterium malmoense and Mycobacterium tuberculosis: comparison of radiographic features. Non-tuberculous mycobacterial lung an infection difficult by chronic necrotising pulmonary aspergillosis. Nontuberculous mycobacterial disease and Aspergillus-related lung illness in bronchiectasis. Mycobacterium abscessus and other nontuberculous mycobacteria: evolving respiratory pathogens in cystic fibrosis: a case report and evaluate. Clinical and chest radiographic findings among individuals with sputum culture positive for Mycobacterium gordonae: a evaluation of 19 cases. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: relationship to silicosis and pulmonary an infection. Infection with Nocardia species: clinical spectrum of illness and species distribution in Madrid, Spain, 1978�2001. Pulmonary nocardiosis in human immunodeficiency virus an infection: a tuberculosis mimic. Nocardiosis presenting as an anterior mediastinal mass in a affected person with sarcoidosis. Cardiac actinomycosis in a affected person presenting with acute cardiac tamponade and a mass mimicking pericardial tumour. Actinomycosis with involvement of the vertebral column: case report and evaluation of the literature. Primary pulmonary botryomycosis: an necessary differential analysis for lung most cancers. Histoplasmosis in Europe: Report on an epidemiological survey from the European Confederation of Medical Mycology Working Group. Redefining the medical spectrum of chronic pulmonary histoplasmosis: a retrospective case collection of forty six sufferers. Our experience with histoplasmosis: an analysis of seventy instances with follow-up examine. Acute histoplasmosis: scientific, epidemiologic and serologic findings of an outbreak related to publicity to a fallen tree. Concept of a tumor-like phenomenon encompassing the tuberculoma and coccidioidoma. The evolution of pulmonary cryptococcosis: scientific implications from a study of forty one patients with and without compromising host components. Pulmonary cryptococcosis: Clinical, radiographical and serological markers of dissemination. Acute respiratory failure associated with pulmonary cryptococcosis in non-aids patients. Pulmonary cryptococcosis mimicking solitary lung most cancers in an immunocompetent patient. Cryptococcus an infection in a affected person with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: imaging findings mimicking pulmonary metastases. Pulmonary cryptococcosis: a case report and evaluate of the Asian-Pacific expertise. Pleural effusions as a result of Cryptococcus neoformans: a evaluate of the literature and report of two circumstances with cryptococcal antigen determinations. Expanding understanding of epidemiology of coccidioidomycosis in the Western hemisphere. Primary and progressive primary coccidioidal pneumonias � diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic considerations. Coccidioidomycosis in rheumatology sufferers: incidence and potential risk components. Risk elements for extreme pulmonary and disseminated coccidioidomycosis: Kern County, California, 1995�1996. Rapid diagnostic evaluation of bronchial washings in sufferers with suspected coccidioidomycosis. Isolation of Blastomyces dermatitidis from riverbank soil and evidence of its transmission alongside waterways. Cluster of pulmonary blastomycosis in a rural group: evidence for a number of high-risk environmental foci following a sustained period of diminished precipitation. Diagnosis of pulmonary histoplasmosis and blastomycosis by detection of antigen in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid using an improved second-generation enzymelinked immunoassay. Acute respiratory distress syndrome and blastomycosis: presentation of 9 circumstances and evaluate of the literature. Clinical presentation, radiographic findings, and diagnostic methods of pulmonary blastomycosis: a evaluation of one hundred consecutive instances. Pulmonary blastomycosis masquerading as metastatic disease within the lung: a case report. Pulmonary aspergillosis in immunocompetent hosts without underlying lesions of the lung: radiologic and pathologic findings. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an emerging fungal pathogen. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with persistent obstructive pulmonary illness. Spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis: histologic, clinical, and radiologic findings. Aspergilloma formation in a pneumatocele associated with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. The histological spectrum of persistent necrotizing forms of pulmonary aspergillosis. Lateral cavity wall thickening as an early radiographic sign of mycetoma formation. Pulmonary aspergilloma: evaluation of prognosis in relation to haemoptysis and survey of remedy. Granulomatous mediastinitis as a end result of Aspergillus flavus in a nonimmunosuppressed affected person. Mycotic pseudoaneurysm of the aortic arch: an uncommon complication of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.

Order leflunomide 20mg without prescriptionNonetheless, an more and more growing physique of literature is suggestive that direct injection of post-dose organic fluids for quantification functions has become a routine and efficient process. The downside can be further difficult by (a) differential ion suppression as a outcome of intersubject variability and (b) the usage of blank bio-matrix with various lot numbers. Differences in ion suppression between the analytes and structurally totally different internal standards may also be problematic. The extent of ion suppression relies on the strategies for sample preparation and chromatographic separation. Further studies on the molecular identities of co-eluting endogenous compounds, resulting in ion suppression, are required to clearly delineate their contribution. Note that this experiment must be performed "prior" to the tactic improvement and validation, so needed modifications to the sample preparation protocol and chromatographic technique are made. Hence, intra- and interlaboratory specificity, accuracy, precision, and ruggedness have to be established [54]. New formulations might include sustained-release products that exhibit a lag time in quantifiable plasma concentration. Some of the necessary thing validation traits embody accuracy, precision, specificity, detection limit, quantification restrict, dynamic range, linearity, matrix effect, sample, restoration, sample stability, and total ruggedness of the assay. Calibration curves consisting of single clean (drug free + inside standard), double blank (drug and internal commonplace free), and a minimum of six to eight nonzero calibrators overlaying the expected dynamic range are often used. In addition, stability checks referring to 3-cycles of freeze�thaw, autosampler, bench prime, freezer storage, and stock resolution (neat) are established. In addition, in some cases a racemic drug formulation may contain an enantiomer that will be more potent (pharmacologically active) than the other enantiomer(s). For example, carvedilol, a drug that interacts with adrenoceptors, has one chiral middle yielding two enantiomers. The (-)-enantiomer is a potent betareceptor blocker while the (+)-enantiomer is about 100-fold weaker on the beta-receptor. Ketamine is an intravenous anesthetic where the (+)enantiomer is more potent and fewer poisonous than the (-)-enantiomer. Furthermore, the chance of in vivo chiral inversion-that is, prochiral chiral, chiral nonchiral, chiral diastereoisomer, and chiral chiral transformations-could create critical points in the interpretation of the metabolism and pharmacokinetics of the drug. Therefore, selective analytical methods for separations of enantionmers and diastereomers, the place applicable, are inherently essential. Therefore, the process of enantioselective chromatography method improvement tends to be time-consuming and requires planning and careful experimentation. A good/methodical design of experiments must be applied to understand the role of the organic modifier, pH of the mobile phase, and the choice of the bonded section on the enantiomeric separation. First, optimum separation efficiency (baseline resolution) is desired in order to facilitate the quantitative evaluation of hint levels of enantiomers with high accuracy and precision. Fourth, for quantitative evaluation of a giant quantity of samples, corresponding to those encountered during a medical trial, a relatively short chromatographic run is desired. The high-throughput evaluation must be achieved without compromising sensitivity and chromatographic decision of the critical pairs. Fifth, a drawback of a variety of chiral chromatographic assays is that they might require derivatization. The plasma concentrations have been determined utilizing a validated method described elsewhere. The plasma levels for the pharmacologically inactive enantiomer was considerably decrease than those of the lively enantiomer, consistent with previous findings [58 and references cited therein]. If for any purpose these signaling proteins are subjected to oncogenic mutation(s), a cellular deregulation may occur, yielding an imbalance between cell division, cell progress, and cell death (apoptosis). The Philadelphia (Ph) chromosome is the consequence of a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22 yielding a fusion oncoprotein referred to as Bcr-Abl (210 kDa). This molecular consequence results in an elevated catalytic activity of Bcr-Abl, leading to a resistance to apoptosis, cell transformation, and malignancy. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation requires the supply of an acceptable donor and presents a threat of mortality in older patients. Extensive pattern clean-up was not needed to ensure column longevity due to the reduced column sample loading. The dosing routine was escalated from 25 to 600 mg/day till a positive hematologic response was noticed. A 3M Empore octyl (C8)-standard density 96-well plate was used for plasma sample extraction. Furthermore, the time between the initial preclinical studies to advertising can range from three. Clearly, the task of discovery and growth of novel therapeutic brokers has become increasingly expensive, advanced, inefficient, and competitive. To this finish, validated biomarkers and their reproducible measurement have the potential to shorten the drug discovery course of (proof-of-concept), determine toxicity in actual time. Recent developments in genomics and proteomics have generated appreciable curiosity within the discovery and validation of biomarkers in mechanismbased drug improvement [69�71]. These advances have been welcomed to scale back the cost, increase success rates, and accelerate timelines within the drug discovery and improvement process. Herein, a short overview of the applying of biological markers in early discovery, development, toxicological assessments, and efficacy research in humans is introduced. The dose routine was escalated from 25 to 600 mg/day until a good hematologic response was observed. Although the concept of biological markers has lengthy been established in the medical arena, current technological advancements in genomics, molecular profiling, imaging, and bioinformatics have brought a brand new significance to the identification of disease biomarkers [72]. Biomarker research and validation is turning into an integral part of early discovery, safety evaluation research, preventive drugs, and scientific studies for compound prioritization, proof-of-concept, as prognostic indicators, and predictors of responses to medicine. Consequently, many ever-proliferating "-omics" disciplines have emerged together with proteomics [73], genomics [74], metabolomics [75], metabonomics [76], pharmacogenomics [77], toxicogenomics [78], lipidomics [79], and glycomics [80]. An integral a part of the proposed expeditious and early efficacy and toxicology assessments is the utilization of biomarkers. As the lead optimization continues, the necessity for the sort of biomarker may change, including preclinical efficacy biomarker, toxicity biomarker, and clinical biomarker. The therapeutic index relates to the dose of a drug needed to provide efficacy versus the dose leading to undesired unwanted facet effects. Furthermore, illness state, interspecies variations, attainable lack of reference requirements, the correct sampling location (an invasive procedure versus acquiring peripheral fluids), and presence of variable types of a biomarker can result in further challenges. For instance, many biomarkers are endogenous and, within the case of macromolecules, heterogeneous. Hence, obtaining analyte-free matrices to put together normal curves could be difficult. In some instances, reference standards and applicable internal normal can be tough to get hold of due to complex and expensive synthetic routes. Lastly, a biomarker concentration in peripheral fluids could be a lot decrease than that on the site of production/action.
Diseases - Cluster headache
- Vertical talus
- Thyroid carcinoma, follicular
- Hyperphenylalaninemia due to dihydropteridine reductase deficiency
- WAGR syndrome
- Biemond syndrome type 1
- Cerebro facio articular syndrome
- Epidem
- Cortical hyperostosis syndactyly
Cheap leflunomide 20 mgBronchoscopic and bronchographic findings in 12 sufferers with sarcoidosis and severe or progressive airways obstruction. Computed tomography scan assessment of lung disease in primary immunodeficiencies. Lung ailments in patients with common variable immunodeficiency: chest radiographic, and computed tomographic findings. Vasculitis and bronchiectasis in a patient with antibodies to bactericidal/ permeability-increasing protein and alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency. Interpretation of bronchograms and chest radiographs in sufferers with persistent sputum production. Effects of airway infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a computed tomographic study. Interobserver variation in the diagnosis of bronchiectasis on high-resolution computed tomography. Airflow obstruction in bronchiectasis: correlation between computed tomography options and pulmonary operate tests. High resolution computed tomography in emphysema associated with alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency. A comparison of serial computed tomography and useful change in bronchiectasis. Traction bronchiectasis in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis: related computed tomographic features and physiological significance. How useful is computed tomography in the diagnosis and evaluation of bronchiectasis Comparison of thin section computed tomography with bronchography for identifying bronchiectatic segments in sufferers with persistent sputum production. Computerised tomography within the evaluation of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. High resolution computed tomography in grownup cystic fibrosis sufferers with gentle lung disease. Cystic fibrosis: a short have a glance at some highlights of a decade of research centered on elucidating and correcting the molecular basis of the illness. Prospective examine on nontuberculous mycobacteria in sufferers with and with out cystic fibrosis. Early focal abnormalities on chest radiographs and respiratory prognosis in children with cystic fibrosis. Pulmonary cystic fibrosis within the grownup: early and late radiologic findings with pathologic correlations. The radiographic prevalence of hilar and mediastinal adenopathy in adult cystic fibrosis. Application of chest high-resolution pc tomography in young youngsters with cystic fibrosis. Radiographic adjustments in acute exacerbations of cystic fibrosis in adults: a pilot research. The chest radiograph in cystic fibrosis: a model new scoring system in contrast with the Chrispin-Norman and Brasfield scores (see comments). Bronchial arteriography and embolotherapy for hemoptysis in patients with cystic fibrosis. Spirometer-triggered high-resolution computed tomography and pulmonary operate measurements throughout an acute exacerbation in sufferers with cystic fibrosis. Computed tomography correlates with pulmonary exacerbations in children with cystic fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis: when ought to highresolution computed tomography of the chest be obtained High-resolution computed tomography in younger sufferers with cystic fibrosis: distribution of abnormalities and correlation with pulmonary operate tests. Computed tomographic imaging of the airways: relationship to structure and function. Is restricted computed tomography the longer term for imaging the lungs of youngsters with cystic fibrosis Progressive damage on excessive resolution computed tomography regardless of steady lung function in cystic fibrosis. Structural airway abnormalities in infants and young children with cystic fibrosis. Magnetic resonance scanning in cystic fibrosis: comparison with computed tomography. Applications of hyperpolarized helium-3 gasoline magnetic resonance imaging in pediatric lung disease. Immotile cilia syndrome (primary ciliary dyskinesia) and inflammatory lung disease. Primary ciliary dyskinesia as a explanation for neonatal respiratory distress: implications for the neonatologist. Broncholithiasis: its detection by computed tomography in patients with recurrent hemoptysis of unknown etiology. Management of obstructing pulmonary broncholithiasis with three-dimensional imaging and holmium laser lithotripsy. Clinical and histologic spectrum of bronchiolitis obliterans, including bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia. Peribronchiolar metaplasia: a standard histologic lesion in diffuse lung disease and a uncommon reason for interstitial lung illness: clinicopathologic features of 15 circumstances. Bronchiolitis obliterans, bronchiectasis, and different sequelae of adenovirus sort 21 infection in younger 423. Early observations on lung function studies in symptomatic fuel uncovered inhabitants of Bhopal. Bronchiolitis obliterans following exposure to sulfur mustard: chest excessive resolution computed tomography. Progressive airway obliteration in adults and its affiliation with rheumatoid arthritis. Further studies on the natural historical past of obliterative bronchiolitis following heart-lung transplantation. Value of high-resolution computed tomography in routine analysis of lung transplantation recipients throughout improvement of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. Upper and decrease airway illness in penicillamine treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia: an under-recognised spectrum of illness.
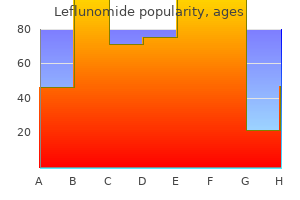
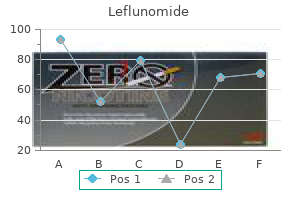
Generic leflunomide 10 mg amexSarcoidosis can produce a quantity of nodules in the lung that will resemble metastases or lymphoma. Also, the comparatively young age of the patient and the frequent lack of indicators and signs of malignant neoplastic disease typically assist resolve the diagnostic issue. There was thus no advantage in performing short-interval follow-up for nodules smaller than 5 mm, even in high-risk sufferers. As is so often the case in sarcoidosis, the nodules are ill defined in outline and much the identical dimension. The set of guidelines proposed by the Fleischner Society are summarized in Table 3. Patients with a cancer that could be a reason for lung metastases must be cared for in accordance with the related protocol or particular clinical situation. Pertinent components will include the location, cell sort, and stage of the primary tumor and whether or not early detection of lung metastases will affect care. In sure clinical settings, corresponding to a patient presenting with neutropenic fever, the presence of a nodule may point out lively infection, and short-term imaging follow-up or intervention could also be acceptable. Although these pointers are likely to be revised in the mild of newer evidence, they presently provide a great tool for the medical management of pulmonary nodules. These lesions may be of any dimension and could also be single or a quantity of, unilocular or multilocular. They are the tip results of earlier linear atelectasis, pulmonary infarction or infection. Since scarring so typically entails focal lack of volume and, due to this fact, indrawing of the pleura, the peripheral portion of the resulting opacities is sometimes composed of pleura. Mucoid impaction Mucoid impaction (bronchocele, mucocele) causes a quantity of branching bandlike opacities pointing to the hilum. Wall of a bleb or pneumatocele Bronchial or peribronchial thickening, the causes of that are: � Pulmonary edema � Neoplastic infiltration � Lymphangitis carcinomatosa � Recurrent bronchial asthma, notably allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis � Bronchiolitis � Bronchiectasis Bronchocele (mucoid impaction) Parenchymal or pleuroparenchymal scar Discoid atelectasis Organizing pneumonia (bandlike pattern) Anomalous blood vessels or feeding and draining vessels to arteriovenous malformations Thickening of pleural fissures Pleural tail related to pleural nodule Septal lines (Kerley lines), the causes of that are given in Box 3. Septal lines on chest radiographs have been first described by Kerley in patients with pulmonary edema. Interlobular septal strains (Kerley B lines) are normally lower than 1 cm in size and parallel to each other at right angles to the pleura. They may be very skinny and sharply outlined or could also be a few millimeters in width and fairly ill-defined. They are situated peripherally involved with the pleura, but are generally absent along fissural surfaces. Blood vessels of such a slim diameter can be either invisible or of extremely low density. The identification of septal strains is an especially useful diagnostic feature, since septal traces that are sufficiently thick to be visible on chest radiographs happen in comparatively few situations (Box three. Portions of the walls of the lobar bronchi throughout the hila are also routinely visible within the wholesome person. When edema or inflammatory or neoplastic cells infiltrate the peribronchial interstitial area, the combination of the bronchial wall and the widened interstitium produces so-called bronchial wall thickening. Although bronchial wall thickening might resemble two adjoining blood vessels, the distinction may be made by figuring out the parallelism of the walls and by observing Y-shaped branching parallel partitions the place the bronchi divide. It can be seen in recurrent bronchial asthma and bronchiectasis, together with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and cystic fibrosis. C, D, An axial part and a lateral view three-dimensional reconstruction of an analogous case. Kerley B lines are brief horizontal strains at the lung periphery (yellow arrows) and A strains radiate from the hila (red arrow). Arrows point to parallel lines of thickened partitions of a consultant, reasonably dilated bronchus. Arrows point to two examples of ring opacities brought on by thickened bronchial walls seen finish on. Occasionally the chest radiograph provides sufficient info for a specific prognosis, however usually it is only one piece of information together with medical options and different tests. The following section is confined to a discussion of the appearance on chest radiography. Carstairs214 showed that, when a quantity of superimposed sheets of small nodules are radiographed, the ensuing image is a reticulonodular sample. Many descriptive terms have been proposed for widespread small lung opacities on the plain chest radiograph; only a few are extensively accepted. Septal (Kerley A and B) strains are a specific form of linear opacities of diagnostic worth as a result of their presence is reliable evidence of interstitial thickening. Reticulonodular sample, representing a mixture of nodular and reticular patterns. A reticulonodular look is far more frequent than a purely reticular or purely nodular pattern. The appearance corresponds to what pathologists call honeycomb lung when viewing the surface of a minimize section of lung. It is a nonspecific function of delicate airspace filling, interstitial thickening, or a mixture of the 2 and is subsequently seen in a big number of circumstances. These six primary phrases often provide a fairly accurate description of diffuse lung disease. Two classes of diffuse lung disease, alveolar and interstitial, primarily based on plain radiographic findings, have been advocated. The problem with this division is that widespread small opacities are often difficult to categorize into one or the other group on plain movie findings. The abnormality is commonly delicate, a hundred and forty Nodular and Reticulonodular Opacities and Honeycombing Box 3. Other factors to observe when deciding on differential diagnostic possibilities are zonal predominance, if any, and such signs as reduction in lung volume, bronchial wall thickening, presence of airspace shadowing, masses, lymphadenopathy, and pleural effusions. The packing containers current a simplified method, and it is very important realize that many exceptions exist. Certain generalizations may be applied with caution: � Acute circumstances should be thought-about individually. In the immunocompetent patient with fever, viral or Mycoplasma pneumonia ought to be the major consideration. The strains point out thickening of the interstitial septa of the lung, which may produce clear-cut septal strains or if quite a few could appear as a reticular sample owing to the superimposition of many thickened septa. In the case of cardiogenic edema the other indicators of circulatory overload will often be present. With chronic bilateral aspiration, bronchopneumonia may convert from consolidation to interstitial fibrosis and bronchiectasis, causing reticulonodular opacities that may resemble late-stage usual interstitial pneumonia. Aspiration pneumonia might often give this appearance, and traditional interstitial pneumonia and sarcoidosis may very hardly ever cause unilateral reticulonodular opacities. The elements of the pattern itself may be of help: � Obvious septal traces are seen solely within the circumstances listed in Box 3. The most common cause by far is pulmonary edema; the following most frequent causes are lymphangitis carcinomatosa and viral or Mycoplasma pneumonia.
Purchase leflunomide with american expressMassive pulmonary embolism is a theoretic risk for widespread pulmonary oligemia however in apply is just about by no means seen. Focal improve in transradiancy is seen with emphysema and bullous disease in constrictive bronchiolitis and in some sufferers with pulmonary emboli. Increased transradiancy of one lung (also generally recognized as unilateral hyperlucent lung) is a fairly generally encountered radiographic discovering. The causes of unilateral elevated transradiancy may be broken down as follows: � Radiographic artifact. Output of X-rays from the X-ray tube is probably not uniform throughout the radiographic area. This so-called heel�toe effect is often adjusted vertically in order that output increases from the apices to the bases. If the heel�toe impact operates across the thorax, one hemithorax might seem more penetrated (that is, more transradiant) than the other. A related appearance may end result from slight rotation of the affected person; the side rotated to which the affected person is rotated is the extra penetrated, regardless of whether the movie has been taken posteroanterior or anteroposterior. A clear-cut difference in penetration of those buildings signifies that the explanation for elevated transradiancy is technical quite than pathologic. Thoracic wall and delicate tissue abnormalities are the most common reason for a unilateral hyperlucent lung, notably a mastectomy on the ipsilateral aspect. Other causes embody a congenital defect of the pectoral muscular tissues (Poland syndrome). A substantial reduction in perfusion of one lung could cause that lung to be abnormally lucent. The lung as an entire may be comparatively hyperexpanded when compared with the alternative lung. Note the mix of small irregular opacities within the upper lobe, bronchial wall thickening, and overinflation of the lung in a 20-year-old man. Note the relative transradiancy of the right hemithorax, discount in measurement of the hilar vessels, and the small intrapulmonary vessels in the right lung. Lobar collapse on one facet with compensatory emphysema in the rest of the lung can superficially resemble a transradiant hemithorax, notably if the collapse is chronic and extreme, because the collapsed lobe could also be a relatively inconspicuous sliver of tissue wedged in opposition to the mediastinum. Careful research of the hilar airway and vascular anatomy should resolve this confusion. On event, a lobar resection could have been performed, leaving remarkably little radiographic evidence of earlier surgical intervention apart from increased transradiancy. Mild generalized elevated opacity of one lung may be misinterpreted as elevated transradiancy of the alternative regular lung. Examples are the filtering impact of a giant pleural effusion layering out posteriorly in a supine patient and the occasional case of uniform lack of quantity of a lung. Some patchy pulmonary parenchymal density is more doubtless to be current, indicating the true state of affairs. Localization of intrathoracic leisons via the postero-anterior roentgenogram: the silhouette sign. Pulmonary actinomycosis masquerading as a malignant lung tumor in a 9-year-old boy. Peripheral opacities in continual eosinophilic pneumonia: the photographic negative of pulmonary edema. The impact of bronchostenosis upon the roentgen-ray shadows in carcinoma of the bronchus. Computed tomography correlation in atypical (peripheral) proper upper lobe collapse: the minor fissure as an evidence for the pleural-based density. Atypical collapse of the higher lobe of the proper lung simulating mixed right higher and middle lobe collapse: report of two cases. Computed tomography in pulmonary pseudotumors and their relation to asbestos publicity. The solitary pulmonary nodule: report of a cooperative research of resected asymptomatic solitary pulmonary nodules in males. The solitary circumscribed pulmonary nodule: examine of seven hundred and five cases encountered roentgenologically in a period of three and one half years. Computerized tomographic densitometry of the solitary pulmonary nodule utilizing a nodule phantom. Somatostatin receptor imaging of non-small cell lung cancer with 99mTc depreotide. A multicenter trial with a somatostatin analog (99m)Tc depreotide in the evaluation of solitary pulmonary nodules. Relationship between tumor doubling time and anatomo-clinical options in 50 measurable pulmonary cancers. The rate of growth and obvious duration of untreated main bronchial carcinoma. The frequency distribution of the charges of growth and the estimated duration of primary pulmonary carcinomas. Tumor doubling time and prognostic evaluation of patients with main lung most cancers. Heterogeneity of epidermal growth factor receptor mutations within a blended adenocarcinoma lung nodule. An analysis of 155 solitary lung lesions illustrating the differential prognosis of mixed tumors of the lung. A useful roentgen signal in the diagnosis of localized bronchioloalveolar cell carcinoma. Bronchioloalveolar cell carcinoma: medical, histopathologic, and radiologic findings. Significance of wall thickness in solitary cavities of the lung: a follow-up research. Computed tomography halo check in pulmonary nodules: frequency and diagnostic value. Pulmonary nodular opacities after transbronchial biopsy in sufferers with lung transplants. Determining the chance of malignancy in solitary pulmonary nodules with Bayesian evaluation: half I. Carcinoma metastatic from the thyroid to the lungs; a twenty-four-year radiographic follow-up. The interpretation of shadows in a restricted area of the lung area on a chest radiograph. Radiologic-pathologic correlations of small lung nodules with special reference to peribronchiolar nodules. The hypertransradiant hemithorax: the significance of lateral decentring, and the reason for its appearance as a outcome of rotation.

Generic 20mg leflunomide fast deliveryThe instrument band-spreading can adversely have an result on column performance, especially as the scale of the column and support particle dimension are decreased. Since peak volumes are a lot smaller in high-speed columns, extra-column contributions to band-broadening are extra important and thus have to be reduced as a lot as attainable. A good rule of thumb is that, generally, extra-column bandspreading ought to contribute no extra than 10% loss in effectivity of the column, which corresponds to 5% drop in decision. Maximum allowable extra-column broadening for 10% loss in effectivity for varied column dimensions packed with three. Calculated with equations (17-25) and (17-27), assuming optimum column efficiency (H = 2dp) and k = 5. This plot emphasizes that extra-column band broadening must be optimized to achieve expected efficiency of columns, especially as column dimensions and particle size are decreased. Peaks eluting sooner than k = 5 would require even smaller allowable extra-column broadening. Recently, a number of commercially available methods have been designed to operate such columns. In addition to low extra-column volumes, systems should operate in excess of 500 bar to obtain mobile-phase linear velocity within the optimum performance region. Theoretical plates versus retention issue for sequence of parabens separated by isocratic chromatography. Extra-column results result in decreased efficiency for early-eluting elements (low values of k). In isocratic strategies, nonetheless, extra-column band-spreading is more important, particularly for the early eluting peaks. Instrument dispersion could be lowered by optimizing injector and detector systems and decreasing diameter of connection capillaries. Furthermore, as the column diameter is lowered, decrease volumetric move charges are required and therefore further reduction in capillary dispersion could be achieved by decreasing capillary diameter. In addition, since unions are also used, ferrules should be correctly set and capillary ends must be squarely cut to get rid of unnecessary gaps in the connection. Thus, a helpful "1/3 rule" can be used for figuring out acceptable extra-column broadening: All particular person contributions to broadening, in addition to the injection and detector flow cell volumes, should be not extra than 1/3 of whole peak width quantity to give 10% loss in column efficiency. To correctly combine a peak, a minimal of 15 data points throughout a Gaussian peak or 21 points for a non-Gaussian peak is required. The optimum sampling price for the narrowest peak of interest can be calculated by the next formulation: Sample fee = n W (17-31) the place n is the minimum number of points/peak for accurate sampling fee and W is the narrowest peak width in seconds. The detector time constant (or digital filter for modern instruments) is used to remove high-frequency noise. The "1/3 rule" could additionally be utilized right here as properly: As a rule of thumb, the utmost detector time fixed (seconds) tolerable is about 1/3 the usual deviation of the height in seconds. Although noise-free chromatograms are desirable, decision and sensitivity could be adversely affected by excessively massive time constants due to peak distortion. Chromatographic noise may also be lowered via Savitzky�Golay smoothing of the unfiltered raw signal (time constant = 0). Effect of sampling rate on peak form for a 1-second-wide peak with retention issue k = 1. Injection volumes that are too giant can cause volume overload of the column, which finally ends up in broad, flat-top formed peaks with low plate counts which are extra pronounced for earlier eluting parts. As injection volume is increased, peak height ought to enhance; nevertheless, peak width ought to remain the identical. As column dimensions are reduced, the maximum injection volume must be lowered by the ratio of the column volumes [see equation (17-33) in Section 17. Higher injection volumes are potential within the gradient mode due the concentration of the pattern band on the head of the column. When we decrease injection quantity to avoid quantity overload, the pattern concentration should be elevated proportionally so that the identical mass of analyte is being injected. This can occur even for small injection volumes if the concentration of pattern is excessive sufficient. Injecting much less quantity of pattern, either by a smaller injection quantity or by diluting the sample, can clear up the issue of mass overload. Another injection-related effect that may diminish the separation efficiency is the "diluent impact," also identified as solvent mismatch. This occurs when the elution strength of the pattern solvent is larger than the beginning mobile-phase power. Consequently, some analyte molecules will be "carried" ahead of the analyte zone by the plug of sample solvent because it migrates down the column. When the sample diluent have to be stronger than the starting cellular phase, reducing the injection quantity can lessen the effect, as a end result of the smaller plug of pattern solvent is extra rapidly diluted by the cell section. The move fee is scaled to preserve the identical linear velocity as the unique methodology. The variety of column volumes per step can be calculated by multiplying the move fee by the step duration, and dividing by the column volume for the particular column in question. A prerequisite to fast separations, nonetheless, is that adequate selectivity between elements is achieved. Understanding the parameters governing isocratic and gradient separations can lead to vital enhancements within the velocity of present strategies. Additionally, new exciting applied sciences coming into the marketplace promise even greater pace of study than is presently attainable with typical columns and gear. It is anticipated that run times of <5 minutes will turn out to be commonplace in the close to future. Horvath, An Introduction to Separation Science, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1973, p. Poppe, Some reflections on pace and effectivity of contemporary chromatographic strategies, J. Klinkenberg, Longitudinal diffusion and resistance to mass transfer as causes of nonideality in chromatography, Chem. McCalley, Comparison of typical microparticulate and a monolithic reversed-phase column for high-efficiency fast liquid chromatography for primary compounds, J. Ikegami, Monolithic silica columns for high-efficiency chromatographic separations, J. Tanaka, Performance of octadecylsilylated steady porous silica column in polypeptide separations, J. Spoendlin, Practical elements of fast reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography using 3 m particle packed columns and monolithic columns in pharmaceutical development and manufacturing working underneath current good manufacturing apply, J. Jorgenson, Ultrahigh-pressure reversed-phase liquid chromatography in packed capillary columns, Anal. Jorgenson, Ultrahigh-pressure reversed-phase capillary liquid chromatography: Isocratic and gradient elution utilizing columns packed with 1.
References - Hungerhuber E, Schlenker B, Karl A, et al: Risk stratification in penile carcinoma: 25-year experience with surgical inguinal lymph node staging, Urology 68:621n625, 2006.
- Britten RA, Nazaryan V, Davis LK, et al: Variations in the RBE for cell killing along the depth-dose profile of a modulated proton therapy beam, Radiat Res 179(1):21n28, 2013.
- Schafer W, Watervar F, Langen P-H, et al: A simplified graphic procedure for detailed analysis of detrusor and outlet function during voiding, Neurourol Urodyn 8:405n407, 1989.
|
|

