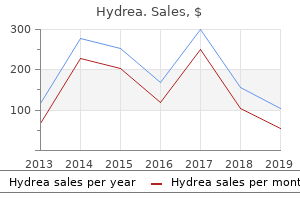
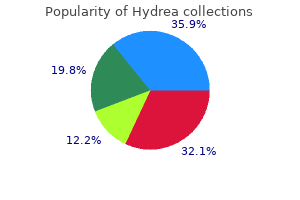
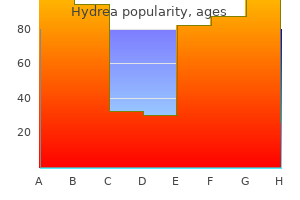
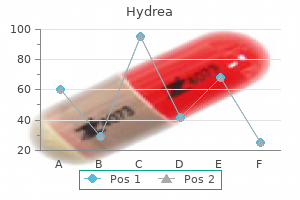
"Cheap hydrea 500mg with amex, symptoms gout."By: Danielle Marie Brander, MD - Assistant Professor of Medicine
- Member of the Duke Cancer Institute
 https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/danielle-marie-brander-md
Order hydrea overnightChromosome segregation errors often happen during multipolar cell division [17, 21]. For instance, microtubules related to the outer poles often connect to the same kinetochore throughout multipolar spindle development. If left unchecked, this error prevents chromosomes from migrating to discrete poles during anaphase. Consequently, these "lagging" chromosomes are regularly excluded from the daughter cell nuclei and kind what is considered a micronucleus. Cytogenetic analyses of hepatocytes have shown that liver aneuploidy is widespread, with chromosome features and losses occurring in an unbiased trend [13, 23]. Polyploidy in liver gene expression and function While the mechanisms that produce polyploid hepatocytes have been nicely characterised, the relationship between ploidy and gene expression remains unclear. Experiments have shown that polyploidy is related to specific gene expression patterns in yeast [24]. In regards to mammals, research have demonstrated that nuclear content material impacts expression ranges of genes regulating megakaryocyte differentiation [25] and that giant trophoblast cells might exhibit biallelic Xchromosome gene expression as a result of incomplete Xinactivation [26]. Additionally, a largescale genome comparative examine illustrated that cardiac stress genes had been expressed at completely different levels between diploid and polyploid cardiomyocytes [27]. One speculation is that gene expression ranges increase proportionally with ploidy. In this case, tetraploids and octaploids would have 2� and 4� greater gene expression ranges, respectively, compared to diploids. Another hypothesis is that diploid and polyploid hepatocytes exhibit differential gene expression. In this situation, gene expression levels would range on a gene to gene basis between ploidy populations, with polyploids exhibiting larger expression of particular genes versus diploids and vice versa. Surprisingly, the research found gene expression was largely equal between ploidy populations, and the magnitude of distinction was small for these genes with completely different expression levels [28]. This instructed that few genes are differentially expressed, no much less than in quiescent hepatocytes. Further research are needed to decide if differential gene expression occurs in illness circumstances or in response to particular stimuli as a end result of variations on the molecular degree might ultimately endow sure ploidy subsets with unique practical capabilities [2, 29]. Liver ploidy supports hepatic adaptation It has been hypothesized that the diverse population of polyploid and aneuploid hepatocytes endows the liver with the power to adapt to a wide selection of environmental stresses [23]. Healthy mouse livers include randomly aneuploid hepatocytes, which are illustrated by multicolored cells. In response to continual injury (induced by tyrosinemia in Hgd+/- Fah-/- mice), liver operate was severely impaired. Hepatocytes missing chromosome 16 (blue) were immune to the injury and capable of proliferation. Clonal enlargement by these injuryresistant hepatocytes spontaneously repopulated the liver and restored liver function. In the context of the liver, it has been demonstrated that aneuploid hepatocytes might shield in opposition to chronic liver disease. Karyotyping and array comparative genomic hybridization analyses revealed that many of the healthy nodules have been comprised of aneuploid hepatocytes lacking a duplicate of chromosome 16, which incorporates the wildtype copy of Hgd. It was hypothesized that persistent injury was poisonous to the majority of hepatocytes besides those who had beforehand lost the chromosome with the Hgd wildtype copy. The diseaseresistant hepatocytes (monosomic for chromosome 16), proliferated and repopulated the liver and restored regular liver perform [23]. Another examine confirmed that mice with druginduced necrosis and cirrhosis developed regenerating nodules enriched with diploid hepatocytes [38]. In contrast, it was shown that transplanted octaploid and diploid hepatocytes proliferate equivalently within the Fah-/- liver repopulation model. Taken collectively, these experiments illustrate that additional research are needed to decide the precise proliferative capacities of diploid and polyploid hepatocyte populations, and the mechanisms regulating proliferation of every ploidy population. Polyploidy in growing older and impaired liver regeneration Aging is thought to lead to the buildup of senescent cells in multiple tissues and organ systems, including the liver [42]. Senescence is the irreversible exit of the cell cycle, driven by the shortening of telomeres. Many hypothesize that senescence is a protective mechanism in opposition to tumorigenesis that may arise from genomic instability, but senescence also has the effect of limiting tissue regeneration and selling the secretion of inflammatory mediators that may be damaging to surrounding tissue [43]. Aged octaploid cells have been discovered to express a better proportion of senescence markers compared to tetraploid and diploid cells, together with p16, p21, and p53, which also serve necessary tumor suppressor roles [44]. Polyploidy and liver regeneration the regenerative capacity of the liver has been nicely documented, however the function of polyploidy on this course of remains unclear. It is hypothesized that diploid and polyploid populations could play distinctive roles within the process. Originally, it was believed that polyploid hepatocytes had been mature, terminally differentiated cells with little proliferative capacity. This was suggested from studies demonstrating that hepatocytes in livers of mice and rats become more and more polyploid with age, and that greater than 99% of hepatocytes in grownup livers had been quiescent [34, 35]. Aged hepatocytes that bear ploidy reversal also downregulate expression of senescence markers, appearing as a type of cell rejuvenation [44]. Ploidy reversal may partially clarify the capacity of the aged liver to regenerate, though regeneration is substantially lowered in elderly people. Notably, when the circulatory methods of younger and aged mice are connected via heterochronic parabiosis, the variety of hepatocytes present process proliferation elevated within the aged livers. When aged diploid or octaploid hepatocytes are implanted into younger Fah-/- mice, the octaploid hepatocytes bear ploidy reversal, giving rise to lower hepatic ploidy states that no longer express markers of senescence [17, 44]. This examine not only implicated the power of a younger systemic environment to rejuvenate hepatocyte proliferative capability, but in addition advised that hepatocytes with differential ploidy states have equal proliferation kinetics throughout longterm repopulation. Future research will want to decipher the function of cell intrinsic factors, such as ploidy and gene stability, mitochondrial perform, and autophagy, versus extrinsic components within the local or systemic surroundings, within the strategy of hepatocyte perform and regeneration after injury and through growing older. Desdouets and colleagues recently showed that superior fatty liver illness, known as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, is related to enhanced polyploidy [55]. Furthermore, in these fatty liver models, oxidative stress was discovered to be the primary driver of increased polyploidy. Thus, there appears to be an intricate nexus between mitochondrial dysfunction, correlating with metabolic liver illness and polyploidization. Moreover, many genes that regulate mitochondrial metabolism are reported to alter hepatic polyploidy such as Mir122, members of the E2F family (E2F1, E2F7, and E2F8), Birc5, Ercc1, Myc, p53, Rb, and Skp2 [2, 19, 58, 59]. Together, these observations strongly counsel that mitochondrial metabolism and hepatic polyploidy are closely linked and could play a job in development of liver illnesses. These observations counsel that the regulation of power expenditure or the breakdown of mitochondrial operate is linked to the development of differential ploidy states. This section describes the metabolic states and molecular regulators that connect mitochondrial metabolism and polyploidy within the liver. E2F1 regulates metabolism in organs similar to liver, muscle, pancreas, and adipose tissue that decide metabolic homeostasis.
Order hydrea 500mg with mastercardThis elevated sensitivity is likely due to elevated expression of hormone receptor quite than variations in downstream signaling parts such as G proteins or InsP3R [48]. Cells with elevated expression of hormone receptor produce larger concentrations of InsP3, in order that they reply ahead of other cells stimulated with the identical concentration of hormone. As a result, cells with the greatest degree of hormone receptor expression act as pacemakers, and totally different cells can act as the pacemaker for different hormones. Thus, the sample of Cai2+ waves and oscillations in the intact liver relies upon upon multiple factors, which embrace: (i) the institution of pacemaker cells by virtue of elevated expression of hormone receptors, (ii) simultaneous stimulation of both pacemaker and nonpacemaker cells, and (iii) communication of second messengers amongst these cells via gap junctions [49]. The liver additionally possesses paracrine mechanisms for producing and regulating Cai2+ signals. This paracrine signaling mechanism thus permits increases in Cai2+ to unfold among neighboring cells impartial of communication through hole junctions. Cai2+ signaling in liver additionally can be modified rather than initiated by paracrine pathways. These Ca2+ storage pumps and release channels have distinct distributions within the nuclear envelope. Both InsP3Rs and RyRs are localized along invaginations of the nuclear envelope, denoted the nucleoplasmic reticulum, which work as a regulatory Ca2+ domain throughout the nucleus [59]. The importance of nuclear Ca2+ is also highlighted by findings demonstrating that totally different transcription components are instantly or indirectly depending on Ca2+ within the nucleus [60]. Evidence suggests that InsP3 releases Ca2+ immediately from the nuclear envelope into the nucleus. InsP3 releases 45Ca2+ into isolated hepatocyte nuclei, and InsP3 will increase free nuclear Ca2+ even if the nucleus is surrounded by a Ca2+ chelator. Moreover, activation of this highly localized cascade was depending on translocation of the activated receptor to the nucleus [3]. In the absence of a gating mechanism, a pore this size would allow speedy equilibration of Ca2+ between the nucleus and cytosol. Under certain circumstances, free diffusion of Ca2+ through the nuclear pore indeed happens. However, a nuclearcytosolic Ca2+ gradient has been demonstrated in a quantity of cell sorts [63], suggesting that the permeability of nuclear pores can be regulated. Moreover, electrophysiological studies counsel that Ca2+ permeability via nuclear pores is restricted. Atomic drive microscopy studies similarly suggest that nuclear pore permeability is regulated, and that depletion of Ca2+ within the nuclear envelope closes the pores. Other work using fluorescent dyes or aequorin additionally demonstrates that depletion of Ca2+ attenuates the permeability of the pores to intermediatesized molecules that lack a nuclear localization sequence. There is additional evidence that nuclear Ca2+ typically passively follows Cai2+ [65]. For example, stimulation of hepatocytes with vasopressin ends in a Ca2+ wave that appears to unfold from the cytosol into the nucleus. Moreover, a mathematical evaluation of Ca2+ waves in hepatocytes stimulated with vasopressin means that nuclear Ca2+ alerts may be described just by diffusion of Ca2+ inward from the nuclear envelope. For instance, localized increases of Ca2+ in the cytosol (Ca2+ puffs) can spread throughout the cell by diffusing throughout the nucleus. Ca2+ puffs are extremely transient and localized Cai2+ signals that result from the coordinated opening of small clusters of InsP3Rs. Puffs can be triggered by a subthreshold focus of agonist and the resulting Cai2+ signal quickly dissipates by diffusion within the cytosol and sequestration of Ca2+ into intracellular stores. However, the range of diffusion of Ca2+ in the nucleus can be much higher than in cytosol, so Ca2+ puffs generated near the nuclear envelope can spread into and throughout the nucleus to be able to unfold to different, more distant regions of the cytosol [65]. Thus, the nucleus might operate as a tunnel that helps distribute Ca2+ to the cytosol. As in hepatocytes and different epithelia, the vary of patterns of agonist induced Cai2+ signals embody sustained and transient Cai2+ increases and Cai2+ oscillations. Cai2+ signaling is mediated by InsP3 in bile duct cells, as a outcome of increases in Cai2+ are blocked by InsP3R antagonists. Bile duct cells are coupled by way of connexin forty three (Cx43) gap junctions, and expression of Cx43 synchronizes their Ca2+ oscillations. Moreover, Cx43 permeability is beneath hormonal management, and activation of both protein kinase A or C decreases permeability and impairs intercellular communication [66]. The following sections are meant to present illustrative examples of the different ways during which Ca2+ regulates regular and abnormal liver function, rather than to present an exhaustive listing of Ca2+mediated functions. Energy metabolism Storage and launch of glucose was among the many first features of the liver proven to be regulated by Cai2+. Synthesis of glycogen is regulated by glycogen synthase, while phosphorylase is the ratelimiting enzyme for glycogenolysis. Both enzymes are regulated by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, and an increase in Cai2+ is likely one of the most necessary indicators for regulating these occasions [67]. For instance, hormones corresponding to vasopressin and angiotensin improve InsP3 in hepatocytes, which mobilize Ca2+, resulting in phosphorylation and activation of glycogen phosphorylase, after which glycogenolysis. Similarly, extracellular nucleotides activate glycogen phosphorylase and thus stimulate glycogenolysis by binding to P2Y nucleotide receptors [68]. These bile acids activate phosphorylase through a Ca2+dependent however InsP3independent mechanism, in maintaining with the observation that they improve Cai2+ in an InsP3independent style [69]. Gluconeogenic enzymes are preferentially positioned in the periportal area [70], though different elements also may be involved in regional differences in glycogenolytic capacity. This might partly mirror the reality that pericentral hepatocytes are more delicate than periportal hepatocytes to vasopressin and norepinephrine [37]. For example, glucose launch is impaired in perfused livers from Cx32deficient mice upon stimulation with either norepinephrine or glucagon [44]. Hormoneinduced glucose launch is also impaired if gap junctions are blocked in isolated rat hepatocytes, or if hepatocytes are dispersed. This integration of metabolic operate is especially important in occasions of stress, because fasting induces hypoglycemia in Cx32deficient but not wildtype mice, and because endotoxininduced hypoglycemia is exacerbated in the knockout mice as well [40]. Similarly, liver glucose production upon stimulation with glucagon and norepinephrine is decreased in Cx32 knockout mice [44]. In a physiological context, this kinase is activated by InsP3R dependent Ca2+ release during fasting and promotes translocation of the transcription issue FoxO1 to the nucleus of hepatocytes. This translocation in turn controls a transcriptional program that potentiates glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis and results in elevated glucose output by the liver. This mechanism is potentiated in experimental weight problems and contributes to the excessive serum ranges of glucose found in obese mice. This phosphorylation renders the receptor more susceptible to activation by InsP3 and thus Ca2+ is extra readily released in the cytosol.
Cheap hydrea 500mg with amexProtection after immunization with antigens of Toxoplasma gondii incorporated into liposomes. Toxoplasma gondii: flat-mounting of retina as a new tool for the remark of ocular an infection in mice. Activity of pure and synthetic naphthoquinones towards Toxoplasma gondii, in vitro and in murine models of infection. Effect of Toxoplasma gondii an infection kinetics on trophoblast cell population in Calomys callosus, a mannequin of congenital toxoplasmosis. Evaluation of vertical transmission of Toxoplasma gondii in Calomys callosus mannequin after reinfection with heterologous and virulent pressure. Host, pressure and treatment variation as elements in the pathogenesis of toxoplasmosis. Immunosuppression and toxoplasmic encephalitis: scientific and experimental aspects. Toxoplasma gondii: partial crossprotection amongst a quantity of strains of the parasite towards congenital transmission in a rat model. The effect of a subretinal � injection of Toxoplasma gondii on the serum antibody titer in a rabbit model of ocular toxoplasmosis. Species and pressure variations in sensitivity to Toxoplasma infection amongst laboratory rodents. Prevention of vertical illness transmission by therapy and reproductive failure in persistent an infection. Effects of drug therapy on Toxoplasma cysts in an animal mannequin of acute and persistent disease. Retinochoroiditis is induced by oral administration of Toxoplasma gondii cysts within the hamster model. The impact of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole on Toxoplasma gondii in vitro and in vivo. Fundal with dots: observations from a murine model of congenital ocular toxoplasmosis. Foetal infection through the acute � and continual section of latent toxoplasmosis in rats. Toxoplasma gondii comprises three clonal lineages: correlation of parasite genotype with human disease. Mic1-3 knockout of Toxoplasma gondii is a successful vaccine towards persistent and congenital toxoplasmosis in mice. Activity of gamma interferon together with pyrimethamine or clindamycin in treatment of murine toxoplasmosis. Transplacental transmission of Toxoplasma gondii in minipigs contaminated with strains of different virulence. Toxoplasma gondii and cognitive deficits in schizophrenia: an animal mannequin perspective. Two 2-hydroxy-3alkyl-1,4-naphthoquinones with in vitro and in vivo activities against Toxoplasma gondii. Murine neonatal infection supplies an efficient mannequin for congenital ocular toxoplasmosis. Muller cell activation and � photoreceptor depletion in a mice mannequin of congenital ocular toxoplasmosis. � Reciprocal virulence and resistance polymorphism within the relationship between Toxoplasma gondii and the home mouse. Azithromycin reduces ocular infection throughout congenital transmission of toxoplasmosis within the Calomys callosus mannequin. Efficacy of epiroprim (Ro11-8958), a brand new dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor, in the remedy of acute Toxoplasma an infection in mice. Toxoplasma gondii: fluconazole and itraconalzole activity towards toxoplasmosis in a murine model. Ciprofloxacin derivatives have an effect on parasite cell division and enhance the survival of mice contaminated with Toxoplasma gondii. Immune response of mice to ingested Toxoplasma gondii: a mannequin of Toxoplasma infection acquired by ingestion. Subcutaneous and intestinal vaccination with tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii and acquisition of immunity to peroral and congenital Toxoplasma challenge. Immune responses related to early survival after peroral infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Parasitemia and parasitic masses in acute an infection and after anti-gamma-interferon treatment in a toxoplasmic mouse model. Prevention of recrudescent toxoplasmic encephalitis utilizing ponazuril in an immunodeficient mouse mannequin. Development of neurological mouse model for toxoplasmosis utilizing Toxoplasma gondii isolated from hen in Kenya. Evaluation of the efficacy of atovaquone alone or in combination with azithromycin in opposition to acute murine toxoplasmosis. The function of hypersensitivity reactions to Toxoplasma antigens in experimental ocular toxoplasmosis in nonhuman primates. Comparative effects of cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole) and spiramycin in pregnant mice infected with Toxoplasma gondii (Beverley strain). Effects of sulfamethoxazole on murine ocular toxoplasmosis in interferon-gamma knockout mice. Anti-Toxoplasma activity of estragole and thymol in murine fashions of congenital and non-congenital toxoplasmosis. Atovaquone ameliorate gastrointestinal toxoplasmosis complications in a being pregnant model. Diclazuril protects in opposition to maternal gastrointestinal syndrome and congenital toxoplasmosis. The effect of minocycline, doxycycline and oxytetracycline on experimental mouse toxoplasmosis. Acquired and congenital ocular toxoplasmosis experimentally induced in Calomys callosus (Rodentia, Cricetidae). Reactivation of Toxoplasma gondii by cytomegalovirus disease in mice: antimicrobial actions of macrophages. Toxopain-1 is important for infection in a novel hen embryo mannequin of congenital toxoplasmosis. Comparison of Uteroplacental Vasculature and Circulation within the Rhesus Monkey and Man, vol. Studies on persistent toxoplasmosis; the relation of infective dose to residual an infection and to the potential for congenital transmission. Congenital transmission of toxoplasmosis from mother animals with acute and chronic infections.
Generic hydrea 500mg lineEndothelin antagonism in portal hypertensive mice: implications for endothelin receptorspecific signaling in liver disease. Increased contractility of hepatic stellate cells in cirrhosis is mediated by enhanced Ca2+dependent and Ca2+ sensitization pathways. An electron microscopic study of the fenestrated endothelial lining of rat liver sinusoids. Capillarization and venularization of hepatic sinusoids in porcine seruminduced rat liver fibrosis: a mechanism to preserve liver blood circulate. Alcoholic liver harm: defenestration in noncirrhotic livers � a scanning electron microscopic examine. Both an increase and decrease in cerebral blood move have been described in acute and continual liver diseases, respectively [141]. An enhance in cerebral blood move has been primarily related to acute liver failure, which may probably result in the development of mind edema [142]. In distinction, cerebral blood move is decreased in chronic liver disease, and this lower runs in parallel with the abovementioned discount in renal blood circulate, suggesting that the mechanisms of blood move reductions in continual liver illness could additionally be related in these two organs [143]. Because of the disparate situations of vascular tone in the intrahepatic and extrahepatic circulations. Evolution in the understanding of the pathophysiological foundation of portal hypertension: How adjustments in paradigm are resulting in profitable new therapies. The molecules: mechanisms of arterial vasodilatation noticed within the splanchnic and systemic circulation in portal hypertension. The hyperdynamic circulation of chronic liver ailments: from the affected person to the molecule. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, prognosis, and administration: 2016 26. Rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cell phenotype is maintained by paracrine and autocrine regulation. Role of extracellular matrix in regulating fenestrations of sinusoidal endothelial cells isolated from normal rat liver. Fibronectin further domainA promotes hepatic stellate cell motility but not differentiation into myofibroblasts. Exosome adherence and internalization by hepatic stellate cells triggers sphingosine 1phosphatedependent migration. Sinusoidal endothelial cells prevent rat stellate cell activation and promote reversion to quiescence. Nitrovasodilators inhibit platelet derived development factorinduced proliferation and migration of activated human hepatic stellate cells. Protein kinase G signaling disrupts Rac1dependent focal adhesion assembly in liver particular pericytes. Nitric oxide promotes caspaseindependent hepatic stellate cell apoptosis by way of the generation of reactive oxygen species. Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells are liable for nitric oxide modulation of resistance within the hepatic sinusoids. Mild increases in portal stress upregulate vascular endothelial progress issue and endothelial nitric oxide synthase within the intestinal microcirculatory bed, resulting in a hyperdynamic state. Impaired endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity associated with enhanced caveolin binding in experimental cirrhosis in the rat. Regulation of endothelium derived nitric oxide production by the protein kinase Akt. Reciprocal regulation of endothelial nitricoxide synthase by Ca2+calmodulin and caveolin. Atorvastatin lowers portal pressure in cirrhotic rats by inhibition of RhoA/Rhokinase and activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Intrahepatic angiogenesis and sinusoidal remodeling in persistent liver disease: new targets for the remedy of portal hypertension Thrombelastographyguided blood product use before invasive procedures in cirrhosis with severe coagulopathy: a randomized, managed trial. Existence of a plateletadhesion defect in patients with cirrhosis unbiased of hematocrit: research under flow circumstances. Measurement of portalsystemic shunting in the rat by utilizing gammalabeled microspheres. Splanchnic hemodynamics in portalhypertensive rats: measurement with gammalabeled microspheres. Hyperdynamic circulation in portalhypertensive rat model: a major issue for maintenance of continual portal hypertension. Evolution of portal hypertension and mechanisms involved in its upkeep in a rat mannequin. Hyperdynamic circulation in a persistent murine schistosomiasis model of portal hypertension. Temporal relationship of peripheral vasodilatation, plasma quantity growth and the hyperdynamic circulatory state in portalhypertensive rats. Splanchnic hyposensitivity to glypressin in a haemorrhage/transfused rat mannequin of portal hypertension: role of nitric oxide and bradykinin. Splanchnic hyposensitivity to glypressin in a hemorrhagetransfused common bile ductligated rat model of portal hypertension: position of nitric oxide and bradykinin. Vasopressin reverses mesenteric hyperemia and vasoconstrictor hyporesponsiveness in anesthetized portal hypertensive rats. Hyperdynamic circulation in portal hypertensive rats depends on central cfos gene expression. Atrophy of mesenteric sympathetic innervation might contribute to splanchnic vasodilation in rat portal hypertension. Blockage of the afferent sensitive pathway prevents sympathetic atrophy and hemodynamic alterations in rat portal hypertension. Nitric oxide synthase 3dependent vascular transforming and circulatory dysfunction in cirrhosis. In vivo angiogenesis in regular and portal hypertensive rats: role of basic fibroblast progress issue and nitric oxide. Different patterns of portasystemic shunting in cirrhosis of the liver studied by an indicator dilution method. Increased angiogenesis and permeability within the mesenteric microvasculature of rats with cirrhosis and portal hypertension: an in vivo research. Role of placental progress factor in mesenteric neoangiogenesis in a mouse model of portal hypertension. Reversal of portal hypertension and hyperdynamic splanchnic circulation by combined vascular endothelial development issue and plateletderived development issue blockade in rats.
Quality 500 mg hydreaThe diameter of fenestrations has a Gaussian distribution, which is skewed to the best by the presence of some larger pores. Very small nonperforating pores are called pits and larger pores (greater than about 300 nm diameter, depending upon the fixation and microscopy method) are known as gaps. Gaps are known to occur as a result of cellular damage, technical issues associated to excessive stress perfusion either physiologically or experimentally, hypoxia, fixation, or pathological states. Fenestrations are additionally present in meshlike, labyrinthine structures paying homage to vesiculovacuolar organelles and pored domes [13]. The diameter of fenestrations is smaller than the decision of ordinary gentle microscopy subsequently most morphological research up to now have utilized transmission and scanning electron microscopy. However, preparation of tissue for electron microscopy, notably scanning electron microscopy generates artefacts including tissue shrinkage, which has led to underestimation of the diameter of fenestrations by as a lot as a 3rd. Moreover there has been huge variability in specimen preparation and statistical methods, which has led to printed conclusions about fenestration morphology and response to interventions that can be troublesome to interpret. Standardized methods for electron microscopy and reporting of fenestrations have been proposed but not yet widely adopted [15]. At a minimum the following data ought to be supplied: the methods used to measure fenestrations; the values for the quantity, frequency, diameter, and porosity of fenestrations that had been measured; and the diameter limits used to outline fenestrations. Recent developments in microscopic methods have been utilized to fenestrations [16, 17]. The reduced thickness of the cell in regions of fenestrations and sieves plates is evident. This is most likely because of the constraints within the subject attributable to the absence of recognized markers or proteins that outline, label, or visualize fenestrations directly. Physiological role of fenestrations Fenestrations facilitate the highly efficient bidirectional transfer of substrates between the blood and hepatocytes, while preventing the entry of blood cells and enormous particulate substrates (such as platelets and chylomicrons) to the extracellular space. The fenestrated endothelium acts as a filter, hence, is usually referred to as "the liver sieve" [6, 11]. Fenestrations allow the unimpeded move of a variety of substrates (plasma and substrates within plasma, plasma proteins including albumin, smaller lipoproteins) into the extracellular house of Disse. The narrowness of hepatic endothelial cells and the dearth of basal lamina and collagen within the house of Disse be certain that any other permeability limitations to the diffusion of substrates between blood and hepatocytes are minimized. In ultrafiltration, the quantity flux (J) is described by the fR 2 P where f is the porosity of eight l the membrane, R diameter of the pores, P the pressure gradient throughout the membrane, viscosity, and l the thickness of the membrane. Fenestrations influence the hepatic uptake of lipoproteins, particularly chylomicron remnants [30, 31]. The first stage within the metabolism of lipoproteins is the manufacturing of chylomicrons which are triglyceriderich lipoproteins formed within the gut from dietary lipids. Chylomicrons are metabolized to chylomicron remnants by lipoprotein lipase present on the endothelium of systemic capillaries. Chylomicron remnants are smaller particles (30�80 nm) which have acquired apolipoprotein E (apoE). Electron microscopy has demonstrated that chylomicrons are solely found within the sinusoid whereas remnants are additionally observed in the area of Disse. There is differential trapping by the liver of radiolabeled lipoproteins of different sizes such that smaller particles are trapped to a larger extent than those larger than 100 nm [6]. Similar outcomes indicating exclusion on the basis of size have been reported for big and small liposomes and colloidal gold particles of various diameters [32, 33]. Reduction within the quantity or diameter of fenestrations ("defenestration") results in impaired clearance of chylomicron remnants after meals and, because remnants are nonetheless relatively wealthy in triglycerides, this is manifested as postprandial hypertriglyceridemia [30, 31]. Fenestrations have been proven to be a portal for the switch of several other substrates. Defenestration associated with poloxamer 407 and old age has been discovered to scale back the hepatic uptake of some medicine (paracetamol, diazepam [38, 39]) and insulin [40]. The effect of defenestration on insulin uptake in the liver is particularly significant because it offers a brand new mechanism for hepatic insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. As well as their function in substrate switch, fenestrations allow interactions between cells within the sinusoidal lumen and the cell membrane of underlying hepatocytes. Activated lymphocytes and other leukocytes accessed the liver tissue in an experimental model of autoimmune hepatitis by way of passage by way of the fenestrations and conversely defenestration virtually absolutely abolished any hepatitis [44]. Contraction of fenestrations might increase vascular resistance thereby influencing hepatic blood circulate and strain [46]. For example, an endothelin antagonist was discovered to dilate fenestrations and trigger a discount in portal perfusion stress of about 2. The area of Disse is continuous with lymphatic vessels found in the portal triads. This morphology suggests that plasma flows via the fenestrations, upstream alongside the area of Disse, lastly emptying into the lymphatic vessels across the portal vein [28]. A hydrodynamic evaluation of move within the hepatic sinusoids is in maintaining with the idea of retrograde plasma circulate alongside the area of Disse [48]. Regulation of fenestrations Fenestrations are dynamic structures that change in frequency and diameter in response to quite a few stimuli in vitro. There is commonly an inverse relationship between the results of an agent on fenestration diameter and frequency. Lipid rafts Recently a "sieveraft" hypothesis was proposed whereby fenestrations kind in nonraft membranes when the membrane stabilizing effects of the cytoskeleton and membrane rafts are diminished. Cell membranes are heterogeneous structures composed of lipid rafts (liquidordered microdomains, 10�200 nm) and nonraft, liquiddisordered regions. Lipid rafts are regions of cell membrane enriched in cholesterol, sphingolipids, and proteins that provide a platform for lots of membrane proteins. Superresolution microscopy has shown that liver sieve plates are distributed between lipid rafts within the nonraft regions. Depletion of lipid rafts (with 7ketocholesterol) increases fenestrations while depletion of nonraft membrane (with Triton X) reduces fenestrations [22, 23]. The Rho pathway, through its results on the cytoskeleton, is also concerned in regulation fenestrations. Inhibition of the Rho pathway by C3 transferase brought on discount of myosin gentle chain phosphorylation, loss and retraction of actin filaments, and led to elevated porosity and the formation of large gaps. On the other hand activating Rho with lysophosphatidic acid elevated myosin light chain phosphorylation and actin filaments and led to defenestration [60]. Nutritional factors Acute fasting increases the diameter of fenestrations while lowering their frequency [63]. Chronic reduction of food intake over a lifetime (caloric restriction) reversed agerelated loss of fenestrations [64]. In longterm feeding experiments the place mice were fed totally different ratios of macronutrients, it was discovered that each fenestration porosity and frequency have been inversely related to fat intake, while diameter was inversely associated with protein or carbohydrate consumption [65]. Overall it seems that lower quantities of food intake are associated with increased fenestrations. Cytoskeleton Liver sieve plates are supported by the actin cytoskeleton [49, 50] and a wide selection of actinbased structures concerned with the upkeep of fenestrations have been identified such because the fenestrae related cytoskeleton ring, sieve plate related cytoskeleton, fenestrae forming center, and defenestrationassociated center.
Syndromes - Too much calcium lost in the urine
- Rash with very small blisters on the hands, feet, and diaper area that may be tender or painful when pressed
- Feeding and fluids (hydration)
- Large tongue, which may fall back and block the airway
- Testing for the GALC gene defect
- Growth and development
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Wear a face mask if you have had flu symptoms, or preferably stay away from children.
Hydrea 500mg overnight deliveryUveitis and retinochoroiditis are additionally common medical signs in cats with toxoplasmosis. Gross and microscopic lesions are found in many organs but are most common within the lungs. Gross lesions in the lungs include edema and congestion, failure to collapse, and multifocal areas of firm, white to yellow, discoloration. The liver is essentially the most frequently affected abdominal organ and diffuse necrotizing hepatitis may be visible grossly. Gross lesions related to necrosis may additionally be observed in the mesenteric lymph nodes and pancreas. Transplacentally or lactogenically infected kittens will excrete oocysts, however the prepatent interval is usually three weeks or extra, because the kittens are contaminated with tachyzoites (Dubey et al. Oocysts begin to be excreted within the feces before IgM, IgG, or IgA antibodies are current in the serum (Lappin et al. Partial growth of the enteroepithelial levels happen in the intestines of immune cats, but oocyst production is prevented (Davis and Dubey, 1995). No reversion to oocyst excretion or enhance in virulence has been observed in over 200 inoculated cats. It is logical to assume that cat owners and veterinarians could be at a greater danger for Toxoplasma Gondii 6. Many research have been conducted to decide the affiliation between cat possession or cat publicity and the prevalence of T. Inhalation of oocysts stirred up within the mud by horses has been related to an outbreak of human toxoplasmosis at a using secure (Teutsch et al. Washing vegetables and fruits and carrying gloves whereas gardening are technique of preventing publicity to oocysts. Clinical toxoplasmosis in dogs is often related to immunosuppression induced by canine distemper virus an infection. Clinical indicators are often most apparent in the respiratory and hepatic methods and probably result from reactivation of latent infections (Dubey et al. Dogs are proof against experimental an infection with tissue cysts and oocysts (Lindsay et al. It is believed that canines can bring oocysts to a home after ingesting them and deposit them in or across the house once they defecate. Genotypes of feline isolates are similar to isolates from different animals in the same geographic space. Thirty % of the kits on the farm died acutely and had lesions of disseminated toxoplasmosis. An epizootic of toxoplasmosis occurred amongst a population of endangered black-footed ferrets (Mustela nigripes) at a zoo within the United States (Burns et al. Twenty-two adults and 30 kits died from acute toxoplasmosis and an additional thirteen adults died from persistent toxoplasmosis after the initial outbreak. Abortions are uncommon in most pork producing regions of the world excluding Taiwan. Undercooked pork is a source of human infection, and viable tissue cysts can stay in pork for up to 865 days (Dubey, 1988). Genotypes of pig isolates are much like isolates from other animals in the identical geographic area. The practice of feeding nonfrozen slaughter offal was blamed for acute toxoplasmosis in one report (Smielewska-Los and Turniak, 2004). However, viable tissue cysts can stay in cattle for up to 1191 days (Dubey and Thulliez, 1993). Multiple abortions can happen in a flock indicating a typical oocyst source for ewes. A vaccine to stop abortion in ewes is on the market in a number of nations (Buxton and Innes, 1995). Genotypes of sheep isolates are just like isolates from other animals in the identical geographic space. Dyspnea was the primary scientific sign and tons of tachyzoites were found in its lungs and plural exudates. Naturally occurring toxoplasmosis has not been reported in llamas, alpacas (Lama pacos), or vicunas (Lama vicugna). Multiple abortions can occur in a flock indicating a standard oocyst source for does. Genotypes of goat isolates are just like isolates from other animals in the same geographic area. None of 2094 samples from industrial chickens in retail markets from the United States contained viable T. Genotypes of chicken isolates are just like isolates from other animals in the same geographic area. The prevalence of isolation is dependent on the strategies used to raze the chickens with chickens razed outdoors having a better prevalence of infection. Genotypes of turkey isolates are similar to isolates from other animals in the same geographic space. The prevalence of isolation depends on the methods used to raze the turkeys with turkeys razed exterior having a higher prevalence of infection. Clinical indicators in zebrafish included bilateral exopthalmia, swollen abdomens, whirling swimming habits, and generalized subdermal hemorrhaging. Tachyzoites have been present in tissue sections of parasites developing in muscle, coronary heart, liver, spleen, kidney, pancreas, reproductive organs, eyes, and brain (Sanders et al. Toxoplasma gondii in Vancouver Island cougars (Felis concolor vancouverensis): serology and oocyst shedding. Molecular and bioassay-based detection of Toxoplasma gondii oocyst uptake by mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Environmental and behavioral changes could affect the publicity of an Arctic apex predator to pathogens and contaminants. Molecular and biological traits of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from wildlife in France. Toxoplasmosis in a woodchuck (Marmota monax) and two American purple squirrels (Tamiasciurus hudsonicus). Fish and reptiles can be manipulated to make Toxoplasma Gondii References 313 � Basso, W. Isolation and molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii from captive slender-tailed meerkats (Suricata suricatta) with deadly toxoplasmosis in Argentina. Toxoplasmic encephalitis in a free-ranging Rocky Mountain bighorn sheep from Washington. Disseminated toxoplasmosis in Antillean manatees (Trichechus manatus manatus) from Puerto Rico. Toxoplasmosis in IndoPacific humpbacked dolphins (Sousa chinensis), from Queensland.
Best 500 mg hydreaCongenital toxoplasmosis in the Balb/c mouse: prevention of vertical illness transmission and foetal dying by vaccination. Comparative exercise of a quantity of antibiotics towards Toxoplasma gondii in a mouse model. In vitro and in vivo activities of roxithromycin in combination with pyrimethamine or sulphadiazine against Toxoplasma gondii. In vitro and in vivo results of rifabutin alone or mixed with atovaquone against Toxoplasma gondii. Bioluminescence imaging of Toxoplasma gondii infection in dwelling mice reveals Toxoplasma Gondii References 363 dramatic variations between strains. Interferon consensus sequence binding protein-deficient mice display impaired resistance to intracellular an infection due to a major defect in interleukin 12 p40 induction. Atovaquone nanosuspensions show glorious therapeutic effect in a model new murine model of reactivated toxoplasmosis. Congenital toxoplasmosis: an experimental study in rhesus monkeys for transmission and prenatal analysis. Pharmacokinetics of spiramycin within the rhesus monkey: transplacental passage and distribution in tissue in the foetus. Effectiveness of spiramycin for remedy of congenital Toxoplasma gondii infection in rhesus monkeys. Study of therapy of congenital Toxoplasma gondii infection in rhesus monkeys with pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine. A thiazole spinoff of artemisinin moderately reduces Toxoplasma gondii cyst burden in contaminated mice. A new combined flow-cytometry-based assay reveals glorious exercise towards Toxoplasma gondii and low toxicity of latest bisphosphonates in vitro and in vivo. The position of apolipoprotein E in uptake of atovaquone into the brain in murine acute and reactivated toxoplasmosis. Assessment of the activity of atovaquone-loaded nanocapsules within the therapy of acute and continual murine toxoplasmosis. Modification of subclinical toxoplasmosis in mice by cortisone, 6mercaptopurine and splenectomy. Effect of immunosuppressive drug regimens on acute and chronic murine toxoplasmosis. A gene(s) within the H-2D region determines the event of toxoplasmic encephalitis in mice. Toxoplasma animal fashions and therapeutics improvement of toxoplasmic encephalitis in mice. Genetic resistance in opposition to acute toxoplasmosis depends on the pressure of Toxoplasma gondii. Immune response in a murine mannequin of congenital toxoplasmosis: increased susceptibility of pregnant mice and transplacental passage of Toxoplasma gondii are sort 2-dependent. Vertical transmission and fetal harm in animal models of congenital toxoplasmosis: a systematic evaluate. Mouse model of congenital infection with a non-virulent Toxoplasma gondii strain: vertical transmission, "sterile" fetal damage, or each Toxoplasma gondii: the results of an infection at completely different phases of pregnancy on the offspring of mice. Toxoplasma gondii: induction of toxoplasmic encephalitis in mice with continual an infection by inoculation of a murine leukemia virus inducing immunodeficiency. Systematic review and meta-analysis of variation in Toxoplasma gondii cyst burden in the murine model. Pyrimethamine concentrations in serum throughout treatment of acute murine experimental toxoplasmosis. Communication: investigations on the query of placental transmission of Toxoplasma in immunised pregnant animals. In vivo activities of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase inhibitors against Toxoplasma Gondii References 365 Leishmania donovani and Toxoplasma gondii. Rat mannequin of congenital toxoplasmosis: rate of transmission of three Toxoplasma gondii strains to foetuses and protective impact of a persistent an infection. Toxoplasma gondii: kinetics of the dissemination in the host tissues throughout acute part of infection of mice and rats. Protective immunity within the rat mannequin of congenital toxoplasmosis and the potential of excreted-secreted antigens as vaccine components. Lipid metabolism within the parasite is crucial for the manufacturing of infectious progeny, sign transduction for proper interactions with mammalian cells, and the long-term persistence in the host. Among lipids, glycero(phospho)lipids, sterols, and sphingolipids are major constructing blocks of biological membranes, whose composition and homeostasis outline the physical properties and capabilities of the compartment the place they reside. Other lipids, particularly fatty acids and phosphatidic acid, are important signal transducers involved in a quantity of mobile and metabolic pathways. Bioinformatic tools, for instance, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes framework have delineated the metabolic maps for lipid synthesis in T. In addition, current lipidomic and fluxomic approaches have unveiled that some phospholipid species have a combined composition, containing one fatty acyl chain synthesized by the parasite and the other one coming from the host cell on account of scavenging actions. Toxoplasma has also uncommon lipid molecular species that can function signatures, indicating the presence of unique biosynthetic enzymes and translocators/transporters for lipid acquisition. Biochemistry and metabolism of Toxoplasma gondii: lipid synthesis and uptake organelle has highlighted that the parasite synthesizes prokaryotic-like lipids which may be essential for its survival. This raises the prospect that lipid homeostatic, trafficking, and reworking pathways in the parasite may abound in potential drug targets. As a major instance, fatty acid biosynthetic pathways are being successfully exploited as antimicrobial targets towards Toxoplasma infections. This article summarizes the completely different classes of lipids present in Toxoplasma, because of biosynthesis in the parasite and/or salvage from the host cell. In addition to being the hydrophobic constructing blocks of membrane lipids, fatty acids are important vitality storage molecules, and fatty acyl derivatives possess quite a lot of physiological capabilities, together with posttranslational modification of numerous proteins. The elementary strategy of fatty acid biosynthesis is very conserved among species and includes main metabolites in the central carbon metabolism as substrates, including acetyl-CoA. The central feature of the pathway is the sequential extension of an alkanoic chain, two carbons at a time, by a series of decarboxylative condensation reactions. This course of is usually initiated with the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to yield malonyl-CoA (Smith et al. In distinction, bacteria, algae, plants, organisms bearing chloroplast-like organelles including Apicomplexa, most mitochondria, and a few decrease eukaryotes categorical multiple enzymes that act as one complex from a prokaryotic origin (White et al. In these completely different environments the parasite should encounter totally different dietary and metabolic challenges.

Purchase hydrea 500mg with visaHedgehog signaling is critical for regular liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice. The age associated decline of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta performs a crucial position within the inhibition of liver regeneration. P2Y2 purinergic receptor activation is important for environment friendly hepatocyte proliferation in response to partial hepatectomy. Promotion of liver regeneration by natural killer cells in a murine mannequin relies on extracellular adenosine triphosphate phosphohydrolysis. Differential regulation of urokinasetype plasminogen activator expression by fluid shear stress in human coronary artery endothelial cells. Presence of urokinase in serumfree major rat hepatocyte cultures and its position in activating hepatocyte progress issue. Role and regulation of p65/betacatenin affiliation during liver damage and regeneration: a "complex" relationship. Differential expression and distribution of focal adhesion and cell adhesion molecules in rat hepatocyte differentiation. Liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy: important evaluation of mechanistic dilemmas. Conditional genetic elimination of hepatocyte growth factor in mice compromises liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors direct Cell, fate during most cancers growth. Protooncogenes and progress factors related to normal and abnormal liver progress. Kinetics of hepatocellular proliferation as a operate of the microvascular structure and practical state of the liver. A transgenic mouse marking reside replicating Cell,s reveals in vivo transcriptional program of proliferation. Disruption of hepatic adipogenesis is related to impaired liver regeneration in mice (see comment). Caveolin1 orchestrates the balance between glucose and lipiddependent power metabolism: implications for liver regeneration. Suppression of autophagy throughout liver regeneration impairs vitality cost and hepatocyte senescence in mice. Prediction and validation of cell alignment alongside microvessels as order principle to restore tissue structure in liver regeneration. Gene expression within the liver remnant is considerably affected by the dimensions of partial hepatectomy: an experimental rat study. Spatiotemporal expression of angiogenesis progress factor receptors during the revascularization of regenerating rat liver. Liverspecific ablation of integrin linked kinase in mice leads to abnormal histology, enhanced cell proliferation, and hepatomegaly. Platelets prime hematopoietic and vascular niche to drive angiocrinemediated liver regeneration. Capacity of regeneration in liver epithelia of juvenile, repeated partially hepatectomized rats. Independent and overlapping transcriptional activation during liver growth and regeneration in mice. Transcriptional regulatory alerts define cytokinedependent and impartial pathways in liver regeneration. Growth factor sign transduction instantly after twothirds partial hepatectomy within the rat. Increased levels of forkhead box M1B transcription factor in transgenic mouse hepatocytes stop agerelated proliferation defects in regenerating liver. Rapid hepatocyte nuclear translocation of the Forkhead Box M1B (FoxM1B) transcription issue brought on a transient increase in dimension of regenerating transgenic hepatocytes. Sinusoidal ultrastructure evaluated through the revascularization of regenerating rat liver. Ito cells, stellate cells, and myofibroblasts: new actors in antigen presentation. Proliferation of mononuclear phagocytes (Kupffer cells) and endothelial cells in regenerating rat liver. Contribution of bone marrow cells to liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in mice. Distinct development and capabilities of resident and recruited liver Kupffer cells/macrophages. Hepatic expression of mature transforming development factor beta 1 in transgenic mice results in multiple tissue lesions. Transcriptomic and genomic evaluation of human hepatocellular carcinomas and hepatoblastomas. Suppression of liver regeneration and hepatocyte proliferation in hepatocytetargeted glypican three transgenic mice. Leukocytespecific protein 1: a novel regulator of hepatocellular proliferation and migration deleted in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Combined systemic disruption of MeT and epidermal progress issue receptor signaling causes liver failure in normal mice. The processing and utilization of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor following partial hepatectomy within the rat. Studies on the proliferation and destiny of oval cells within the liver of rats handled with 2 acetylaminofluorene and partial hepatectomy. Proliferation, apoptosis, and induction of hepatic transcription components are characteristics of the early response of biliary epithelial (oval) cells to chemical carcinogens. Bile ductular damage induced by methylene dianiline inhibits oval cell activation. Mechanisms of hepatocyte development factormediated and epidermal development factormediated signaling in transdifferentiation of rat hepatocytes to biliary epithelium. Hepatocytes, somewhat than cholangiocytes, could be the major supply of primitive ductules within the chronically injured mouse liver. Notch signaling regulates formation of the threedimensional architecture of intrahepatic bile ducts in mice. Preexisting epithelial diversity in regular human livers: a tissuetethered cytometric analysis in portal/periportal epithelial cells. Hepatic oval cell activation in response to injury following chemically induced periportal or pericentral damage in rats. Carbon tetrachloride toxicity as a model for studying freeradical mediated liver damage. Proregenerative signaling after acetaminopheninduced acute liver damage in mice recognized utilizing a novel incremental dose model. Dual position of epidermal growth factor receptor in liver injury and regeneration after acetaminophen overdose in mice. The streaming liver: can the age of a hepatocyte be determined from its place on the portohepatic radius Continuous cell provide from a Sox9expressing progenitor zone in grownup liver, exocrine pancreas and gut.

Trusted 500 mg hydreaExtracellular vesicles from mice with alcoholic liver disease carry a definite protein cargo and induce macrophage activation by way of warmth shock protein ninety. The role of immune mechanisms in alcoholic and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a 2015 update. Highthroughput Tcell receptor sequencing across persistent liver ailments reveals distinct diseaseassociated repertoires. Invariant pure killer T cells contribute to chronicplusbinge ethanolmediated liver damage by selling hepatic neutrophil infiltration. Mucosaassociated invariant T cells hyperlink intestinal immunity with antibacterial immune defects in alcoholic liver illness. Keratins: Biomarkers and modulators of apoptotic and necrotic cell dying in the liver. Systematic evaluation: pentoxifylline for the treatment of extreme alcoholic hepatitis. Hepatoprotective and antifibrotic capabilities of interleukin22:therapeutic potential for the remedy of alcoholic liver illness. Alcohol, adipose tissue and liver disease: mechanistic hyperlinks and medical issues. Chronic alcohol publicity stimulates adipose tissue lipolysis in mice: position of reverse triglyceride transport in the pathogenesis of alcoholic steatosis. Identification of a cytochrome P4502E1/Bid/C1qdependent axis mediating inflammation in adipose tissue after continual ethanol feeding to mice. Linking pathogenic mechanisms of alcoholic liver illness with clinical phenotypes. Systemic inflammatory response and serum lipopolysaccharide ranges predict a number of organ failure and demise in alcoholic hepatitis. Infection in sufferers with extreme alcoholic hepatitis treated with steroids: early response to therapy is the key factor. Abrogation of the antifibrotic effects of pure killer cells/interferongamma contributes to alcohol acceleration of liver fibrosis. Intestinal microbiota contributes to particular person susceptibility to alcoholic liver illness. Epigenetic regulation of hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways within the ethanolfed cystathionine beta synthasedeficient mouse. Allostatic view of motivation: implications for psychopathology, in Motivational Factors within the Etiology of Drug Abuse, (eds. Neurocircuitry of alcohol habit: synthesis from animal fashions, in Alcohol and the Nervous System (eds. Oral alcohol selfadministration stimulates dopamine launch within the rat nucleus accumbens: genetic and motivational determinants. Striatonigrostriatal pathways in primates type an ascending spiral from the shell to the dorsolateral striatum. Profound decrement of mesolimbic dopaminergic neuronal exercise throughout ethanol withdrawal syndrome in rats: electrophysiological and biochemical evidence. New views in basal forebrain group of special relevance for neuropsychiatric problems: the striatopallidal, amygdaloid, and corticopetal components of substantia innominata. Corticotropin releasing factor induced amygdala gammaaminobutyric acid launch performs a key position in alcohol dependence. Alcohol dependence conceptualized as a stress disorder, in: Oxford Handbook of Stress and Mental Health, (eds. Alcohol selfadministration acutely stimulates the hypothalamicpituitaryadrenal axis, but alcohol dependence leads to a dampened neuroendocrine state. Herpes simplex virus mediated gene switch as a device for neuropsychiatric analysis. Neurobiology of addiction, in Textbook of Substance Abuse Treatment, 5th edn, (eds. Endocannabinoid affect in drug reinforcement, dependence and addictionrelated behaviors. Metaanalytic evidence for a superordinate cognitive management community subserving numerous government features. Brain activation throughout longing for alcohol measured by positron emission tomography. Factors modulating neural reactivity to drug cues in habit: a survey of human neuroimaging studies. Determinants of relapse: implications for the upkeep of behavioral change, in Behavioral Medicine: Changing Health Lifestyles, (eds. Neural mechanisms underlying the vulnerability to develop compulsive drugseeking habits and habit. Impulsivity resulting from frontostriatal dysfunction in drug abuse: implications for the management of conduct by reward associated stimuli. Reduction of alcohol consumption by temporary alcohol intervention in main care: systematic evaluation and metaanalysis. Efficacy of psychosocial interventions in inducing and sustaining alcohol abstinence in patients with chronic liver disease: a scientific evaluation. New developments for the pharmacological treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Baclofen in the remedy of alcohol dependence with or with out liver illness: multisite, randomised, doubleblind, placebocontrolled trial. Pharmacotherapy for adults with alcohol use problems in outpatient settings: a systematic evaluation and metaanalysis. Most medication have a novel signature which could be decided by calculating the Rvalue. Druginduced hepatitis, when accompanied by jaundice, results in 10% mortality without transplant. Although mother or father drug accumulation might participate, often toxic intermediates the Liver: Biology and Pathobiology, Sixth Edition. The metabolism of medication can lead to the formation of intermediates which generate haptenicpeptide antigens. This affiliation strongly suggests a genetically determined immune predisposition in sure individuals leading to an adaptive immune response directed at drug hapten or modified autoantigens. This led to the development of the antidote, Nacetylcysteine (Mucomyst), which provides cysteine to the liver and is very effective if administered inside 10 hours of overdose in humans and 1. These adducts have been shown by immunoblot analysis to originate from the liver [15]. Furthermore, the development of the nitrated proteins in hepatocytes correlated with the necrotic cell dying [20]. A liver biopsy could be useful if eosinophilic infiltrates, granulomas, or centrilobular necrosis is noted. For instance, certain drugs similar to halothane, dihydralazine, and anticonvulsants are associated with an allergic type hypersensitivity and current with rash and eosinophilia. Other notable drugs that have been reported to current with rash and eosinophilia embody: trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, cefazolin, and ciprofloxacin [39].
Discount hydrea 500 mg onlineFurther discussion relating to mind manganese deposition in cirrhosis seems in the Manganese section of the current chapter. These adjustments occur in distinct mind buildings and have been attributed to a spectrum of numerous pathophysiologic mechanisms. The neuropathological and clinical characteristics of those neurodegenerative problems are summarized in the following sections. The neuropathology consists of spongiform degeneration in deep cerebrocortical layers in addition to in basal ganglia buildings, cerebellum, and subcortical white matter. Patients with cirrhosis generally develop intra and extrahepatic portalsystemic shunts and this shunting combined with the lack of metabolic capability of hepatocytes results in impaired elimination of ammonia and consequent hyperammonemia. These studies went on to show that, opposite to earlier reviews, this increase of brain ammonia in sufferers with cirrhosis was primarily a consequence of increased arterial blood concentrations quite than to altered kinetics of blood�brain switch of ammonia. Gutderived ammonia is normally removed as urea (periportal hepatocytes) or glutamine (perivenous hepatocytes). In distinction, skeletal muscle becomes the principal route for ammonia elimination due to posttranslational improve within the enzyme glutamine synthetase. This mechanism is covered in larger detail within the section on Inhibitory neurotransmission of the present chapter. In a landmark study of fifty one patients with cirrhosis who were listed for liver transplantation and have been assessed prospectively over a oneyear interval, 11 sufferers (21. Neurological symptoms included a symmetric akineticrigid syndrome, tremor, stooped posture, and gait impairment with rapid development over months [16]. Alternative checks with less dependency on unimpaired motor efficiency can be found. The trail of evidence consists of the next: glutamate is the principal excitatory neurotransmitter of mammalian brain and the termination of its action relies on transport into surrounding astrocytes by way of particular transporters. Both ammonia and manganese have been proven to inhibit these transporters resulting in an extra of glutamate in the synaptic cleft resulting in hyperexcitability and activation of postsynaptic glutamate receptors. Microglial activation appears to be a comparatively early occurrence in sufferers with decompensated cirrhosis. Factors other than ammonia and manganese which are increased in mind in liver failure also have the potential to elicit a neuroinflammatory response. Not surprisingly, decreased brain glucose uptake in these sufferers was correlated with impaired efficiency on psychometric testing. However, the character and pathological traits of the brain edema in the two circumstances are fairly distinct. However, it has the potential to end in impairments of cell�cell signalling and to cause malfunction of astrocytic proteins. This results in inhibition of central neurotransmission by diminishing the prospect that an action potential happens. In all cases, these parameters were discovered to be current in normal quantities in animal fashions of acute and chronic liver failure and, extra importantly, in autopsied brain tissue from sufferers with decompensated cirrhosis who died in hepatic coma [46]. No important alterations of binding web site affinities or densities of these sites had been observed when compared to knowledge from agematched management material [46]. Quantitative mass spectrometric analysis adopted to unequivocally establish the identity of those substances. They have been recognized as wellestablished pharmaceutical benzodiazepines or their metabolites [48] that had been traced to their administration as muscle relaxants during prior endoscopic workup or as sedatives. Nutritional management the pathogenesis of malnutrition in liver illness is advanced and multifactorial involving reduction of dietary consumption as a result of anorexia and dietary restriction, alterations of nutrient biosynthesis, impaired intestinal absorption, disturbances of substrate utilization, elevated protein loss, and abnormal metabolism resulting from, for instance, the proinflammatory state. The practical integrity of the liver is crucial for the availability, interorgan switch, and metabolism of important vitamins. Sarcopenia or loss of muscle mass is usually encountered in cirrhosis where it has antagonistic results on survival, healthrelated quality of life, as properly as outcome following liver transplantation [51]. The acknowledged aims of nutritional management in sufferers with cirrhosis include the correction of specific dietary deficiencies, prevention and remedy of the issues of cirrhosis as properly as the complications of liver transplantation, and the support of liver regeneration. Energy necessities of 35�45 kcal g-1 every day are beneficial for sufferers with cirrhosis with small meals evenly distributed throughout the day and a latenight snack of complex carbohydrates to reduce protein utilization. The follow of dietary protein restriction that was prevalent till the late Nineteen Nineties [54] has now been widely discontinued following the report [55] that patients with cirrhosis benefit from normal protein (1. Diets wealthy in vegetable and dairy protein are encouraged and sufferers illiberal to dietary protein could contemplate branched chain amino acid supplements as a substitute for protein [53]. Vitamin deficiencies in cirrhosis end result from impaired hepatic operate and diminished hepatic reserves in addition to inadequate dietary intake and malabsorption. The B1 deficiency in these sufferers was attributed to a loss of hepatic stores of the vitamin and the prevalence of lesions was threefold greater than that reported in materials from nonliver illness controls. It was beneficial that B1 supplements be administered to all sufferers with decompensated cirrhosis significantly these with alcoholic etiology [51]. It has been suggested that malnutrition is a factor that increases both prices and posttransplant complications [57]. Neurological problems post transplantation are numerous and may embrace diffuse encephalopathy, seizures, intracranial hemorrhage, stroke, progressive neurological deterioration, central pontine myelinolysis, ataxia, psychosis, confabulation, and peripheral neuropathy. While a few of these problems doubtless end result from particular dietary and metabolic deficits alluded to above, further research are required to determine the precise nutritional factors implicated and facilitate specific dietary recommendations. Several remedies aimed at decreasing the manufacturing of ammonia and/or its removing have been found to be efficient on this regard. Nonabsorbable disaccharides Nonabsorbable disaccharides such as lactulose and lactitol remain firstline brokers for the decreasing of the production and absorption of ammonia. They are metabolized by bacteria within the colon with manufacturing of acetic and lactic acids and the consequent acidification of the colon creates a hostile setting for ureaserich intestinal bacteria which are answerable for the production of ammonia. In an evaluation of ten research, it was concluded that there was inadequate proof to suggest them for traditional remedy till they had been proven to confer profit over placebo [59]. Suggested mechanisms embody useful effects on their use as substrates for hepatic protein synthesis in addition to stimulation of liver regeneration and will increase of cerebral perfusion. Benzoate, phenylacetate Benzoate and phenylacetate are agents that have been used extensively for the reducing of blood ammonia in children with congenital urea cycle problems. Phenylacetate condenses with glutamine to form phenylacetyl glutamine whereas benzoate condenses with glycine to form hippurate. The ammonialowering action outcomes from removing of these ammoniagenic substrates in addition to the diversion of accessible ammonia for the replenishment of the amino acid pools. Modifications of the gut microflora steadiness by the introduction of bacteria that compete with those expressing urease (probiotics) are effective ammonialowering agents. The diploma of improvement was equivalent to that of lactulose [68] or rifaximin [69]. Lcarnitine Lcarnitine has been shown to manifest a significant protecting effect in patients with cirrhosis and ammoniaprecipitated encephalopathy [82].
References - doi:10.2164/jandrol.110.012013.
- Zhang VY, Westphalen A: The role of metabolic imaging in radiation therapy of prostate cancer, NMR Biomed 27(1):100-111, 2014.
- Damgaard IN, Jensen TK: Nordic Cryptorchidism Study Group. Risk factors for congenital cryptorchidism in a prospective birth cohort study, PLoS ONE 3(8):e3051, 2008.
|
|