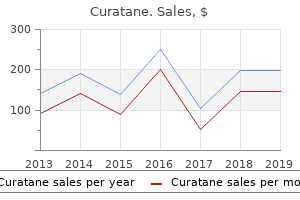
"Discount 20 mg curatane mastercard, acne 3 weeks pregnant."By: Noreen A Hynes, M.D., M.P.H. - Director, Geographic Medicine Center of the Division of Infectious Diseases
- Associate Professor of Medicine
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/0010761/noreen-hynes
Cheap curatane online master cardUsually this can be a single greatest agent, but generally combos of antimicrobials which have completely different modes of motion are used for enhanced impact. The major indications for mixtures are to cut back the probability of emergence of resistance (which is necessary in continual infections like tuberculosis and lung infections in cystic fibrosis), and profiting from recognized synergy between two antimicrobials. The risk for the individual affected person: subsequent infection with a special, extra resistant organism. After many years of expertise, the indications for antimicrobial prophylaxis have been narrowed to a small number of conditions during which antimicrobials have been proven to decrease transmission during a interval of excessive threat. For example, individuals known to have been uncovered to highly infectious and virulent pathogens like N meningitidis (meningitis), Bacillus anthracis (anthrax), or Yersinia pestis (plague) can abort an an infection during the incubation interval by the administration of ciprofloxacin. Prophylaxis also can cut back the danger of endogenous an infection associated with sure surgical and dental procedures if given through the process. Minimize the danger of passing resistance genes to M bystander bacteria by keeping drug-resistant pathogens away from other patients-and yourself. Clean hands earlier than and after each encounter, obey other particular precaution protocols, and keep a clear examination area or hospital room. Encourage patients to "get sensible" about antibiotics, treat their signs, and emphasize the importance of sustaining the effectiveness of antimicrobials if they need to eventually require them. If broad-spectrum empiric treatment was initiated for extreme an infection, be willing to trust the outcomes of constructive cultures and focus therapy. In truth, narrower spectrum brokers are often extra bactericidal-and cause much less collateral harm to useful commensal microbiota-than broad-spectrum medication. Using the briefest period of remedy possible could cut back selecS tive stress on bystander, regular microbes. Subtherapeutic doses or intermittent, haphazard administration are unhealthy apply, however treating at a full dose for a brief period might have advantages for resistance-so lengthy because the underlying infection has been adequately handled. Medicine are C at all times desperate to work with other physicians, both to generate protocols and to care for specific sufferers. Staphylococci Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epidermidis Thou artwork a boil, A plague sore, an embossed carbuncle In my corrupted blood. Infections produced by Staphyloccocus aureus are typified by acute, aggressive, regionally damaging purulent lesions. The most familiar of these is the widespread boil, a painful lump in the pores and skin that has a necrotic heart and fibrous reactive shell. Infections in organs aside from the skin such because the lung, kidney, or bone are additionally focal and damaging, however have higher potential for extension throughout the organ and beyond to the blood and other organs. Such infections usually produce high fever and systemic toxicity and could additionally be fatal in only a few days. The main virulence elements for these results are floor attachment proteins, fibrinogen-binding proteins, and a pore-forming exotoxin. A subgroup (less than 10%) of S aureus infections has manifestations produced by secreted toxins in addition to those related to the first infection. Ingestion of preformed staphylococcal enterotoxin causes a form of meals poisoning by which vomiting begins in only some hours. Staphylococcus epidermidis and different non-aureus species produce much less aggressive illness typically associated with biofilm-mediated attachment to medical devices such as indwelling catheters and biomedical implants like heart valves and artificial joints. More than one dozen species of staphylococci colonize people; of these, S aureus is by far probably the most virulent. The capacity of S aureus to form coagulase separates it from other, much less virulent species (Table 24�1). Gram stain displaying the gram-positive cocci in clusters resembling bunches of grapes (arrows) and neutrophils (arrowhead). The peptidoglycan of the cell wall is commonly overlaid with polysaccharide and floor proteins. Another protein, floor protein A (SpA), is exclusive in that it binds the Fc portion of IgG molecules, leaving the antigen-reacting Fab portion directed externally (turned around). The most necessary laboratory check used to distinguish S aureus from different staphylococci is the production of coagulase, an enzyme which binds prothrombin in a fashion that provides for the cleavage of fibrinogen to fibrin. It is demonstrated by incubating staphylococci in plasma; this produces a fibrin clot in a few hours. This action is just like streptolysin O, complement, and the effector proteins of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. It causes tissue necrosis however until lately was present in only a small portion of clinical isolates (less than 10%). It binds to a selected cell membrane ganglioside discovered solely within the stratum granulosum of the keratinized epidermis of the pores and skin. There it causes intercellular splitting of the epidermis between the stratum spinosum and stratum granulosum, presumably by disruption of intercellular junctions. The toxin itself is a protease which acts on desmosomes important to interkeratinocyte adhesion. This process not solely bypasses the specificity of antigen processing however ends in huge cytokine launch due to the flexibility of these superantigens to activate up to 20% of the total T-cell pool. Once fashioned, these toxins are quite steady, retaining exercise even after boiling or publicity to gastric and jejunal enzymes. In addition to their superantigen actions, they appear to act by stimulating reflexes within the abdominal viscera, which are transmitted to medullary emetic centers in the mind stem via the vagus nerve. He has simply chosen two prototype staphylococcal lesions (boil, carbuncle) as the vilest of symbols to characterize his ungrateful daughters and his remedy at their arms. Today, in any hospital on the planet S aureus nonetheless heads the list of pathogens isolated from the bloodstream of seriously unwell patients. Ten to thirty % of the inhabitants carry the organism at this website at any given time, and charges among hospital personnel and sufferers could also be a lot higher. Most S aureus infections acquired locally are autoinfections with strains that the topic has been carrying within the anterior nares, on the pores and skin, or each. Does a doctor colonized with S aureus have to suspend practice and/or be handled The supply of an infection is mostly endogenous from colonized anterior nares or by direct contact with someone carrying Staphylococcus aureus. This evidence might be bacteriophage typing, molecular testing, or a particular antimicrobial resistance profile. Unlike many pathogenic bacteria, S aureus can survive durations of drying; for instance, recurrent pores and skin infections may result from use of clothing contaminated with pus from a previous infection. The source of the outbreak could additionally be a patient with an overt or unapparent staphylococcal infection (eg, decubitus ulcer), which is then spread directly to other sufferers on the palms of hospital personnel. A nasal or perineal provider amongst medical, nursing, or different hospital personnel can also be the supply of an outbreak, especially when carriage is heavy and numerous organisms are disseminated. The most hazardous source is a medical attendant who works regardless of having a staphylococcal lesion corresponding to a boil. Staphylococcal food poisoning is amongst the most common foodborne sicknesses on the planet. It has been an unhappy and embarrassing sequel to innumerable group picnics and wedding receptions in which gastronomic delicacies have been exposed to temperatures that allow bacterial multiplication.
Buy genuine curatane lineAlthough that is useful in eliminating the dominant inhabitants of trypanosomes current, one other wave of parasites arises because of antigenic variation. Antibodies, if current in excessive sufficient focus, can neutralize sporozoites and merozoites of malaria, thereby preventing them from invading their goal host cells, hepatocytes, and pink blood cells. Antibody technology against malarial sporozoites using attenuated and recombinant vaccines is at present undergoing a quantity of pilot medical trials in developing countries where malaria is endemic. In fact, many protozoan parasites have evolved mechanisms to avoid complement-mediated killing. On invasion of tissue, many helminths, and the schistosomes particularly, stimulate the manufacturing of IgE, the Fc portion of which binds to mast cells and basophils. Interaction of the antibody with parasitic antigen triggers the release of histamine and other mediators from the connected cells. These could injure the worm immediately or, by increasing vascular permeability and stimulating the discharge of chemotactic elements, may result in the accumulation of different cells and IgE antibodies able to initiating antibody-dependent, cell-mediated destruction of the parasite. Skin lesion biopsies show the presence of lymphocytes and macrophages working in synergy to include parasites. Activated macrophages are fairly able to destroying engulfed leishmanial parasites. However, defects in this kind of cooperation can be seen in leishmanial infections that end in mucocutaneal leishmaniasis. Lesions containing these parasites contain plenty of macrophages, however few or no lymphocytes. Collectively, all of the cytokines have been proven to have varying roles for protecting responses in toxoplasmosis, malaria, Chagas illness, and leishmaniasis. Many cellular responses also work in consort with antibody responses to help in modulating parasitic infections. Such interactions lead to inflammatory responses that are the results of antigen signaling through the Peyer patches, motion of cells to mesenteric lymph nodes, and clonal enlargement of each T and B cells that migrate back to the intestinal epithelium to promote inflammatory responses that depend on both antibody and cell-mediated constituents. The entire concept of inflammation in this occasion is to produce an surroundings inhospitable for the worms, or to induce worm expulsion as in the case of Trichinella. The strategies used vary considerably and allow the parasite to successfully propagate and spread to different hosts. If immune responses had been fully profitable in eliminating parasites, parasites would now not be an issue. Several Protozoa are shielded from the host defenses by advantage of their intracellular location. Some have even discovered methods to keep away from or survive the usually lethal environment of the macrophage, a first-line protection cell normally intent on destroying pathogens it encounters. Trypanosoma cruzi, for example, escapes from phagosomes into the cytoplasm early throughout host infection. Toxoplasma gondii inhibits the fusion of phagosomes with lysosomes, thus preventing phagolysosome formation. Leishmania species, capable of neither of these feats, are resistant to the motion of lysosomal enzymes and survive in macrophage phagolysosomes. Once macrophages have been activated to enough levels; however, the tables are somewhat turned on these parasites. In the examples given above, T cruzi and T gondii have alternate mechanisms for escaping host responses. They achieve this by becoming intracellular in cell types not normally concerned in immune responsiveness. The gut lumen is probably the largest immunologic sanctuary within the body, as a result of, except the integrity of the intestinal mucosa is breached by injury or irritation, this barrier protects lumen-dwelling parasites, a lot of which are surrounded by a protecting tegument, or cuticle, from a lot of the efficient humoral and mobile immune mechanisms of the host, permitting survival and the chance to reproduce. Most immune effector mechanisms are directed in opposition to the surface antigens of the parasite, and alteration of these antigens could blunt the immunologic attack. Many parasites undergo developmental changes inside their hosts which may be usually accompanied by alterations in floor antigens. Immune responses directed at an early developmental stage could also be totally ineffective towards a later stage of the same parasite. Such stage-specific immunity is very evident in malaria because different life cycle phases express completely different antigens and even give rise to various varieties of responses. The issue of stage-specific immunity in malaria is further compounded by species-specific immunity. Even more intriguing is the flexibility of some parasites to range the antigenic traits of a single developmental stage. The trypanosomes that cause African sleeping sickness flow into within the bloodstream coated with a thick glycoprotein surface coat. The improvement of humoral antibody to this coating ends in the elimination of parasites from the blood expressing the dominant floor coat. However, inside this dominant inhabitants of parasites are a few that have undergone antigenic variation and produced a new variant floor glycoprotein coat. This less dominant inhabitants gives rise to the following dominant population and this process repeats itself again and again. The expression of particular person genes from this large genetic repertoire is managed by the sequential transfer of a duplicate copy of every gene to an area of the parasite genome liable for gene expression. Continued antigenic variation, sadly, causes host immunosuppression with attendant penalties. Several protozoan and helminthic pathogens are thought to be able to neutralizing antibody-mediated assault by shedding and, later, regenerating particular surface antigens. Tapeworm larvae produce anticomplementary chemical substances, and T cruzi splits the Fc element of hooked up antibodies, rendering it incapable of activating complement. Several Protozoa, most notably T brucei species that are answerable for African sleeping illness, induce polyclonal B-cell activation leading to the production of nonspecific immunoglobulins and eventual exhaustion of the antibody-producing capacity of the host. Patients with disseminated leishmaniasis show a selected incapability to mount a cellular immune response to parasitic antigens within the absence of evidence of generalized immunosuppression. Finally, the thick, tough cuticle of many adult helminths renders them impervious to immune effector mechanisms designed to deal with the less sturdy microbes. In addition, personnel could also be poorly skilled to adequately diagnose these infections. The continuous arrival of travelers and immigrants from endemic areas, and the reality that parasitic infections may at times be life threatening, necessitates consideration of these diseases in differential diagnoses. It is incumbent upon the doctor to ask questions associated to travel history, food and liquid intake, actions, publicity to biting bugs, and so forth, to elevate the possibility that the person might have acquired a parasitic illness. Typically, prognosis rests on the demonstration and morphologic identification of the parasite or its progeny within the stool, urine, sputum, blood, or tissues of the human host. Eosinophilia has been recognized as an necessary clue to the prognosis of parasitic illness. Eosinophilia, which presumably displays an immunologic response to the complicated foreign proteins possessed by worms, is most marked throughout tissue migration. This could involve focus procedures such as floatation or sedimentation, followed by a wet mount or stained smear, or both, of the stool pattern.
Diseases - Anotia
- Inhalant abuse, haloalkanes
- Vocal cord dysfunction familial
- Coproporhyria
- Bowing congenital short bones
- Split hand urinary anomalies spina bifida
- Acne rosacea
Discount 20 mg curatane mastercardFailure of this side of the immune response is the first purpose for many instances of progressive Legionnaires disease within the immunocompromised. Chills, pleuritic chest pain, vomiting, diarrhea, confusion, and delirium all could also be seen. Radiologically, patchy or interstitial infiltrates with a tendency to progress towards nodular consolidation are present unilaterally or bilaterally. In the more serious circumstances, the patient turns into progressively sick and toxic over the primary 3 to 6 days, and the disease terminates in shock, respiratory failure, or both. The general mortality fee is about 15%, nevertheless it has been greater than 50% in some hospital outbreaks. Mortality is particularly high in sufferers with critical underlying disease or suppression of cell-mediated immunity. A less frequent form of disease referred to as Pontiac fever (named for a 1968 Michigan outbreak), is a nonpneumonic sickness that resembles influenza with fever, myalgia, dry cough, and a short incubation interval (6-48 hours). Pontiac fever is a self-limiting sickness and should characterize a response to endotoxin or hypersensitivity to components of the Legionella or their protozoan hosts. For this function, a high-quality specimen corresponding to lung aspirates, bronchoalveolar lavage, or biopsies are most well-liked, as a end result of the organism may not be found in sputum. These conjugates use monoclonal antibodies, which bind to all serogroups of L pneumophila, but not the non-L pneumophila species. The primary barrier to making these methods extra widely used is that Legionnaires illness is rare besides in immunocompromised populations. This tends to limit their availability to reference laboratories and hospitals serving immunocompromised sufferers. Demonstrating a major rise in serum antibody is used primarily for retrospective diagnosis and in epidemiologic research. Because the cause of Legionnaires illness was utterly obscure on the time, the instances were handled with many various regimens. Patients handled with erythromycin clearly did better than these given the penicillins, cephalosporins, or aminoglycosides. In-vitro susceptibility exams and animal research have confirmed the exercise of erythromycin and have proven that azithromycin, fluoroquinolones, doxycycline, rifampin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole are also energetic. Prevention is complicated by the truth that, in contrast with different environmental micro organism, Legionella micro organism are comparatively resistant to chlorine and heat. Some outbreaks have been terminated by hyperchlorination, by correcting malfunctions in water methods, or by quickly elevating the system temperature above 70�C. The installation of silver and copper ionization systems much like these used in giant swimming pools has been effective as a final resort in hospitals plagued with recurrent nosocomial legionellosis. An outbreak reported from a neonatal intensive care unit in Cyprus was traced to free-standing humidifiers which had been full of tap water. This underscores both the ubiquity of Legionella and the necessity to a minimal of start with sterile water wherever attainable. It is felt that this accounts for the ability of C burnetii to produce infection by aerosol inhalation, typically at appreciable distance from the presumed supply. Its distribution is worldwide amongst a variety of mammals, of which cattle, sheep, and goats are most associated with transmission to humans. Coxiella burnetii grows significantly nicely in placental tissue, attaining huge numbers (less than 1010 per gram), which on the time of parturition contaminate the soil and fomites, where it may survive for years. Q fever happens in those that are exposed to contaminated animals or their products, notably farmers, veterinarians, and workers concerned in slaughtering. Infection in all of these circumstances is believed to result from inhalation, which may be at some distance from the site of generation of the infectious aerosols. Infection also can happen from ingestion of animal merchandise such as unpasteurized milk. When clinically evident, Q fever usually begins at an average of 20 days after inhalation, with abrupt onset of fever, chills, and headache. A delicate, dry, hacking cough and patchy interstitial pneumonia may or will not be present. Chronic infection can also be uncommon, however notably necessary when it takes the form of endocarditis. There is proof that the strains related to endocarditis represent an antigenic subgroup of C burnetii. Although most infections resolve spontaneously, doxycycline therapy is believed to shorten the period of fever and reduce the chance of persistent an infection. Vaccines have been shown to stimulate antibodies, and a few studies have advised a protective impact for closely exposed staff. Biofilm formation and dormancy facilitate survival within the pipes of enormous buildings. His lungs have been initially clear, however during the first 3 days of his hospitalization he developed a progressive proper lower lobe pneumonia and pleural effusion. On day thirteen, his respiratory difficulties increased, with frank bleeding from the higher respiratory tract, and he died. At autopsy, the most prominent findings were bronchopneumonia with focal group and hemorrhage in the right lung. Stains of the lung tissue were negative by Gram, methenamine silver, and acid-fast methods, but Dieterle silver stains revealed quick bacilli. Lung cultures yielded gram-negative bacilli, which grew aerobically on buffered charcoal�yeast extract, but not on blood or chocolate agar. The organism was sent to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the place it was ultimately recognized as a new species of Legionella. Which of the next contributes most to the flexibility of Legionella to multiply in host phagocytes With the exception of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, they hardly ever trigger true illness, and all are frequently encountered as superficial colonizers or contaminants. The significance of their isolation from medical materials thus depends on the circumstance and website of culture and the clinical scenario of the patient. Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces infection at a wide range of pulmonary, urinary, and gentle tissue websites, very similar to the opportunistic Enterobacteriaceae. However, once established, infections are notably virulent and troublesome to treat. Affected patients virtually at all times have some type of debilitation or compromise of immune defenses. The variety of human infections produced by the other species together is way lower than that produced by P aeruginosa alone. Pseudomonas species are most frequently seen as colonizers and contaminants, but are in a place to trigger opportunistic infections. The project of species names has little scientific significance past differentiation from P aeruginosa.
Discount curatane 40mg with visaNot all bacterial species typically harbor plasmids, but those who do could carry one or numerous plasmids ranging in measurement from lower than 1 to more than 50 kilobases. Lanes show complete plasmids of varied sizes indicated by extent of migration in the gel. The specificity of these results may be improved by digesting the plasmids with restriction endonucleases earlier than electrophoresis. Two plasmids of the same measurement from totally different strains may not be the same, but if an similar sample of fragments is generated from the digestion, they virtually definitely are. Because of their bigger dimension, the chromosomes of bacteria have to be digested with endonucleases to resolve them on gels. For viruses, the result is much like that with plasmids, relying on the genomic size and the endonuclease used. Digested bacterial chromosomes may be in contrast on this method, however the number of fragments may be very giant and the patterns complicated. The combined use of endonucleases, which make infrequent cuts, and electrophoretic strategies capable of resolve large fragments can produce a comparability comparable to that attainable with plasmids. This method can be used for analysis of the multiple chromosomes of fungi and parasites. They might contain a gene of known operate or just sequences empirically found to be useful for the appliance in query. Three bacterial strains of the same species are proven every with chromosome and plasmid(s). An almost steady vary of fragment sizes is generated for each strain, making them troublesome to distinguish. The restriction fragments in A are transferred to a membrane (Southern transfer) and hybridized with a probe. The probe binds to a single fragment from every pressure, however the bigger measurement of the fragment from strain three indicates variation in restriction sites and, thus, a genomic distinction between it and strains 1 and 2. The positive end result with the biggest of the pressure 1 and a pair of fragments confirms their relatedness. A quantity of probes have been developed that may rapidly and reliably identify organisms already isolated in culture. The utility of probes for detection of infectious brokers immediately in clinical specimens corresponding to blood, urine, and sputum is tougher as a outcome of solely a small number of organisms may be current. This method provides the potential for speedy analysis and the detection of traits not possible by routine methods. For example, a bacterial toxin gene probe can reveal each the presence of the related organism and its toxigenicity without the necessity for culture. Primers + polymerase Cycle 2 Sequencing Cycle three Hybridization with goal sequence 5. A probe could be designed to bind to a sequence positioned between (internal to) the primers. In this type, a big selection of molecular manipulations or sequencing could also be carried out. The example exhibits detection of amplified fragments in two of three lanes on the gel. This strategy has been profitable for a broad range of infectious agents and awaits solely further decision of sensible problems for wider use. This sequence can then be in contrast with sequences published for other organisms utilizing computers. Thus, taxonomic relationships could be inferred for an organism that has never been isolated in tradition. The sample of bands produced by epidemiologically related strains can then be in contrast aspect by aspect. The usefulness of any individual technique differs among infectious brokers as a result of biologic variation and uneven study. In common, for agents that may be grown in vitro, tradition remains the "gold standard" as each probably the most delicate and particular methodology. Molecular strategies have the potential to exchange culture and have in some areas, especially virology. Aside from price, their broader software in infectious illness prognosis must cope with their extremely specific nature. Depending on the medical situation, the specimen launched at the beginning of this chapter might be directed at a really narrow or very broad question. Very typically, however, the query is "almost something" or a minimum of a extensive range of prospects. Some form of nutrient broth is used for tradition of blood and all direct tissue samples from websites that are usually sterile to acquire the utmost tradition sensitivity. Selective or indicator agents are omitted to prevent inhibition of extra fastidious organisms. The addition of defibrinated blood to a nutrient agar base enhances the growth of some bacteria, such as streptococci. This often yields distinctive colonies and supplies an indicator system for hemolysis. Two major kinds of hemolysis are seen: -hemolysis, a complete clearing of purple cells from a zone surrounding the colony; and -hemolysis, which is incomplete (ie, intact pink cells are nonetheless current within the hemolytic zone), but exhibits a green color caused by hemoglobin breakdown merchandise. A third type, -hemolysis, produces a hazy, incomplete hemolytic zone much like that brought on by -hemolysis, however without the green coloration. If blood is added to molten nutrient agar at approximately 80�C and maintained at this temperature, the purple cells are gently lysed, hemoglobin products are released, and the medium turns a chocolate brown shade. The nutrients released allow the growth of some fastidious organisms similar to H influenzae, which fail to grow on blood or nutrient agars. This high quality is particularly pronounced when the medium is further enriched with vitamin dietary supplements. Given the same incubation conditions, any organism that grows on blood agar additionally grows on chocolate agar. A variant of chocolate agar, Martin�Lewis medium is a strong medium selective for the pathogenic Neisseria (N gonorrhoeae and N meningitidis). Growth of most different bacteria and fungi within the genital or respiratory flora is inhibited by the addition of antimicrobial agents. This agar is both a selective and an indicator medium for gram-negative rods, particularly members of the family Enterobacteriaceae and the genus Pseudomonas. In addition to a peptone base, the medium accommodates bile salts, crystal violet, lactose, and impartial red as a pH indicator. The bile salts and crystal violet inhibit gram-positive micro organism and the extra fastidious gram-negative organisms, such as Neisseria and Pasteurella. Gram-negative rods that develop and ferment lactose produce a red (acid) colony, often with a distinctive colonial morphology. The Hektoen medium is considered one of many highly selective media developed for the isolation of Salmonella and Shigella species from stool specimens.
Purchase curatane cheapThree serotypes called Paratyphi A, B, and C have options just like S Typhi, together with the production of an enteric fever syndrome; circumstances are likewise traceable to a human source. Typhoid fever is still an essential explanation for morbidity and mortality worldwide with sixteen million cases and 600 000 deaths a year. The decline in illness in industrialized nations largely displays the supply of fresh water provides and improved disposal of fecal waste. The details of the cellular events are inferred from studies of Typhimurium, which in mice produces a disease just like typhoid (thus the name). The invasion and killing of intestinal M cells and macrophages are presumed to comply with the identical sample as that of S enterica. Two differences are the Vi floor polysaccharide and the prolonged multiplication of Typhi in macrophages. In the submucosa, Vi (for virulence) retards neutrophil phagocytosis by interfering with complement deposition in a manner much like that of other bacterial floor polysaccharides. This could favor uptake by macrophages, where at least some Typhi cells establish a privileged area of interest and the Vi+ phenotype favors intracellular multiplication. Like different serotypes of Salmonella, Typhi stays within a membrane-bound vacuole, however in distinction to them, rather than killing the macrophage, it enters a stage of extended replication. The primary distinction between Typhi and the opposite serotypes is the prolonged intracellular survival in macrophages. Rather than the acute inflammatory response seen with S enterica, S Typhi generates a mononuclear response and infrequently not sufficient irritation to cause diarrhea. This could additionally be as a end result of the downregulation of innate tolllike receptor responses in the intestinal mucosa by the Vi antigen. This generally leads to metastatic an infection of different organs together with the urinary tract and the biliary tree; the latter causes reinfection of the bowel. This cycle, starting and ending within the small gut, takes roughly 2 weeks to complete. In nonfatal instances, antibody and activated macrophages eventually subdue the untreated infection over a period of about three weeks. The Vi antigen is often credited, but numerous floor proteins are additionally candidates. Any Salmonella serotype can in all probability trigger any of those scientific manifestations beneath appropriate situations, however in practice the S enterica serotypes are related primarily with gastroenteritis, while Typhi and related serotypes (Paratyphi) cause enteric fever. Gastroenteritis S enterica = gastroenteritis Typhi = enteric fever Diarrhea, vomiting, and cramps are widespread Typically, the episode begins 24 to 48 hours after ingestion, with nausea and vomiting adopted by, or concomitant with, stomach cramps and diarrhea. Diarrhea persists because the predominant symptom for three to 4 days and often resolves spontaneously inside 7 days. The spectrum of illness ranges from a few loose stools to a extreme dysentery-like syndrome. Bacteremia and Metastatic Infection Bacteremia is most typical and severe within the immunocompromised Metastatic sites linked to previous damage, notably sickle cell anemia the acute gastroenteritis caused by S enterica can be related to transient or persistent bacteremia. These organisms have a unique capability to colonize sites of preexisting structural abnormality, together with atherosclerotic plaques, sites of malignancy, and the meninges (especially in infants). Salmonella an infection of the bone usually involves the long bones; particularly, sites of trauma, sickle cell injury, and skeletal prostheses are in danger. Enteric Fever Enteric fever is a multiorgan Salmonella an infection characterized by prolonged fever, sustained bacteremia, and profound involvement of the mesenteric lymph nodes, liver, and spleen. The imply incubation period is thirteen days, and the first signal of disease is fever related to a headache. Culture and agglutinating antibody present timing and probability of positive leads to a group of typhoid fever patients. A comparatively slow pulse is attribute and out of character with the elevated temperature. A faint rash (rose spots) seems in the course of the first few days on the abdomen and chest. Few in number, these spots are readily missed, particularly in dark-skinned individuals. Many sufferers are constipated, though maybe onethird of sufferers have gentle diarrhea. As the untreated illness progresses, an growing number of patients complain of diarrhea. Obviously, extended infection of the bloodstream is severe, and the effects of endotoxin can result in myocarditis, encephalopathy, or intravascular coagulation. Of explicit importance is the biliary tree, with reinfection of the intestinal tract and diarrhea late within the disease. Urinary tract an infection and metastatic lesions in bone, joint, liver, and meninges may happen. However, crucial complication of typhoid fever is intra-abdominal hemorrhage, resulting from perforations via the wall of the terminal ileum or proximal colon on the website of necrotic Peyer patches. Early in the middle of enteric fever, blood is way more more probably to give a optimistic tradition end result than culture from any other site. Failure to ferment lactose and the production of hydrogen sulfides (H2S) from sulfur-containing amino acids are attribute options used to determine suspect colonies on the selective isolation media. Characteristics of biochemical tests are used to determine the genus, and O serogroup antisera are available in bigger laboratories for affirmation. All isolates ought to be referred to public well being laboratories for affirmation and epidemiologic tracing. There could also be a transient diarrhea but too mild for most to search medical consideration and have a culture taken. Antibiotic therapy is normally not acceptable as a outcome of it tends to increase the duration and frequency of the service state. When used to eradicate the carrier state, it meets with erratic success and often fails in the presence of coexisting biliary tract disease. Therefore, the use of antimicrobial brokers in S enterica gastroenteritis is restricted to these with severe infections or underlying danger factors, significantly kids. In these situations, antimicrobials are considered as a measure to stop systemic unfold. Chloramphenicol and then ampicillin were the first antibiotics used and lowered the mortality fee from 20% to less than 2%. Use of ampicillin is now restricted by widespread resistance, leaving the extendedspectrum cephalosporins (ceftriaxone, cefixime) and ciprofloxacin as most popular first-line brokers. As seen in different pathogenic species (E coli, K pneumoniae), world patterns of antimicrobial resistance in S Typhi have been reshaped by the current emergence of a single multidrug-resistant clone, generally identified as H58. Newer vaccines embody one which uses a live attenuated Typhi strain and a polysaccharide vaccine containing the Vi antigen. The newer vaccines give barely larger safety, however none offers protection lasting quite a lot of years. The newest vaccine accommodates Vi antigen conjugated to a bacterial protein within the method of Hib, meningococcal, and pneumococcal vaccines.
Syndromes - Preschooler test or procedure preparation (3 to 6 years)
- Use sunglasses to protect your eyes.
- Liver disease such as hepatitis
- Heart attack
- Renal tubular acidosis (rare)
- Recent joint arthroscopy or other surgery
Cheap curatane 30mgCommunicability of a illness is the power of the organism to shed in secretions, which can occur early within the incubation interval. This dormancy or latency is harmful as a outcome of the virus could emerge long after the unique an infection has occurred and potentially infect others. Localized infections embrace influenza, parainfluenza, frequent chilly (rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, adenoviruses), gastrointestinal infections (rotaviruses, Norwalk viruses), and pores and skin infections (papillomaviruses). In localized infections, the virus spreads primarily by infecting adjacent or neighboring cells. Several viruses that trigger systemic disease in the host spread from the location of entry to the goal tissue, where they trigger cell harm after multiplication. Poliovirus replicates on the sites of entry within the small intestine and spreads to the regional lymph nodes where it multiplies once more and enters the bloodstream, resulting in primary viremia. The improvement of viremia allows the immune system to mount humoral and cell-mediated responses to control the poliovirus infection. Cellular or tissue tropism is most often decided by the particular interplay of viral surface proteins (spikes) and cellular receptors on the host cells. Some examples are sialic acid residues functioning as essential components of the receptor for influenza, corona, and reoviruses. Tropism may also be determined by intracellular elements, together with host transcription components and other elements essential for viral replication. After attachment of viral floor proteins to the cellular receptor, the viral genome-protein advanced is launched in the cytoplasm adopted by transcription, replication, and virus assembly. While enveloped viruses use two mechanisms for entry-fusion and receptor-mediated endocytosis (viropexis), naked capsid viruses use viropexis without membrane�membrane fusion. Naked capsid viruses, similar to poliovirus and hepatitis A virus, use outer capsid spikes to start attachment to the cellular receptor; the virion is internalized and the viral genome is launched in the cytoplasm without membrane�membrane fusion. Viral tropism can be altered within the case of some viruses due to genetic variation in the viral surface proteins. Although interaction of the viral surface proteins with the receptors on the host cell performs a important role in determining the tropism, other factors corresponding to viral gene expression, particularly in the case of retroviruses, hepatitis B viruses, and papillomaviruses, contribute to tropism. The capacity of a virus to cause degenerative modifications in cells or cell demise is called cytopathogenicity. If two intently related viruses infect a bunch, then an infection by the first virus can inhibit the function of the second virus; this is termed interference. A permissive cell permits production of progeny virus particles and/or viral transformation. Replication of the virus leads to alterations of cellular morphology and function as properly as antigenicity of the virus. As beforehand described, viral surface proteins, both in enveloped and naked capsid viruses, determine tropism and unfold, and alterations in these surface proteins could lead to changes in tropism, spread, and virulence. However, other areas of the viral genome contribute to pathogenicity and virulence. Some viruses encode a new class of proteins referred to as virokines and viroreceptors, which contribute to viral virulence by mimicking cellular proteins. Virokines are secreted from infected cells and act as cytokines, helping the cells to proliferate and improve virus manufacturing. In addition, some viruses encode proteins that bind antibodies or components of complement pathways to keep away from lysis of virus-infected cells. Infection entails multiplication of the virus in the host, whereas disease represents a clinically obvious response. Infections are rather more common than disease; unapparent infections are termed subclinical, and the person is referred to as a provider. Relative susceptibility of a host for a viral infection when it comes to severity of the illness is decided by a quantity of factors such as virulence, molecular and genetic determinants of the virus, and host components (immune status of the host, age, health, and genetic background). After viral transmission, the virus multiplies within the host; this part is referred to because the incubation period, which varies for different viruses (Table 7�3). Initial virus replication generally leads to viremia, which allows the virus to travel to the target tissues and replicate further to trigger cell damage and medical symptoms. The host immune system plays a pivotal role in determining the course of an infection and development of disease. Viral an infection leads to both a lytic or persistent (latent or chronic) infection. Several viruses intervene with the synthesis of cellular macromolecules and different factors that stop mobile development, upkeep, and repair, thus leading to cell dying. Accumulation of progeny viruses and viral proteins can destroy the structure and function, and enhance the process of apoptosis, leading to cell demise. Persistent viral infections are those in which the infected cells survive the effect of viral replication. Persistent infections are of two varieties: latent (viral genome without virus production) and persistent (low stage of virus production with out immune clearance). In acute infection, the virus enters the host, then multiplies on the site of entry and within the goal tissue, and this is adopted by viremia and cytopathic results. The immune system mounts both mobile and humoral responses and successfully eliminates the virus from the host. Examples of acute viral infections followed by clearance of the virus from the host by immune responses are hepatitis A, influenza, parainfluenza, rhino, and corona viruses. Most of the viruses opting to persist within the host have developed numerous mechanisms for persistence, including restriction of viral cytopathic effects, infection of immunologically privileged sites, upkeep of viral genomes with out full viral gene expression, antigenic variation, suppression of immune elements, and transformation of host cells. In some viral infections, acute infection might result in both asymptomatic or symptomatic disease followed by latent an infection during which the viral genome persists with none infectious virus production. In this case, productive (lytic) an infection takes place in permissive cells (mucoepithelial cells), whereas latent infection happens in nonpermissive cells (neurons). In some persistent infections, acute infection causes preliminary disease, which is adopted by a chronic infection during which a low stage of infectious virus is constantly produced with little or no damage to the goal tissue. Initially, the immune system controls the an infection by bringing the viral load lower than seen in acute an infection; nonetheless, the immune system is unable to eliminate the an infection through the acute section. During chronicity, the virus is maintained via a quantity of mechanisms, such as infection of nonpermissive cells, unfold to different cell types, antigenic variation, and lack of ability of the immune response to fully get rid of the virus. Acute infection adopted by chronic an infection Levels of an infection by virus Time D. In these line diagrams, various patterns of viral infection are proven, including: A. Acute viral an infection adopted by viral clearance by the immune response (eg, Hepatitis A virus, influenza virus, parainfluenza virus, rhinovirus). Acute viral an infection followed by viral latency and periodic reactivation (eg, herpes simplex viruses). Slow continual infection Time Some unconventional infectious agents cause gradual, persistent an infection without acute signs Some unconventional infectious brokers trigger sluggish, continual infection with out acute an infection such as attributable to prions. This course of is recognized as viral transformation, and these viruses are oncogenic viruses. Viruses that may either trigger tumors of their pure hosts or other species or can rework cells in vitro are thought of to have oncogenic potential.
Buy curatane 40 mg mastercardOnce inside host cells, including professional phagocytes, these secreted proteins disrupt signaling pathways, destroy cytoskeleton structure, trigger apoptosis, and inhibit cytokine production and acidification of phagosomes. The organisms finally reach the regional lymph nodes by way of the lymphatics, where they multiply rapidly and produce a hemorrhagic suppurative lymphadenitis known clinically because the bubo. The bacteremia causes seeding of different organs, most notably the lungs, and produces a necrotizing hemorrhagic pneumonia generally identified as pneumonic plague. Here, triggered by environmental cues corresponding to a new warmer temperature (37�C), they begin to produce a new set of virulence factors unique to mammalian victims such because the F1 protein capsule. Animal studies recommend that antibody against the F1 capsular glycoprotein is protective by enhancing phagocytosis, but cell-mediated mechanisms are required for intracellular killing. Without remedy, 50% to 75% of patients progress to bacteremia and die in gram-negative septic shock inside hours or days of growth of the bubo. Primary pneumonic plague has a shorter incubation period (2-3 days) and begins only with fever, malaise, and a sense of tightness within the chest. A terminal cyanosis seen with pneumonic plague is liable for the term Black Death. Even at present, plague pneumonia is sort of always fatal if acceptable treatment is delayed more than a day from the onset. An immunofluorescence technique is on the market in public health laboratories for immediate identification of smears or cultures. Yersinia pestis is instantly isolated on the media used for other members of the Enterobacteriaceae (blood agar, MacConkey agar), though growth may require greater than 24 hours of incubation. Laboratories have to be notified of the suspicion of plague to keep away from delay within the bacteriologic analysis and to guard in opposition to laboratory an infection. Timely therapy reduces the mortality of bubonic plague to lower than 10%, but the mortality rate of human cases of plague reported in developed countries remains to be round 20% because of delays in initiation of acceptable therapy. Sylvatic plague is nearly inconceivable to eliminate due to the dimensions and dispersion of the multiple rodent reservoirs. Eradication of fleas on domestic pets, which have been recognized to transport infected fleas from wild rodents to humans, is recommended in endemic areas. The continued presence of totally virulent plague in its sylvatic cycle poses a threat of extension to the urban cycle and epidemic disease within the occasion of main catastrophe or social breakdown. Chemoprophylaxis with doxycycline or ciprofloxacin is recommended for individuals who have had close contact with a case of pneumonic plague. It is also used for the family contacts of a person with bubonic plague, because they could have had the identical flea contact. A formalin-killed plague vaccine once used for these in high-risk occupations is now not out there. Because the infecting dose may be very low (less than 100 organisms), many routes of an infection are possible. A tick bite or direct contact with a minor pores and skin abrasion are the most common mechanisms of infection. Many wild mammals may be contaminated, including squirrels, muskrats, beavers, and deer. In an outbreak of pulmonary tularemia on Cape Cod, consultants believed that lawn mowing and brush cutting facilitated inhalation. Occasionally, the bite or scratch of a home canine or cat has been implicated when the animal has ingested or mouthed an contaminated wild mammal. Infected animals may not present indicators of an infection, as a result of the organism is well tailored to its pure host. Ticks may also function a reservoir of the organism by transovarial transmission to their offspring. Tularemia is distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, though there are extensive variations in particular areas. In the United States, one hundred to 200 circumstances are reported annually, half of which are in the decrease midwestern states (Arkansas, Missouri, Oklahoma). Once ingested by macrophages, Francisella resides in a phagosome for a time but resists lysosome fusion and escapes to the host cell cytoplasm. These are the overall properties of a facultative intracellular pathogen and indeed the virulence of F tularensis has been linked to its capability to multiply inside many cell varieties, including hepatocytes, kidney, and alveolar epithelial cells. The organism then infects the reticuloendothelial organs, often forming granulomas. Antibody titers remain elevated for many years, however cellular immunity plays the most important function in resistance to reinfection. The oculoglandular kind, which follows conjunctival inoculation, is comparable except that the native lesion is a painful purulent conjunctivitis. Inhalation of the organisms may find yourself in pneumonic tularemia or a extra generalized an infection similar to the typhoidal form. Similar to plague pneumonia, tularemic pneumonia may also develop through seeding of the lungs by bacteremic spread of one of many different forms. Any type of tularemia may progress to a systemic infection with lesions in multiple organs. Without therapy, mortality price ranges from 5% to 30%, depending on the type of infection. Ulceroglandular tularemia, the commonest kind, usually carries the bottom threat of a deadly end result estimated at 2%. Although most strains develop on chocolate agar, laboratories have to be alerted to the suspicion of tularemia so that specialized media supplemented with cysteine may be ready and precautions taken in opposition to the appreciable threat of laboratory infection. An immunofluorescent reagent is out there in reference laboratories for use instantly on smears from clinical material. Because of the difficulty and risk of cultural techniques, many circumstances of tularemia are diagnosed by serologic exams. Agglutinating antibodies are usually current in titers of 1:40 by the second week of sickness, rising to 1:320 or higher after three to 4 weeks. Unless earlier publicity is thought, single excessive antibody titers are thought-about diagnostic. Doxycycline or ciprofloxacin have also been effective, but relapses are extra common than with an aminoglycoside and doxycycline mixture. Prevention primarily includes the use of rubber gloves and eye protection when handling probably infected wild mammals. This small, coccobacillary, gram-negative organism grows readily on blood agar however not on MacConkey agar. The typical an infection is a diffuse cellulitis with a well-defined erythematous border. Pasteurella multocida is by far the most typical cause of an contaminated canine or cat chew. For unknown reasons, P multocida is often isolated from the sputum of patients with bronchiectasis.
Discount curatane 30mgUse of the antimicrobial in animal models after which human infections must even have demonstrated a therapeutic response. Once these factors are established, the routine choice of therapy may be based on known or expected traits of organisms and pharmacologic features of antimicrobial agents. The antimicrobial in query should be used to deal with these organisms, however at elevated doses. For example, less toxic antibiotics such because the penicillins and cephalosporins can be administered in massive amounts and will thereby inhibit some pathogens that would normally be considered resistant in vitro. Furthermore, in urinary infections, urine ranges of some antimicrobial brokers may be very high (eg, fluoroquinolones), and organisms that are resistant in vitro could also be eliminated in the patient. Important pharmacologic characteristics of antimicrobial brokers include dosage in addition to the routes and frequency of administration. Most agents are sure to some extent to serum albumin, and the protein-bound kind is usually unavailable for antimicrobial motion. The quantity of free to sure antibiotic can be expressed as an equilibrium constant, which varies for different antibiotics. In general, high degrees of binding lead to more extended but decrease serum levels of an energetic antimicrobial after a single dose. The methods used are standardized, together with a measured inoculum of the micro organism and managed development conditions (eg, medium, temperature, atmosphere, and time). In deciding on remedy, clinicians should contemplate more than the results of laboratory checks. The clinical pharmacology of the drug, the cause of the illness, the location of an infection, the immune perform of the patient, and the pathology of the lesion should be taken into account as nicely. For example, the antimicrobial should reach the subarachnoid area and cerebrospinal fluid in meningitis. Similarly, therapy could also be ineffective for an an infection that has resulted in abscess formation unless the abscess is surgically drained. The dilutions are prepared in tubes or microdilution wells, and by conference, their concentrations are doubled utilizing a base of 1 g/mL (0. Automated Tests Automated methods read dilution exams in a few hours Instruments are actually obtainable that perform fast, automated variants of the broth dilution take a look at. In these techniques the micro organism are incubated with the antimicrobial in specialised modules which may be read mechanically on a frequent basis. While the plates are incubating, the antimicrobial diffuses into the medium to produce a round gradient across the disk. It is also influenced by the growth price of the organism, the diffusibility of the drug, and other technical factors. The diameters of the zones of inhibition obtained with the assorted antibiotics are transformed to "susceptible," "intermediate," or "resistant" classes by referring to a desk. This method is handy and flexible for rapidly growing aerobic and facultative bacteria such as the Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas, and staphylococci. This strategy is slower and extra laborious than automated broth methods, however it has the advantage of showing the presence of multiple colony morphologies, combined infections, or resistant subpopulations that appear as "inside colonies" within an in any other case clear zone of inhibition. Molecular Testing Molecular methods detect identified resistance genes the molecular techniques of nucleic acid hybridization, sequencing, and amplification (see Chapter 4) have been utilized to the detection and study of resistance. Phenotypic gene expression remains the "backside line" that guides most resistance testing today. A strip containing a gradient of antimicrobial content creates an elliptical zone of inhibition. To do so requires quantitative subculture of the clear tubes within the broth dilution take a look at and comparison of the variety of viable micro organism at the beginning and end of the take a look at. The least quantity required to kill a predetermined portion of the inoculum (usually ninety nine. Most of the antimicrobials used for acute and life-threatening infections (eg, -lactams, aminoglycosides) act by bactericidal mechanisms. A variety of biologic, immunoassay, and chemical procedures have been developed for this purpose. This resistance may be inherent to the organism or seem in a previously prone species by mutation or the acquisition of recent genes. Keeping forward of the microbes requires that we understand the mechanisms by which micro organism develop resistance, and the methods this resistance spreads. The following sections discuss the biochemical mechanisms of resistance, how resistance is genetically controlled, and how resistant strains survive and spread in our society. How these features relate to the antimicrobial groups is summarized in Table 23�2 and additional discussed within the chapters on specific micro organism (see Chapters 24-41). Antimicrobial resistance has survival value for the organism, and its expression within the medical setting requires that virulence be retained despite the change that mediates resistance. The term "superbug," increasingly used to describe multiresistant bacteria, implies this linkage is more common than it truly is. A highly selective list of resistance emergence that has altered or threatens a significant medical use of the agent. The cell wall, notably the outer membrane, of gram-negative micro organism presents a formidable barrier for access to the interior of the cell. A, B, C, and D molecules are exterior to the cell wall right here proven as what could be either the outer membrane (gram negatives) or the cytoplasmic membrane. A molecules cross through and stay contained in the cell, B molecules are unable to cross as a outcome of their measurement, C molecules move through however are transported back out by an efflux pump, and D molecules have to be pulled through by an active course of. Outer membrane protein porin channels may allow drug penetration relying on their size, cost, diploma of hydrophobicity, or common molecular configuration. This is a serious cause for inherent resistance to antimicrobial agents, but these transport traits could change even in typically prone species due to mutations in the porin proteins. For instance, strains of P aeruginosa generally develop resistance to carbapenems as a outcome of lack of the outer membrane protein most essential for his or her penetration. For instance, bacteria which lack the metabolic pathways required for transport of aminoglycosides across the cytoplasmic membrane (streptococci, enterococci, anaerobes) are intrinsically resistant. A number of bacterial species have energy-dependent efflux mechanisms that literally pump antimicrobial agents which have entered the cell again out. The membrane transporter systems which drive these efflux pumps typically have an effect on antimicrobials of several courses. If the target is altered in a way that decreases its affinity for the antimicrobial, the inhibitory impact might be proportionately decreased. Substitution of a single amino acid at a sure location in a protein may alter its binding to the antimicrobial with out affecting its perform in the bacterial cell. If an alteration at a single website on the goal renders it nonsusceptible, mutation to resistance can occur in a single step, even during therapy. This occurred with the early aminoglycosides (streptomycin), which certain to a single ribosomal web site, and the first quinolone (nalidixic acid), which connected to solely certainly one of four attainable topoisomerase subunits. Newer brokers in every class bind at a quantity of sites on their goal, making mutation to resistance less possible. In broadly divergent gram-positive and gram-negative species, adjustments in a number of of those proteins correlate with decreased susceptibility to a quantity of -lactams. These changes have now been traced to point mutations, substitutions of amino acid sequences, and even synthesis of a new enzyme.
Generic curatane 40 mg on-lineAll too often the containment is less effective, and unfold with a number of metastatic lesions occurs. In all these situations, diabetes, leukocyte defects, or basic discount of host defenses by alcoholism, malignancy, old age, or steroid or cytotoxic remedy can be predisposing components. Severe S aureus infections, together with endocarditis, are notably frequent in drug abusers utilizing injection methods. The face, axilla, and groin are inclined to be affected first, however the erythema, bullous formation, and subsequent desquamation of epithelial sheets, can unfold to all elements of the body. The illness occasionally happens in adults, notably those that are immunocompromised. The illness is characterized by excessive fever, vomiting, diarrhea, sore throat, and muscle ache. Within forty eight hours, it might progress to extreme shock with evidence of renal and hepatic harm. A pores and skin rash may develop, later followed by desquamation at a deeper level than in scalded skin syndrome. Staphylococcal Food Poisoning Vomiting is outstanding without fever Ingestion of staphylococcal enterotoxin-contaminated food leads to acute vomiting and diarrhea inside 1 to 5 hours. Recovery is rapid, except sometimes in the aged and in those with one other illness. Most acute, untreated lesions include numerous polymorphonuclear leukocytes and enormous numbers of gram-positive cocci in clusters. Catalase and coagulase tests performed immediately from the colonies are sufficient for identification. In epidemiologic investigations, molecular strategies similar to pulsed subject gel electrophoresis are now used to "fingerprint" the spread of virulent clones. Blood cultures are usually constructive in situations similar to acute staphylococcal arthritis, osteomyelitis, and endocarditis, however much less typically in localized an infection such as deep abscesses. Those which might be extra intensive, deeper, or in very important organs require a mixture of surgical drainage and antimicrobials for optimal consequence. Since the introduction of penicillin the antimicrobial aspect of this equation has resembled an arms race between the ability of S aureus to develop resistance and the flexibility of drug firms to overcome it with a brand new antibiotic. Since then, the selection of preexisting strains containing a plasmid coding for a penicillinase. This enzyme opens the -lactam ring, making the drug unable to bind with its goal. Laboratory susceptibility tests are carried out under technical circumstances that facilitate detection of what may be a small resistant subpopulation, and the results extrapolated to different related agents. For example, oxacillin resistance is considered proof of resistance to nafcillin and all cephalosporins. Methods for direct detection of the mecA gene have been developed but face the interpretive dilemma that the gene could also be present in phenotypically prone isolates. The recent emergence of S aureus with decreased susceptibility to vancomycin continues to be uncommon however of great concern. These and comparable clones have been detected in Europe however at a decrease rate than within the United States. Clothes and bedding that may cause reinfection ought to be dry-cleaned or washed at a sufficiently high temperature (70�C or higher) to destroy staphylococci. In adults, using chlorhexidine or hexachlorophene soaps in showering and washing will increase the bactericidal exercise of the pores and skin. In such people, or individuals discovered to be a source of an outbreak, anterior nasal carriage can be lowered and infrequently eradicated by the mixture of nasal creams containing topical antimicrobials (eg, mupirocin, neomycin, and bacitracin) and oral therapy with antimicrobials which might be concentrated inside phagocytes and nasal secretions (eg, rifampin or ciprofloxacin). Attempts to cut back nasal carriage extra usually amongst medical personnel in an institution are often fruitless and encourage substitute of prone strains with multiresistant ones. Chemoprophylaxis is efficient in surgical procedures corresponding to hip and cardiac valve replacements, by which an infection with staphylococci can have devastating consequences. Oxacillin, a cephalosporin, or vancomycin given during and shortly after surgery might cut back the possibility for intraoperative an infection whereas minimizing the risk for superinfection associated with longer periods of antibiotic administration. Immunization in opposition to virulence factors like -toxin has shown some success in animals. Given the multifactorial nature of S aureus virulence a vaccine seems a great distance off. Antistaphylococcal soaps block infection Elimination of nasal carriage is troublesome Chemoprophylaxis throughout highrisk surgical procedure is efficient Think Apply 24-2. Virulence and resistance are separate properties unlinked by genetics or pathogenic perform. In medical apply, the lower than 20 species which were isolated from human infections are typically lumped together by a unfavorable characteristic-failure to produce coagulase. They have been shown to have floor adhesins and the flexibility to produce extracellular polysaccharide biofilms. Their giant numbers and ubiquitous distribution result in frequent contamination of specimens collected from or via the pores and skin. Immunosuppressed or neutropenic patients and untimely infants have been notably affected. The outcome of the bacterial contamination is decided by the power of the microbe to attach to the surface of the international physique and to multiply there. Central to this course of is the flexibility of these species to kind a viscous extracellular polysaccharide biofilm. The abovementioned circumstances are discovered almost exclusively in hospitals and other medical services. The most common device colonized is the intravenous catheter, but the identical mechanisms apply to any implanted device such as cerebrospinal fluid shunts and synthetic coronary heart valves. The ensuing illness is often low grade with little more than a slowly advancing fever to arouse suspicion. Removal of the contaminated system is the only certain way to avoid these issues. Its traditional habitat is the gastrointestinal tract, and from that location the organism features access to the urinary tract. Staphylococcus epidermidis cocci are proven attached to the floor of a plastic catheter and are starting to produce extracellular polysaccharide biofilm. The infection course of is aided by floor adhesins to uroepithelial cells and elements aiding survival in urine just like the manufacturing of a urease. Resistance to a number of antimicrobials normally energetic towards gram-positive cocci, including vancomycin, is more widespread than with S aureus. He had pharyngeal inflammation, and his blood strain was 60/0 mm Hg while supine and unobtainable when sitting. He was treated with giant volumes of intravenous fluids and with penicillin; his blood pressure rose, however he had multiple episodes of disorientation, and diffuse erythroderma developed. On admission, a small crusted wound had been noticed on the dorsum of his left foot (the result of a bicycle injury 1 week earlier); forty five hours later the wound grew to become red, heat, and pustular, and a left femoral lymph node became tender and enlarged. A culture of the pustule grew S aureus coagulase-positive immune to penicillin.
Cheap 40mg curatane overnight deliveryMost of the studied mixtures no longer require the usage of ribavirin, thereby avoiding its associated anemia. The use of interferon is disappearing, a welcome growth to remove disagreeable side effects and parenteral remedy. Genotype 1A, the reason for approximately 70% of circumstances in the United States is probably the most tough to eradicate. The presence of cirrhosis additionally determines which combination regimen is really helpful as does the subtype of genotype 1 (A vs B) and resistance due to prior remedy. Accordingly, an understanding of resistance to antiviral medicine has evolved; investigation of resistance mechanisms has make clear the function of specific viral genes and the central position of gene mutations. For example, it has become clear that a common mechanism of resistance to nucleosides (eg, acyclovir and ganciclovir) by herpesviruses consists of mutations within the viral-induced enzyme answerable for phosphorylating the nucleoside. Higher rates of replication are related to greater rates of spontaneous mutations. The larger the drug publicity, the extra speedy the emergence of resistant mutants up to a point. With still higher drug exposure, viral replication and resistant mutants decrease till viral replication ceases. In addition to viral replication, the rate of mutations differs amongst different viruses. This is the traditional technique of rising virus in tissue tradition in medium containing growing concentrations of an antiviral agent. The degree of viral replication is obtained by counting viral plaques (ie, equal to viral "colonies") or by measuring viral antigen or nucleic acid focus. Unfortunately, phenotypic assays are very time-consuming, requiring days to weeks for completion. If solely 1% to 5% of the population has the mutation, this end result will not be detected. Various methods of quantitating virus (eg, culture, polymerase chain reaction, antigen assay) provide a way of assessing the decline of viral titer in response to treatment with an antiviral agent. If no decline occurs regardless of sufficient dosage and compliance, viral resistance may be responsible. Likewise, if viral titer initially decreases but subsequently recurs and/or will increase, then resistance might have developed. Respiratory Viruses Influenza Virus Parainfluenza Virus Respiratory Syncytial Virus Adenovirus Human Metapneumovirus Rhinovirus Coronavirus Bocavirus 9 Considering how frequent sickness is, how large the religious change that it brings, how astonishing, when the lights of health go down, the undiscovered countries which may be then disclosed, what wastes and deserts of the soul a slight assault of influenza brings to view. Although a majority of the episodes might not require medical attention, the overall common is three to four diseases per year per individual. Although the incidence varies inversely with age (ie, greater amongst youthful kids than wholesome younger adults), the morbidity is significantly larger in aged inhabitants. Seasonality can also be a feature; incidence is lowest in the summertime months and highest within the winter. Transmission is direct, by infective droplet nuclei, or indirect, by hand switch of contaminated secretions to nasal or conjunctival epithelium. These respiratory viral brokers are associated with an increased danger of bacterial superinfection of the damaged tissue of the respiratory tract, and all have a worldwide distribution. Influenza virus types A and B each cause more severe signs than does influenza virus type C. Influenza virus A, which has a number of subtypes primarily based on hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N), endure more genetic adjustments than varieties B and C. Direct droplet unfold is the most typical mode of transmission and the incubation is period is about 2 days. The virus multiply in ciliated respiratory epithelial cells, resulting in useful and structural ciliary abnormalities, together with interference with the mechanical clearance mechanism of the respiratory tract. The typical influenza sickness is characterised by an abrupt onset (over several hours) of fever, diffuse muscle aches, and chills. This is adopted within 12 to 36 hours by respiratory symptoms similar to rhinitis, fever, myalgia, headache, cough, sometimes shaking chills, respiratory misery. The acute part usually lasts 3 to 5 days, but a complete return to normal activities might take 2 to 6 weeks. The most typical complication of influenza infection is bacterial superinfection usually leading to bacterial pneumonia. Influenza virus an infection can be prevented by annual vaccination, which is formulated every year because of antigenic drift that permits the virus to escape preexisting immunity from previous vaccination or an infection. Influenza A viruses are the most extensively studied due to their predominance in epidemics, and far of the following dialogue relies on knowledge of this sort. They usually trigger more severe disease and more extensive epidemics than the other types; naturally infect a extensive variety of species, including mammals and birds; and have an excellent tendency to endure important antigenic adjustments (Table 9�1). Influenza B viruses are extra antigenically stable, are known to infect humans and seals, and usually happen in more localized outbreaks. Influenza C viruses appear to be relatively minor causes of illness, affecting humans and pigs. The inner aspect of the envelope accommodates a layer of virus-specified matrix protein (M1). Three kinds of membrane proteins are inserted within the lipid bilayer: hemagglutinin (as trimer), neuraminidase (as tetramer), and M2 ion channel protein. There is another integral membrane protein in influenza A often identified as M2 ion channel protein. The virus-specific glycoproteins are antigenic and have particular practical importance in pathogenesis and immunity. Hemagglutinin has the power to agglutinate red blood cells from sure species (eg, chickens and guinea pigs) in vitro. Its main biologic perform is to connect to N-acetylneuraminic (sialic) acid-only containing glycoprotein or glycolipid receptor websites on human respiratory cell surfaces, which is a crucial first step in initiating infection of the cell. Neuraminidase is an antigenic hydrolytic enzyme that acts on the hemagglutinin receptors by splitting off their terminal neuraminic (sialic) acid. It may inactivate a free mucoprotein receptor substance in respiratory secretions that could in any other case bind to viral hemagglutinin and stop access of the virus to the cell floor. Neuraminidase might promote fusion of the viral envelope with the host cell membrane for viral entry. More importantly, neuraminidase aids within the release of newly fashioned virus particles from contaminated cells. The newly fashioned virus particles mixture on the cell surface by attaching to sialic acid by way of their hemagglutinins however neuraminidase removes the sialic acid from the cell surface receptor allowing the virus to be launched and infect different cells. Type-specific antibodies to neuraminidase seem to inhibit the spread of virus in the infected host and to limit the quantity of virus launched from host cells. The ribonucleoproteins are enveloped by the plasma membrane, which by then accommodates hemagglutinin and neuraminidase. Influenza A viruses were initially isolated in 1933 by intranasal inoculation of ferrets, which developed febrile respiratory sicknesses.
References - Lang RJ, Tonta MA, Zoltkowski BZ, et al: Pyeloureteric peristalsis: role of atypical smooth muscle cells and interstitial cells of Cajal-like cells as pacemakers, J Physiol 576:695, 2006.
- Shulman B, Aronson H: Capnography in the early diagnosis of carbon dioxide embolus during laparoscopy, Can Anaesth Soc J 31:455-459, 1984.
- Leung AKC, Robson WLM: Labial fusion and asymptomatic bacteriuria, Eur J Pediatr 152(3):250-251, 1993.
- MacLeod M, Kelly R, Robb SA, et al: Bladder dysfunction in Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Arch Dis Child 88(4):347n349, 2003.
|
|