"Cheap 500mg altezym fast delivery, bacteria unicellular."By: Keira A Cohen, M.D. - Co-Director, The Johns Hopkins Center for Nontuberculous Mycobacteria and Bronchiectasis
- Assistant Professor of Medicine
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/10003818/keira-cohen
Buy genuine altezym on lineIt is estimated that greater than 70% of all surgical procedures in the United States are actually carried out on an outpatient foundation. For instance, in areas the place regional and epidural blocks are administered, Intralipid must be stocked in anticipation of treating local anesthetic toxicity. This interval is characterized by a comparatively excessive incidence of probably life-threatening respiratory and circulatory complications. The supply of anesthesia services in areas remote from the main working room, such as endoscopy, interventional radiology, and magnetic resonance imaging suites is increasingly frequent. Patients recovering from anesthesia delivered in these areas must obtain the same commonplace of care as sufferers recovering from anesthesia obtained in the main operating room. A central location in the working room space itself is desirable, as it ensures that the patient can be rushed back to surgery, if wanted, or that members of the operating room group can shortly reply to pressing or emergent affected person care issues. Proximity to radiographic, laboratory, and different intensive care facilities on the identical floor can also be advantageous. The transfer of critically ill patients in elevators or by way of long corridors can jeopardize their care as a outcome of urgent issues may come up alongside the means in which. However, an appropriate variety of individually enclosed affected person care areas is required for patients needing isolation for infection management. Each patient house should be well-lighted and huge sufficient to allow quick access to patients regardless of poles for intravenous infusion pumps, a ventilator, or radiographic equipment; development pointers dictate a minimum of 7 ft between beds and a hundred and twenty sq ft/patient. Multiple electrical shops, together with a minimum of one with backup emergency energy, and at least one outlet every for oxygen and suction, ought to be current at every bed house. A forced-air warming gadget, heating lamp, and/or a warming/cooling blanket must be available. A available provide of catheters for vascular cannulation (venous, arterial, central venous) is necessary. A defibrillation gadget with transcutaneous pacing capabilities, and an emergency cart with drugs and provides for superior life support (see Chapter 55) and infusion pumps, should be current and periodically inspected. Transvenous pacing catheters; pulse turbines; and tracheostomy, chest tube, and vascular cut-down trays are sometimes present, depending on the surgical patient inhabitants. Appropriate gear have to be out there for those patients requiring invasive arterial, central venous, pulmonary artery, or intracranial stress monitoring. Capnography is helpful for intubated patients and is more and more employed for extubated sufferers as properly. They should have expertise in airway management and superior cardiac life support, as properly as problems commonly encountered in surgical sufferers relating to wound care, drainage catheters, and postoperative bleeding. The anesthesia staff emphasizes management of analgesia, airway, cardiac, pulmonary, and metabolic problems, whereas the surgical staff generally manages any issues immediately related to the surgical process itself. However, staffing for nursing care ought to be tailored to the unique caseload necessities of every facility. If the operating room schedule frequently contains pediatric sufferers or frequent brief procedures, a ratio of 1 nurse to one affected person is commonly needed. A charge nurse ought to be assigned to ensure optimal staffing at all times, including the appropriate response to urgent or emergent patient care problems. Emergence from common anesthesia ought to ideally be characterised by a clean and gradual awakening in a controlled setting. However, problems corresponding to airway obstruction, shivering, agitation, delirium, pain, nausea and vomiting, hypothermia, and autonomic lability are incessantly encountered. Patients receiving spinal or epidural anesthesia might expertise decreases in blood stress throughout transport or restoration; the sympatholytic effects of major conduction blocks forestall compensatory reflex vasoconstriction when sufferers are moved or after they sit up. As the period of anesthesia will increase, emergence additionally turns into more and more dependent on whole tissue uptake, which is a perform of agent solubility, the common concentration used, and the duration of publicity to the anesthetic. Recovery from most intravenous anesthetic agents is dependent totally on redistribution quite than metabolism and elimination. As the total administered dose increases, nevertheless, cumulative effects turn into clinically obvious in the type of extended emergence; the termination of action turns into more and more dependent on the metabolism or elimination. This is the basis for the concept of a context-sensitive half-time (see Chapter 7). Short and ultrashort-acting anesthetic brokers, such as propofol and remifentanil, significantly shorten emergence, time to awakening, and discharge. Premedication with brokers that outlast the procedure (eg, lorazepam) could also be expected to delay emergence. The brief duration of motion of midazolam makes it a suitable premedication agent for brief procedures. The results of preoperative sleep deprivation or drug ingestion (alcohol, sedatives) can also be additive to those of anesthetic agents and can delay emergence. Delayed Emergence essentially the most frequent cause of delayed emergence (when the affected person fails to regain consciousness 30�60 min after common anesthesia) is residual anesthetic, sedative, and analgesic drug impact. Delayed emergence could occur because of absolute or relative drug overdose or potentiation of anesthetic brokers by prior drug or alcohol ingestion. Less common causes of delayed emergence embody hypothermia, marked metabolic disturbances, and perioperative stroke. A core temperature of lower than 33�C has an anesthetic impact and significantly potentiates the actions of central nervous system depressants. Hypoxemia and hypercarbia are readily excluded by pulse oximetry, capnography, and/or blood gasoline evaluation. Hypercalcemia, hypermagnesemia, hyponatremia, and hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia are rare causes of delayed emergence that require laboratory measurements for prognosis. Perioperative stroke is uncommon, except after neurological, cardiac, and cerebrovascular surgery (see Chapter 28); prognosis is facilitated by neurological analysis and radiological imaging. The head-down position is useful for hypovolemic sufferers, whereas the back-up position is helpful for patients with underlying pulmonary dysfunction (see Chapters 20 and 23). Patients at increased threat of vomiting or higher airway bleeding (eg, following tonsillectomy) must be transported within the lateral place. This place additionally helps forestall airway obstruction and facilitates drainage of secretions. Subsequent blood pressure, heart fee, and respiratory rate measurements are routinely made at least every 5 min for 15 min or until stable, and each 15 min thereafter. Neuromuscular operate should be assessed clinically (eg, head-lift and grip strength). Additional monitoring contains ache evaluation (eg, numerical or descriptive scales); the presence or absence of nausea or vomiting; and fluid enter and output, together with urine move, drainage, and bleeding. Supplemental oxygen must be administered during transport to sufferers vulnerable to hypoxemia. Patients should typically be nursed in the back-up place, each time possible, to optimize oxygenation. However, elevating the head of the bed before the affected person is responsive can lead to airway obstruction.
Generic altezym 250 mg on lineThey are normally bilaterally 2�10 mm in dimension; cysts that exceed 2 mm in dimension are rare. Heschle in 1856 to determine intracerebral cysts fashioned as a result of impairment of embryonic development. Etiological factors are anoxia, accidents and infections that influence the creating brain postnatally. Erickson in 1941 described the "locked" porencephaly triggered, as they thought, by thrombosis or embolism of the center cerebral artery branches. Wadsworth in 1946 distinguished agenetic (developed earlier than 6 months of intrauterine life) and encephaloclastic cysts (developed within the last trimester of pregnancy or after delivery). In almost half of cases, porencephaly is mixed with different developmental defects. Posttraumatic porencephaly is a separate type seen after primary mind tissue destruction (contusion, haemorrhage) with subsequent rupture of the ventricular ependyma. In the latter, concomitant posttraumatic pathological changes are incessantly seen. Hydrocephalus features could also be seen, and sometimes outpouching of cranial bones on the affected side. Angiographic options of congenital porencephaly are particular and depend upon the developmental defects of cerebral tissue formation of a cavity with invaginated borders. Opercular irregular vessels (operculation is an invagination of vessels with simultaneously invaginated cortex) and areas with no vessels are the factors for diagnosis of congenital origin of the cyst. Porencephaly fashioned within the adult mind manifests on angiograms by areas with out vessels, absence of operculation and dislocation of vessels acceptable to the placement of the cyst. They are a benign disorder from the group of reticuloendothelial tumours and have a gentle course. In half of cases, bone lesions are a quantity of and are disseminated all through the skeleton. The most frequent areas are cranial bones, ribs, pelvic bones and proximal segments of femoral bones. Asymptomatic programs for a couple of years could additionally be encountered, and in these cases, a pathological fracture may be the first manifestation. Mild neutrophilic leukocytosis and gentle anaemia are typical in routine blood cell rely. Arrows idicate the wall of the cyst, which separates it from the cavity of lateral ventricle. T2-weighted image (a) and T1-weighted images (b,c) show the porencephalic cavity with a large link to the body of the best lateral ventricle Supratentorial Tumours 479. T2-weighted images (d,e) and T1-weighted image (f) clarify the placement and construction of the cyst 480 Chapter 4. A hypodense (�63 H U) focus with microcalcifications is visualised within the projection of choroid plexus. Confluent defects might retain remnants of bone septi, which supplies a markedly mobile look. In all sequences, granuloma has clear-cut contours with hypointense signal of cranial bones. Myeloma accounts for 1% of all human cancer illnesses, contributing to 2% of cancer mortality. Solitary lesion is taken into account plasmacytoma and is seen very not often, especially in cranial bones (not greater than zero. Ribs, cranial bones, pelvic bones, vertebral column and diaphyses of tubular bones are affected. The disease begins with basic fatigue, pain in bones (70% of cases) and weight reduction. Less typically scarcity of inspiration, chest ache, cryoglobulinaemia, amyloidosis and arterial hypertension are seen. Diagnosis is made by laboratory and instrumental examinations: normochromic normocytic anaemia (60%), renal failure (55%), hypercalcaemia with simultaneous hypercalciuria (30�50%), proteinuria (up to 90%) and Bens-Jones protein in urine (50%). Diagnosis is made by sternal puncture: if over 10% of plasmocytes are found, then myeloma diagnosis is considered possible. Large cavities kind no matter periosteal or endosteal location, due to confluence of smaller cavities. The illness disseminates further, and pathological fractures, compression of vertebral bodies and cachexia happen. The diagnostic standards of the disease are a quantity of osteolytic lesions of cranial vault bones (Angtuaco et al. Multiple lesions in vertebrae are typical for a number of myeloma (50%); solitary lesions (plasmacytoma) also have an effect on the vertebral column more typically than the cranial vault. Final diagnosis is made on the stage of dissemination when all skeleton is affected. Heterogeneous contrast enhancement of lytic foci and meninges is seen (if meningeal myelomatosis is present). It must be famous that the risk of renal failure increases ten occasions after injection of distinction medium in myeloma patients in contrast with other conditions. On T1-weighted images, lytic bone lesions are iso- or hypointense compared with mind tissue. X-ray craniograms in a left parietal bone detect an spherical space of bone destruction, with the lesion involving inner and exterior compact layers of bone (a lateral projection, b direct projection). The delicate tissue lesion with destruction of pari- etal bone and intensive and homogeneous distinction accumulation is detected in the left parietal area. The soft tissue mass lesion with destruction of parietal bone and peripheral distinction accumulation is detected in the left parietal space. T2-weighted picture (c) and T1-weighted pictures in axial (d) and coronal (e) projections reveal a soft tissue lesion, which is hyperintense on T2-weighted imaging and predominantly isointense on T1-weighted imaging, in the left parietal bone close to the coronary suture. The contrast accumulation is comparatively intense predominantly in peripheral components of granuloma (f) 484 Chapter 4. The multiple small foci of destruction within the bones of cranial vault are visualised on the craniogram Supratentorial Tumours 485 9. Convex mind veins and superior sagittal sinus are pushed contained in the cranial cavity 486 Chapter four. Comparative clinico-radiologic study with cerebral toxoplasmosis, cerebral tuberculoma and primary cerebral lymphoma in non-immunodepressed patients. Med Clin (Barc) ninety nine:128�131 Armao D et al (2000) Colloid cyst of the third ventricle: imaging� pathologic correlation. Cancer 89:1111�1120 Berens M, Rutka J et al (1990) Brain tumour epidemiology, growth and invasion. Am J Neuroradiol one hundred sixty five:1245�1250 Cuccia V et al (2003) Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma in youngsters with tuberous sclerosis. Child Nerv Syst 19:232�243 Dolgushin M, Kornienko, Pronin I et al (2004) Complex diagnostics of metastatic ailments of the brain. Med Visualis three:89�96 (in Russian) Dropcho E, Wisoff J, Walker R et al (1987) Supratentorial malignant gliomas in childhood: A evaluate of fifty instances.
Diseases - Pfeiffer Mayer syndrome
- Giant papillary conjunctivitis
- Deafness mesenteric diverticula of small bowel neuropathy
- Endomyocardial fibroelastosis
- Angiosarcoma
- Palindromic rheumatism
- Malignant hyperthermia susceptibility type 2
- HEC syndrome
- Chromosome 21, tetrasomy 21q
- Opportunistic infections
Cheap 500mg altezym fast deliveryFeb 27(2):243�246 Provenzale J, Sorensen A, Yuh W (2000) Contemporary stroke imaging: early prognosis, triage, and remedy. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 189 Suzuki J, Takaku A (1969) Cerebrovascular "moyamoya" illness. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:99�108 Valavanis A (1996) the role of angiography within the analysis of cerebral vascular malformation. Radiology 19:39�49 Wolpert S, Caplan L (1992) Current function of cerebral angiography within the diagnosis of cerebrovascular disease. According to incidence fee, the neuroepithelial tumours are second, among which glioblastoma prevails. Solid tumours, by far, are one of the frequent brain tumours in kids, and in accordance with their incidence, they rank second place after leukaemia (in accordance with some data). Excluding first-year youngsters and adolescents, about 70% of all intracranial tumours have infratentorial location, amongst them 75% are positioned in hemispheres of cerebellum and 25% in brainstem (Farwell 1977). The morbidity peak is in elderly and senile sufferers, whereas in children the incidence is far lower, about 2�4 cases per a hundred,000. Presumably, the minimal annual morbidity of primary mind tumours in Russia and Moscow is about 14,000 and 1,000 sufferers accordingly (Yartsev 1997). Annually, as much as eleven per one hundred,000 new cases of 334 Histological Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System 1. Primary mind gliomas constituted the biggest group amongst neuroepithelial tumours, observed in around 80% of all cases. However, the proportions of various neuroglial mobile sorts can vary in numerous mind tissues. So, according to statistical information, approximately two thirds of mind tumours are major ones, and among them greater than 50% are glial neoplasm. In this regard, glial tumours are divided into three fundamental subgroups�astrocytic glioma, oligodendroglioma and ependymoma. The statistical information is attention-grabbing, because more than three quarters of all glioma are astrocytoma, and the proportion of malignant tumours (anaplastic astrocytoma) among them is the most important (more than three quarters). The first classification of neuroepithelial tumours belongs to Bailey and Cushing (1926). The classifications bearing in mind other points of view have been developed afterward. Among them, the classifications of Kernohan and Sayre (1952), Smirnov (1962), Hominskyi (1969), Zulch (1965, 1986), and Russell and Rubinstein (1989) are probably the most identified. New morphological strategies, such as immunohistochemistry and molecular genetic analysis, have gained widespread utilization. New information about tumour structure led to modification for a quantity of instances and broadening of this classification in 1993, 2000 (Kleihues and Cavanee 2000) and Louis (2007). According to varied estimates, neuroepithelial tumours make up 50% of all brain tumours, and this is the most representative group. In adults, these tumours mainly have supratentorial areas, while for children the lesions of the posterior cranial fossa are extra typical. Unlike adults, tumours originating from neuroglia are seldom observed in youngsters. Among these neoplasms the astrocytoma is essentially the most frequent kind; its incidence is close to 30% of all supratentorial tumours. According to their histological types the gliomas are divided into the next groups: (1) astrocytoma, (2) oligodendroglioma and (3) ependymoma. The last type also includes tumours of choroid plexus, which include modified ependymal cells; the expansion of such tumours has many common characters with others gliomas. In addition, in teams of neuroepithelial tumours there are combined types of gliomas (oligoastrocytoma and others), tumours of unknown origin (for instance, mind gliomatosis), and neuronal or neuroglial tumours. According to Russell (1989), about 40�45% of all intracranial tumours are gliomas, they usually form the heterogeneous group of mind neoplasms that include relatively benign types in addition to very malignant tumours. Tumours with diffuse progress, characterised by poor prognosis, belong to the primary category. Tumours with increasing (different) degree of anaplasia from low-malignant astrocytoma to glioblastoma, characterised by the absence of clear macro- and microscopic borders separating tumour with surrounding tissue, belong to this category. The second category of tumours is delimited tumours, with better prognosis (pilocytic astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma and subependymal big cell astrocytoma). They make up about 6�21% of all intracranial tumours and about 40% of all glial tumours. In kids, the incidence of cerebrum astrocytoma reaches roughly 30% of all supratentorial mind tumours. Taking under consideration that proven reality that diffuse astrocytoma develops from neuroglia, they are often divided according to the histological criteria of malignancy and likewise based on the type of astrocyte (fibrillary or pilocytic one) for cellular proliferation. The incidence of diffuse astrocytomas is about 25�30% of all hemispheric gliomas, and roughly about 30% of all cerebellar gliomas are present in youngsters. These tumours can develop in any mind lobe; however, the occipital lobes are affected much less incessantly. According to Piepmeier (1987), 50% of surgically handled benign tumours remodel into anaplastic astrocytoma or glioblastoma. The progressive development of fibrillary astrocytoma may additionally be observed without improve of the extent of anaplasia. Division of diffuse glioma depending on the grade of malignancy is an important point in remedy selection and subsequent prognosis. The standards embody the presence of nuclear and cellular polymorphisms, proliferation of vessel endothelium, presence of mitosis, and foci of necrosis. It must be famous, nevertheless, that despite benign histological structure, all infiltrative low-malignant astrocytoma have poor prognosis. The foci of cystic degeneration could be noticed in tumour, whereas the foci of necrosis are by no means discovered. Microscopically, the fibrillar astrocytoma consists of mature tumour astrocytes, with a uncommon arrangement of cellular bodies and rather monomorphic nuclei. However, extra typically the angiography information are unfavorable, or minimal in the type of an insignificant disposition of the cerebral arteries (more often anterior and center cerebral arteries) from their typical location. Calcifications in the form of small or massive hyperintense foci are recognized in 15�20% of circumstances. Radiological clearness of tumour borders varies and depends on the level of change of tumour tissue density. Borders are higher visualised in instances of astrocytoma of low density, whereas isodense tumours are characterised by their much worse visibility. After distinction administration, the density of astrocytoma, positioned in the bottom of the third ventricle, subcortical ganglia, and posterior cranial fossa, increases; the formation of cysts can additionally be typical for these astrocytomas. However, as a rule, according to histological construction, these tumours are pilo- Supratentorial Tumours 337. The unfold hypodense space without clear borders is detected within the left temporal lobe.
Order altezym with american expressPenetrating and nonpenetrating accidents as properly as impactions may trigger focal ischaemia. Posttraumatic aneurysms and pseudo-aneurysms, based on Osborn (2002), extra regularly occur in the middle cerebral arteries (50%), distal branches of the anterior cerebral arteries (25%), and the petrous or cavernous elements of the interior carotid or basilar arteries (25%). Among other posttraumatic vascular events, arteriovenous fistulas (including carotid cavernous fistula) and thromboses should be talked about. Hyperhydration used in resuscitation may generally cause mind oedema however extra incessantly, it causes oedema of the soft tissues of head. Redistribution of liquid in neural and glial cells (swelling) and extracellular area (oedema) happens in posttraumatic water-electrolyte imbalance. In focal contusions, focal, perifocal, or hemispheric oedema develops extra frequently, and fewer frequently, oedema is diffuse. Contrast-accumulating inflammatory granulations are detected around this body 872 Chapter 9. In contrast, within the elderly mind oedema is less distinguished, regularly focal, slowly progresses, and reduces. Five types of brain oedema are distinguished: vasogenic, cytotoxic, hydrostatic, hypo-osmotic, and interstitial (Orrison 2000). Vasogenic oedema is attributable to local increase of cerebrovascular permeability, which outcomes in enhance of extracellular liquid content with predominant accumulation within the white matter. Cytotoxic oedema reaches its nadir on the fifth day, compared with 24 h in vasogenic oedema. Cytotoxic oedema is brought on by accumulation of intracellular fluid, with injury to all kinds of cells. Dysfunction of the sodium�potassium pump and insufficient excretion of water out of cells are two causes of cytotoxic oedema. Hydrostatic oedema develops as a outcome of abrupt an rise in intravascular stress, which exceeds normal cerebrovascular resistance. Hydrostatic oedema differs from vasogenic oedema, because the blood�brain barrier remains intact within the former. This type of oedema is seen in patients with considerably raised intracranial strain and abrupt change of the intravascular strain, for instance, after decompression craniotomy. Hypo-osmotic oedema develops as a end result of reduction of plasma osmolarity, which leads to excretion of fluid into the extravasal area. Disordered secretion of antidiuretic hormone is a reason for reduction of plasma osmolarity in these instances. Direct excretion of fluid out of ventricles into the adjoining white matter is marked. Posttraumatic oedema usually resolves within 2 weeks, frequently with consequent brain atrophy. Compression of parenchyma, nerves, and vessels in opposition to cranial bones and dural processes (falx, tentorium) are signs of primary injury. The diploma of impaction depends on the positioning of injury, progression price, particular person anatomic peculiarities, initial atrophy, and so on. The following types of impactions are distinguished: lateral (beneath the falx), transtentorial (ascending and descending) uni- and bilateral, transalar, impaction of cerebellar tonsils, and impaction of mind into the cranial defect. Lateral dislocation is a displacement of the cingulated gyrus beneath the free edge of falx across the median line. Compression and dislocation of the anterior or posterior cerebral arteries or their branches, occlusion occurs and as a consequence ischaemia and infarctions occurs. In this kind of impaction uncus and parahippocampal gyri are medially displaced and seen above the free fringe of tentorium. Herniation of the mind tissue into tentorial foramen with compression of the brain stem and ventricular system dislocation to the alternative side are revealed Head Trauma 881 of initiated impaction is smoothening of perimesencephalic and suprasellar cisterns ipsilaterally, and the ipsilateral cerebellopontine angle dilates as brainstem is displaced contralaterally to the dislocated temporal lobe. With progression of supratentorial mass impact, impaction of both medial elements of temporal lobes happens, which outcomes in complete obliteration of basal cisterns. The tentorial incisure is full of temporal lobes and inferior parts of midbrain. The latter is compressed and shortens in its transverse part; paresis or extra frequently palsy of oculomotor nerves occurs. The anterior choroid artery, posterior communicating artery, and posterior cerebral artery are additionally displaced within the inferior medial path in extreme descending impactions. Infarctions of occipital lobes are brought on by compression of the posterior cerebral artery between the brainstem and tentorium cerebelli. Secondary haemorrhages of the midbrain may also occur in transtentorial impactions and are brought on by compression of perforans arteries within the interpeduncular cistern. Foci of oedema, ischaemia, and haemorrhagic necrosis in the cerebral peduncle contralateral to the temporal lobe impaction are because of compression against tentorium, when brainstem is displaced from the affected side. Ascending transtentorial impaction is the upward impaction of cerebellar vermis and hemispheres via the tentorial incisure and is incessantly combined with infratentorial traumatic injury. They could additionally be ascending because of injury of the middle cranial fossa buildings with enlargement of the latter, and descending-the similar occasion within the frontal region. Displacement of the center cerebral artery, and temporal and frontal lobe via the big wing of the sphenoidal bone occurs. Impactions into the cranial defects happen soon after trauma, open cranium fractures, in postsurgical defects, or oedema. Lateral displacement regularly occurs, for instance, of the Sylvian fissure, middle cerebral artery, and the temporal lobe. The brain area, which is out-pouched, acquires form of fungus and haemorrhages might happen inside it. Angiography is mandatory in blunt and penetrating cervical wounds, as it might reveal occlusion of the carotid arteries, rupture and dissection of intima, arteriovenous fistulas, and vasospasm-diffuse or native narrowing of vessels. Carotid and vertebral artery territories are examined (special attention should be paid to their petrous parts), in addition to anterior and center cerebral arteries. Examination of sufferers with suspected arteriovenous fistulae must be made solely with cerebral angiography. Damage of squama of right temporal bone, traumatic injury of the right frontotemporal space, oe- dema, and descending transtentorial herniation. Pathological dumping circulate from the proper vertebral artery to the venous system of the best posterior cervical region. Selective angiography of the vertebral artery reveals pathological move from the left vertebral artery into the venous plexus at C1 degree (a direct and b lateral projections) Head Trauma 887. Brain demise occurs as a end result of severe traumatic or ischaemic brain harm; however, exact pathophysiology of intracranial blood move in mind dying is but to be additional elucidated. As is believed, the main explanation for brain demise is rise of intracranial pressure due to diffuse mind oedema (Kornienko 1981; Walner 1998; Ishii et al. Prolongation of T1 and T2 rest occasions is seen within the affected gyri and grey matter nuclei. Angiographic examinations (angiography, R, C) fail to reveal intracranial blood flow-it is absent above the supraclinoid a half of the internal carotid arteries and in the distal components of the vertebral arteries. According to medical and neuroimaging findings, the first group consists of posttraumatic focal and diffuse atrophy, cortical and subcortical gliosis, encephalomalacy, posttraumatic skull defects, acquired encephalocele, and meningoencephalocele. Meningoencephalitis, empyema, abscess, and meningitis compose a separate subgroup.

Purchase altezym 500mg visaThe first cervical vertebra, the atlas, lacks a body and has distinctive articulations with the base of the skull and the second vertebra. The second vertebra, referred to as the axis, consequently has atypical articulating surfaces. The laminae extend between the transverse processes and the spinous processes, and the pedicle extends between the vertebral physique and the transverse processes. When stacked vertically, the hole rings turn out to be the spinal canal during which the spinal cord and its coverings sit. There are four small synovial joints at every vertebra, two articulating with the vertebra above it and two with the vertebra below. The pedicles are notched superiorly and inferiorly, these notches forming the intervertebral foramina from which the spinal nerves exit. Sacral vertebrae normally fuse into one large bone, the sacrum, however each one retains discrete anterior and posterior intervertebral foramina. Ligamentous parts provide structural assist, and, along with supporting muscles, help to preserve the distinctive shape. Sacral hiatus interspinous ligament, and supraspinous ligament present extra stability. The pia mater is carefully adherent to the spinal cord, whereas the arachnoid mater is often closely adherent to the thicker and denser dura mater. The spinal subdural space is generally a poorly demarcated, potential space that exists between the dura and arachnoid membranes. At the cervical level, the nerves arise above their respective vertebrae, but starting at T1, exit under their vertebrae. As a outcome, there are eight cervical nerve roots, however only seven cervical vertebrae. Therefore, performing a lumbar (subarachnoid) puncture beneath L1 in an adult (L3 in a child) often avoids potential needle trauma to the twine; injury to the cauda equina is unlikely, as these nerve roots float in the dural sac beneath L1 and have a tendency to be pushed away (rather than pierced) by an advancing needle. Note the tip of the spinal wire rises with development from approximately L3 to L1. The dural sac and the subarachnoid and subdural areas normally lengthen to S2 in adults and infrequently to S3 in kids. Because of this fact and the smaller physique measurement, caudal anesthesia carries a larger threat of subarachnoid injection in kids than in adults. The anterior spinal artery is formed from the vertebral artery at the base of the cranium and courses down along the anterior surface of the wire. The anterior spinal artery provides the anterior two-thirds of the twine, whereas the two posterior spinal arteries supply the posterior one-third. B: Cross-sectional view through the spinal cord exhibiting paired posterior spinal arteries and a single anterior spinal artery. The anterior and posterior spinal arteries receive extra blood circulate from the intercostal arteries within the thorax and the lumbar arteries within the stomach. It is often unilateral and almost all the time arises on the left aspect, providing the main blood provide to the anterior, lower two-thirds of the spinal twine. In contrast, the identical local anesthetic concentration is achieved within nerve roots only with much bigger volumes and portions of native anesthetic molecules throughout epidural and caudal anesthesia. Moreover, the injection website (level) for epidural anesthesia should typically be close to the nerve roots that have to be anesthetized. Blockade of neural transmission (conduction) within the posterior nerve root fibers interrupts somatic and visceral sensation, whereas blockade of anterior nerve root fibers prevents efferent motor and autonomic outflow. Local anesthetics may have actions on constructions inside the spinal wire during epidural and spinal anesthesia. Smaller and myelinated fibers are generally more simply blocked than bigger and unmyelinated ones. The dimension and character of the fiber varieties, and the fact that the concentration of native anesthetic decreases with rising distance from the extent of injection, explains the phenomenon of differential blockade 4 throughout neuraxial anesthesia. Differential blockade usually ends in sympathetic blockade (judged by temperature sensitivity) which may be two segments or more cephalad than the sensory block (pain, light touch), which, in flip, is often several segments more cephalad than the motor blockade. Sympathetic outflow from the spinal twine could additionally be described as thoracolumbar, whereas parasympathetic outflow is craniosacral. Sympathetic preganglionic nerve fibers (small, myelinated B fibers) exit the spinal cord with the spinal nerves from T1�L2 and will course many levels up or down the sympathetic chain before synapsing with a postganglionic cell in a sympathetic ganglion. In distinction, parasympathetic preganglionic fibers exit the spinal cord with the cranial and sacral nerves. The physiological responses of neuraxial blockade subsequently outcome from decreased sympathetic tone and/or unopposed parasympathetic tone. Sensory Cardiovascular Manifestations in blood stress which could be accompanied by a lower in coronary heart rate. Vasomotor tone is primarily determined by sympathetic fibers arising from T5� L1, innervating arterial and venous easy muscle. Blocking these nerves causes vasodilation of the venous capacitance vessels and pooling of blood in the viscera and decrease extremities, thereby reducing the effective circulating blood volume and venous return to the guts. The effects of arterial vasodilation could also be minimized by compensatory vasoconstriction above the extent of the block, particularly when the extent of sensory anesthesia is proscribed to the decrease thoracic dermatomes. A high sympathetic block not solely prevents compensatory vasoconstriction, however may block the sympathetic cardiac accelerator fibers that arise at T1�T4. Profound hypotension might outcome from arterial dilation and venous pooling mixed with bradycardia (and presumably also milder degrees of decreased contractility). These effects are exaggerated if venous pooling is further augmented by a head-up position or the load of a gravid uterus. Unopposed vagal tone could explain the sudden cardiac arrest generally seen with spinal anesthesia. However, volume loading with 10�20 mL/kg of intravenous fluid in a healthy affected person earlier than initiation of the block has been proven repeatedly to fail to forestall hypotension (in the absence of preexisting hypovolemia). Left uterine displacement within the third trimester of being pregnant helps to reduce physical obstruction to venous return. Despite these efforts, hypotension should still occur and ought to be treated promptly. Autotransfusion may be achieved by inserting the patient in a head-down position. Excessive or symptomatic bradycardia must be treated with atropine, and hypotension should be treated with vasopressors. Direct -adrenergic agonists (such as phenylephrine) primarily produce arteriolar constriction and will reflexively increase bradycardia, increasing systemic vascular resistance. The "blended" agent ephedrine has direct and oblique -adrenergic effects that enhance heart rate and contractility and oblique results that also produce vasoconstriction. Much like ephedrine, small doses of epinephrine (2�5 mcg boluses) are significantly useful in treating spinal anesthesia induced hypotension.
Buy altezym 250mg visaThe potential importance of intracellular potassium focus is quickly obvious from this equation. In pathological states, glucose and-to a a lot lesser extent-urea can contribute significantly to extracellular osmolality. Urea is an ineffective osmole as a result of it readily permeates cell membranes and is therefore frequently omitted from this calculation: Effective plasma osmolality = [Na+] � 2 + glucose 18 Plasma osmolality usually varies between 280 and 290 mOsm/L. Plasma sodium focus decreases roughly 1 mEq/L for each 62 mg/dL enhance in glucose focus. A discrepancy between the measured and calculated osmolality is referred to as an osmolal gap. Significant osmolal gaps point out a high focus of an irregular osmotically energetic molecule in plasma corresponding to ethanol, mannitol, methanol, ethylene glycol, or isopropyl alcohol. Osmolal gaps may be seen in sufferers with continual kidney failure (attributed to retention of small solutes), patients with ketoacidosis (as a result of a excessive focus of Based on a 70-kg adult male. Lastly, osmolal gaps may also be present in sufferers with marked hyperlipidemia or hyperproteinemia. The water part of plasma is generally only 93% of its quantity; the remaining 7% consists of plasma lipids and proteins. Plasma osmolality is due to this fact maintained inside relatively slim limits by varying both water intake and water excretion. Hyperosmolality without hypernatremia may be seen throughout marked hyperglycemia or following the buildup of abnormal osmotically lively substances in plasma (see above). In the latter two instances, plasma sodium concentration may very well lower as water is drawn from the intracellular to the extracellular compartment. For each one hundred mg/dL increase in plasma glucose focus, plasma sodium decreases approximately 1. Hypernatremia is kind of all the time the outcomes of either a relative lack of water in extra of sodium (hypotonic fluid loss) or the retention of enormous portions of sodium. Even when renal concentrating capability is impaired, thirst is normally highly efficient in stopping hypernatremia. Patients with hypernatremia might have a low, regular, or high total physique sodium content material (Table 49�4). Secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone Specialized neurons within the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus are very sensitive to modifications in extracellular osmolality. Hypernatremia & Low Total Body Sodium Content these sufferers have lost both sodium and water, however the water loss is in relative extra to that of the sodium loss. Urinary sodium concentration is generally larger than 20 mEq/L with renal losses and less than 10 mEq/L with extrarenal losses. Impaired thirst Coma Essential hypernatremia Solute diuresis Osmotic diuresis: diabetic ketoacidosis, nonketotic hyperosmolar coma, mannitol administration Excessive water losses Renal Neurogenic diabetes insipidus Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus Extrarenal Sweating Combined issues Coma plus hypertonic nasogastric feeding Hypernatremia & Normal Total Body Sodium Content this group of patients generally manifests indicators of water loss without overt hypovolemia except the water loss is very large. Occasionally transient hypernatremia is observed with motion of water into cells following exercise, seizures, or rhabdomyolysis. The most common cause of hypernatremia in conscious patients with normal total body sodium content is diabetes insipidus. Rarely, "essential hypernatremia" may be encountered in patients with central nervous system issues. These patients seem to have "reset" osmoreceptors that perform at the next baseline osmolality. The diagnosis is typically recommended by a historical past of polydipsia, polyuria (often >6 L/d), and the absence of hyperglycemia. In the perioperative setting, the analysis of diabetes insipidus is sometimes recommended by marked polyuria without glycosuria and a urinary osmolality decrease than plasma osmolality. The absence of thirst in unconscious individuals leads to marked water losses and may rapidly produce hypovolemia. Aqueous vasopressin (5�10 items subcutaneously or intramuscularly each 4�6 h) is the remedy of alternative for acute central diabetes insipidus. Central Diabetes Insipidus Lesions in or around the hypothalamus and the pituitary stalk incessantly produce diabetes insipidus. Transient diabetes insipidus is also commonly seen following neurosurgical procedures and B. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus can be congenital but is extra commonly secondary to other disorders, together with persistent kidney illness, hypokalemia and hypercalcemia, sickle cell disease, and hyperproteinemias. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus may additionally be secondary to the side effects of some drugs (amphotericin B, lithium, demeclocycline, ifosfamide, mannitol). Volume depletion by a thiazide diuretic can paradoxically lower urinary output by decreasing water supply to amassing tubules. As intracellular solute concentration increases, neuronal water content slowly returns to normal. Treatment of Hypernatremia the therapy of hypernatremia is geared toward restoring plasma osmolality to normal in addition to correcting the underlying cause. Water deficits should usually be corrected over 48 h with a hypotonic solution such as 5% dextrose in water (see below). Hypernatremic patients with decreased complete body sodium ought to be given isotonic fluids to restore plasma quantity to regular prior to therapy with a hypotonic answer. Hypernatremic sufferers with elevated whole body sodium should be handled with a loop diuretic along with intravenous 5% dextrose in water. Rapid correction of hypernatremia can outcome in seizures, brain edema, permanent neurological harm, and even dying. Clinical Manifestations of Hypernatremia Neurological manifestations predominate in patients with hypernatremia and are generally thought to end result from mobile dehydration. Restlessness, lethargy, and hyperreflexia can progress to seizures, coma, and ultimately dying. Symptoms correlate more intently with the rate of movement of water out of brain cells than with absolutely the degree of hypernatremia. Rapid decreases in brain quantity can rupture cerebral veins and lead to focal intracerebral or subarachnoid hemorrhage. Seizures and severe neurological damage are frequent, particularly in kids with acute hypernatremia when plasma [Na+] exceeds 158 mEq/L. After 24�48 h, intracellular osmolality begins to rise as a end result of will increase in intracellular inositol and amino Example A 70-kg man is discovered to have a plasma [Na+] of one hundred sixty mEq/L. Note that this technique ignores any coexisting isotonic fluid deficits, which if current must be changed with an isotonic resolution. Anesthetic Considerations Hypernatremia has been demonstrated to improve the minimum alveolar focus for inhalation anesthetics in animal research, however its medical significance is more carefully associated to the related fluid deficits. Hypovolemia accentuates any vasodilation or cardiac melancholy from anesthetic brokers and predisposes to hypotension and hypoperfusion of tissues. Decreases in the quantity of distribution for medicine necessitate dose reductions for many intravenous agents, whereas decreases in cardiac output enhance the uptake of inhalation anesthetics. Elective surgical procedure ought to be postponed in sufferers with significant hypernatremia (>150 mEq/L) till the trigger is established and fluid deficits are corrected.
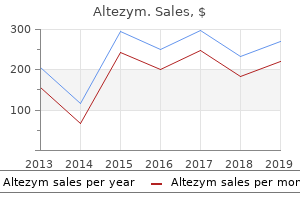
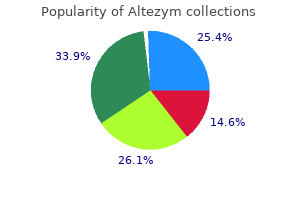
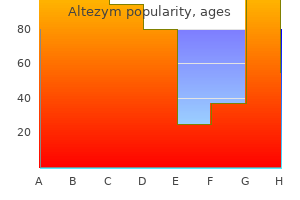
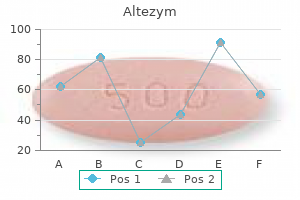
Heavenly Elixir (Tinospora Cordifolia). Altezym. - What is Tinospora Cordifolia?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
- How does Tinospora Cordifolia work?
- Allergies (Hayfever).
- Dosing considerations for Tinospora Cordifolia.
- Diabetes, high cholesterol, upset stomach, gout, cancer including lymphoma, rheumatoid arthritis, liver disease, stomach ulcer, fever, gonorrhea, syphilis, and to counteract a suppressed immune system.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97101
Buy genuine altezym on-lineAs previously famous, applicable documentation of affected person care activities, differential diagnoses, and therapeutic interventions helps to present a defensible report of the care that was supplied, immune to the passage of time and the stress of the litigation expertise. When an opposed end result happens, the hospital and/or follow risk administration group ought to be immediately notified. Some policies have a clause that disallows the practitioner from admitting errors to sufferers and families. Nevertheless, most threat managers advocate a frank and honest disclosure of opposed occasions to sufferers or approved relations. It is possible to specific sorrow about an adverse end result with out admitting "guilt. Malpractice insurers will rent a protection firm to characterize the anesthesia employees concerned. In some systems (usually when everyone in a well being system is insured by the same carrier), all the named entities are represented by one defense team. More commonly, numerous insurers and attorneys represent particular practitioners and institutional suppliers. In this instance, these involved might deflect and diffuse blame from themselves and focus blame on others also named within the motion. Oftentimes, expediency and monetary threat publicity will argue for settlement of the case. The practitioner might or might not be capable of take part in this decision relying upon the insurance policy. Moreover, malpractice fits, settlements, and judgments should be reported to hospital authorities as part of the credentialing course of. When applying for licensure or hospital appointment, all such actions have to be reported. The litigation process begins with the delivery of a summons indicating that an action is pending. Once delivered, the anesthesia defendant should contact his or her malpractice insurer/risk management department, who will appoint legal counsel. Counsel for each the plaintiff and protection will determine "independent specialists" to review the circumstances. These "consultants" are paid for his or her time and bills and can arrive at dramatically totally different assessments of the case supplies. Most defense attorneys will advise their purchasers to reply questions as actually and simply as possible, without providing extraneous commentary. Following discovery, the insurers, plaintiffs, and protection attorneys will "value" the case and try and monetize the damages. Items, corresponding to pain and struggling, lack of consortium with spouses, misplaced wages, and tons of other factors, are included in determining what the harm is price. Juries are unpredictable, and each parties are sometimes hesitant to take a case to trial. There are bills associated with litigation, and, consequently, both plaintiff and defense attorneys will try to keep away from uncertainties. Nonetheless, an award in extra of the insurance policy maximum could (depending on the jurisdiction) place the personal property of the defendant suppliers at risk. This underscores the significance of our recommendation to all practitioners (not only these involved in a lawsuit) to assemble their private property (house, retirement fund, etc. One should do not neglect that an adverse judgment may come up from a case during which most anesthesiologists would find the care to meet acceptable standards! When a case proceeds to trial, step one is jury selection in the process of voir dire-from the French-"to see, to say. Each lawyer is prepared to strike a certain variety of jurors from the pool as a result of they understand an inherent bias. The jurors shall be questioned about such matters as their educational level, historical past of litigation themselves, professions, and so forth. Expert witnesses will try and define what the standard of care is for the neighborhood, and the plaintiff and defendant will present experts with views which would possibly be favorable to their respective cause. Many instances will settle through the course of the trial, as neither celebration needs to be subject to the arbitrary selections of an unpredictable jury. Consultation with a psychological health skilled may be acceptable for the defendant when the litigation process ends in unmanageable stress, depression, elevated alcohol consumption, or substance abuse. In the United Sates, the definition of "normal of care" is made separately by every state. Generally, the standard of care is met when a patient receives care that other affordable physicians in related circumstances would regard as enough. Increasingly, numerous "tips" have been developed by the multiple specialty societies to identify greatest practices in accordance with assessments of the evidence in the literature. The increasing variety of guidelines proffered by the quite a few anesthesia and other societies and their frequent updating can make it troublesome for clinicians to keep abreast of the changing nature of apply. This is a selected problem when two societies produce conflicting tips on the same subject using the identical data. Likewise, the information upon which guidelines are based can vary from randomized medical trials to the opinion of "experts" in the field. Guidelines produced by reputable societies will generally embrace an acceptable disclaimer based on the extent of proof used to generate the rule. Clinically essential measurable outcomes are relatively rare after elective anesthetics. For instance, death is a clear endpoint, and perioperative deaths do occur with some regularity. But, because deaths attributable to anesthesia are much rarer, a very massive sequence of patients must be studied to assemble conclusions that have statistical significance. Nonetheless, many studies have attempted to decide the incidence of problems due to anesthesia. Unfortunately, studies range in criteria for outlining an anesthesiarelated opposed consequence and are restricted by retrospective analysis. In a research carried out between 1948 and 1952, anesthesia mortality in the United States was roughly 5100 deaths per yr or three. A evaluate of reason for demise information within the United States showed that the speed of anesthesia-related deaths was 1. However, a 2002 study reported an estimated rate of 1 death per thirteen,000 anesthetics. Due to variations in methodology, there are discrepancies in the literature as to how properly anesthesiology is doing in attaining secure follow. A subsequent evaluation of the 88 deaths that occurred on the surgical day noted that 13 of (Reproduced, with permission, from Li G, Warner M, Lang B, et al: Epidemiology of anesthesia-related mortality in the United States 1999-2005. Additionally, this research reported Spine Intracranial Urologic Abdominal Head/Neck Other Vasc. Indeed, usually missed opportunities for improved anesthetic care occur following problems when "failure to rescue" contributes to affected person demise.
100mg altezym otcIt is possible to differentiate abscesses from necrotising tumours on this regimen in almost 100 percent of instances. Infection may expand into the subdural and epidural areas, with development of subdural and epidural empyemas. The most frequent places of subdural empyemas are the convex brain floor above the cerebral hemispheres (80%), interhemispheric fissure (12%), and frontal region, for epidural empyemas (Sze and Lee 1999). Multiplanar examination (especially when coronal part is used) improved diagnostics for instances with paratentorial or subtemporal suppuration. Dura mater seems as hypointense rim separating mind tissue and the epidural area. The pathogens of posttraumatic meningitis could additionally be of a bacterial, fungal, viral, or parasitic nature. When an infection continues to develop, mild hyperdensity may be seen in basal cisterns, interhemispheric fissure, and choroid plexus, which is the results of the mix of hypervascularity of contaminated meninges Head Trauma 905. Thrombosis of sinuses (revealed on angiography), hydrocephalus with the subsequent calcinosis of meninges might complicate meningitis. Ependymitis could develop secondarily to leptomeningitis in retrograde expansion of an infection, after spontaneous or iatrogenic rupture of an abscess into the ventricles, or if shunts placed for hydrocephalus are infected. In extreme instances 1-weighted imaging might reveal distinguished hyperintense signal in the periventricular area, and 2-weighted imaging may reveal hyperintense signal round cerebral ventricles, which is extra focal and irregular than in hydrocephalus. Accumulation of contrast medium is more typically seen alongside the walls of the lateral ventricles. Mechanism of flow-void sign within the aqueduct is just like what we see in blood circulate. It is best seen on T2weighted imaging and proton density photographs on axial and sagittal scans by way of the aqueduct. Flow-void phenomenon within the Sylvian aqueduct is an indicator of pathological situation wherever it develops (occlusion superior or inferior to the aqueduct). Prominent flow-void phenomenon can also be physiological in youngsters as a end result of tachycardia and larger volume of choroid plexus compared to adults. However, it requires high-resolution acquisition of thin slices, particularly at the degree of foramen magnum and midbrain. In communicating of the aresorptive hydrocephalus, symmetrical dilatation of all components of the ventricular system is present. Obstruction usually involves convex subarachnoid areas however may also contain basal cisterns. On T2-weighted imaging, flow-void phenomenon is absent not solely in the aqueduct, but in addition proxi- mally, within the third ventricle and distally, in the dilated fourth ventricle. At current normotense hydrocephalus is defined as a combination of persistent communicating hydrocephalus and atrophic parenchymal brain modifications. According to our knowledge, average narrowing of ventricles and discount of periventricular oedema is seen in 1�2 weeks after shunting; 3�4 weeks after shunting ventricles continue to lower in dimension, and 3 months after shunting their sizes normalise and periventricular oedema disappears. In different instances, it developed later, and in several circumstances in the delayed period-months or years later. Spontaneous closure of fistula is observed in adhesive processes, displacement of brain tissue towards bone defect, and fewer frequently in instances with formatted granulation tissue after concomitant meningitis. Pneumocephalus is among the options that prove communication of the subarachnoid spaces and the exterior house. Meningoencephalitis, ventriculitis, empyema, and mind abscess may complicate traumatic basal liquorrhea along with meningitis. The most vital issue of their improvement is duration of liquorrhea over than 14 days. They may happen throughout the first 10 days in these patients who underwent urgent evacuation of acute intracerebral haematomas. One of attainable causes is impairment of coagulation alongside with primary brain damage, which results in consequent intracerebral bleeding and haemorrhagic infarctions. Delayed intracerebral haematomas are most always lobar, and regularly multifocal, and may be present in those areas the place contusion lesions have been seen earlier. There are observations of patients who underwent urgent craniotomy with extracerebral haematoma evacuation, and later delayed contralateral haemorrhage developed within the following two weeks (Zee et al. New neuroimaging methods study complex and ultrastructural neuropathophysiological events and then to map them anatomically. Lippincott Williams & Wilkinson, New York, pp 257�271 918 Cooper P (1982) Head damage. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkinson, New York Evans S, Gean A (1999) Craniocerebral trauma. Louis, pp 1347�1360 Firsching R et al (2001) Classification of severe head harm based mostly on magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Neurochir (Vienna) 143:263�271 Friedman J, Ebersold M, Quast L (2001) Post-traumatic cerebrospinal fluid leakage. Petersburg, Russia Gavrilov A, Potapov A, Kravchuk A et al (2003) [Skull base fractures: medical and prognostic features. Raven, New York Gentleman S et al (1995) Axonal harm: a common consequence of deadly closed head injsury. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 10:309�331 Kim S, Chang K, Song I et al (1997) Brain abscess and brain tumor. Radiology 204:239�245 Konovalov A, Lihterman L, Potapov A (eds) (2002) Clinical guide on traumatic mind damage. Antidor, Moscow (in Russian) Kornienko V, Vasin V, Kuzmenko V (1987) Computed tomography in diagnostics of traumatic mind damage. Medicina, Moscow (in Russian) Kornienko V (1981) Angiographic examine of the brain hemodynamic in neurosurgery patients with irreversible changes. Neuroimaging Clin N Am12:2 Lichterman L, Potapov A (1998) [Classification of head trauma. Acta Radiol 42:365�9 Ommaya A (1996) Cerebrospinal fluid fistula and pneumocephalus. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 2773�2782 Orrison W (2000) Neuroimaging and head trauma. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 884�915 Osborn A (1991) Secondary effects of intracranial trauma. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 25�27 Potapov A, Lihterman L, Zelman V et al (2003) Evident neurotraumatology. Medicine, Moscow (in Russian) Wilde E, Chu Z, Bigler E et al (2006) Diffusion tensor imaging within the corpus callosum in youngsters after average to severe traumatic brain injury. Radiology 232:211�220 Yasokawa Y et al (2007) Correlation between diffusion-tensor magnetic resonance imaging and motor-evoked potential in continual extreme diffuse axonal harm.

Best purchase for altezymIncreased cardiovascular threat associated with the perioperative use of celecoxib or valdecoxib in sufferers with minimal cardiovascular danger components and present process nonvascular surgery has not been proven. Acetaminophen (paracetamol)-Oral, rectal, and parenteral acetaminophen is a typical part of multimodal analgesia. Opioids-Despite the increasing use of latest, nonopioid analgesic medicines and adjuvants and of regional anesthesia and analgesia methods meant to decrease opioid requirements and opioid-related side effects (Table 48�4), the use of systemic opioids stays a cornerstone in the administration of surgical ache. Parenteral opioids are incessantly prescribed in the postoperative interval during the transitional section 10 to oral analgesia. Preoperative administration of extended-release oxycodone in patients present process surgical procedure of short length offers sufficient plasma focus and analgesia following discontinuance of remifentanil infusion. Epidural analgesia-In addition to providing wonderful analgesia, epidural blockade blunts the stress response associated with surgery, decreases postoperative morbidity, attenuates catabolism, and accelerates postoperative useful restoration. Compared with systemic opioid analgesia, thoracic epidural analgesia provides better static and dynamic pain relief. Administering low doses of native anesthetic through thoracic epidural infusion avoids decrease extremity motor blockade which will delay postoperative mobilization and restoration. Adding fentanyl or sufentanil to epidural local anesthetics improves the quality of postoperative analgesia with out delaying restoration of bowel function. A recent meta-analysis of greater than 2700 sufferers who underwent cardiac surgical procedure and received high thoracic epidural analgesia showed an total reduction of pulmonary problems (relative danger = zero. Due to considerations concerning the danger of epidural hematoma and its devastating neurological penalties in patients absolutely heparinized throughout cardiopulmonary bypass, using excessive thoracic epidural analgesia is understandably restricted. Peripheral nerve block-Single-shot and continuous peripheral nerve blockade is regularly utilized for fast-track ambulatory and inpatient orthopedic surgery, and may speed up restoration from surgery and enhance analgesia and affected person satisfaction (see Chapter 46). The opioidsparing effect of nerve blocks minimizes the chance of opioid-related unwanted effects. Appropriate patient selection and strict adherence to institutional medical pathways helps make sure the success of peripheral nerve blockade as a fast-track orthopedic analgesia method. Local anesthetic wound infusion-The analgesic efficacy of local anesthetic wound infusion has been established for multiple surgical procedures. Inconsistent outcomes could also be because of elements that embody sort, focus, and dose of native anesthetic, catheter placement approach and sort of catheter, mode of native anesthetic supply, incision location, and dislodgment of the catheter throughout affected person mobilization. Comfortable chairs and walkers must be made available close to each patient mattress to encourage patients to sit, stand, and walk. The advantages of mobilization for cardiovascular homeostasis and bowel perform have been shown repeatedly. Patients ought to be encouraged to sit the night following surgery, with ambulation starting the next day for no much less than 4�6 h each day. The high quality of ache reduction and symptom management closely influences postoperative restoration; optimal mobilization and dietary intake rely upon enough analgesia. The patient should be snug ambulating and performing physiotherapy, with minimal side effects corresponding to lightheadedness, sedation, nausea and vomiting, and leg weak spot. Strategies to Minimize Postoperative Ileus 12 Postoperative ileus delays enteral feeding, causes affected person discomfort, and is amongst the most common causes of extended postoperative hospital keep. Three primary mechanisms contribute to ileus: sympathetic inhibitory reflexes, local inflammation attributable to surgery, and postoperative opioid analgesia. The nasogastric tube, regularly inserted Strategies to Facilitate Recovery on the Surgical Unit A. Therefore, nasogastric tubes ought to be discouraged each time attainable or used for under a really short time period, even in gastric and hepatic surgery. Continuous epidural local anesthetic infusion improves the recovery of bowel function by suppressing the inhibitory sympathetic spinal twine reflexes. Thoracic epidural analgesia with local anesthetics and small doses of opioids reduces the incidence of ileus and improves postoperative ache reduction. Minimally invasive surgical procedure decreases surgical stress and irritation, leading to a faster return of bowel perform. Any function of epidural analgesia in accelerating the restoration of bowel operate after laparoscopic surgery remains controversial, at finest. Laxatives, corresponding to milk of magnesia and bisacodyl, cut back postoperative ileus period. Excessive perioperative fluid administration generally causes bowel mucosal edema and delays postoperative return of bowel operate. However, results from a randomized double-blind study of liberal versus restricted fluid administration confirmed no variations with regard to recovery of bowel perform in sufferers present process fast-track belly surgery. No studies have in contrast crystalloid versus colloid administration in terms of their effect thirteen on the return of bowel operate. Because either excessive, or excessively restricted, perioperative fluid therapy could improve the incidence and severity of postoperative ileus, a goal-directed fluid technique (discussed earlier) must be chosen to lower postoperative morbidities and improve restoration and must be utilized based on the type of surgical procedure and patient comorbidities. Postoperative chewing gum, by stimulating gastrointestinal reflexes, might decrease ileus period. Peripheral opioid -receptor antagonists methylnaltrexone and alvimopan have been introduced to decrease the antagonistic effects of opioids on bowel operate with out antagonizing opioid analgesia. In patients receiving large-dose intravenous morphine analgesia, alvimopan decreases the period of postoperative ileus by 16�18 h, the incidence of nasogastric tube reinsertion, postoperative morbidity, and hospital length of keep and readmission rates, especially in sufferers present process bowel resection. Patient involvement and affected person and household expectations are critically essential, however frequently missed, aspects of these programs. New surgical strategies, like transverse incisions or minimally invasive surgical procedure, could require surgeons to acquire and excellent new abilities. Aggressive analgesia and symptom management, early ambulation and physiotherapy, early nutrition protocols, and early removal or total avoidance of urinary drainage catheters significantly change the finest way patients are cared for within the postanesthesia recovery unit and on the surgical unit and require a well-organized, extremely educated, extremely motivated nursing workers. Each household of comparable surgical procedures requires a standardized interdisciplinary scientific protocol or pathway, with specialized enter from a staff with experience in caring for these sufferers. The current era is one by which optimal surgical care requires the anesthesia supplier to be part of the perioperative medication team. Carli F, Kehlet H, Baldini G, et al: Evidence foundation for regional anesthesia in multidisciplinary fast-track surgical care pathways. Chappell D, Jacob M, Hofmann-Kiefer K, et al: Rational strategy to perioperative fluid administration. Collard V, Mistraletti G, Taqi A, et al: Intraoperative esmolol infusion within the absence of opioids spares postoperative fentanyl in patients undergoing ambulatory laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Coulter A, Ellins J: Effectiveness of strategies for informing, educating, and involving sufferers. Dunkelgrun M, Boersma E, Schouten O, et al: Dutch Echocardiographic Cardiac Risk Evaluation Applying Stress Echocardiography Study Group. Kelin J: Multimodal multidisciplinary standardization of perioperative care: Still a protracted way to go This is as a outcome of the average kinetic energy of particles in resolution is analogous no matter their mass. Potassium is crucial determinant of intracellular osmotic pressure, whereas sodium is the most important determinant of extracellular osmotic pressure. Fluid change between the intracellular and interstitial areas is governed by the osmotic forces created by differences in nondiffusible solute concentrations.
Order altezym 250 mg onlineOn 2-weighted imaging () and 1-weighted imaging (b�d), a tumour of heterogeneous structure with a large cyst is seen in the right half of pons Infratentorial Tumours 687. On 2-weighted imaging (c) and 1-weighted imaging (d), a tumour with cystic element is seen. Large cysts encircle the tumour within the fourth ventricle and the left pontocerebellar cistern 688 Chapter 7 in the site of tumour. Distribution of the tumour process with involvement of two levels of brainstem and its complete length with involvement of basal ganglia and cerebellar hemispheres are necessary tumour traits. The tumour affecting the medulla might involve the superior parties of the spinal cord. In some instances when a tumour has infiltrative growth, there are areas revealed during which compact growth predominates, with a comparatively clear border with brain tissue, and causes as compression of intact constructions. The whole transverse section of brainstem could additionally be affected, or the process might are inclined to be extra unilateral. As talked about above, tumours could include cysts of varied sizes, as much as complete cystic transformation. A tumour may develop onto the brainstem floor, forming exophytic tumours laterally, anteriorly, or contained in the fourth ventricle. On 2-weighted imaging (b,c) and 1-weighted imaging (d), a diffuse tumour development is seen within the basal ganglia bilaterally with involvement of midbrain, pons, and the left cerebellar hemisphere Infratentorial Tumours. The backside of fossa rhomboidea is evaginated, and the flattened fourth ventricle is displaced backwards 689. Pseudonodular, infiltrative tumours are the least frequent among brainstem tumours. However, on microscopy, infiltrative progress is revealed, with destruction of brain tissue. According to the modern idea, the management plan in sufferers with brainstem tumours relies on advanced assessment of such parameters as topography, type of progress, histology if out there, and presence of cystic and exophytic elements. Most neurosurgeons imagine that not more than 20% of all brainstem tumours are operable (Knovalov et al. It is essential to confirm the distribution of the exophytic element of a tumour. Besides those within the brainstem, forms of major tumours or metastases, such as ganglioastrocytomas, astroblastomas, angioreticulomas, melanoma metastases, etc. On T1-weighted imaging, a hypointensive, and on T2-weighted imaging, a hyperintensive signal, are revealed. On T2weighted imaging (), a tumour of heterogeneous structure is seen with an exophytic part. On 1-weighted imaging (b,c), hyperintensive foci are revealed within the tumour stroma (haemorrhages within a tumour). On 2-weighted imaging () and 1-weighted imaging (b), a tumour of pons is revealed with growth onto midbrain. On the background of a generally hypodensive zone into the pons, an space of heterogeneous accumulation of distinction medium is seen, and the central a part of the lesion is necrotic. The tumour is hypointensive to brain tissue on 1-weighted imaging and intensively accumulates contrast medium. Brainstem haemorrhages should be distinguished from tegmental basilar brainstem haemorrhage, which develops in aged folks with arterial hypertension. Haemorrhagic transformation of the mind tissue is typical for the latter and not only tegmental, but in addition brainstem base involvement occurs. This time period was introduced by Russell and Rubinstein (1989) in Fifties to outline vascular malformations not revealed on cerebral angiography. Capillary telangiectasias present as one of many branched (racemous) vascular malformations. Accumulation of dilated capillaries with alternating mind tissue inside is an important histological function. On microscopy, telangiectasias are seen as dilated vessels lined with endothelium lying on basal membranes. Elastic and muscle tissues are absent, and an argyrophilic matrix is identified in each vessel. The pons is the standard location of telangiectasias-the predominant website of brainstem haemorrhages. Cavernous malformations or angiomas (C) have been distinguished as a group of pure developmental defects only in 1979 inside the International Histological Classification of Tumours. C represents a system of speaking vascular cavities of various dimension and of a sinusoid kind filled with blood. Vascular cavities are separated by connective tissue septi, which are frequent for a number of adjoining cavities. Walls of these cavities are lined with endothelium that types papillary exophytic growths. Intrinsic argyrophilic matrix is current in each cavity, and muscle and elastics layer are absent. Capillaries and intermingling strands of endothelial cells without lumen are situated between vessels. Reactive glial adjustments stained yellow are typical in the perifocal zone and are due to imbibition of the mind tissue with haemosiderin amassed in macrophages. Often accumulations of branching vessels resembling capillaries are seen on the periphery of a malformation. Depending on the sort of onset (neurological event), three variants are distinguished: stroke-like, pseudotumour, and combined (encompassing elements of the former two). In some instances, displacement of cerebral arteries, typical for a mass lesion within the brainstem, is found. In instances of large venous angiomas, pathologically dilated veins seen in the capillary part and smaller inletting branches ("brush" sign) are an exception. If located on the degree of inferior brainstem, artefacts caused by bone may hinder imaging of the haemorrhage. After liquefaction and resorption of a blood clot, which begins on a haemorrhage periphery, if there have been no repeated haemorrhages, then an initial haemorrhage turns into much less hyperdensive. Abnormally situated small veins within the left half of the posterior fossa are seen in the venous phase, which drain into a single hypertrophied vein-the "brush" signal (arrows) 702 Chapter 7. Then, a haemorrhage turns into hypodensive, which represents the liquefaction and resorption of the blood clot. This is why the quality of imaging of an acute haemorrhage is determined by the presence of water molecules-they look isointensive on 1-weighed images and hyperintensive on 2-weighted photographs. Later, oxyhemoglobin transforms into deoxyhaemoglobin, which shortens 2 within the space of a haemorrhage, but the latter nonetheless remains isointensive on T1-weighted imaging. Further oxidation results in formation of methaemoglobin, which markedly will increase signal of haemorrhage on 1- and 2-weighted imaging.
References - Severi G, Morris HA, MacInnis RJ, et al: Circulating steroid hormones and the risk of prostate cancer, Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15:86n91, 2006.
- Yuan B, Xu Y, Woo JH, et al: Increased expression of mitotic checkpoint genes in breast cancer cells with chromosomal instability, Clin Cancer Res 12:405n410, 2006.
- Goh JT: A new classification for female genital tract fistula, Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 44:502n504, 2004.
- Gallai, V., Sarchielli P., Trequattrini, A. et al. (1994). Neuropeptide Y in juvenile migraine and tension-type headache. Headache, 34, 35n40.
- Asgari MA, Hosseini SY, Safarinejad MR, et al: Penile fractures: evaluation, therapeutic approaches and long-term results, J Urol 155:148n149, 1996.
|
|