"Purchase benzac american express, skin care videos youtube."By: Jonathan Tze-Wei Ho, M.A., M.D. - Assistant Professor of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine
 https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/10003132/jonathan-ho
20 gr benzac saleIn addition, she had a loss of two-point, vibration, and proprioception senses on the right side within the higher and lower limbs, trunk, and neck and a loss of pinprick sensations on the best aspect of her face. Account for the lack of pain in the best eye but the presence of a corneal reflex on stimulating this eye. If these phenomena are a results of a vascular occlusion (thrombosis), which major mind artery is most probably concerned Her historical past confirmed that these abnormalities have been the newest in a long collection of occasions. About 5 years previously, the lady had a collection of dizzy spells and complained of tinnitus in the proper ear. Several years later, the noise disappeared, and the patient noticed a hearing loss in the identical ear. These current occasions have been accompanied by difficulty in swallowing and hoarseness. Neurologic examination additionally revealed a lack of taste on the proper aspect of her tongue. Name the buildings involved and specify which abnormality is associated with each. A 29-year-old lady, who because the delivery of her fourth child 2 years in the past had been taking 3. An extensor plantar response was current on the best aspect, tendon reflexes of the best limbs had been exaggerated, and resistance to passive actions was elevated. Pinprick was not sharp and was poorly localized, and a lack of tactile and proprioception senses on the proper aspect of the complete body was evident. Account for (1) the weak spot of the best decrease facial muscles and never the higher and (2) the presence of decreased sensation to pinprick, but the complete absence of tactile and proprioception senses on the proper side. She was unable to supinate and pronate her proper arm repetitively for even brief periods. Why did the abnormalities happen only when the affected person performed a volitional movement On entering the examining room, he strikes slowly and deliberately, shuffling his feet, his shoulders and trunk are stooped forward, and his arms are at his sides and never swinging. In each arms, a resting tremor of the pill-rolling sort stops solely when the affected person performs a voluntary movement corresponding to lighting a cigarette or picking up a pencil. Examination reveals the presence of lead-pipe rigidity manifested by a generalized hypertonicity with significantly increased resistance to passive motion. Which are the positive indicators and which are the adverse signs manifested by this affected person Name the likely analysis and the rationale for the pharmaceutical and the surgical therapies of this situation. A 63-year-old man has been bothered by the shaking of his arms and generalized stiffness of 8. There was no Chapter 27 Principles for Locating Lesions and Clinical Illustrations 351 Neurologic examination revealed a left Horner syndrome. His upper and lower limb reflexes were symmetric, and the plantar responses had been flexor. Seven weeks after the harm, he experienced sudden onset of dysphagia, unsteadiness of gait, and left ptosis-all precipitated by lifting a light-weight load. Several months later, the lack of speech endured, and she or he showed a spastic weak spot of the proper arm and hand with elevated resistance to passive movement and exaggerated tendon reflexes. He was conscious that he was unable to perceive what other individuals were saying to him during these episodes. While experiencing the puzzling episodes, he seemed preoccupied, and typically his lips and tongue moved as if he had a hair in his mouth. A 63-year-old man complained of brief episodes lasting a few minute throughout which he 11. She drank copious quantities of water because she was all the time thirsty, and he or she urinated excessively. Neurologic examination confirmed marked weak point in the left leg and foot accompanied by an extensor plantar response, increased resistance to passive stretch, and exaggerated knee and ankle jerks. Give the extent and site of the lesion and determine the constructions involved in the above abnormalities. Identify the extent and area of the lesion, and name the constructions involved and the abnormalities related to every. Shortly after a fall in which he struck his head, he complained of lack of ability to use his left eye, and his left higher eyelid drooped. Later, his left eyelid was completely closed, and, when the eyelid was lifted, the attention was turned down and out. Examination revealed that muscle tone and reflexes in the best limbs were elevated. After sustaining too many blows to the head whereas taking part in racquetball, Mary offered 15. A man came into the city hospital one morning after an evening of extreme drinking. Chapter 27 Principles for Locating Lesions and Clinical Illustrations 353 Answers 1. Acute anterior poliomyelitis was an infective illness that resulted in degenerative lesions primarily affecting the alpha motor neurons within the anterior horn of the spinal cord. Left thalamocortical radiation: pinprick not sharp and poorly localized and extreme lack of tactile and proprioception senses on the whole proper facet of the physique four. Decreased sensation to pinprick happens as a outcome of the pain paths within the brainstem and forebrain are diffuse; hence, only exact localization, depth, and sharpness of pinprick (the cortical phenomena) are lost with a lesion of the trail distal to the thalamus. Loss of two-point, vibration, and proprioception senses on the proper side from the sole of the foot up the decrease limb and trunk to the axilla and medial surface of the upper limb (right gracile and cuneate tracts) four. Decreased ache and temperature sensations within the pores and skin on the medial floor of the proper higher limb (right tract of Lissauer) 5. Right ptosis, miosis of the best eye, and anhidrosis on the right side of the face: Horner syndrome (right ciliospinal center) b. Paralysis and extreme atrophy of the intrinsic muscular tissues in the proper hand (lower motor neuron syndrome) 2. Right lower limb paralysis accompanied by elevated resistance to passive stretch, exaggerated myotatic reflexes, clonus, and extensor plantar response (upper motor neuron syndrome) three. Dyskinesia is a disorder of movement that occurs spontaneously and is usually associated with basal ganglia disease. Negative indicators: gradual actions (bradykinesia), shoulders and trunk stooped forward, arms at sides and never swinging, and masklike facial expression d. Paralysis agitans (Parkinson disease)-pharmaceutical remedy with levodopa replaces the dopamine within the striatum. Level: Rostral medulla Structures and Abnormalities: Left spinal trigeminal tract: decreased pinprick in left facet of face Left spinothalamic tract: decreased pinprick in neck, trunk, and limbs on proper facet Left inferior cerebellar peduncle: ataxia and dysmetria in left limbs Left vagus nerve rootlets: absence of left gag reflex Interruption of fibers in left lateral reticular formation carrying descending input to ciliospinal heart: left Horner syndrome b. Level: Cerebral cortex Structures and Abnormalities: Broca speech area in left inferior frontal gyri: lack of speech (motor aphasia) Ventral part of the left precentral gyrus: spastic weakness of proper hand and weak point of right decrease facial muscular tissues b. Middle cerebral artery: branches to the inferior frontal and ventral precentral areas c. Level: Cerebral cortex Structures and Abnormalities: Anterior part of proper paracentral lobule: spastic weakness and so forth in left leg and foot Posterior a part of proper paracentral lobule: somatosensory loss in left leg and foot b.
Nettle (Stinging Nettle). Benzac. - What is Stinging Nettle?
- Allergies, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), arthritis, water retention, internal bleeding, anemia, poor circulation, diabetes, diarrhea, asthma, cancer, improving wound healing, and other conditions.
- Dosing considerations for Stinging Nettle.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Are there safety concerns?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96654
Order line benzacEffect of route of inoculation on experimental respiratory viral illness in volunteers and proof for airborne transmission. A model for obtaining predictable natural transmission of rhinoviruses in human volunteers. Bronchial reactivity to histamine and bradykinin is unchanged after rhinovirus an infection in regular subjects. Nasal and otologic effects of experimental respiratory syncytial virus an infection in adults. Prophylactic activity of intranasal enviroxime against experimentally induced rhinovirus sort 39 infection. Mouse models of rhinovirus-induced illness and exacerbation of allergic airway irritation. Experimental infection with respiratory syncytial virus in several species of animals. Sustained will increase in numbers of pulmonary dendritic cells after respiratory syncytial virus infection. Respiratory syncytial virus decreases the capacity of myeloid dendritic cells to induce interferon-gamma in na�ve T cells. Respiratory syncytial virus infection ends in airway hyperresponsiveness and enhanced airway sensitization to allergen. Transfer of the enhancing impact of respiratory syncytial virus infection on subsequent allergic airway sensitization by T lymphocytes. Parainfluenza type 3 virus infection in hamsters: Virologic, serologic, and pathologic studies. Development of a guinea pig colony free of complement-fixing antibodies to parainfluenza virus. Enabled interferon signaling evasion in an immune-competent transgenic mouse model of parainfluenza virus 5 an infection. Dendritic cells are associated with augmentation of antigen sensitization by influenza A virus infection in mice. Vaccination of macaques with adjuvanted formalin-inactivated influenza A virus (H5N1) vaccines: protection against H5N1 challenge with out disease enhancement. Cross-protection in opposition to H5N1 influenza virus an infection is afforded by intranasal inoculation with seasonal trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine. Genomic evaluation of increased host immune and cell demise responses induced by 1918 influenza virus. Newly found coronavirus as the primary reason for severe acute respiratory syndrome. Conservation of amino acids in human rhinovirus 3C protease correlates with broad-spectrum antiviral exercise of rupintrivir, a novel human rhinovirus 3C protease inhibitor. Amplicon sequencing and improved detection of human rhinovirus in respiratory samples. Improved detection of rhinoviruses by nucleic acid sequence-based amplification after nucleotide sequence willpower of the fifty nine noncoding areas of additional rhinovirus strains. Genetic clustering of all 102 human rhinovirus prototype strains: serotype 87 is close to human enterovirus 70. New full genome sequences of human rhinoviruses shed mild on their phylogeny and genomic features. Proposals for the classification of human rhinovirus species C into genotypically assigned types. The September epidemic of asthma exacerbations in kids: a seek for etiology. Rhinovirus higher respiratory an infection will increase airway hyperreactivity and late asthmatic reactions. A frequent cold virus, rhinovirus sixteen, potentiates airway inflammation after segmental antigen bronchoprovocation in allergic subjects. Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of rhinovirus an infection in bronchial tissues. Rhinovirus-16 colds in wholesome and in asthmatic topics: related modifications in upper and decrease airways. Transcriptional activation of the interleukin-8 gene by respiratory syncytial virus infection in alveolar epithelial cells: nuclear translocation of the RelA transcription factor as a mechanism producing airway mucosal irritation. Induction of cytokine release and modulation of susceptibility to an infection by cytokine publicity. Interleukin-17A modulates human airway epithelial responses to human rhinovirus infection. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2007;293(2):L505�L515 eleven Infectious Rhinitis 316. Interleukin-17 in sputum correlates with airway hyperresponsiveness to methacholine. Human rhinovirus an infection induces airway epithelial cell production of human beta-defensin 2 each in vitro and in vivo. Rhinovirus inhalation causes long-lasting extreme airway narrowing in response to methacholine in asthmatic topics in vivo. Association of viral and Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections with acute respiratory illness in sufferers with chronic obstructive pulmonary illnesses. Differences in interleukin-8 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in induced sputum from sufferers with continual obstructive pulmonary disease or bronchial asthma. Microarray detection of human parainfluenzavirus four an infection related to respiratory failure in an immunocompetent adult. MassTag polymerasechain-reaction detection of respiratory pathogens, including a new rhinovirus genotype, that brought on influenza-like sickness in New York State during 2004-2005. A newly discovered human pneumovirus isolated from younger children with respiratory tract illness. Human metapneumovirus and decrease respiratory tract disease in in any other case healthy infants and children. Wold Rhinosinusitis is quite common in the basic population of the United States, accounting for an estimated 25 million ambulatory visits in 1996. Due in part to the customarily indiscriminate prescribing of antibiotics for acute and persistent respiratory infections, drugresistant organisms have increased in prevalence up to now few many years, especially S. Antibiotic resistance has leveled off in current years, however the antibiotic resistance rate remains high. Antibiotic resistance rates can differ extensively relying on geographic location, so local antibiograms ought to be reviewed to be cognizant of locoregional developments in antimicrobial resistance. Pathophysiology Appreciation of the pathophysiology of acute bacterial rhinosinusitis first calls for familiarity with the regional anatomy. In basic, though some geographic and populationbased variability exists among the spectrum of etiologies for acute rhinosinusitis, the most frequently implicated offenders are viruses corresponding to rhinovirus, influenza, and parainfluenza. Aspiration studies from the maxillary sinus of sufferers with suspected acute bacterial rhinosinusitis have recognized S. Presence of anatomic variations corresponding to septal deviation, concha bullosa, infraorbital ethmoid cell, interfrontal sinus septal air cell, and frontal cell are extra likely to encourage the development of obstructive rhinosinusitis. Other obstructive etiologies embody nasal polyps, neoplasm, indwelling nasotracheal or nasogastric tubes, and nasal international bodies.
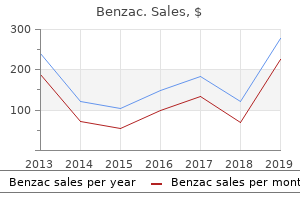
Purchase benzac american expressCare should be taken to keep away from injury to the nasolacrimal system and to tooth buds, which can abut the nasal ground. When the stents are eliminated, we use topical steroid/antibiotic drops to facilitate mucosal healing. Tracheotomy can be thought-about if definitive surgical procedure must be delayed due to associated anomalies. Regardless of the method, the important thing to a successful repair is creating an adequate three-dimensional opening by removing the widened posterior vomer and thinning the lateral pterygoid plate. With the transnasal method, a nasal endoscopy is performed and a perforation is made in the atretic plate on the junction of the nasal flooring and septum using a no. Subsequently, the posterior vomer is resected and the lateral nasal wall and pterygoid plates are thinned underneath direct visualization with a drill. When a direct nasal endoscopy with resection is troublesome, we prefer a sublabial transseptal strategy utilizing endoscopy. The vomer is resected en bloc via a common cavity provided by lateralization of the anterior septum. Moreover, by initially performing the bony resection, the mucosa within the posterior nostril is preserved and one can create mucosal flaps that cover the neo-choanae in a sensible and consistent style. Historically, as soon as the choanae have been opened appropriately, stents made from polyethylene endotracheal tubes were placed for 1 to eight weeks. Recent literature, however, has challenged the need for stents, citing excessive rates of long-term nasal patency with out stenting. There is controversy with this method because of considerations about orthodontic progress and development. Although the reported incidence of malocclusion has been reported to be as high as 50% in younger patients present process transpalatal repair, we question the validity of these findings. With this method, the mucosa is elevated off the onerous palate back to its posterior edge and pedicled on the larger palatine artery. The atresia plate and a considerable portion of the posterior vomer are obliterated with an otologic drill. Both the transnasal and transpalatal approaches lead to a useful nasal airway in 50 to 80% of kids. Postsurgical topical drugs, corresponding to mitomycin C, have shown promise in stopping restenosis. In addition, the authors will occasionally inject steroids (Kenalog 40 mg/mL) to the borders of the neo-choanae. The condition happens in 1:5000 to 1:8000 stay births and impacts females twice as typically as males. The 4 components of the anatomic deformity embrace a slim nasal cavity, medialization of the lateral pterygoid plate, widening of the vomer right into a diamond form, and a thinning of the atresia plate inferomedially. Exam findings embody the shortcoming to pass a small catheter into the nasopharynx and an absence of condensation on a mirror placed at the nares. In distinction, bilateral atresia will trigger vital respiratory distress in a newborn and must be addressed within the perinatal period. A purple rubber catheter has been passed via the patent left choana (arrow) lateral to the nasal septum (asterisk). We favor bringing the children back to the working room after 1 week to take away the stents. Common problems of paranasal constructions that may manifest as nasal anomalies embody lacrimal cysts and congenital midline nasal plenty, which embrace nasal gliomas, encephaloceles, and nasal dermoids. The obstruction of the lacrimal drainage system resolves spontaneously in 85% of infants by 9 months. Indications for surgery embrace an infection, respiratory distress, feeding difficulties, or failure to spontaneously regress. Surgical restore, when needed, is completed by marsupializing the cyst into the nose, concurrently relieving the obstruction and restoring lacrimal drainage. Lacrimal cysts are typically unilateral but can be bilateral and have a strong feminine preponderance. Patients typically present with epiphora and ranging levels of nasal obstruction. These cysts generally develop close to the medial canthal tendon, presenting as a bulge close to the medial canthus. However, intranasal lacrimal cysts can kind, typically originating beneath the inferior turbinate on the valve of Hasner. Endoscopically, their look is just like a big polyp originating beneath the inferior turbinate. When these cysts are giant, their origin is probably not apparent; consequently, you will need to differentiate Congenital Midline Nasal Masses: Nasal Gliomas, Encephaloceles, and Nasal Dermoids Congenital midline nasal plenty are uncommon anomalies that embody nasal gliomas, encephaloceles, and nasal dermoids. Whereas gliomas are composed of unencapsulated glial cells within a connective tissue matrix, encephaloceles are herniations of meninges, with or with out mind tissue, out of the cranial cavity. In contrast, dermoids are lesions derived from entrapped ectoderm and mesoderm and comprise pores and skin, hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. Congenital midline nasal plenty happen in 1:30,000 stay births in the United States but are extra widespread amongst Asians, occurring in 1:6000 stay births. Closure begins in the midportion earlier than progressing both anteriorly and posteriorly. The frontal, nasal, and ethmoid buildings type proximal to the anterior neuropore. Neural crest cells migrate by way of this area wealthy with ectoderm and mesoderm, which form skin, cartilage, and bone. Once in position, the mesenchyme organizes into skeletal constructions, forming necessary areas that are normally closed by birth. These include the fonticulus nasofrontalis, which is the hole between the frontal and nasal bones, and the prenasal area, which is the area between the nasal bones and the nasal capsule. The nasal capsule is the precursor of the nasal cartilages and septum and is continuous with the ethmoid bone. Finally, the foramen cecum is the area between the ethmoid and frontal bones and connects with the prenasal house. Failure of those areas to shut allows for the herniation of glial tissue and intracranial contents, forming gliomas and encephaloceles. Similarly, ingrowth and entrapment of ectodermal and mesodermal components by way of these spaces can lead to dermoid formation. These lesions can range in size and site, and large lesions could cause respiratory misery. Nasal gliomas could present as extranasal (60%), intranasal (30%), or mixed (10%) lesions. If intranasal, they could resemble a unilateral giant polyp, which is neither compressible nor pulsatile. In contrast, encephaloceles are bluish, gentle, compressible lots which may be pulsatile. Whereas meningoceles include only meninges, meningoencephaloceles include meninges and mind tissue.
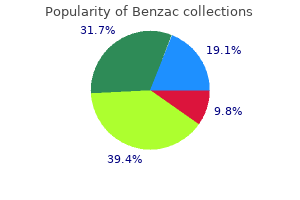
Cheap benzac 20 gr lineDiabetic ketoacidosis: It is a hyperosmolar state and for all sensible purposes most kids would have an estimated fluid deficit between 8% and 10%. These sufferers have moderately low sodium, normal potassium and complete body depletion of phosphate. Maintenance fluid calculated by HollidaySegar formulation may typically overestimate the fluid requirement in acute illness state. Significant decrease in insensible water loss, altered neurohormonal response together with elevated fluid administration contributes to fluid overload on this patient population. While well timed administration of fluids is lifesaving, constructive fluid stability after hemodynamic stabilization is detrimental to organ perform and negatively influences important outcomes in critically sick sufferers. Management: If the kid has >10% of cumulative fluid overload, low dose furosemide infusion (0. If the kid stays unresponsive to diuretics and cumulative fluid overload will increase past 20%, early initiation of renal alternative therapy must be strongly considered. Frequent (6�12 hourly) fluid balance calculation would assist to make such selections at the earliest. Early initiation of renal replacement remedy might enhance the prognosis in these children. Monitoring of the central venous strain and acidbase values are obligatory to guide the preliminary therapy. Subsequent fluid and electrolyte therapy relies upon upon the status of serum electrolytes and problems corresponding to cerebral edema. Acid is a substance that tends to dissociate or give a hydrogen ion (proton donor) whereas base is a substance that tends to bind or affiliate a hydrogen ion (proton acceptor). Disturbances in acidbase stability can happen because of major respiratory or metabolic events. The affected person may have high anion gap metabolic acidosis when the calculated anion hole is more than sixteen. Worsening acidosis may produce hypotension, lethargy, stupor and progresses to coma. Child could develop hypoventilation which might result in hypoxemia, difficulty in weaning from ventilator, increased digoxin toxicity, worsening of hepatic encephalopathy. In case of diureticinduced metabolic alkalosis, stop the loop diuretic and it can be replaced by K sparing diuretics. If hyperkalemia or ventricular fibrillation develops in a toddler with acute respiratory acidosis, sodium bicarbonate may be life saving. In the continual section renal suppression of H+ ion excretion and chloride retention happens. Treatment Breathing in a closed circuit would trigger accumulation of carbon dioxide. Understanding that the body water compartments and their electrolyte composition is crucial for effective fluid administration 2. Current scientific evidence helps the utilization of N/2 saline as maintenance fluid in all acutely sick hospitalized children 3. Clinical conditions that have an result on the quantity of water loss or total caloric expenditure mandate the modification within the amount of upkeep fluid four. Symptomatic hyponatremia requires instant 3% saline administration at 5�10 ml/kg focusing on the protected margin a hundred and twenty mEq/l 7. Sodium bicarbonate therapy is probably not helpful in correcting excessive anion hole acidosis the place correcting the first cause would correct the acidosis Mixed Acid-base Disorders Mixed acidbase disturbances are conditions where more than one major acid disturbance happens. The four generally encountered blended acidbase disorders are: (1) respiratory acidosis + metabolic acidosis, (2) respiratory acidosis + metabolic alkalosis, (3) respiratory alkalosis + metabolic acidosis and (4) respiratory alkalosis + metabolic alkalosis (Table 17. The most critical acidbase disorders are of combined kind when respiratory and metabolic disturbances result in a pH change in the same course. Subsequently recording intake and output, body weight to detect renal compensatory mechanisms or penalties due to fluid extra or deficit are an important considerations. A chart must be maintained to document the related parameters at common intervals. Clinical parameters ought to be reviewed no less than 6 hourly and laboratory tests every 12�24 hours to adjust intake of water and electrolytes accordingly. Diabetic ketoacidosis: predictors of outcome in a pediatric intensive care unit of a creating country. Respiration is defined as the method of gas exchange within the lungs (external) or on the tissue degree (internal). Assisted ventilation entails an exterior device linked on to the affected person which supplies the movement of air out and in of the lung. Negative strain ventilators vary from tank ventilators (iron lungs) to belly and thoracic cuirasses. The peak inspiratory stress degree is usually kept as little as possible since it has been implicated as one of the causes of barotraumas. The approach is very useful when lungs are stiff and noncompliant and has turn out to be the mainstay of remedy of acute respiratory misery syndrome and pulmonary edema. Inspiratory time and I:e ratios: the I:E ratio refers to the connection between inspiratory time (I) and the expiratory time (E). Adjustment of the inspiratory time is the first technique by which the I:E ratio is altered. FiO2: It stands for fractional impressed oxygen concentration the place 100 percent oxygen is represented as 1. Mean airway pressure is crucial factor in determining each oxygenation and the potential for barotraumas. Setting the sensitivity too excessive may improve the work of breathing (the affected person must create the next intrathoracic unfavorable strain in order to get help from the ventilator). Setting the sensitivity too low might lead to over-triggering and the potential for ventilator-patient dyssynchrony. Controlled mechanical air flow In this mode, all breaths are initiated, sustained and 969 terminated by the ventilator with the patient taking no vip. Here volume is assured but stress is variable depending on the lung mechanics. Here, whereas the clinician has guarantee over the preset strain, delivered volumes may be variable and depend upon the mechanics of the patients lungs, airways and ventilator circuit. All work on the identical precept, using a continuous fuel move, a reservoir bag, a valve to keep positive strain above atmospheric pressure and a humidification gadget. Other modes of utility embody face mask, nasal prongs or nasopharyngeal tube. The patient performs only the triggering work, while the ventilator completes the remaining limiting and cycling work.
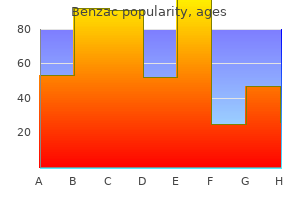
Order 20gr benzac otcA baby that has difficulty in figuring out colors by 3�4 years of age could probably be colour blind. All kids, particularly boys, should have a routine shade vision examine as quickly as during a school health checkup. Color blindness can also be acquired in circumstances that involve the cones or the visible pathway (chorioretinitis, diabetic retinopathy, optic neuritis, partial optic atrophy, migraine, stroke and cerebral trauma). Unlike congenital color blindness, the acquired varieties could additionally be unilateral, progressive or transient, and show no gender predisposition. Screening checks are used to detect if a shade imaginative and prescient defect is current or not (Ishihara pseudoisochromatic plates). More sophisticated checks are required, if the target is to precisely classify the kind and degree of defect (Farnsworth-Munsell 100-Hue take a look at or Lantern test). Treatment includes replacement of vitamin A, therapy of the precipitating situation, basic well being of the kid and ocular condition. The kind of discharge helps in differentiating between viral (watery) and bacterial conjunctivitis (mucopurulent). Viral conjunctivitis as a result of adenovirus or picorna virus is quite common, occurs in epidemics, and may cause preauricular lymphadenopathy. The pediatrician ought to advise frequent handwashing, separate towels, handkerchieves, and so forth. Bacterial conjunctivitis resolves spontaneously with out particular remedy; nevertheless, topical, empirical antibacterial remedy ends in earlier microbiological remission. There is watering and purulent discharge from each eyes in the 1st few days of life. If Gonococcal, the local symptoms and indicators are severe; xerophthalmia Xerophthalmia is a bilateral, dry, lusterless condition of the conjunctiva and cornea because of vitamin A deficiency. A conjunctival swab will assist determine the organism, however therapy ought to begin directly. In chlamydial an infection (the most common), instill tetracycline/erythromycin eye ointment and provides oral erythromycin. Pregnant girls with suspected vaginal infections ought to be treated well before supply. Diphtheritic membranes are difficult to peel off; remedy is directed to both the native and systemic situations; the kid have to be isolated. Membranes that do peel off should be removed (pseudomembranes) as this reduces the infective load in the eye, and appropriate specific antimicrobial remedy be given. There is painful proptosis, lid edema, restricted ocular actions, and the cornea might develop publicity keratitis. The condition mandates admission, and instant local and systemic broad spectrum antibiotic therapy. There could additionally be a history of injury with vegetative material (plant leaf, twig, animal tail; fungal ulcer), fever (viral ulcer) or abuse of steroid eye drops. The patient presents with a number of phlyctens (blisters) on the bulbar or palpebral conjunctiva, limbus or cornea. The blisters ulcerate and heal by scarring, and are recurrent until the endogenous an infection is treated. Treatment consists of topical steroids, along with investigation and remedy of infective cause elsewhere within the physique. Uncorrected refractive errors and lowered immunity could additionally be answerable for recurrent lid infections. If a lid abscess forms, it should be drained beneath cover of systemic and topical antibiotics. Chalazion, additionally due to blockage of meibomian gland, is a painless granulomatous reaction to lipid content of the gland. Spring catarrh Spring Catarrh is an allergic conjunctivitis because of exogenous allergens like pollen, animal hair, and so on. It has a seasonal recurrence (in the warm months, subsiding in winter); it often subsides by puberty. In the palpebral type, there are large papillae in the palpebral conjunctiva, giving a 1021 vip. Just before the good and cozy months, to delay onset of symptoms, begin topical antihistaminics and mast cell stabilizers. During symptomatic durations, give topical corticosteroids (low dose/full dose) and chilly compresses. A general medical historical past, bodily examination and particular laboratory checks may elicit cause. A full examination of the attention and ocular adnexa is essential, together with the cornea (H. A fundus examination is necessary to detect cystoid macular edema in eyes with continual uveitis and to rule out posterior uveitis. Topical cycloplegics, and topical or periocular corticosteroids are the mainstay of treatment. The misalignment may be horizontal or vertical leading to esotropia (one eye is relatively convergent), exotropia (one eye is relatively divergent;. Squint may be constant, being current throughout the day, or it could appear intermittently. Newborn babies may squint often, till their binocular reflexes develop; thus, any squint that presents or persists after the age of 3 months must be investigated. Squint might occur in uncorrected hypermetropia (excessive accommodation to see clearly causes extreme convergence, producing convergent squint); because of poor vision in a single eye; or because of cerebral palsy, hydrocephalus or brain damage. In squint, the fovea of each eye is focusing on a unique object; thus, two totally different images reach the brain resulting in confusion. The mind ignores the image coming from the deviated eye, leading ultimately to strabismic amblyopia in that eye. If any squint stays in spite of spectacle correction, it can be corrected by muscle surgery. A small variety of youngsters require surgical procedure on the attention muscle tissue to straighten the alignment. A misunderstanding of squint (pseudostrabismus) may result from a flat, broad bridge of nose, or as a outcome of epicanthal folds so that the eyes look nearer collectively than they really are. They represent surface ectoderm that obtained entrapped throughout bony fusion; thus, they overlie bony sutures. They may leak after trauma; extruded sebaceous materials produces inflammation and ache. While periorbital dermoids are superficial, and thus easier to remove surgically, orbital ones require an orbital approach. Watering from the eyes congenital dacryocystitis this could be a result of incomplete canalization of the nasolacrimal duct, often as a end result of epithelial debris, membranes or valves within the duct.
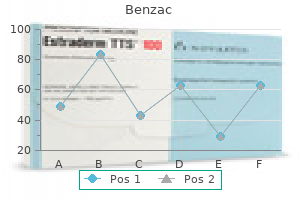
Discount 20gr benzac free shippingChapter 26 Recovery of Function of the Nervous System: Plasticity and Regeneration 335 nucleus to an eccentric location adjacent to the cell membrane and often directly across from the axon hillock. Secondary to altered ionic pump properties and resultant adjustments in membrane permeability, the soma swells. Finally, synaptic boutons disconnect from the dendrites and soma of the now dysfunctional neuron. If the brink for continued degeneration has not been crossed, axotomized neurons will try and regenerate their axon from the site of injury distally. Beginning three to 4 days after damage, mitogens launched by invading macrophages trigger the division of Schwann cells along the size of the nerve phase. Chemoattractants or tropic substances launched by Schwann cells present steerage signals for regrowing axons to extend distally. Clinical Connection A neuroma can develop on the website of peripheral nerve injury when regenerating sensory axons fail to reenter neurolemmal tubes. Once reconnected, trophic alerts are conveyed retrogradely to the cell physique where, over time, the morphologic group of the cell returns to regular and the disengaged synapses reestablish functional connections with the soma and dendritic membrane. Finally, three proteins in the oligodendroglial membrane of myelinated central axons work together with a single receptor (Nogo) on the vanguard of regenerating axonal development cones. Connectional plasticity can be simple changes in synaptic efficacy corresponding to that which happens presynaptically in short-term facilitation and posttetanic potentiation or occurs postsynaptically with long-term potentiation and longterm despair. Generally, new synaptic connections only kind by reactive synaptogenesis, in which synapses misplaced as the outcomes of harm are changed by terminal sprouting from surviving axons within the instant space. Quantitative research of reactive synaptogenesis in adult animals have convincingly shown that new synapses formed by surviving afferent terminals are very comparable in each quantity and physiologic efficacy to the lost synaptic inputs. Some synapses can never get replaced as is the case with affected person #2 within the case historical past firstly of this chapter. As the outcome of ongoing growth-related gene expression, undamaged axons of immature neurons can develop extra axonal terminal arbors or collateral sprouts as nicely as redirect axonal progress to denervated targets. Regenerative sprouting of terminal arbors or extra distant collaterals may develop from broken axons. Clinical Connection Two examples illustrate the plasticity of the grownup sensory techniques. First, after amputation of a digit, the cortical space of illustration for the lost digit is changed by sensory inputs increasing from the immediately adjacent illustration areas of intact digits, thereby increasing the cortical "sensitivity" for these digits. Cross-modality sensory plasticity happens in blind patients educated to "learn" braille. In addition, sound localization and speech discrimination are enhanced in blind individuals in contrast with sighted individuals. Chapter 26 Recovery of Function of the Nervous System: Plasticity and Regeneration 339 Chapter Review Questions 26-1. What are the attribute neurohistologic modifications in the cell body of an axotomized neuron What three elements preclude successful axonal regeneration in the central nervous system What is the operate of neurotropic molecules synthesized by injury-activated Schwann cells What kind of damage to a peripheral nerve the right rostral medulla ends in the loss of coordinated movements of the lower limb on the same side. Does lesion-induced plasticity at all times occur all over the place in the central nervous system A 10-year-old youngster is taken to the emergency room following a bicycle accident the place the left ulnar nerve was cut just proximal to the wrist. The attending neurosurgeon sutures the proximal and distal nerve stumps together with minimal distortion to the nerve fascicles. Lower limb sensations had been normal and muscle energy had been age and gender acceptable. Bilateral harm of the central a part of the spinal cord (central wire syndrome) ends in the loss of sensations and voluntary motor control within the space of peripheral distribution of the extra rostral spinal wire segments beneath the lesion, however not the more caudal. Spinal wire hemisection causes damage to the lateral corticospinal tract and dorsal column, resulting in spastic paralysis and the lack of tactile, vibration, and proprioception senses ipsilaterally, and injury to the spinothalamic tract, resulting in the loss of ache and temperature senses contralaterally. Lesions involving the ventral white commissure result within the loss of pain and temperature sensations Corticospinal tract L Tactile and so forth. This phenomenon usually results from syringomyelia or cavitation of the spinal twine and known as the commissural syndrome. Spastic paralysis and loss of tactile, vibration, and proprioceptive senses on left (L, ipsilateral) side and loss of ache and temperature senses on right (R, contralateral) aspect. Lateral Brainstem Lesions C5-7 Lesions involving the lateral part of the brainstem usually contain the spinothalamic tract. In the medulla and caudal pons, the spinothalamic and spinal trigeminal tracts are near one another. When a lesion entails both tracts, ache and temperature sensations are impaired in the face ipsilaterally and the trunk and limbs contralaterally. Lateral brainstem lesions at more rostral levels contain, in addition to the spinothalamic tract, the motor and principal trigeminal nuclei at midpons. Lesion of ventral white commissure ends in bilaterally symmetric lack of ache and temperature in dermatomal distribution of spinal cord segments involved. The most common web site of long pathway involvement within the cerebral hemisphere is the interior capsule, where the pyramidal tract and thalamic somatosensory radiations are adjoining to one another, and the corticobulbar tract is close by. Such a lesion results in contralateral spastic hemiplegia, contralateral hemianesthesia, and contralateral decrease face weak spot. In general, focal brainstem lesions can be divided into two groups-those located in the medial parts and those situated in the lateral components of the medulla, pons, or midbrain. All somatosensations in ipsilateral face (principal nucleus and spinal trigeminal tract), pain and temperature in contralateral limbs, trunk, and neck (spinothalamic tract). Pain and temperature in ipsilateral face (spinal trigeminal tract), and contralateral limbs, trunk, and neck (spinothalamic tract). Ipsilateral (left) intention tremor (left superior cerebellar peduncle earlier than decussation). Chapter 27 Principles for Locating Lesions and Clinical Illustrations 349 Clinical Illustrations 1. An 11-year-old lady complained of ache in the neck and the left shoulder and had a fever of 102�F to 103�F. A few days later, the left arm, forearm, and hand were paralyzed, the muscular tissues flaccid. With trochlear lesions, the affected eye is slightly extorted, and the particular person compensates by tilting the top downward to the opposite side. Demyelinating course of corresponding to multiple sclerosis Chapter 27 Principles for Locating Lesions and Clinical Illustrations 361 14. Level: Parietal lobe Structures and Abnormalities: Dorsal part of right optic radiation: lower left homonymous quadrantic anopsia Right posterior parietal lobe: neglect of left side of body and surroundings b. A synapse is the location of practical contact where impulses move unidirectionally from one neuron to the opposite. The integrity of axons, some of which may be three ft in size, is maintained by 1-4.
Syndromes - Endoscopy -- camera down the throat to see burns in the esophagus and the stomach
- Bottom of the mouth
- Double vision
- Total cholesterol test
- Pregnancy complications
- Urinate often and completely.
- When sneezing, coughing, or laughing
Cheap benzac ukThe challenge for the clinician is to catch the illness early before extension into the cra nial cavity or different extrasinus tissues. As the disease progresses, fever, headache, facial ache, and swelling are rapidly followed by decreased visible acuity, different cranial nerve deficits, and facial or palatal necrosis. Extension into the cranial vault might trigger seizures, altered mental status, after which death in a matter of days. Physical examination, particularly nasal endoscopy, is extraordinarily helpful for making the diagnosis in the early levels of disease. The middle turbinate is essentially the most commonly involved intranasal website of disease, but the entire mucosa of the nasal cavity must be inspected. As the disease progresses, the nasal tissues will take on a gray to black look with areas of ulceration. Perineural or vascular invasion leads to areas of anesthesia, mycotic thrombosis, and ischemic coagulative necrosis of tissue. The histologic analysis must be sought emergently and will require multiple biopsies and special fungal stains. Pathophysiology and Natural Course Neutropenia is the one most necessary permissive immune defect in most cases of acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis. Diabetic ketoacidosis has also lengthy been recognized as a risk factor for acute invasive fungal rhi nosinusitis caused by Mucoraceae. The hyperglycemia and acidosis create a positive surroundings for the professional liferation of those fungi and cause qualitative neutrophil defects (impaired phagocytosis, reactive oxygen species generation). There is some evidence from animal research that prior viral infection throughout the nose enhances airway susceptibility to invasive Aspergillus rhi nosinusitis. In an Aspergillus an infection, macrophages are the first-line protection and are liable for phagocytosis of inhaled conidia (spores). Thus, profound or prolonged neutropenia is a major threat factor for the event of invasive fungal rhinosinus itis. The position of T cells and humoral immunity in resisting fungal tissue invasion is uncertain. This aggressive course necessitates a excessive index of suspicion for the illness, a speedy pursuit of the prognosis, and an emergent administration of acceptable remedy. Even with appropriate treatment, mortality is critical and in some sequence approaches 90%. The most important factor in determining prognosis is the reversibility of the underlying immunocompromised state. Endoscopic surgical procedure and newer medicines like the lipid formulations of amphoteri cin B and posaconazole have opened up new avenues of treatment. It may be used as a topical agent for irrigation or packing materials postoperatively. The toler ability of amphotericin B is improved through the use of one of the lipid formulations, which permits for the administration of larger cumulative doses of medication with less renal toxicity. A triazole such as itraconazole, voriconazole, or posaconazole may also be added to the regimen and con tinued past the course of amphotericin treatment. An unresolved question about antifungal therapy is the perfect period of treatment to control or get rid of the disease while avoiding or minimizing toxicities. Once objective and subjective illness parameters are resolved, the drugs could additionally be stopped with the expectation that they are going to be restarted should any evidence of illness reactivation present itself. Imaging findings vary from mucosal thickening or air/ fluid ranges or extreme unilateral nasal delicate tissue swelling, to bone erosion or gentle tissue infiltration. There is benignappearing mucosal thickening in the proper nasal cavity and maxillary sinus. Debridement of necrotic tissue additionally reduces fungal load in areas impenetrable by intravenous antifungals. Widely opening the sinuses also facilitates the application of packings soaked in amphotericin B, or for irrigation of antifungal solutions. Available evidence sug gests that patients treated with surgery have a greater prognosis than those handled with medical remedy alone, though there are circumstances which have been cured solely with medical therapy. The forms of operations have modified through the years, however the basic precept stays: surgical procedure ought to take away all tissue grossly concerned with an invasive fungus. This could also be accomplished by open or endoscopic methods to debride back to wholesome bleeding tissue. The endoscopic method is now recognized as an efficient technique, which minimizes the morbidity of surgical procedure, but incessantly permits a whole operation. These external procedures include medial maxillectomy, whole maxillectomy with or without orbital exenteration, or craniofacial resection. Orbital contents should be saved, if at all attainable, although the principle of complete resection ought to prevail. The extent of sur gery undertaken must be modified by due consideration of the overall prognosis. Pa tients should be followed closely after surgical debride ment and should be ready for the chance of staged "second looks" or further operative debridements. Regular, periodic examination should be carried out and the affected person should be endorsed to seek take care of any symptoms such as facial ache, rhinorrhea, or congestion, which may sign a recur rence. Most cases of fungal rhinosinusitis are as a outcome of Aspergillus, the dematiaceous fungi, or the Mucoraceae. The completely different types of fungal rhinosinusitis can be distinguished by their scientific and radiologic presentations. Confirmation of the prognosis of fungal rhinosinus itis requires histopathologic examination. Primary paranasal Aspergillus granuloma: case report and evaluation of the literature. Usefulness of frozen part in rhinocerebral mucormycosis analysis and administration. Risk of maxillary fungus ball in sufferers with endodontic treat ment on maxillary enamel: a casecontrol study. Treatment of allergic fungal sinusitis: a comparison trial of postoperative immuno remedy with particular fungal antigens. New York: Plenum Press; 1994: 242 17 Medical Therapies for Rhinosinusitis: Anti-Infective Howard S. Rhinosinusitis refers to a bunch of heterogeneous problems characterised by irritation of the mucosa of the nose and paranasal sinuses and is categorized by a period of signs. Rhinosi nusitis may be attributable to viral, bacterial, or fungal an infection or hypersensitivity. The period of symptoms predicts the most probably pathogen answerable for the signs. This chapter outlines a sensible approach to either empiric or culturedirected antimicrobial therapy relying on the suspected infectious cause. General Recommendations the aims of antibacterial therapy are to shorten the period of symptoms, eradicate the causative pathogen, cut back the hazard of transmitting the an infection to others, and prevent the development of permanent mucosal dam age, the progression of disease, or severe problems.
20gr benzac free shippingIn these areas, anastomoses exist that can provide collateral circulation via vasodilation in response to Chapter 22 the Blood Supply of the Central Nervous System: Stroke proximal vessel occlusion. The lateral striate arteries provide the dorsal a part of the pinnacle of the caudate nucleus, many of the putamen and adjoining a part of the globus pallidus, and the dorsal part of the posterior limb of the interior capsule. The largest and most lateral of these arteries to enter the brain is the recurrent artery of Heubner. The medial striate arteries are the principal sources of the blood provide to the supraoptic and preoptic areas of the hypothalamus and to the ventral part of the pinnacle of the caudate nucleus and the adjoining elements of the anterior limb of the interior capsule and putamen. The extra anterior vessels provide the tuberal area of the hypothalamus and the anteromedial a half of the thalamus, including the anterior and medial dorsal nuclei. The more posterior vessels provide the mammillary area of the hypothalamus, the subthalamus, the adjoining parts of the thalamus, and the medial components of the rostral midbrain tegmentum and cerebral crus. The superficial veins are bigger and more numerous than the corresponding cortical arteries and have a tendency to lie alongside the arteries within the cerebral sulci. The superficial venous system empties into the more superficially situated sinuses, particularly the superior sagittal, inferior sagittal, and transverse sinuses, through anastomotic or draining veins. The most prominent anastomotic veins are the superficial center cerebral vein draining into the cavernous or sphenoparietal sinus, the great anastomotic vein (of Trolard) draining into the superior sagittal sinus, and the posterior anastomotic vein (of Labb�) draining into the transverse sinus. The deep venous system consists of the great vein (of Galen), the internal cerebral veins, the basal vein (of Rosenthal), and their tributaries including the transcerebral veins, which drain the white matter, and the subependymal veins, which drain the periventricular constructions. The great vein (of Galen) is situated beneath the splenium of the corpus callosum and receives the paired internal cerebral veins, the two basal veins (of Rosenthal), and drainage from the medial and inferior parts of the occipital lobe. Clinically, this space of the spinal twine is susceptible to vascular insult should this radicular artery be compromised. The anterior spinal artery descends along the surface of the wire on the anterior median fissure and provides from five to 9 sulcal arteries to every spinal cord segment. Each sulcal artery passes to the underside of the anterior median fissure, the place it swings right or left to enter the spinal cord and provide that side. In addition to the sulcal arteries, the anterior spinal artery provides coronal arteries that course laterally alongside the surface of the wire to anastomose with related branches from the posterior spinal arteries. Basal vein drainage includes the medial and inferior surfaces of the frontal and temporal lobes, the insular and opercular cortices, and regions of the hypothalamus and midbrain. The venous drainage of the spinal wire is concentrated in a dense plexus of veins located in the epidural space (Batson inner vertebral venous plexus). This high metabolic demand requires a perfusion quantity of approximately fifty five mL/100 g of mind tissue/minute. Cerebral arterioles dilate when systemic blood pressure is elevated and constrict when the stress is lowered. Arteriole diameters can also reply to changes within the respiratory gases pressures. Too little circulate results in ischemic hypoxia (ischemia) that initiates fast biochemical cascades that results in the death of neurons. Antihypertensive pharmacotherapy can control pathophysiological fluctuations in cerebral perfusion pressures. Hemorrhagic strokes as a end result of bleeding can occur throughout the brain (intraparenchymal or intraventricular) or outdoors the brain within the epidural, subdural, or subarachnoid areas. The accumulation of blood within the extracerebral spaces usually ends in elevated intracranial pressure and the displacement of mind tissue or herniation that may in a short time end in coma and dying. What are the chief morphologic features hemianopsia can happen with occlusion of the: a. Anterior or Frontal Horn the segment of the lateral ventricle anterior to the interventricular foramen (of Monro) is called the anterior or frontal horn. Clinical Connection Clinically, the frontal horns are devoid of choroid plexus, making them an excellent place for the positioning of spinal fluid diversion methods (shunts). Lateral Ventricles the lateral ventricles (left and right) are divided into five recognized components: anterior or frontal horn, physique or central half, atrium or trigone, posterior or occipital horn, and inferior or temporal horn. Laterally, the ventricular physique is adjacent to the body of the caudate nucleus, and its floor is shaped by the thalamus with the fornix, choroid plexus, and thalamostriate vein seen on the surface from medial to lateral. Medially, the calcar avis, fashioned by the calcarine fissure, bulges into the occipital horn. Inferior or Temporal Horn the inferior or temporal horn is inside the temporal lobe. Atrium the atrium or trigone is the most expanded a half of the lateral ventricle and is triangular in shape. The atrium contains an abundant tuft of choroid plexus, the glomus or choroid enlargement, along its anterior wall, which is continuous with the choroid plexus of the physique and temporal horn. The third ventricle drains right into a tubular canal, the cerebral aqueduct (of Sylvius). Third Ventricle the third ventricle is bordered bilaterally by the thalamus dorsally and hypothalamus ventrally. Sometimes a connection between the thalami, the interthalamic adhesion or massa intermedia, bridges across the third ventricle. The ground of the third ventricle is fashioned by the infundibular recess and tuber cinereum with the mamillary bodies posteriorly. It expands posteriorly in an inverted kite shape, with its roof bounded by the superior and inferior medullary vela and the superior cerebellar peduncles. A median aperture, the foramen of Magendie, empties into the vallecula, an anterior extension of the cisterna magnum. Extracerebral arteries and veins and cranial nerves are suspended in this house by weblike arachnoid trabeculations. Magnetic resonance picture showing subarachnoid cisterns at or near the median airplane. Its ahead projection between the cerebellar tonsils is the vallecula, into which the median aperture empties. It is triangular in form and bounded anteriorly by the membrane of Liliequist, an unusually powerful arachnoidal trabecula between the interpeduncular cistern and chiasmatic cistern. It lies adjoining to the tentorial edge and incorporates the posterior cerebral artery. The chiasmatic cistern surrounds the optic chiasm and the pituitary stalk, the carotid cistern surrounds the cerebral segment of the carotid artery, and the olfactory cistern surrounds the olfactory tract within the olfactory sulcus. Cerebrospinal fluid produced within the choroid plexus of the lateral and third ventricles flows through the aqueduct, fourth ventricle, and outlet foramina into the subarachnoid cisterns. Through the cisterns, the fluid passes into the subarachnoid area up over the convexities toward the superior sagittal sinus for the ultimate absorption by way of the arachnoid villi. Communicating forms of hydrocephalus often result from processes that happen within the cisternal or subarachnoid area corresponding to hemorrhage or an infection. Thus, a blockage situated wherever alongside the ventricular pathways (such as at the interventricular foramen of Monro, on the aqueduct, or on the outlet foramina of the fourth ventricle) produces obstructive hydrocephalus with enlargement of those ventricles proximal to the obstruction. Communicating hydrocephalus happens with obstructions in the cisternal pathways, along the subarachnoid house, or on the arachnoid villi. Clinical Connection Obstructive hydrocephalus is usually related to congenital malformations such as aqueductal stenosis, as described within the case of the beginning of this chapter, or with tumors 23-3. A 62-year-old male affected person with occipital horn of the lateral ventricle is shaped by: a.
Generic 20gr benzac amexHence, extending laterally from the two foveae to the lateral recess is the vestibular space, and at the lateral recess is a small eminence, the acoustic tubercle. Its caudal half enlarges and is the facial colliculus, which overlies the abducens nucleus. Cerebellar Peduncles the cut surfaces of the cerebellar peduncles are on the lateral features of the pons and in the roof of the fourth ventricle. The huge middle cerebellar peduncle or brachium pontis is steady with the basilar part of the pons. The superior cerebellar peduncle or brachium conjunctivum passes from the roof of the fourth ventricle into the tegmentum of the rostral pons. As a result, it receives input from all elements of the nervous system and, in flip, exerts widespread influences on just about every central nervous system function, as described in Chapter 20. By finding on the brainstem specimen the same surface landmarks in a transverse part, one is in a position to decide precisely from where the part was taken. Rostral Part of Closed Medulla the pyramids are anterior and separated by the anterior median fissure. The gracile and cuneate tubercles are posterior and separated by the posterior intermediate sulcus. Caudal Part of Open Medulla Positioned anteriorly are the pyramids and olives with the rootlets of the hypoglossal nerve between them. The preolivary and postolivary sulci are anterior and posterior to the olive, respectively. Rostral Part of Open Medulla Anteriorly, the surface of the medulla presents, from medial to lateral, the anterior median fissure, the pyramids, the preolivary sulci, the olives, and the postolivary sulci. Lateral to this tubercle is the lateral aperture, an opening into the subarachnoid area. Caudal Part of Pons the anterior or basilar a part of the pons consists of gray matter, the pontine nuclei, and white matter, large round bundles of descending fibers and smaller bundles of transverse fibers, which laterally enter the middle cerebellar peduncle. The basilar part incorporates larger bundles of fibers separated by the pontine nuclei. Caudal Part of the Midbrain Posteriorly, the inferior colliculi are separated by the periaqueductal gray matter surrounding the cerebral aqueduct. Anteriorly is positioned the cerebral peduncle, which, from posterior to anterior, consists of the tegmentum, substantia nigra, and cerebral crus. Middle Part of Pons this section is at the midpontine degree where the trigeminal nerve attaches. Although its dimension and form could vary, the basilar a half of the pons seems comparable at all pontine ranges. Rostral Part of Midbrain Posteriorly, the superior colliculi are partially separated by the periaqueductal gray matter and cerebral aqueduct. The oculomotor nuclei are in the V-shaped anterior part of the periaqueductal gray matter. The brainstem is situated in the: of the ventral surface of the (a) medulla, (b) pons, and (c) midbrain What are the distinguishing characteristics of the dorsal surface of the (a) closed medulla, (b) open medulla, (c) pons, and (d) midbrain The cerebral crus, substantia nigra, and adjoining tegmentum are positioned within the: a. The solely nerve (spinal or cranial) that innervates skeletal muscle on the other side of the physique is the: a. Immediately posterior to the inferior cerebellar peduncle as it arches dorsally into the cerebellum is the: a. The forebrain or prosencephalon consists of the telencephalon, the paired cerebral hemispheres, and the diencephalon. The diencephalon contains functional centers for the integration of all information passing from the brainstem and spinal wire to the cerebral hemispheres in addition to the mixing of motor and visceral activities. The two cerebral hemispheres combine the very best mental capabilities similar to the notice of sensations and emotions, learning and memory, intelligence and creativity, and language. The diencephalon accommodates the third ventricle, and the cerebral hemispheres include the lateral ventricles, which are separated from each other in part by the septum pellucidum. Because of this modification in orientation on the midbrain-forebrain junction, the phrases dorsal and ventral have completely different connotations rostral and caudal to this junction. The hypothalamic sulcus traverses the lateral wall of the third ventricle from the interventricular foramen to the cerebral aqueduct and separates the thalamus, above, from the hypothalamus, below. The diencephalon consists of the thalamus, a large nuclear mass forming the dorsal part of the wall of the third ventricle; the hypothalamus, which lines the ventral part of the wall of the third ventricle and extends ventrally from the medial a part of the thalamus to the base of the mind; the subthalamus, ventral to the lateral a half of the thalamus and lateral to the hypothalamus, but not reaching the floor of the brain; and the epithalamus, a small area dorsal to probably the most posterior a part of the third ventricle. Hypothalamus the only subdivision of the diencephalon on the ventral floor of the brain is the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is subdivided into three primary areas within the anteroposterior aircraft. Between the mamillary and the chiasmatic areas is the tuber cinereum after which the tuberal area is named. Thalamus the thalami are two egg-shaped masses bordering the third ventricle, dorsal to the hypothalamic sulcus. In most brains, the proper and left thalami are partially fused throughout the third ventricle by the interthalamic adhesion or massa intermedia. Thalamic Nuclei the thalamus consists of a lot of nuclei that type eight nuclear plenty named according to their anatomic places. It contains several nuclei, probably the most outstanding of which is the subthalamic nucleus. Embedded deeply in the white matter are the telencephalic nuclei, essentially the most prominent of that are the caudate and lentiform. Chapter four Forebrain: Topography and Functional Levels 43 Lateral Surface the lateral surface. The anterior and posterior walls of the central sulcus are shaped by the precentral and postcentral gyri, respectively. The frontal lobe extends anteriorly from the central sulcus to the anterior tip of the hemisphere, known as the frontal pole. The parietal lobe is superior to the lateral fissure and behind the central sulcus. It is shaped like the thumb of a boxing glove, and its most anterior half is called the temporal pole. Posteriorly, the parietal and temporal lobes turn out to be continuous with the occipital lobe. The most conspicuous clefts on the medial floor are two horizontally oriented sulci, the callosal and cingulate, and the vertically oriented parieto-occipital sulcus. The cingulate sulcus encircles the cingulate gyrus, which is dorsal to the callosal sulcus. In the partitions of the third ventricle, medial to the dorsal parts of the thalamus, are the habenulae of the epithalamus and the medullary striae. The degree additionally consists of parts of the cerebral hemisphere: the corpus callosum, lateral ventricles, and the caudate and lentiform nuclei. The most outstanding thalamic nuclei are the spherical, centrally located centromedian nucleus within the inside medullary lamina and the ventral posteromedial nucleus located ventrolateral to it. Other thalamic nuclei at this degree are the medial dorsal, lateral posterior, and reticular Mamillary this level consists of the diencephalon on the mamillary our bodies and surrounding parts of the cerebral hemispheres. In the midline, from ventral to dorsal, are the hypothalamic space between the mamillary our bodies, the third ventricle, the interthalamic adhesion, and the corpus callosum.
Buy benzac 20 gr lowest priceMass actions, which are propulsive, are more prolonged than the peristaltic actions of the small intestine. It begins in the abdomen and strikes undigested materials from the stomach and small intestine into the colon. A mass movement within the terminal colon fills the rectum, causing a reflex rest of the interior anal sphincter and a reflex contraction of the external anal sphincter. They are nearly totally underneath the management of the parasympathetic system, which promotes secretion. Chief Cells Pepsinogen is converted to pepsin by H+, as illustrated in the diagram beneath. Pepsinogen H+ pepsin (proteins to peptides) � Pepsinogen is initially converted to active pepsin by acid. Pathology Behavioral Science/Social Sciences � Vomiting stomach contents produces a metabolic alkalosis and a lack of body potassium (hypokalemia mainly because of the alkalosis effect on the kidney). Regulation of Parietal Cell Secretion Pancreatic Secretions Exocrine tissue is organized into acini and ducts very comparable to that of the salivary glands. Enzymatic elements � Trypsin inhibitor, a protein current in pancreatic secretions, prevents activation of the proteases within the pancreas. This permits pancreatic lipase to attach to the droplet and digest it, resulting in formation of 2 free fatty acids and one monoglyceride (a 2-monoglyceride, i. Cholesterol esterase (sterol lipase) hydrolyzes ldl cholesterol esters to yield ldl cholesterol and fatty acids. It features to activate some trypsinogen, and the active trypsin generated prompts the remaining proteases. Fluid and electrolyte parts � Aqueous part is secreted by epithelial cells which line the ducts. Control of the Exocrine Pancreas Control of pancreatic secretions Most of the regulation is through 2 hormones: secretin and cholecystokinin. Secretin is released from the duodenum in response to acid getting into from the abdomen. Secretin is a peptide hormone that stimulates chloride entry into the lumen from duct cells. Failure of lower esophageal sphincter to chill out Odynophagia Failure of decrease esophageal sphincter to keep its tone Presents with chest pain Answer: C 398 D. Production and Metabolism of Bile Bile salts and micelles Primary bile acids generally recognized as cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid are synthesized by the liver from ldl cholesterol. Pathology Behavioral Science/Social Sciences � Lithocholic acid has hepatotoxic exercise and is excreted. Microbiology � As such, they provide a vehicle to transport lipid-soluble supplies in the aqueous medium of the bile fluid and the small gut. If severe, bilirubin can accumulate within the mind, producing profound neurological disturbances (kernicterus). Bile pigments A major bile pigment, bilirubin is a lipid-soluble metabolite of hemoglobin. The lively pumping of sodium within the gallbladder causes electrolyte and water reabsorption, which concentrates the bile. Phospholipids (mainly lecithin) Insoluble in water however are solubilized by bile salt micelles Cholesterol Present in small quantities. It is insoluble in water and have to be solubilized by bile salt micelles earlier than it might be secreted within the bile. Microbiology Crypt secretion � A Na+-K+-2Cl� transporter within the basolateral membrane facilitates the ion uptake by secondary active transport. Summary of Digestive Processes Digestive Enzymes and End Products Triglycerides Stomach: Fatty materials are pulverized to decrease particle size and enhance surface area. Small gut: Bile micelles emulsify the fat, and pancreatic lipases digest it. Brush border enzymes (sucrase-isomaltase; maltase; lactase; trehalase) convert limited dextrans and disaccharides into monosaccharides. These monosaccharides are then absorbed (late duodenum and early jejunum) through the mechanisms shown in the determine below. Small intestine: Digestion continues with the pancreatic proteases (trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase, and carboxypeptidases A and B), which are important enzymes. Protein digestion is completed by the small intestinal brush border enzymes, dipeptidases, and an aminopeptidase. Bridge to Pathology Many of the amino acid transporters are selective for particular amino acids. The finish products of triglyceride digestion, 2-monoglycerides and fatty acids, remain as lipid-soluble substances which might be then taken up by the micelles. Digestive products of fats found within the micelles and absorbed from the intestinal lumen may include: � Fatty acids (long chain) � 2-monoglyceride � Cholesterol � Lysolecithin � Vitamins A, D, E, K � Bile salts, which stabilize the micelles Bridge to Biochemistry Chylomicrons comprise apolipoprotein B-48. Micelles diffuse to the brush border of the gut, and the water-soluble exterior permits them to carry fats soluble products into the cell. In the mucosal cell, triglyceride is resynthesized and varieties lipid droplets (chylomicrons). The extra water-soluble short-chain fatty acids could be absorbed by easy diffusion directly into the bloodstream. Absorption of Lipids Electrolytes the web transport of electrolytes along the size of the small and enormous intestine is summarized within the determine under. Duodenum � Hypertonic fluid enters this area, and following the motion of some water into the lumen, the fluid becomes and remains isotonic (see crypt secretion above). The acid Pathology Behavioral Science/Social Sciences setting of the stomach redissolves these salts, which facilitates their absorption within the small gut. Iron and calcium absorption is diminished in people with a poor abdomen acid secretion. Ileum � Net reabsorption of water, sodium, chloride, and potassium continues, however there begins a web secretion of bicarbonate. It commonly presents as hyperchloremic, nonanion hole metabolic acidosis, as described in the acid-base part. A reflex circuit conveys the impulses that end result in an involuntary response similar to muscle contraction or gland secretion. For instance, relay circuits convey impulses from sensory organs in the skin, eyes, ears, and so forth that turn into perceived by the brain as sensations. A useful path could consist of a collection of only two or three neurons or as many as hundreds of neurons. The axons in a functional path usually kind bundles called tracts, fasciculi, or nerves.
References - Adelstein RS, Pato MD, Conti MA: The role of phosphorylation in regulating contractile proteins, Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res 14:361, 1981.
- Yukawa K, Hoshino K, Kishino M, et al: Deletion of the kinase domain in death-associated protein kinase attenuates renal tubular cell apoptosis in chronic obstructive uropathy, Int J Mol Med 13:515n520, 2005. Yukawa K, Kishino M, Goda M, et al: STAT6 deficiency inhibits tubulointerstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy, Int J Mol Med 15:225n230, 2005. Zeisberg EM, Potenta SE, Sugimoto H, et al: Fibroblasts in kidney fibrosis emerge via endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition, J Am Soc Nephrol 19(12):2282n2287, 2008.
- Bagatell R, Beck-Popovic M, London WB, et al: Significance of MYCN amplification in international neuroblastoma staging system stage 1 and 2 neuroblastoma: a report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group, J Clin Oncol 20:365n370, 2009.
|
|

